PSK4U Exam Review
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Which of the following is a function of the skeletal system?
a) protection of internal organs, b) regulation of body temperature, c) synthesis of red blood cells, or d) storage of lipids
a) protection of internal organs
The axial skeleton includes all of the following EXCEPT:
a) skull, b) ribs, c) pelvis, or d) vertebral column
c) pelvis
What type of joint allows for the greatest range of motion?
a) hinge, b) ball-and-socket, c) pivot, or d) saddle
b) ball-and-socket
Which bone is part of the appendicular skeleton?
a) femur, b) sternum, c) spine, or d) rib
b) sternum
The condition characterized by brittle bones due to a decrease in bone density is known as:
a) osteoporosis, b) osteoarthritis, c) scoliosis, or d) rheumatoid arthritis
a) osteoporosis
The primary function of muscle tissue is:
a) circulation of blood, b) movement of the body, c) production of insulin, or d) absorption of nutrients
b) movement of the body
What type of muscle is responsible for involuntary movements in the heart?
a) skeleton, b) smooth, c) cardiac, or d) voluntary
c) cardiac
Which muscle is involved in the flexion of the forearm?
a) biceps brachii, b) trapezius, c) quadriceps femoris, or d) hamstrings
a) biceps brachii
Which of the following is true about skeletal muscle contraction?
a) it requires calcium ions to initiate contraction, b) it occurs in the absence of ATP, c) it is an involuntary process, or d) it does not involve actin any myosin
a) it requires calcium ions to initiate contraction
Which of the following is a characteristic of slow-twitch muscle fibers?
a) they fatigue quickly, b) they are used for short bursts of strength, c) they are more efficient at using oxygen, d) they contract faster than fast-twitch fibers
c) they are more efficient at using oxygen
The part of the brain responsible for controlling balance and coordination is:
a) cerebrum, b) cerebellum, c) medulla oblongata, or d) thalamus
b) cerebellum
Which of the following is a function of the sympathetic nervous system?
a) rest and digest, b) fight or flight, c) produces hormones for sleep, or d) controls voluntary muscle movement
b) fight or flight
Which type of neuron carries impulses away from the central nervous system?
a) sensory neuron, b) motor neuron, c) interneuron, or d) bipolar neuron
b) motor neuron
The myelin sheath on neurons is important because it:
a) increases the speed of electrical impulses, b) prevents the neuron from transmitting signals, c) supports cell metabolism, or d) stores neurotransmitters
a) increases the speed of electrical impulses
Which neurotransmitter is involved in mood regulation and is often linked with depression?
a) serotonin, b) dopamine, c) acetylcholine, or d) glutamate
a) serotonin
The primary muscle involved in breathing is the:
a) diaphragm, b) intercostal muscles, c) rectus abdominis, or d) pectoralis minor
a) diaphragm
Which structure in the respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange?
a) trachea, b) bronchi, c) alveoli, or d) larynx
c) alveoli
The term for the process of breathing in is:
a) exhalation, b) inspiration, c) expiration, or d) ventilation
b) inspiration
Which of the following diseases is characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways?
a) athsma, b) pneumonia, c) tuberculosis, or d) emphysema
a) asthma
The gas that is exchanged during respiration is:
a) oxygen, b) carbon dioxide, c) nitrogen, d) both a and b
d) both a and b
The heart’s primary function is to:
a) oxygenate blood, b) circulate hormones, c) pump blood throughout the body, d) absorb nutrients from food
c) pump blood throughout the body
Which vessel carries oxygenated blood away from the heart?
a) pulmonary artery, b) aorta, c) jugular vein, d) pulmonary vein
b) aorta
The structure responsible for regulating blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle is:
a) aortic valve, b) tricuspid valve, c) bicuspid valve, or d) pulmonary valve
b) tricuspid valve
The term for high blood pressure is:
a) hypertension, b) hypotension, c) atherosclerosis, or d) arrhythmia
a) hypertension
What is the function of platelets in the blood?
a) carry oxygen, b) fight infection, c) aid in clotting, or d) maintain pH balance
c) aid in clotting
The primary source of energy for the body during intense physical activity is:
a) protein, b) carbohydrates, c) fat, or d) oxygen
b) carbohydrates
Which process produces the most ATP in the body?
a) glycolosis, b) fermentation, c) cellular respiration, d) photosynthesis
c) cellular respiration
The breakdown of glucose into pyruvate occurs in which part of the cell?
a) mitochondria, b) cytoplasm, c) nucleus, or d) ribosomes
b) cytoplasm
Which energy system is used for short bursts of high-intensity activity?
a) anaerobic glycolosis, b) aerobic respiration, c) phosphagen system, or d) fatty acid metabolism
c) phosphagen system
The energy molecule produced during the breakdown of glucose is:
a) ATP, b) ADP, c) NADH, or d) glucose
a) ATP
The bone that forms the forehead is called the:
a) maxilla, b) mandible, c) frontal bone, or d) zygomatic bone
c) frontal bone
Which of the following is true about the human rib cage?
a) the first pair of ribs is attached to the sternum via cartilage, b) the ribs are classified as flat bones, c) the rib cage protects the lungs, heart, and other organs, or d) the rib cage is part of the appendicular skeleton
c) the rib cage protects the lungs, heart, and other organs
The process of bone formation is known as:
a) osteoporosis, b) osteogenesis, c) calcification, or d) osteoclast activity
b) osteogenesis
Which bone serves as the attachment point for the tongue and is not directly connected to other bones?
a) mandible, b) hyoid, c) sternum, or d) coccyx
b) hyoid
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cartilage?
a) it is avascular (lacks blood vessels), b) it has a smooth, flexible texture, c) it is harder than bone, or d) it provides cushioning and support
c) it is harder than bone
In what part of a long bone does hematopoiesis (blood cell formation) occur?
a) diaphysis, b) epiphysis, c) medullary cavity, d) periosteum
b) epiphysis
Which of the following muscles is responsible for plantar flexion of the foot?
a) tibialis anterior, b) gastrocnemius, c) rectus femoris, or d) gluteus maximus
b) gastrocnemius
What happens to a muscle during a concentric contraction?
a) the muscle lengthens, b) the muscle remains the same length, c) the muscle shortens, or d) the muscle becomes rigid
c) the muscle shortens
Which of the following is true regarding the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
a) it activates the acetylcholine, b) is binds to tropomyosin, allowing actin and myosin to interact, c) it is released from the mitochondria, or d) it prevents the formation of cross-bridges
b) it binds to tropomyosin, allowing actin and myosin to interact
Which of the following describes the role of myosin in muscle contraction?
a) myosin binds to calcium to initiate contraction, b) myosin pulls actin filaments to shorten the muscle, c) myosin is responsible for muscle relaxation, or d) myosin acts as an energy store for the muscle
b) myosin pulls actin filaments to shorten the muscle
A muscle that opposes the action of another muscle is called;
a) synergist, b) antagonist, c) prime mover, or d) fixator
b) antagonist
Which of the following muscle groups is responsible for extending the leg at the knee?
a) hamstrings, b) quadriceps femoris, c) adductors, or d) gluteus maximus
b) quadriceps femoris
The outer layer of the brain, responsible for higher cognitive functions, is called the:
a) cerebellum, b) thalamus, c) cerebrum, d) medulla oblongata
c) cerebrum
Which of the following is the primary function of the autonomic nervous system?
a) control voluntary muscle movements, b) regulate involuntary body functions like heart rate and digestion, c) transmit sensory information to the brain, or d) process thoughts and emotions
b) regulate involuntary body functions like heart rate and digestion
Which part of the neuron receives incoming signals from other neurons?
a) axon, b) dendrite, c) myelin sheath, or d) axon terminal
b) dendrite
Which of the following statements about the spinal cord is true?
a) it is the primary center for emotions, it transmits sensory and motor signals between the brain and body, c) it stores memories, or d) it only processes voluntary motor signals
b) it transmits sensory and motor signals between the brain and body
The part of the brain involved in regulating sleep and wake cycles in the:
a) pineal gland, b) hypothalamus, c) medulla oblongata, or d) hippocampus
b) hypothalamus
Which of the following is an example of a reflex arc?
a) touching a hot surface and quickly withdrawing your hand, b) moving your eyes to focus on an object, c) tasting food, or d) deciding to move your arm
a) touching a hot surface and quickly withdrawing your hand
Which of the following is the primary function of the respiratory system?
a) to regulate body temperature, b) to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide, c) to circulate blood throughout the body, or d) to produce hormones
b) to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide
Which of the following is a characteristic of emphysema?
a) inflammation of the lungs caused by a bacterial infection, b) destruction of the alveolar walls leading to difficulty in gas exchange, c) overproduction of mucus in the airways, or d) spasms in the bronchial tubes during exhalation
b) destruction of the alveolar walls leading to difficulty in gas exchange
The primary role of hemoglobin in the blood is to:
a) carry oxygen from the lugs to the tissues, b) help in the digestion of food, c) protect against infections, or d) regulate pH levels in the blood
a) carry oxygen fro the lungs to the tissues
Which of the following structures is responsible for controlling the passage of air into the lungs?
a) epiglottis, b) alveoli, c) trachea, d) larynx
a) epiglottis
What happens during expiration?
a) the diaphragm contracts and air is drawn into the lungs, b) the diaphragm relaxes and air is pushed out of the lungs, c) oxygen is absorbed into the blood, or d) the intercostal muscles contract, increasing lung volume
b) the diaphragm relaxes and air is pushed out of the lungs
The exchange of gases between the blood and the body’s cells occurs in the:
a) alveoli, b) bronchioles, c) trachea, or d) capillaries
a) alveoli
The blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body is the:
a) pulmonary artery, b) aorta, c) superior vena cava, d) pulmonary vein
b) aorta
The function of the coronary arteries is to:
a) transport blood to the lungs for oxygenation, b) carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, c) drain deoxygenated blood from the heart, or d) facilitate the exchange of gases in the lungs
b) carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle
Which of the following is true about the atrioventricular (AV) node?
a) it generates the electrical impulse that stimulates the heart to beat, b) it delays the electrical signal to allow the ventricles to fill with blood, c) it is located in the left ventricle, or d) it receives electrical impulses from the brain
b) it delays the electrical signal to allow the ventricles to fill with blood
Which of the following is a risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease?
a) regular physical activity, b) high blood pressure, c) low-fat diet, d) adequate sleep
b) high blood pressure
The term for the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute is:
a) heart rate, b) stroke volume, c) cardiac output, or d) blood pressure
c) cardiac output
Which of the following statements about veins is true?
a) they carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, b) they have thick muscular walls to withstand high pressure, c) they contain valves that prevent backflow of blood, d) they do not carry blood to the heart
c) they contain valves that prevent backflow of blood
The process of converting glucose into energy in the absence of oxygen is called:
a) aerobic respiration, b) anaerobic glycolosis, c) krebs cycle, or d) fatty acid oxidation
b) anaerobic glycolosis
The energy used for high-intensity, short-duration activities is primarily derived from:
a) fat, b) glycogen stored in muscles, c) protein, or d) ATP stored in muscles
d) ATP stored in muscles
The process of converting food into energy occurs in the:
a) mitochondria, b) nucleus, c) ribosomes, or d) cytoplasm
a) mitochondria
Which of the following is the main energy system used during a marathon race?
a) phosphagen system, b) anaerobic glycolosis, c) aerobic respiration, or d) creatine phosphate system
c) aerobic respiration
The body’s ability to use far as a primary energy source is improved with:
a) increase carbohydrate intake, b) enhanced aerobic fitness, c) short bursts of anaerobic activity, or d) high-protein diets
b) enhanced aerobic fitness
Which of the following best describes the relationship between aerobic and anaerobic energy systems during exercise?
a) aerobic systems are used during low-intensity activities, and anaerobic systems are used for short, intense busts, or b) both systems work independently with no overlap
a) aerobic systems are used during low-intensity activities, and anaerobic systems are used for short, intense busts
Which of the following is the function of the medullary cavity in long bones?
a) stores minerals, b) produces red and white blood cells, c) absorbs shock during movement, or d) provides structural support to the bone
b) produces red and white blood cells
What type of joint is found at the elbow, allowing for flexion and extension?
a) ball-and-socket, b) hinge, c) pivot, or d) saddle
b) hinge
Which of the following bone structures provides attachment for muscles and tendons?
a) epiphyseal plate, b) condyle, c) foramen, or d) tuberosity
d) tuberosity
Osteoclasts are responsible for:
a) bone formation, b) bone resorption, c) collagen synthesis, or d) calcium storage
b) bone resorption
The epiphyseal plate is found in:
a) adult bones, b) child and adolescent bones, c) the vertebrae only, or d) all bones
b) child and adolescent bones
What is the main structural difference between compact bone and spongy bone?
a) compact bone is lighter than spongy bone, b) spongy bone contains trabeculae, compact bone does not, c) compact bone is more flexible than spongy bone, or d) spongy bone is more dense than compact bone
b) spongy bone contains trabeculae, compact bone did not
Which of the following is true about the energy source used by muscles during short bursts of activity?
a) fatty acids are the primary energy source, b) muscles rely on stored ATP and creating phosphate for quick energy, c) muscles primarily use glycogen for energy, or d) oxygen is essential for energy production during short bursts
b) muscles rely on stored ATP and creatine phosphate for quick energy
What type of muscle contraction occurs when the muscle lengthens under tension?
a) concentric contraction, b) isometric contraction, c) eccentric contraction, or d) isotonic contraction
c) eccentric contraction
Describe each of the following bone type:
Compact bone, spongy bone, long bone, flat bone, and irregular bone
Compact bone: dense, hard bone tissue
Spongy bone: bone with a honeycomb-like structure
Long bone: bone found in the arms and legs
Flat bone: thin and broad bones, such as the skull and ribs
Irregular bone: found in vertebrae and facial bones
Describe each of the following muscle type’s characteristic:
Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle: voluntary and striated
Cardiac muscle: involuntary and striated
Smooth muscle: found in the walls of blood vessels
Describe the functions of the following structures:
Axon, dendrite, synapse, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata
Axon: transmits signals between neurons
Dendrite: receives signals from other neurons
Synapse: conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron
Cerebellum: coordinates balance and motor control
Medulla oblongata: controls basic life functions like breathing and heart rate
Describe the functions of the following structures:
Alveoli, bronchi, trachea, diaphragm, and nasal cavity
Alveoli: site of gas exchange
Bronchi: airways that lead to the lungs
Trachea: transports air to the lungs
Diaphragm: major muscle for inhalation
Nasal cavity: moistens and filters incoming air
Describe the following:
Veins, arteries, capillaries, aorta, and right atrium
Veins: carry deoxygenated blood to the heart
Arteries: carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
Capillaries: smallest blood vessels, where nutrient and gas exchange occurs
Aorta: largest artery in the body
Right atrium: collects blood from the body and sends it to the right ventricle
Describe what type of activity matches each energy pathway:
Anaerobic glycolosis, aerobic respiration, phosphagen system, and fat metabolism
Anaerobic glycolosis: breakdown of glucose without oxygen
Aerobic respiration: long-duration, low-intensity activity
Phosphagen system: short, explosive bursts of energy; immediate energy system
Fat metabolism: moderate-duration, moderate-intensity activity
Where are the following bones:
Skull, femur, readius, vertebrae, and scapula
Skull: head (axial skeleton)
Femur: upper leg
Radius: arm (appendicular skeleton)
Vertebrae: spine (axial skeleton)
Scapula: shoulder (axial/appendicular skeleton)
What are some examples of each type of bone:
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones
Long bones: femur, radius, ulna, etc.
Short bones: capral bones, etc.
Flat bones: ribs, skull, etc.
Irregular bones: vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, etc.
Define each of the following terms:
Osteoblast, osteoclast, periosteum, articular cartilage
Osteoblast: immature bone cells
Osteoclast: bone breakers
Periosteum: the fibrous sheath that covers bones
Articular cartilage: covers the end of bones in joints and lets the bones move smoothly against each other
Give an example for each type of joint:
Hinge joint, ball-and-socket joint, pivot joint, gliding joint
Hinge joint: elbow, knee, etc.
Ball-and-socket joint: shoulder, hip, etc.
Pivot joint: 1st/2nd vertebrae, radioulnar, etc.
Gliding joint: carpal bones, tarsal joints, etc.
Describe each type of fracture:
Greenstick, comminuted, spiral, compound
Greenstick: a partial break in the bone; occurs when the bone bends and cracks on one side but doesn’t break all the way through
Comminuted: a bone that has separated into three or more pieces
Spiral: occurs when a twisting force is applied to a bone, causing it to split
Compound: breaks through the skin or is exposed through a wound
What is the function of the following bone markings:
Foramen, process, and fossa
Foramen: allows structures to pass from one part of the body to another (eg. holes in vertebrae)
Process: where muscles attach and where they fit with other bones
Fossa: a depression or hollow in a bone
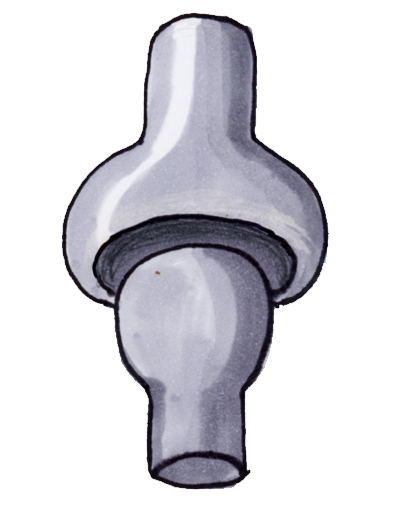
Name and describe the following joint:
Condyloid joint; allows for movement in two planes
Eg. wrist, knuckles, etc.
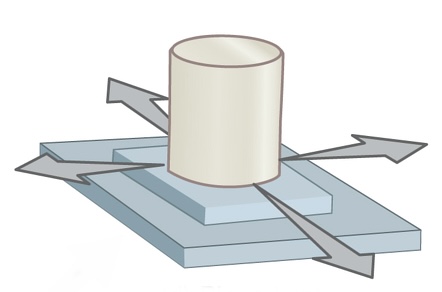
Name and describe the following joint:
Plane joint; gliding/sliding movements
Eg. between vertebrae, wrist
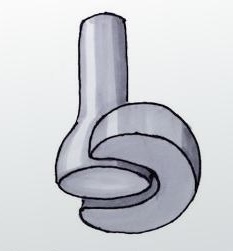
Name and describe the following joint:
Pivot joint; allows for rotation around a single axis
Eg. radioulnar joint
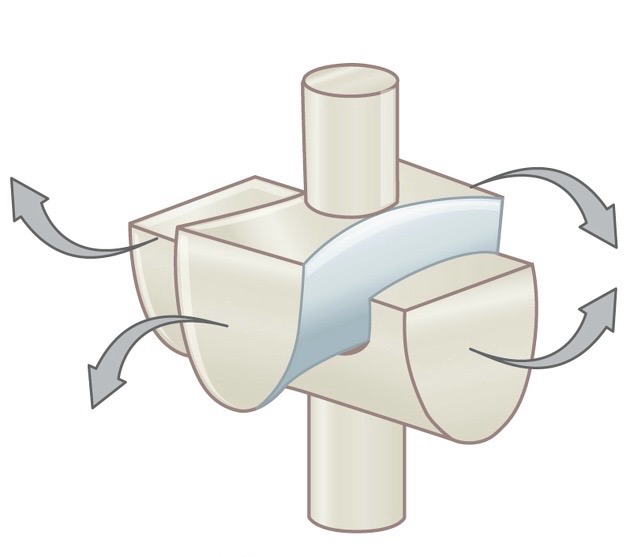
Name and describe the following joint:
Saddle joint; allow movements in two planes of movement (does not allow for axial rotation)
Eg. thumb, sternoclavicular joint
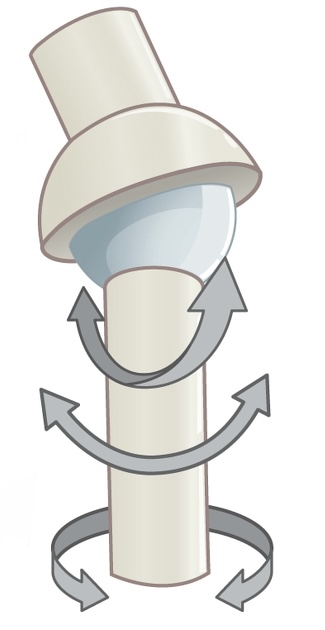
Name and describe the following joint:
Ball and socket joint; allows for the most range of motion
Eg. shoulder, hip
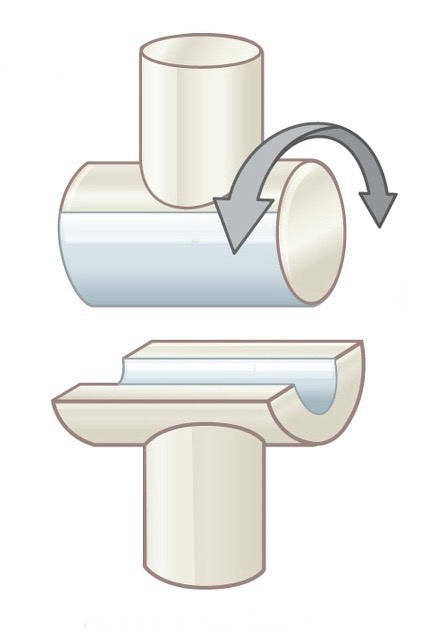
Name and describe the following joint:
Hinge joint; allows for uniaxial movement (flexion/extension)
Eg. elbow, knee
Explain the process of bone remodelling, including the roles of osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Osteoclasts resorb the damaged or dying bone and osteoblasts for new bone; this is essential for maintaining bone health, repairing damage, and adapting to changes in how the bone is being used (Wolff’s law)
Describe how bone structure contributes to its strength and flexibility
Form follows function; bones are modelled for how they will be used. Some are longer, some are meant for holding things together, some are made for absorbing impact, etc.
Analyze the impact of osteoporosis on bone health and suggest preventive measures
Osteoporosis reduces bone density, making them more fragile and prone to fractures. Some ways to prevent this are ensuring proper intake of calcium and vitamin D (to properly feed bone), to exercise regularly (Wolff’s law), etc.
Explain the relationship between the skeletal system and the muscular system in movement
Bones act as levers, joints allow for movement, and muscles generate movement
Describe the difference between the axial and appendicular skeleton
The axial skeleton includes the ribs, skull, and spine, while the appendicular skeleton includes the limbs (or appendages) like the humerus, radius, ulna, etc.
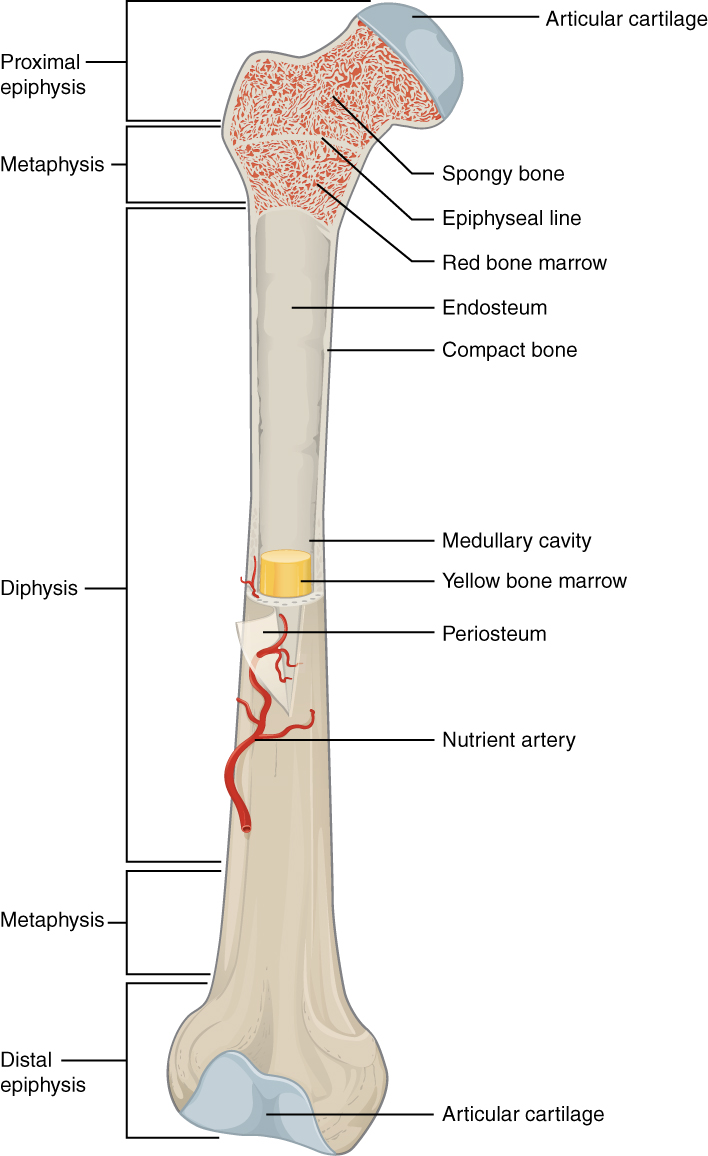
Study this diagram
:)
Explain the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction
Explains how muscle contraction happens through actin and myosin interacting. Calcium ions are released, which lets myosin heads for a cross bridge with actin to perform power strokes, which slides filaments past each other and shortens the muscle
Describe the process of an action potential and its role in neuron communication.
Starts at resting membrane potential (RMP), -70mV. Graded potentials can occur, which is a shift in the electrical charge not strong enough to initiate an action potential. Action potential threshold of -55mV is reached and the cell depolarizes to +40mV. The cell repolarizes back to -55mV before briefly hyperpolarizing to -75mV (this is known as the refractory period where the cell cannot respond to another stimulus)