unit 2 economics
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade ap economics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
law of demand
- inverse relationship between price of good and quantity demanded by consumers
- P↑ = Qd ↓
- P↓ = Qd ↑
law of demand explanations
- law of diminishing marginal utility: bc utility goes down as you consume, you must lower prices
- income effect: as prices increase, consumers consume less bc of income constraint
- substitution effect: as price increase, consumers buy less bc of substitutes
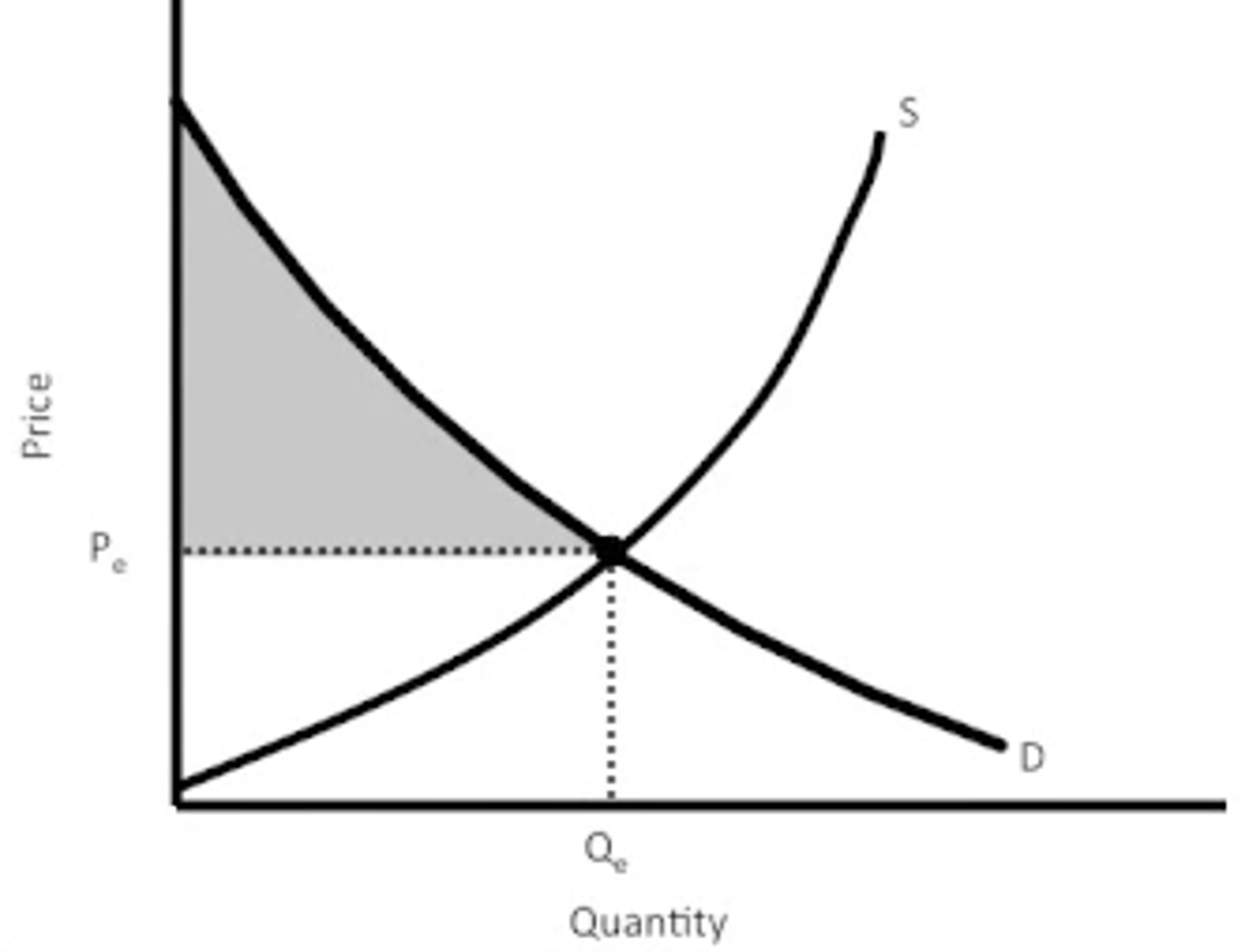
consumer surplus
difference between the price that a consumer is prepared to pay and the actual price paid
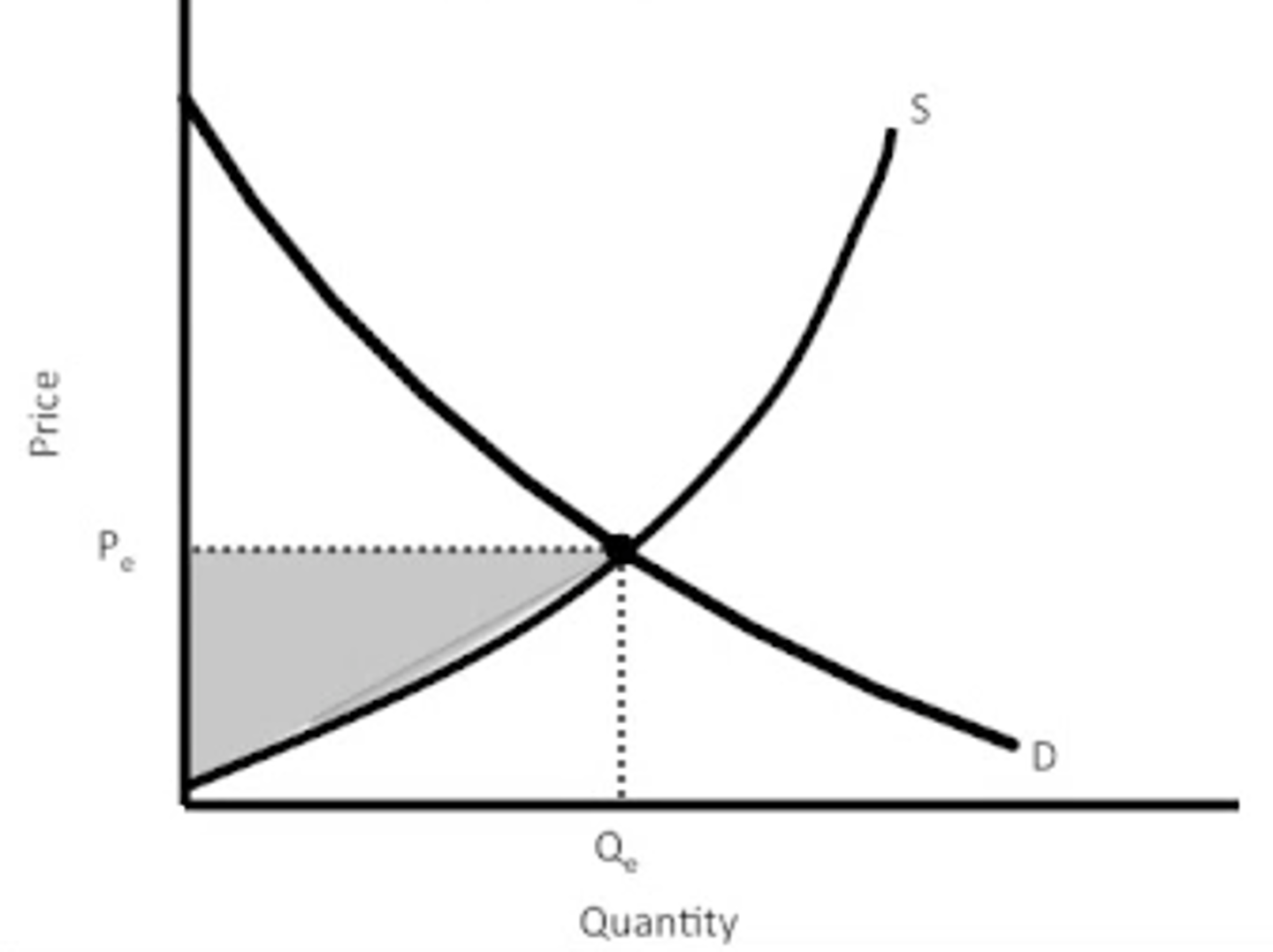
producer surplus
difference between the price that a producer is prepared to offer and the actual price charged
determinants of demand
- Price of related goods: substitute or complements
- Outlook: expectations
- Income: normal or inferior
- Number of buyers
- Taste: attitudes, advertising
change in quantity demanded
- price change
- movement along demand curve
change in demand
- something other than price changed
- shift of demand curve
substitute goods
- direct relationship
- Px↑ = Dy↑
complement goods
- inverse relationship
- Px↑ = Dy↓
normal goods
- direct relationship
- income↑ = D↑
inferior goods
- inverse relationship
- income↑ = D↓
determinants of supply
- Size of industry
- Price of related product lines that share same resources
- Input costs
- Government actions
- Outlook
- Technology
change in quantity supplied
- price change
- movement along supply curve
change in supply
- something other than price changed
- shift of supply curve
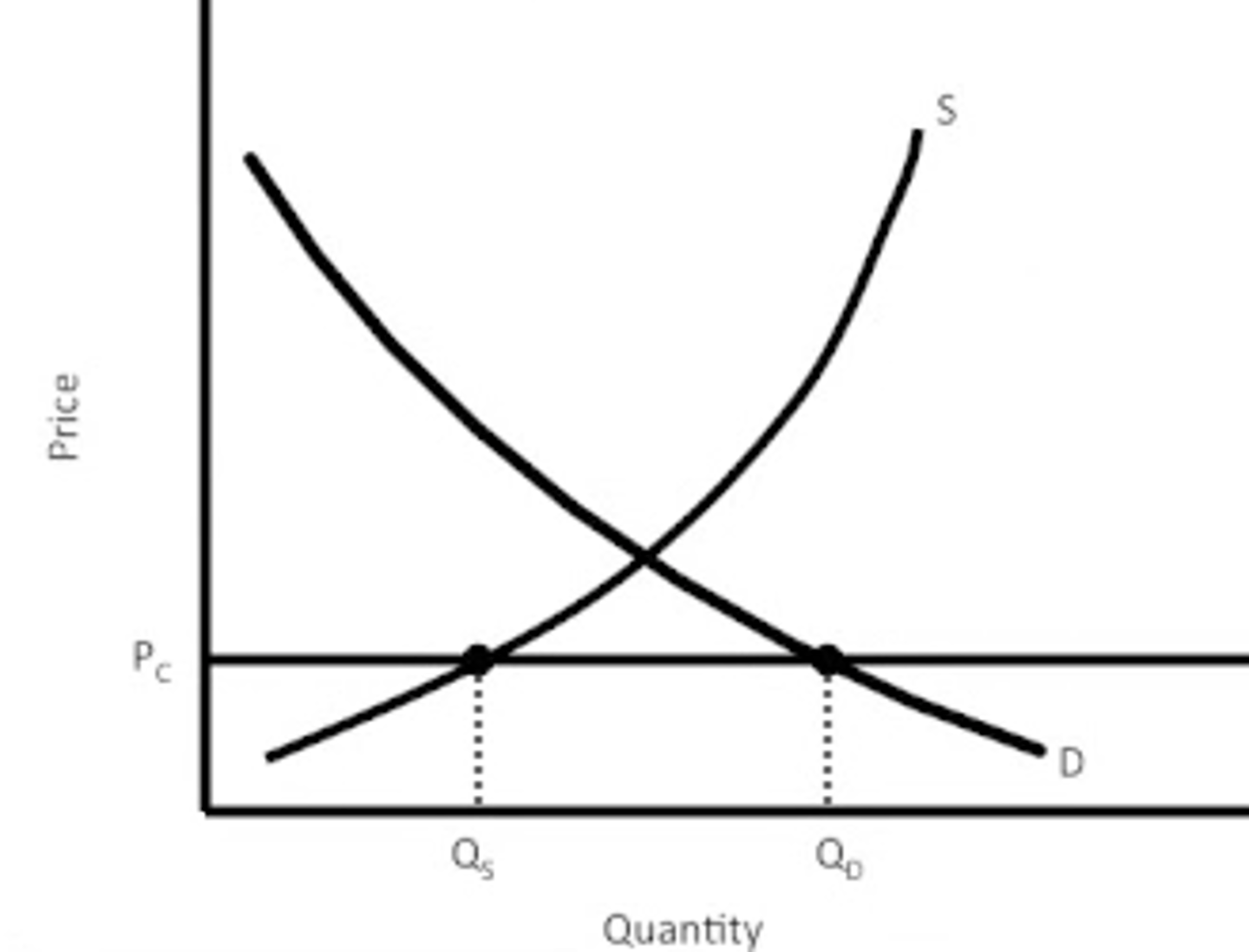
price ceilings
- below equilibrium
- shortage
- protect consumers
- cap on price/price cannot go up to equilibrium (maximum price allowed to charge)
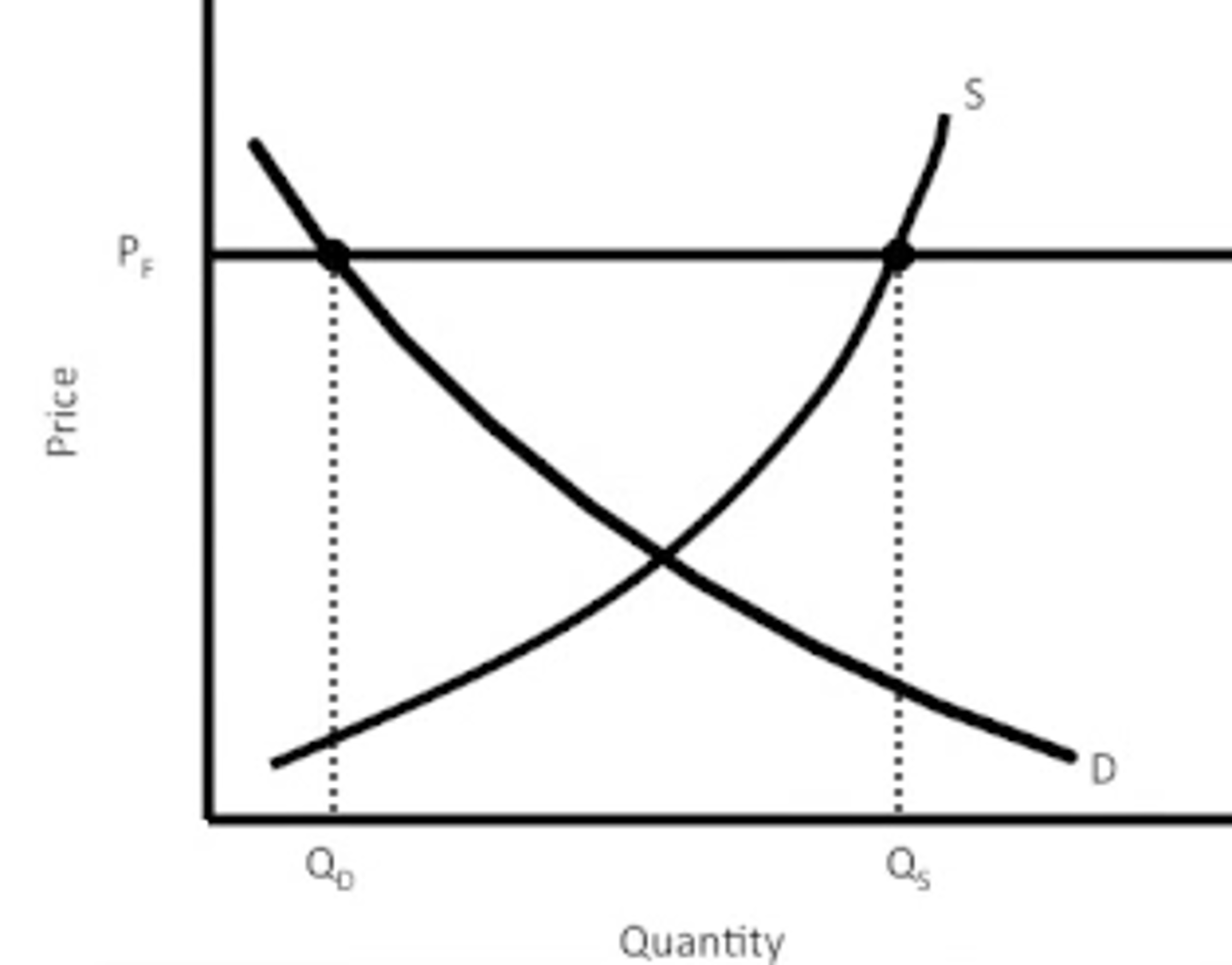
price floors
- above equilibrium
- surplus
- protect producers
- minimum price buyers are expected to pay
elastic
- quantity demanded/supplied is sensitive to price changes
- many substitutes
- P↑ = TR ↓ (inverse relationship)
- MR = positive
inelastic
- quantity demanded/supplied is not sensitive to price changes
- little to no substitutes
- P↑ = TR ↑ (direct relationship)
- MR = negative
price elasticity of demand (PED)
- coefficient test
- perfectly elastic = ∞
- relatively elastic = greater than 1
- unitary elastic = 1
- relatively inelastic = between 0 and 1
- perfectly inelastic = 0
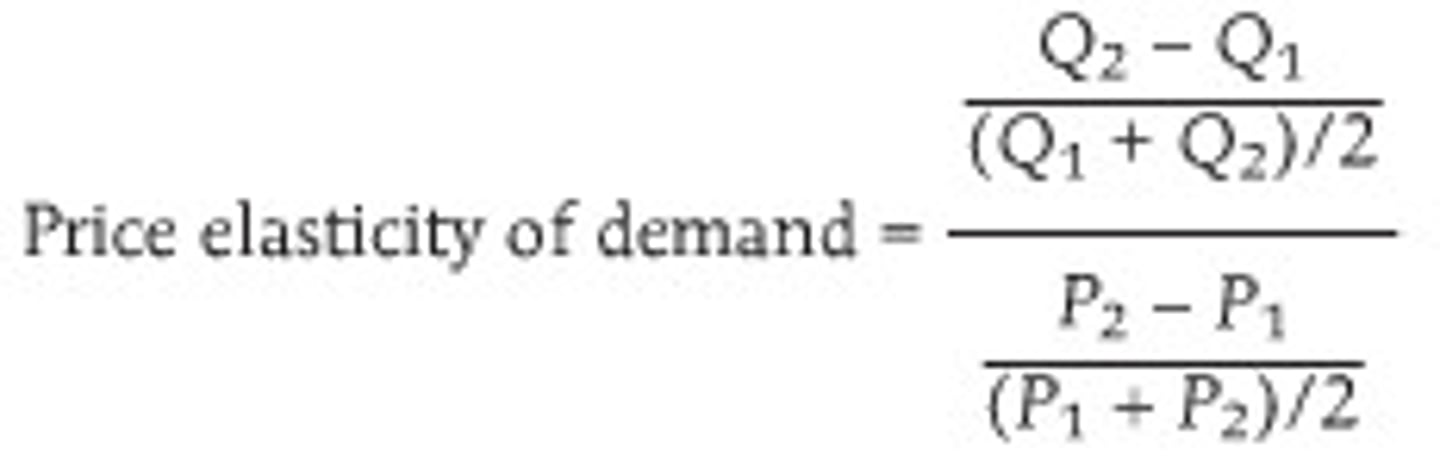
perfectly elastic
horizontal line
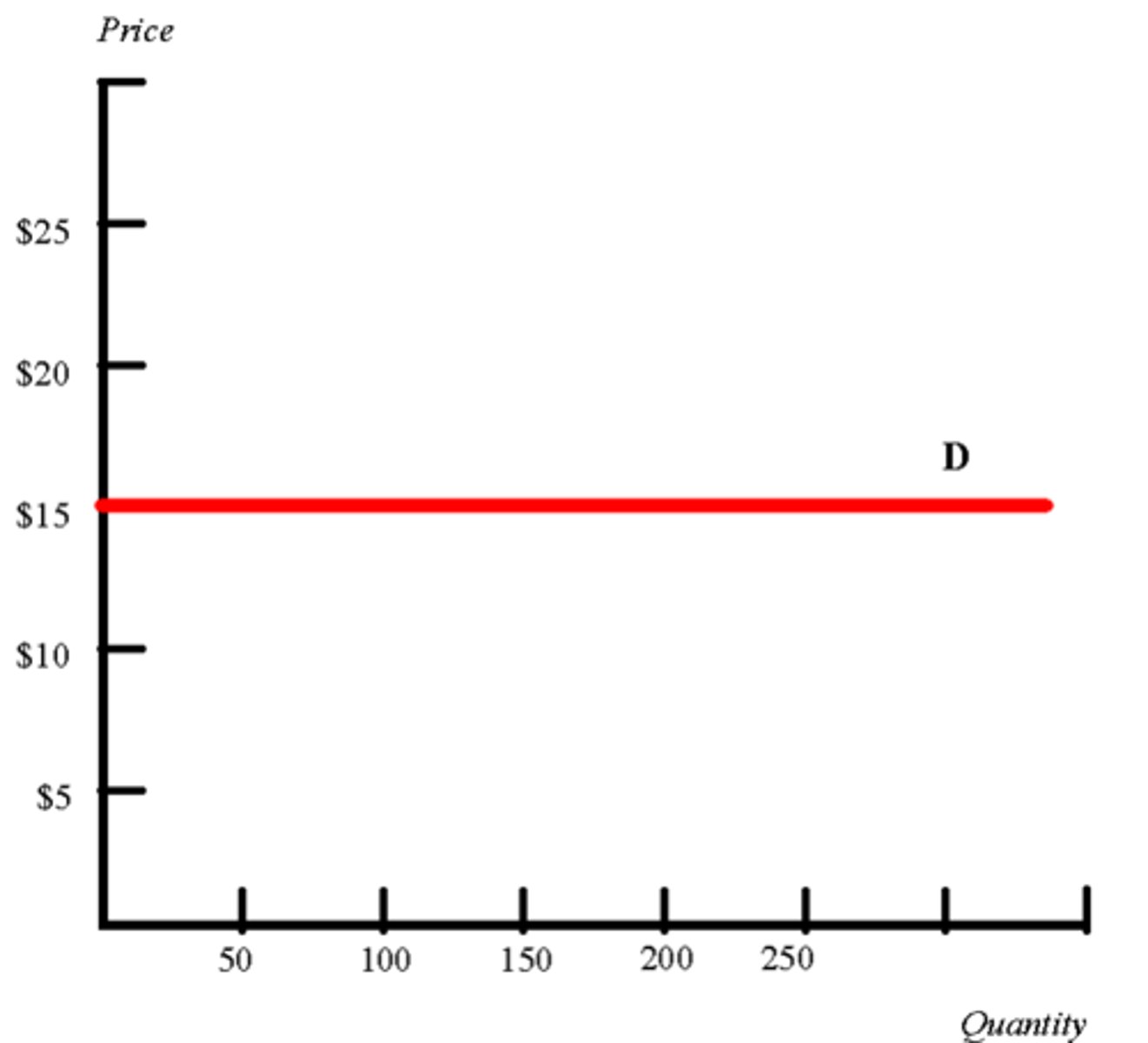
perfectly inelastic
vertical line
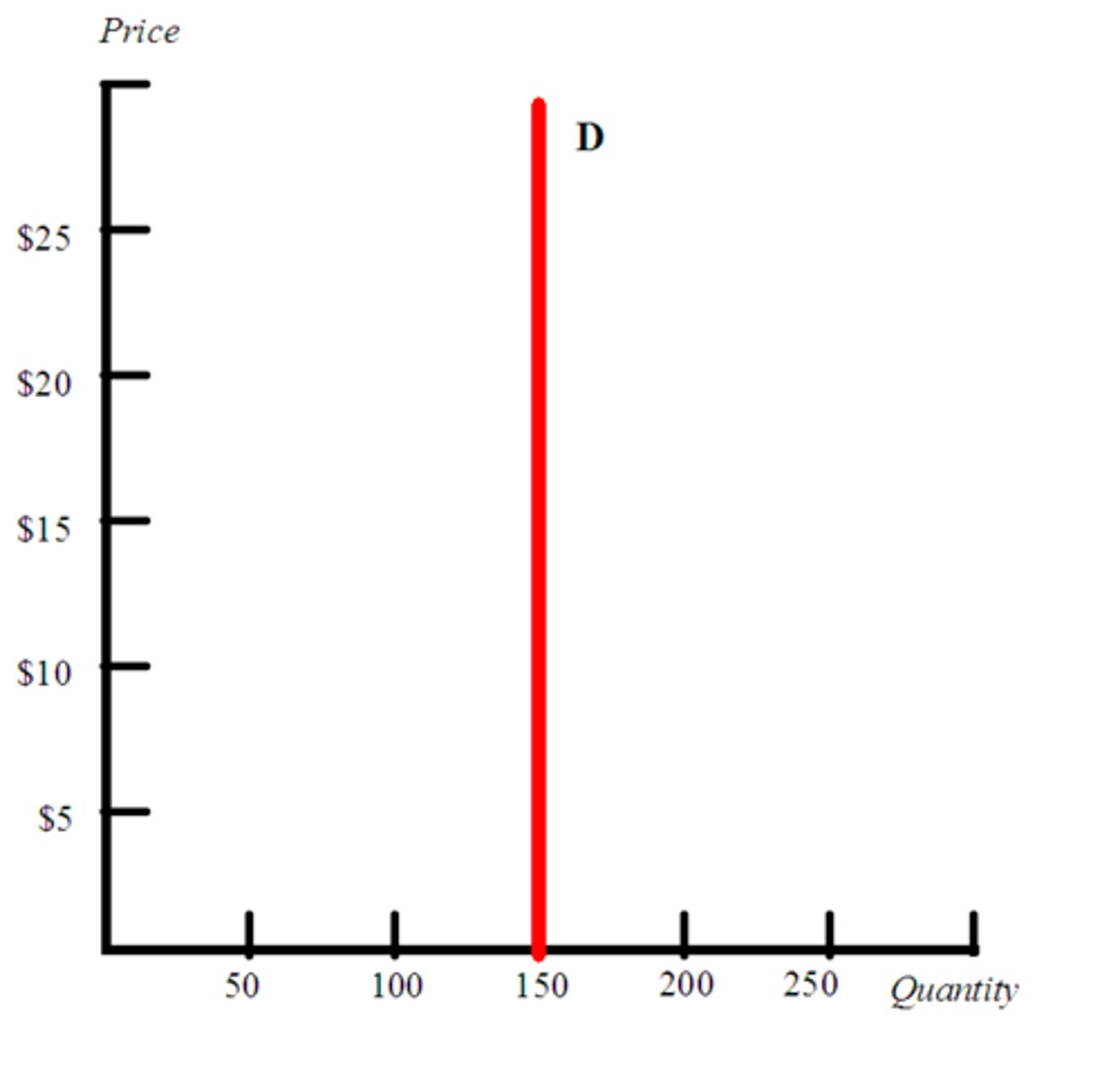
total revenue test
- multiply price by quantity
- elastic: P↓ = TR↑ (inverse relationship)
- inelastic: P↑ = TR↑ (direct relationship)
price elasticity of supply (PES)
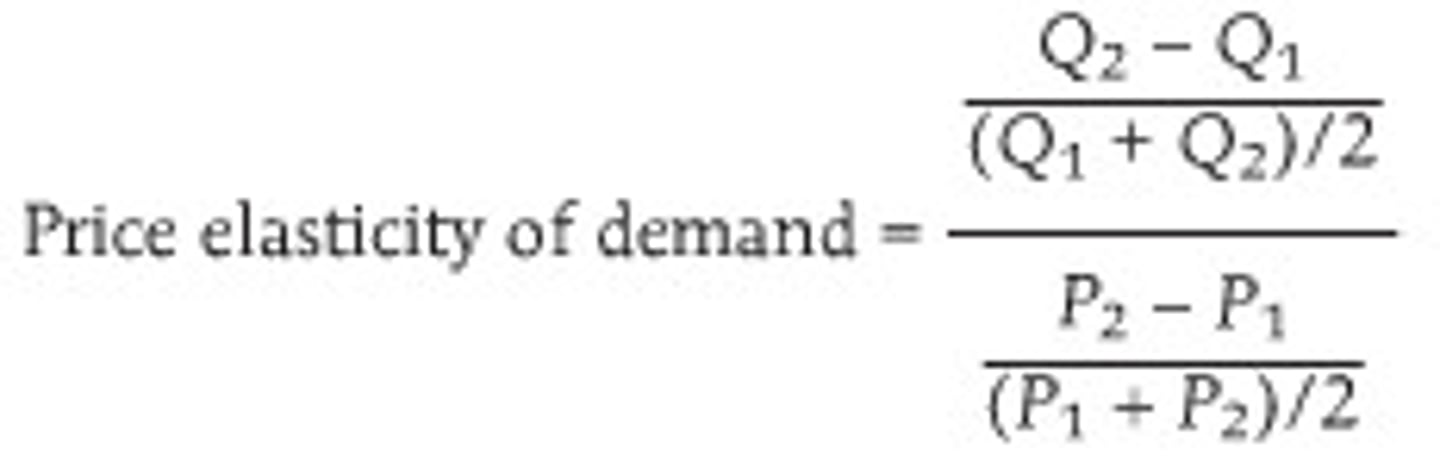
cross price elasticity
- how the price of a good affects the demand of another good
- substitutes = positive (Px↑ = Qy↑; direct relationship)
- complement = negative (Px↑ = Qy↓; inverse relationship)
income elasticity
- how changes in income affects changes in demand
- normal good = positive
- inferior good = negative
incidence of tax
- burden on consumer: inelastic demand, elastic supply
- burden on producers: elastic demand, inelastic supply
- elastic demand: largest DWL, lowest tax revenue
- inelastic demand: lowest DWL, largest tax revenue
shortage
- quantity demanded > quantity supplied
- results in higher prices
surplus
- quantity demanded < quantity supplied
- results in lower prices
D↑, S↓ (double shift)
P↑, Q?
D↑, S↑ (double shift)
P?, Q↑
D↓, S↑ (double shift)
P↓, Q?
D↓, S↓ (double shift)
P?, Q↓
double shifts in demand and supply
- inverse D and S = price agrees with D and quantity is indeterminate
- direct D and S = quantity agrees with S and price is indeterminate