Tides and Waves
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
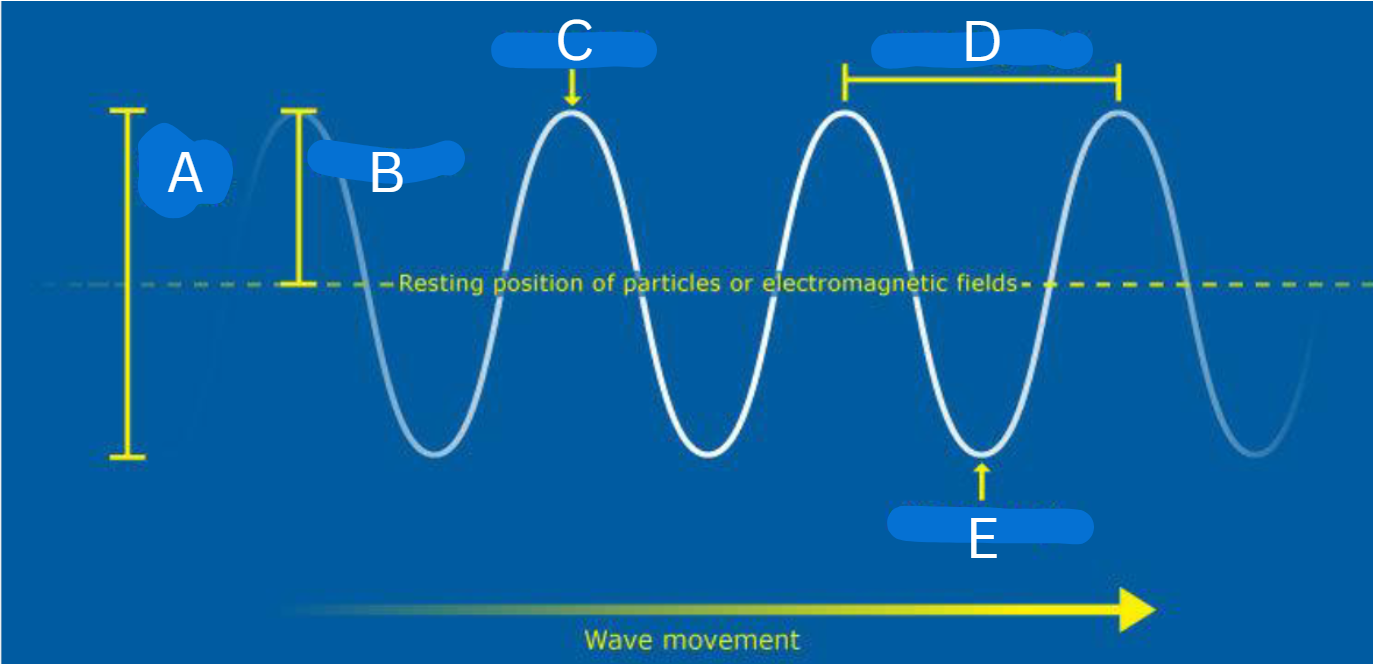
label each letter
A: wave height
B: amplitude
C: crest
D: wave length
E: trough
wave height (H)
vertical change between crest and trough
amplitude (A)
half the height
wavelength (λ)
distance between two crests or troughs
wave period (T)
time between two crests or troughs
frequency (v)
number of crests or troughs passing through a fixed point in 1 second
speed formula
λ x v (wavelength x frequency)
how do waves form?
when energy transfers to a body of water via wind or gravity
restoring forces of water (make it flat again)
gravity and surface tension
surface winds
generated by moving wind
tide waves
generated by gravitational pull of sun and moon
in which way does the wind pull water?
slightly horizontal in clockwise orbitals
deep water waves
don’t interfere with seafloor, form over water deeper than λ/2
shallow water waves
interfere with seafloor, form over water shallower than λ/2
swell waves
waves reaching the shore first
dispersion/sorting
faster, longer λ waves overtake shorter, slower λ waves
wave trains
formed by waves of similar speeds
types of wave interference
constructive and destructive
constructive interference
two waves in the same phase (both waves are in a crest or trough) meet and combine to create a bigger wave
destructive interference
two waves in different phases (one wave is in a crest and the other in a trough) meet and cancel each other out
refraction
deep water waves turn into shallow water waves at different parts along the shore
do waves refract towards or away from a headland (big rock)?
towards
dissipation
energy from waves dissipates as it goes into a bay
types of shallow water waves
spilling, plunging, surging
spilling breakers
flat beach with fine sand and high biodiversity
plunging breakers
sloping beach with coarse sand and high biodiversity
surging breakers
steep beach with pebbles or rocks and no fauna except microscopic ones
tsunamis
massive wave caused by offshore earthquake displacing the seabed, e.g. ache indonesia or tohoku japan
why does the tide retract before a tsunami?
the trough of a very high wave comes in first
diurnal tide
once per day
semidiurnal tide
twice per day
what forms the tide-producing force?
combination of the earth’s centrifugal force and the moon’s gravitational pull
why do tides move forward daily by 50 minutes?
the amount of time it takes for the earth (24hr orbit) and the moon (24hr 50min orbit) to realign
spring tide
greatest tidal range
neap tide
smallest tidal range
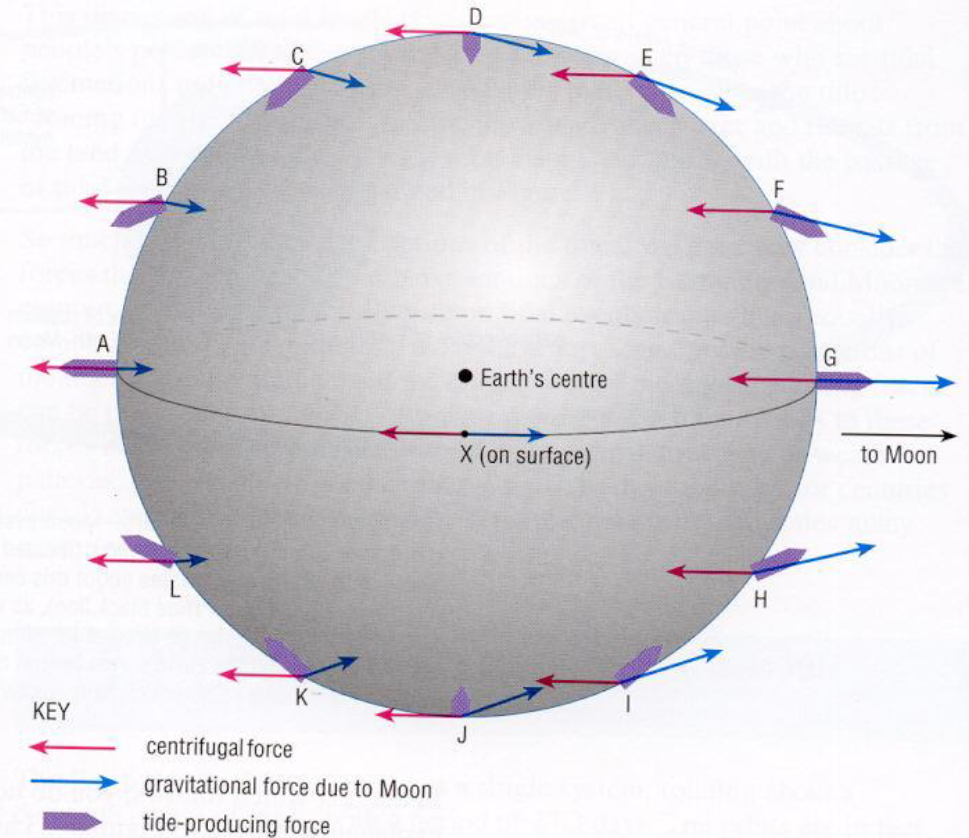
which letters represent high tide and which represent low tide?
high tide: A and G; low tide: D and J
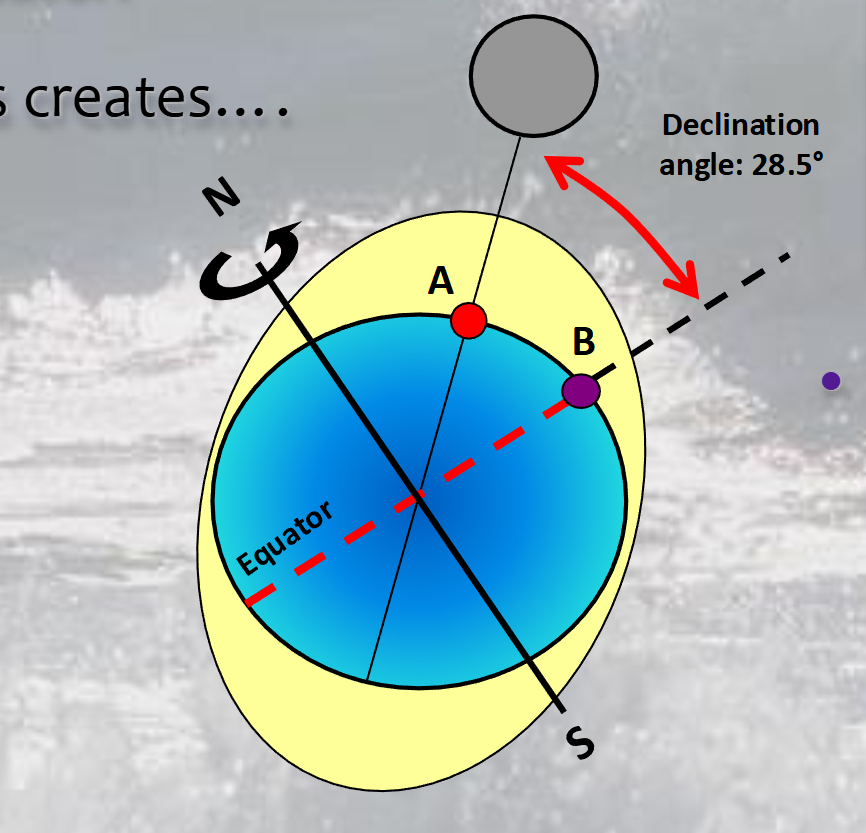
which letter experiences diurnal tides, and which experiences semidiurnal tides?
A diurnal; B semidiurnal
amphidromic system
tidal wave rotates around a fixed point (amphidromic point)
which direction do tidal waves rotate in the N hemisphere?
counterclockwise
which direction do tidal waves rotate in the S hemisphere?
clockwise
tidal bore
rapid incoming tide coming into a narrow inlet faster than the water can move
exposure
the amount of energy a shoreline gets via waves
what is exposure governed by?
shore location, prevailing wind direction, fetch
fetch
distance that wind travels over open water
ballantine scale 1961
exposure scale for rocky shores
zonation
separation of species on a shore by their niche
a reflective beach has exposure
greater
a dissipative beach has exposure
lower
upper limit factors of zonation
abiotic; temperature, salinity, etc.
lower limit factors of zonation
biotic; competition, adaptations, etc.