10.1 The nature of ecosystems
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the definition of ecosystem?
A reasonably self-contained area together with all its living organisms that can range in size (e.g. oak forest, deep sea, garden pond, etc)
What is the definition of trophic levels?
The correct term for feeding level
What difficulties can fieldwork present?
Very large habitats
Very large number of different organisms present
Many mobile organisms & can be difficult to find/identify
Organisms can eat other organisms
Bad weather
What is random sampling?
Used when you want a representative sample of the whole area under study
How is random sampling carried out?
Measuring tapes are placed along two sides of the area & random numbers are generated to choose sampling points in the area
Should always be a large number of samples (at least 10, preferably 100) → to minimise the chance of picking a skewed sample/allow for bad measurements or anomalies
What is systematic sampling?
Used when you choose where to take your samples, because you’re investigating a specific pattern in the ecosystem
How is systematic sampling carried out?
A transect is used where samples are taken along a straight line to investigate changes along the line
What is a line transect?
Organisms touching a piece of string stretched along the transect are recorded
What is a belt transect?
Quadrats are placed at intervals along the transect & organisms in each quadrat are counted
What is an interrupted transect?
Sampling is not continuous; there are are gaps between the samples
What is an advantage & disadvantage of the line and belt transect?
Line transect = quicker but can be unrepresentative
Belt transect = involves more work, but generates more complete data
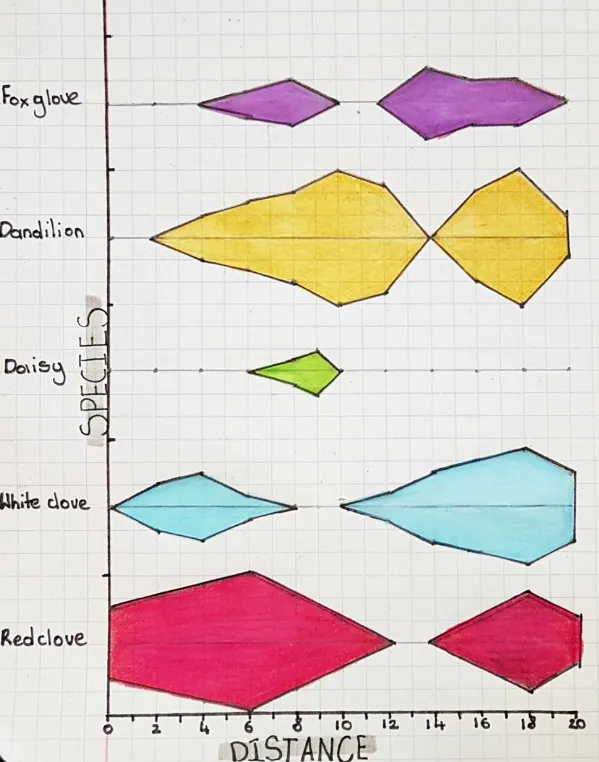
What can the data from a transect be presented as?
A kite graph, which shows biotic data as “kites” and abiotic data as lines
How are abiotic factors usually measured?
With digital electronic equipment:
the electronic devices usually consist of a sensory/probe (e.g. temperature/pH/light probe) connected to an amplifier & digital display
What are the advantages of the digital electronic devices used to measure abiotic factors?
Measurements are quick, quantitative, accurate & calibrated
Measurements can be automatically recorded at regular time intervals over an extended period of time
Data can be transferred to computers for storage & analysis
How can biotic factors be measured using abundance?
Usually, each organism found is identified, but sometimes the total abundance of species is simply counted
For animals, the capture-mark-recapture method is used (since they move)
How is density usually calculated?
Abundance / Sampling area
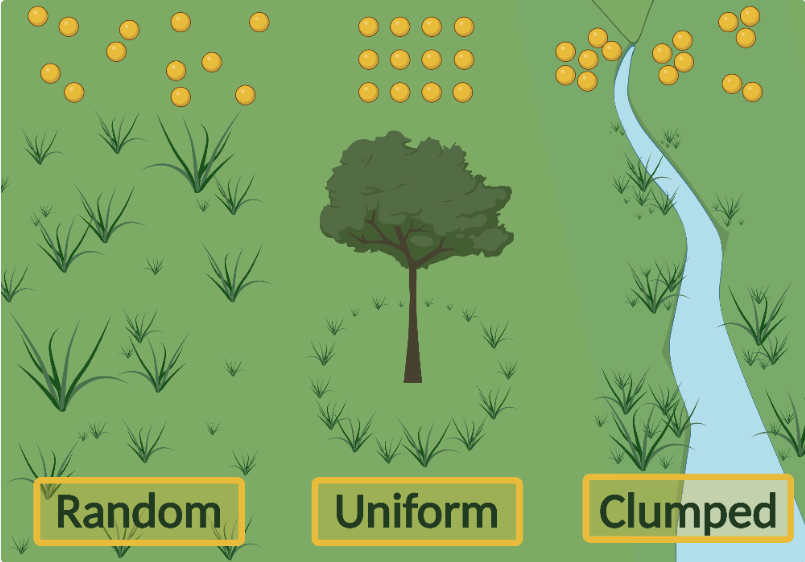
What is clumped distribution?
Most common type:
organisms may be clumped as a defence against predators, or in hunting packs/social groups, or because their resources are localised (e.g. wate hole)
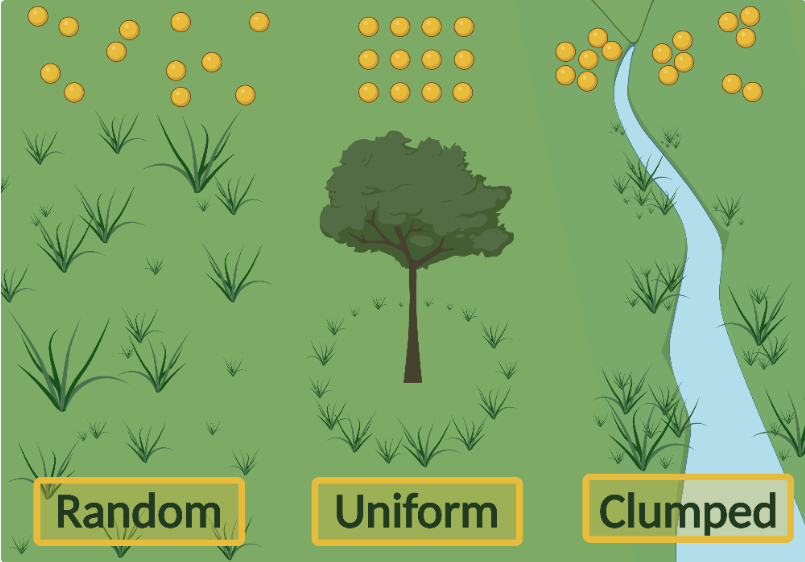
What is uniform distribution?
Individuals are as spread out as possible in a habitat
Occurs when individuals defend a territory for when there is competition for scare, thinly-spread resources
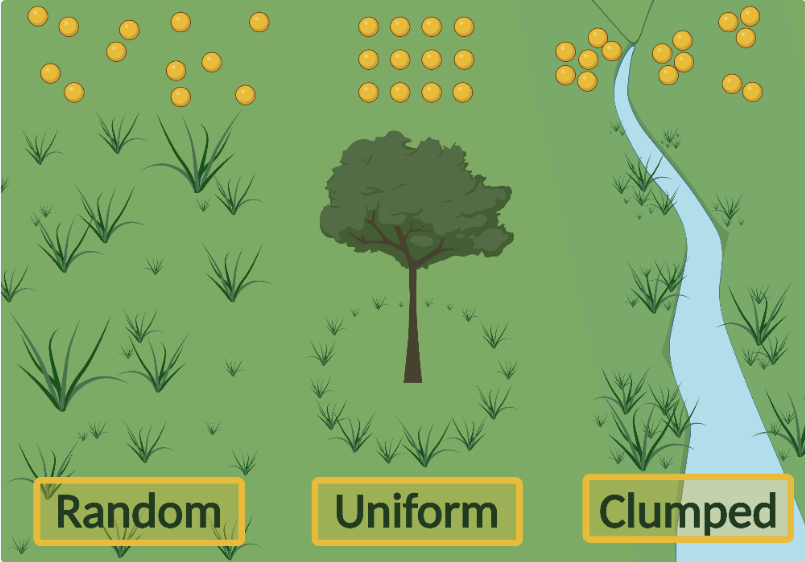
What is random distribution?
Rarest type:
occurs when the dispersal of young is random (e.g. wind-dispersed seeds) and the location of each individual is independent of other individuals
Only happens when resources are abundant & even, so there is little competition
What is the best measure of diversity?
The Simpson Diversity Index - requires you to measure the species richness & the abundance of each species
How might the growth of species be measured?
Animals = might be done by measuring their mean height, or wing span, or recording their mass
Plants = might be done by measuring mean plant height, leaf area, number of leaves, or plant mass
(have to take measurements at the beginning & end of time period)
Why do you need to measure dry mass when studying for productivity & making pyramids of biomass?
Most of a living organism’s mass is made of water, which doesn’t contain energy
How is dry mass measured?
A sample of the organisms must be warmed in an oven at about 80°C to evaporate water, but not burn any organic material
The sample is weighed at intervals until the mass no longer decreases, because all the water has been evaporated (i.e. drying to constant mass)
What are plants most easily sampled by using?
A quadrat, since they’re immobile
How is the best size of frame quadrat for a particular habitat determined?
A preliminary experiment “nesting” different-sized quadrats in the area to be studied & counting the number of species found
Using the species-area graph, a quadrat size can be chosen that is likely to catch all the species, but without wasting unnecessary effort
How is density measured using a quadrat?
Count the abundance, then divide by the area of the quadrat
(this measurement isn’t appropriate when individual plants are difficult to identify)
How is species frequency measured using a quadrat?
Number of quadrats that containing species / total number of quadrats used
(A quadrat divided into smaller squares can be used for densely-packed plants) → number of small squares that contain species / total number of small squares
How is percentage cover measured using a quadrat?
The percentage area of the quadrat covered by that particular species is estimated to nearest 5%
appropriate for when it is difficult to identify individual plants (e.g. grasses)
How can point quadrats be used to measure percentage cover?
The needle is dropped through a hole in the frame until it touches the ground & whatever species the needle hits are recorded
Less subjective than a frame quadrat & can be very quick with practice
What is a qualitative way to assess abundance?
ACFOR scale:
A = abundant
C = common
F = frequent
O = occasional
R = rare
What are the different techniques to trap animals?
Sweep nets → collect insects
D-nets → catch invertebrates dislodged from the mud
Pitfall traps → catch invertebrates that move along the ground
Longworth traps → trap small animals
Light traps = catch flying insects
Sighting method = count number of animals as you move through/fly over an area
What is the capture-recapture technique?
Capture a sample of animals using one of the trapping techniques
Count all the animals in this sample & mark them in a harmless way
Release them all & give them time to mix with rest of population
Capture a second sample & count the animals and the number marked. Calculate the population estimate