Dr. Brown Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
anterior
front
posterior
back
superior
up
inferior
down
lateral
side
medial
middle
proximal
close
distal
far
anatomy
structure and identification of organism's bodies and their different sections
physiology
aims to understand the mechanisms of living things
gross anatomy
organs and tissues
histology
study of tissues
cytology
study of cells
cell biology
structure and function of cells
tissue
group of different cells
organ
group of tissues
organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
organism
living thing
anatomical position
erect, feet forward, arms at side with palms facing forward, head facing forward
dorsal
cranial and spinal
ventral
thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic
cranial
towards head
caudal
towards bottom
a-
not/without
dys-
bad
ex-, exo-
outside
end-, endo-
inner
epi-
around
hem-, hemo-
blood
hyper-
above
hypo-
below
para-
beside
-itis
inflamed
-emia
blood
-phil, -phillic, -philia
love
-phob, -phobic, phobia
scared
arthr-
joint
brachi-
arm
card-
heart
cyt-
cell
derm-
skin
gastr-
stomach
hepat-
liver
hydro-
water
kal-
potassium
my-, myo-
muscle
nephr-
kidney
neur-
nerves
onco-
tumor
sept-
seven
vas-
vessel
leuko-
white
morph-
form
1st level of organization
atom: oxygen, carbon, calcium
2nd level of organization
molecule: water (h2o), nitrogen (n2), ozone (o3)
3rd level of organization
macromolecule: proteins, lipids, carbs
4th level of organization
cell: neurons
5th level of organization
tissue: made up of different cells
6th level of organization
organ: made up of tissues and has a function
7th level of organization
organ system: organs that work together to perform a certain function
8th level of organization
organism: humans
why do we need scientific/medical terminology?
helps medical professionals communicate with each other and is a universal language
homeostasis
balance in your body: when you get hot you sweat, when you get cold you get goosebumps
circulatory (cardiovascular) system
transports oxygen and nutrients
lymphatic system
defense against infection and disease
respiratory system
breathing
integumentary system
skin, hair, nails
endocrine system
regulates metabolism
digestive system
breaking down food into nutrients
urinary system
filters blood and removes toxins
musculoskeletal system
provides shape and movement: muscular and skeletal
nervous system
reactions and processing: central and peripheral
immune system
fights against infection and diseases
reproductive system
helps you to reproduce
chemical symbols for oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chlorine, magnesium, iron, iodine, water, and carbon dioxide
o, c, n, ca, p, k, s, na, ch, m, fe, i, h2o, co2
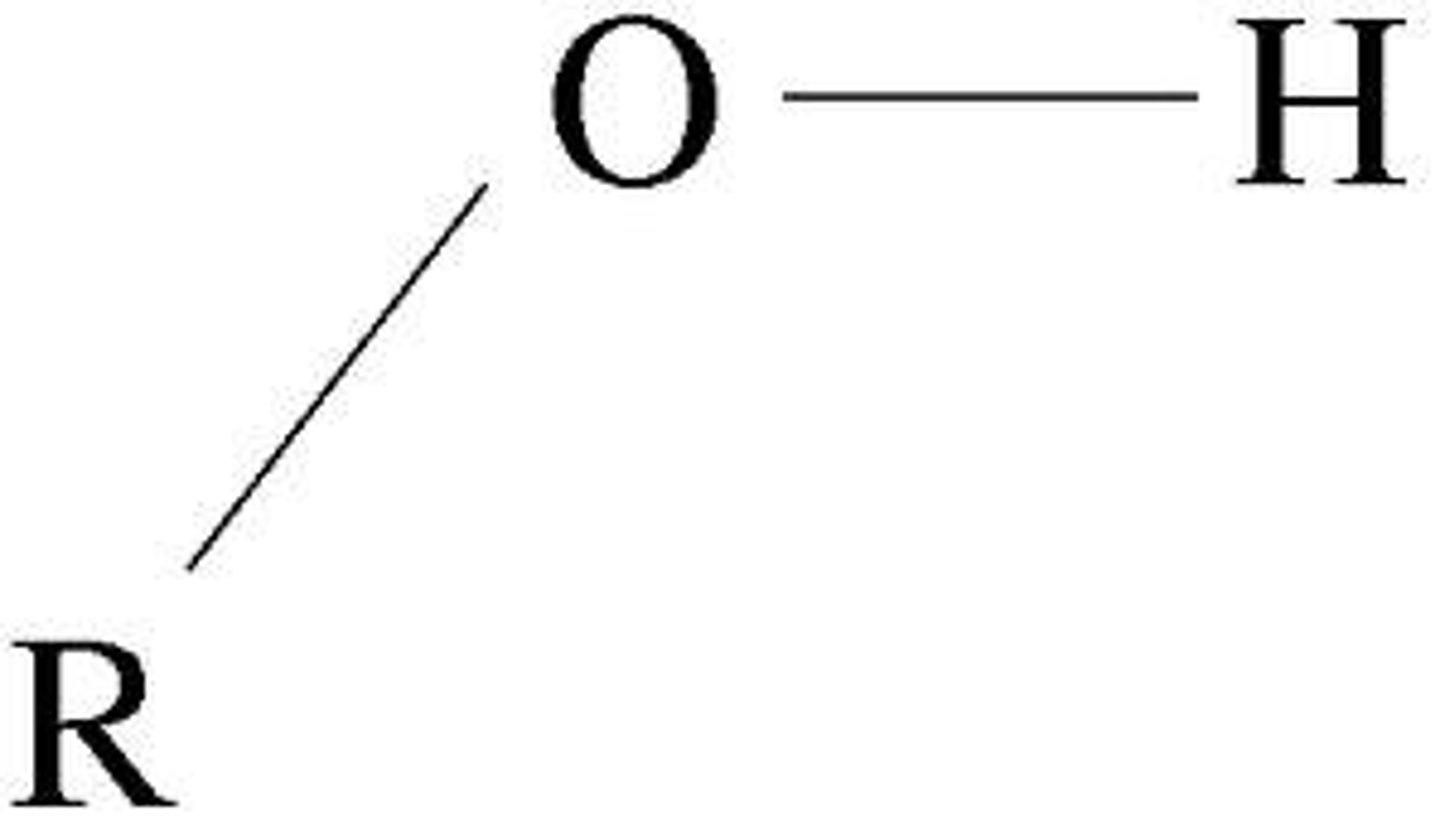
hydroxyl
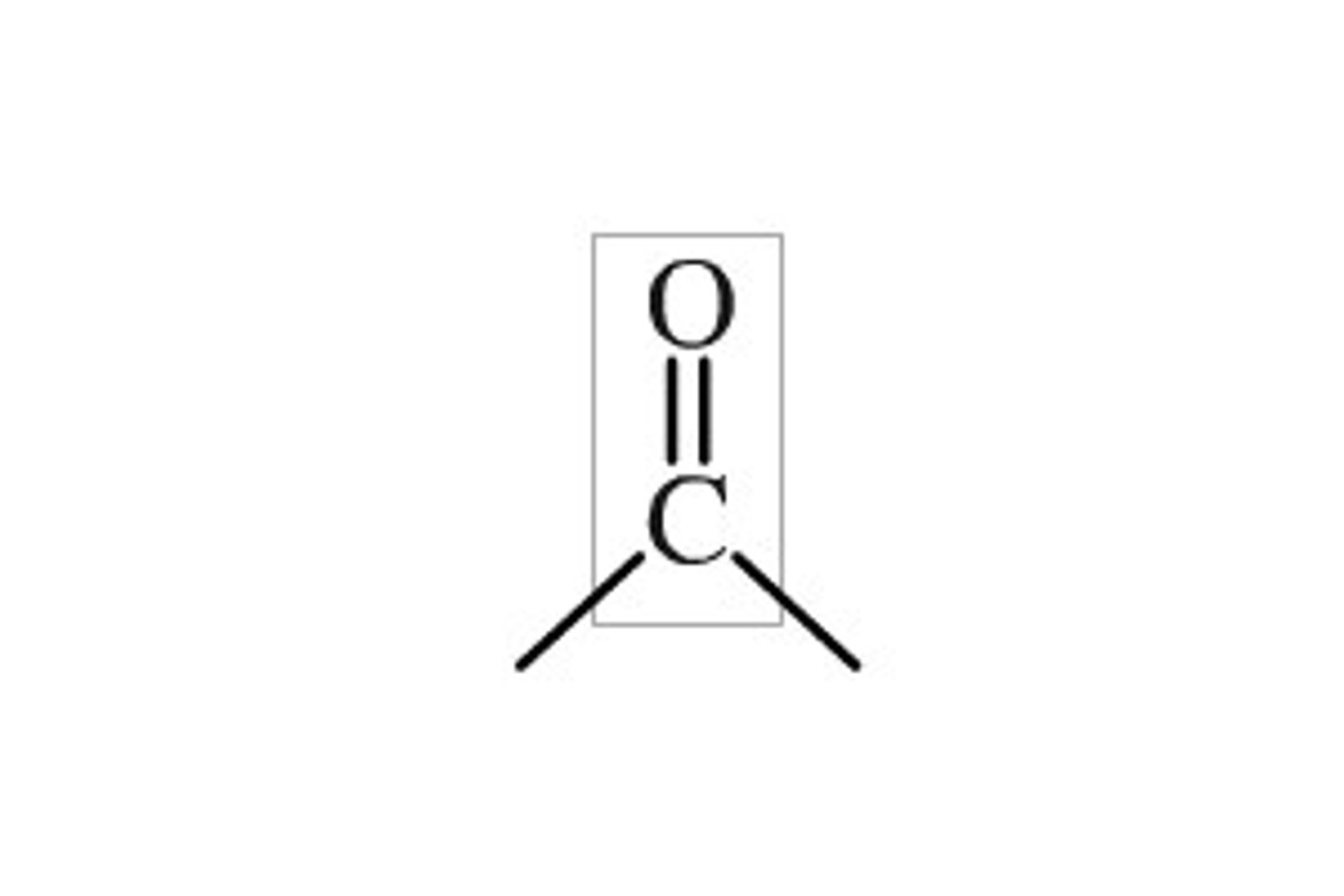
carbonyl
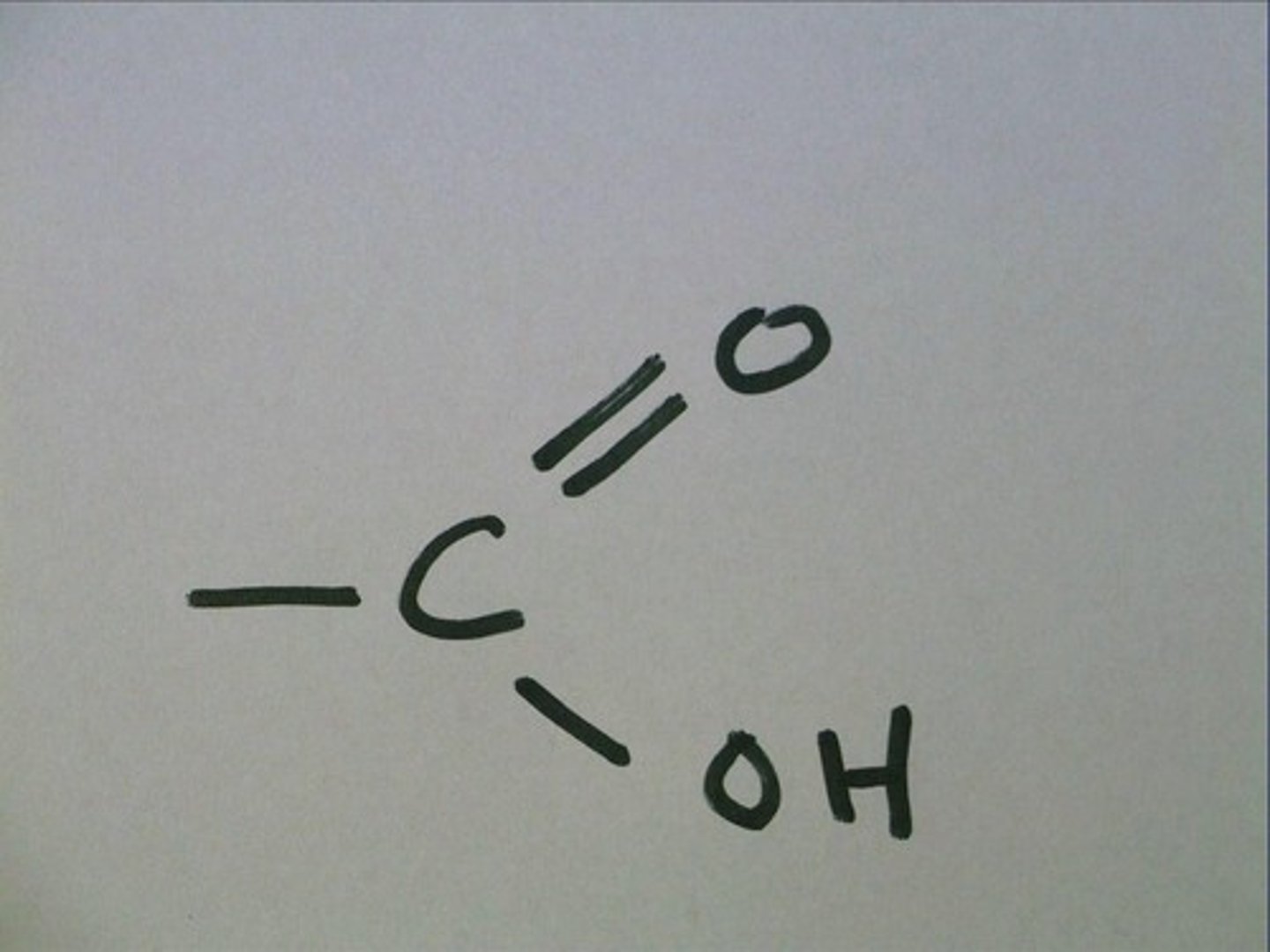
carboxyl
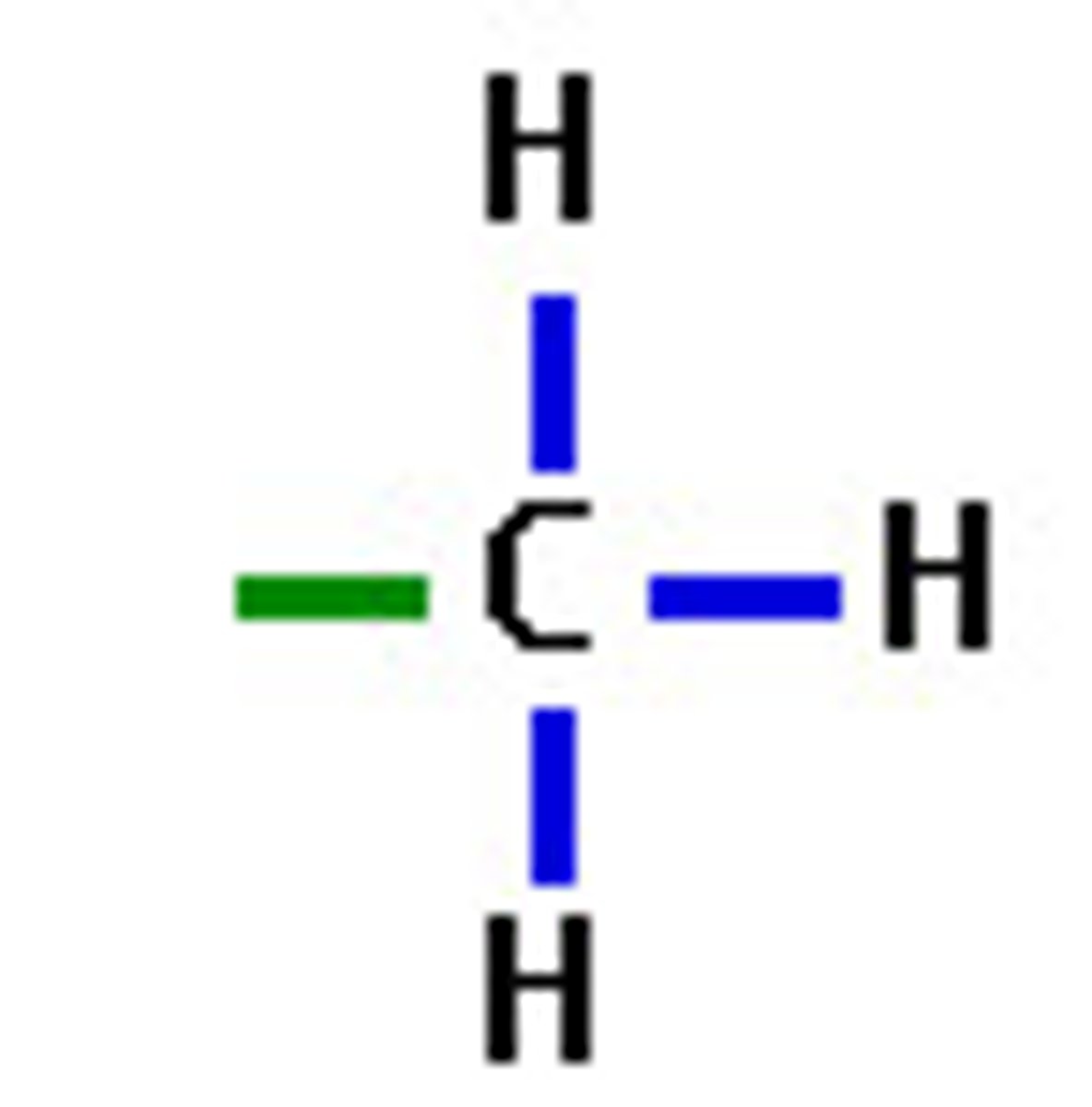
methyl
amino
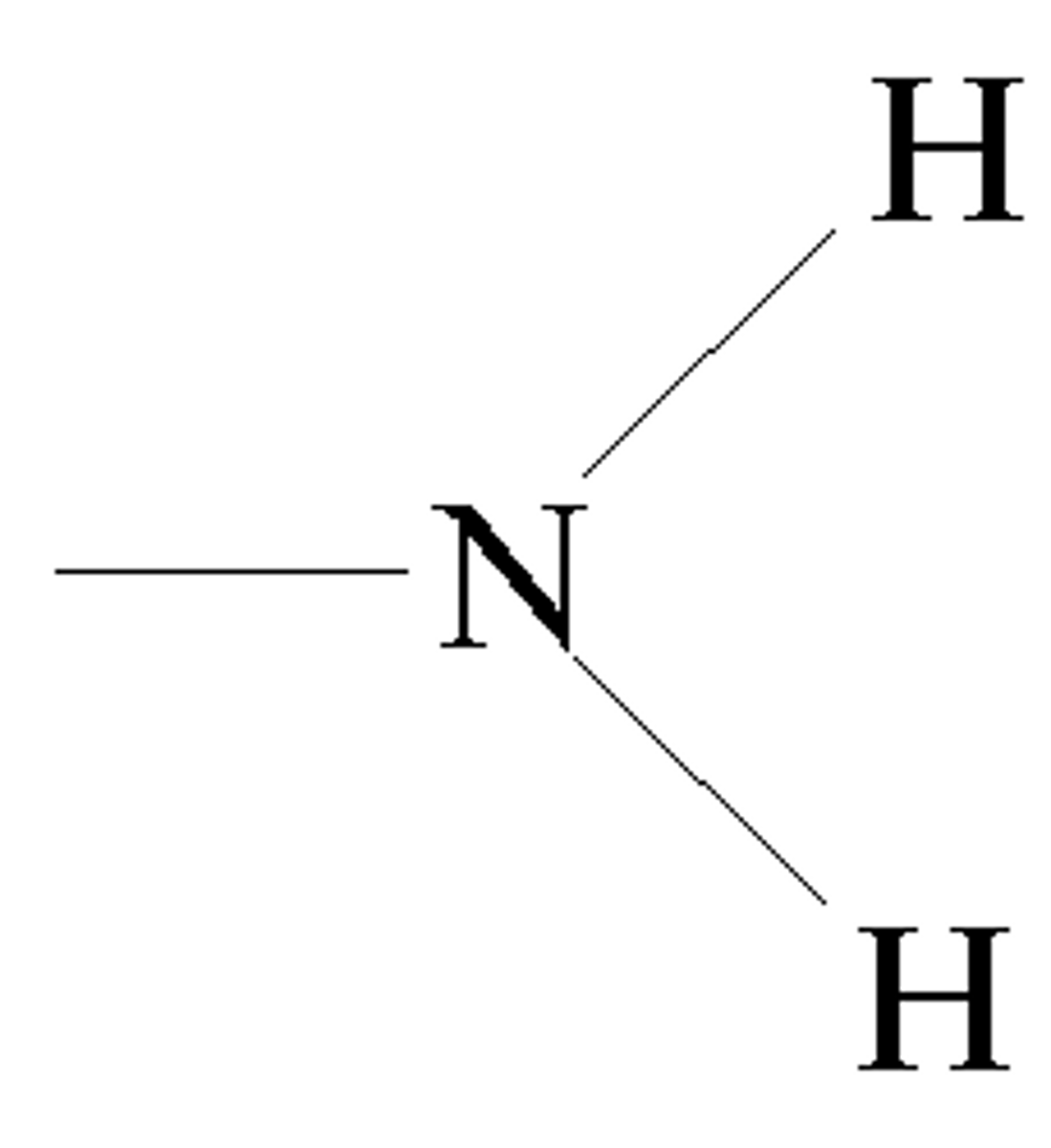
sulfhydryl

atom
combine to form molecules, made of electrons protons and neutrons
ion
electrically charged atom or molecule
element
building blocks for all matter
isotope
atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons and electrons
molecule
made up of a single atom or group of atoms
compound
when elements are joined together by strong chemical bonds
organic molecule
long rings or chains of carbon atoms with atoms of other elements attached
functional group
group of specific atoms, or a specific arrangement of atoms
hydrophillic
things that will dissolve in water (ions, polar molecules, electrolytes)
covalent bond
two atoms share an electron- very strong (1st)
ionic bond
two atoms held together by opposing electrical charge
hydrogen bond
two atoms held together by patrial + or - charge- weakest (3rd)
amino acid
building blocks of protein
peptide bond
covalent bond between two amino acids
protein primary structure
sequence of amino acids
protein secondary structure
the folding of the primary structure of a protein. This folding is caused principally by hydrogen bonds. The result is beta-sheets, alpha-helices, and random coils.
protein tertiary structure
three-dimensional shape formed by interactions between R groups
protein quaternary structure
combo of 2 or more polypeptide chains
carbohydrate
compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms: major source of energy for the human body