Week 10.1 Evolution and Life History Trade-Offs in Organisms
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Life history
Patterns of growth, reproduction, and survival.
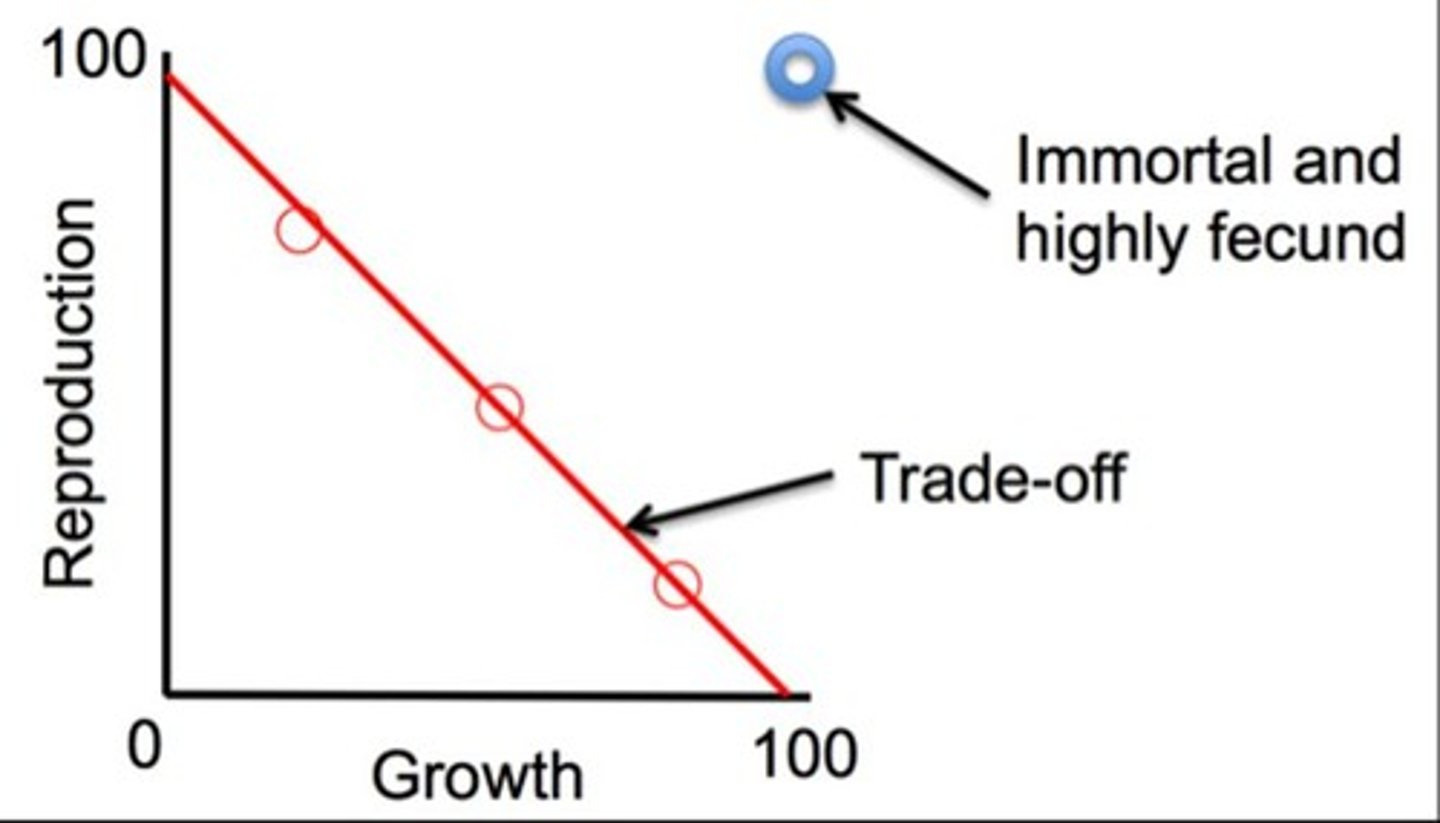
Life history trade-offs
Compromises between incompatible traits in organisms.
Semelparous organisms
Reproduce once in a lifetime, then die.
Iteroparous organisms
Reproduce multiple times throughout their life.
Demography
Statistical study of population changes over time.
Life tables
Tools for analyzing survival data in populations.
Survival data
Information on the likelihood of survival over time.
Reproductive strategies
Methods organisms use to reproduce effectively.
Environmental constraints
Factors limiting resource allocation in organisms.
Natural selection
Process favoring optimal energy allocation for reproduction.
r (growth rate)
Maximum growth rate of a population.
K (carrying capacity)
Maximum population size an environment can sustain.
Life history traits
Traits affecting survival, reproduction, and growth probabilities.
Genotypic variation
Differences in genetic makeup affecting phenotypes.
Phenotypic plasticity
Variation in traits due to environmental interactions.
Heritability
Estimate of genetic variation in a trait.
Physiology
Study of bodily functions and processes.
Longevity
Length of life or lifespan of an organism.
Rate of living theory
Aging theory based on metabolic rate.
Telomeres
Protective DNA sequences at chromosome ends.
Cell senescence
Non-dividing state triggered by short telomeres.
Tumor protein P53
Protein regulating cell division and aging.
Mutation accumulation hypothesis
Late-acting mutations weakly selected in evolution.
Antagonistic pleiotropy hypothesis
Single gene affects multiple traits, influencing aging.
Reproductive effort
Energy invested in producing offspring.
Clutch size
Number of offspring produced at one time.
David Lack's hypothesis
Optimal clutch size maximizes surviving offspring.
Energy balances
Carried over among reproductive years.
Bioenergetic model
Model analyzing energy use in organisms.
Body size
Mass of an organism influencing its traits.
Migration
Seasonal movement of organisms for resources.
Sedentary tortoises
Tortoises that do not migrate for resources.
Crazy organisms
Unique reproductive behaviors in certain species.
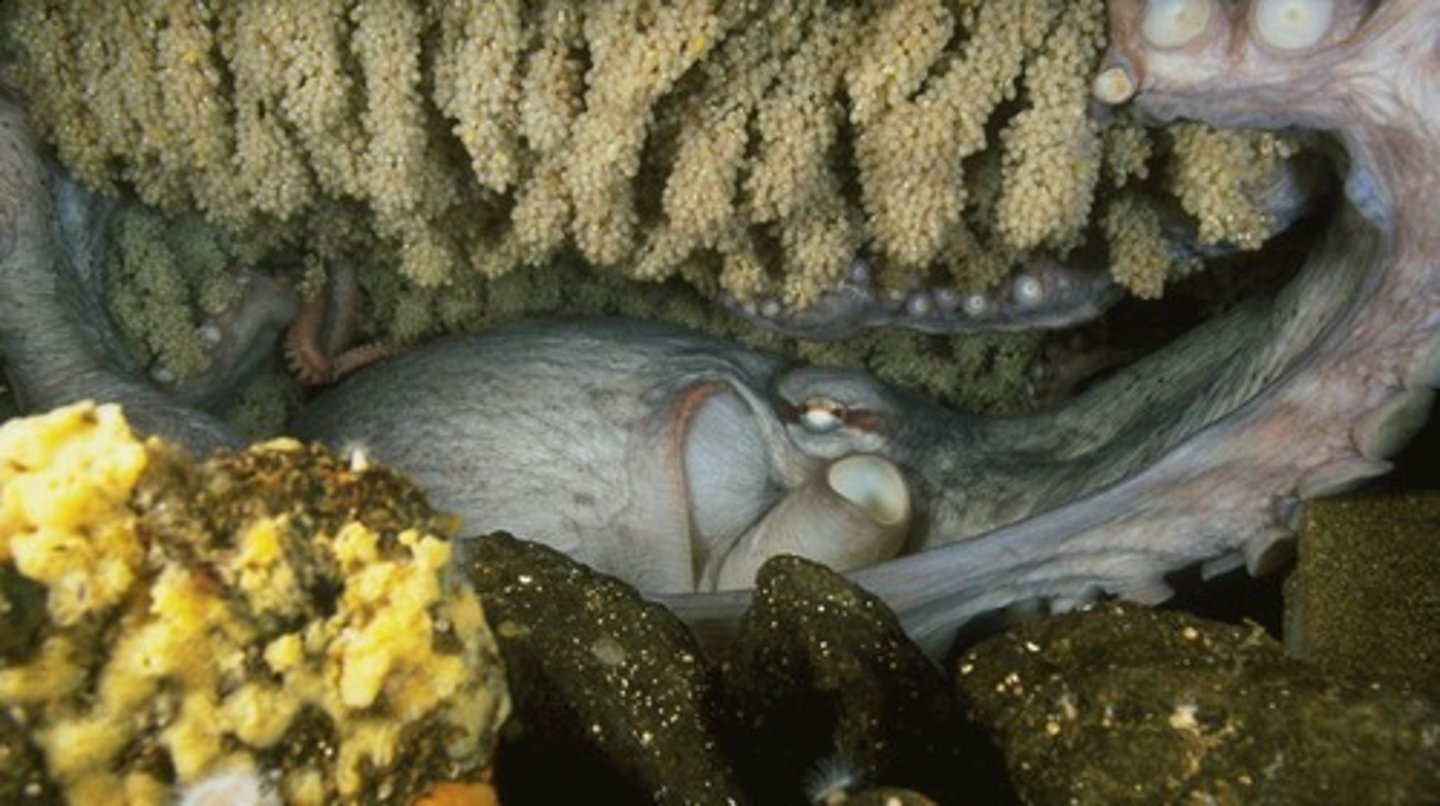
North Pacific Giant Octopus
Lives 3-5 years, reproduces once.

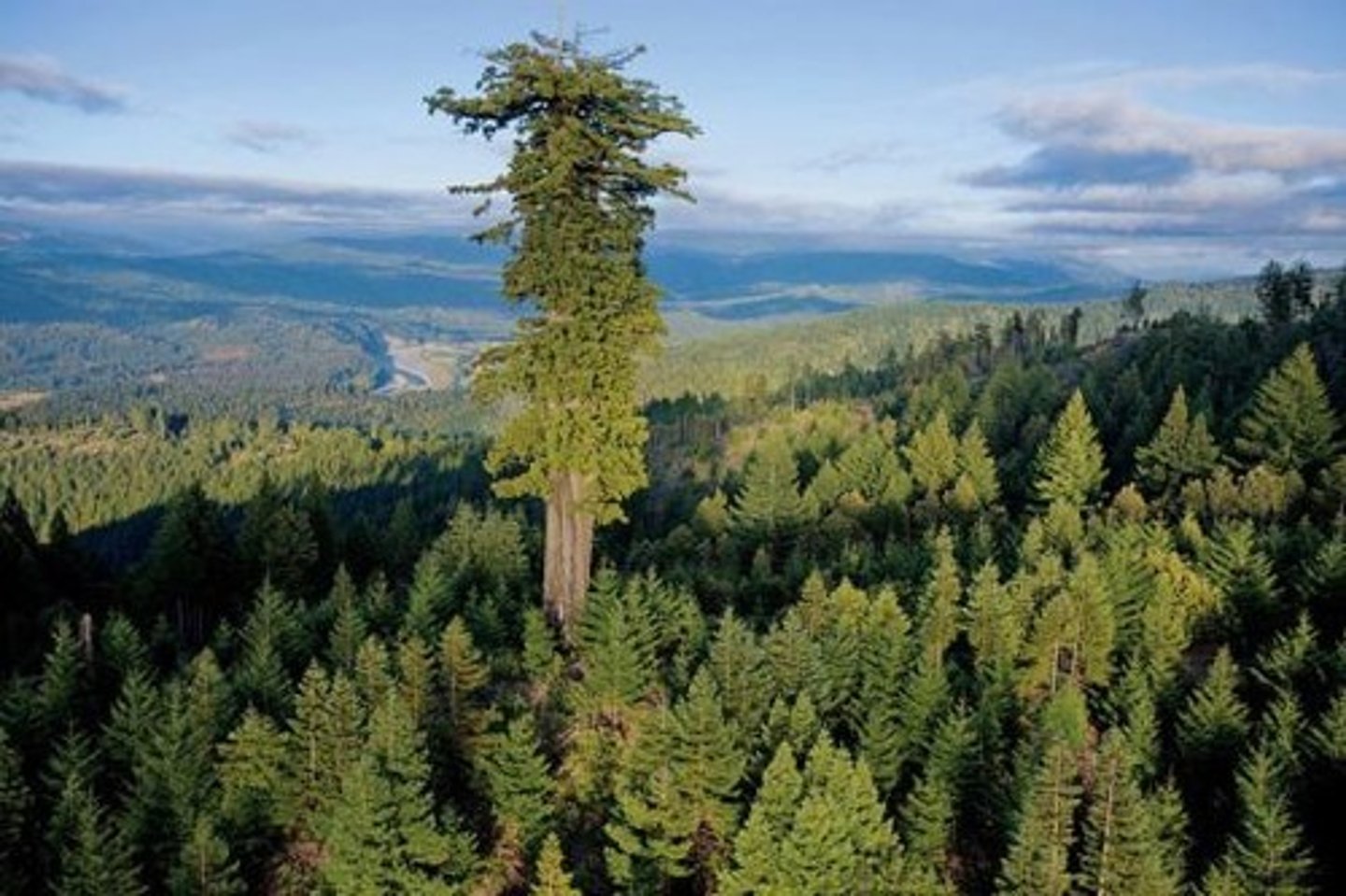
Giant sequoia
Lives thousands of years, reproduces annually.

Sand cricket morphs
Different forms adapting to resource availability.
Age-specific reproductive investments
Resource allocation varies with age.
Age-specific mortality schedules
Patterns of death rates at different ages.
Length of life
Duration an organism lives before dying.
Physiological limits
Biological constraints on cell and tissue function.
Evolutionary responses
Adaptations based on environmental interactions.
Fitness
Organism's ability to survive and reproduce.
Population life table properties
Characteristics derived from individual success rates.
Trade-off between cancer risk and aging
Balancing longevity and cancer susceptibility.
High levels of p53
Reduce stem cell division and cancer risk.
Moderate telomere length
Optimal balance between cancer risk and cell division.