Microbial Disease
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Two types of Immunity
Innate and Adaptive
Innate
- No specificity
- Cells:
Lymphoid cells (Natural Killer cells)
Phagocytes
Adaptive
-Specificity
-Cells:
T & B lymphocytes
Whats the purpose?
Limit Entry and Growth
How to limit entry?
Skin
Membranes
Flora
Skin
Impermeable
hostile
sweat (lactic acid)
low pH
Membranes
Mucus
cillia
antimicrob flushing
Flora
competition
inhib compounds
How to limit growth?
bacteria killing enzyme
phagocytosis
Two types of phagocytes
macrophages
neutrophils = polymorphs
Macrophages
Promonocytes (bone)> monocytes (blood) > macrophage (tissue)
lung, liver, lining of lymph nodes
Polymorphs
White cells
Non dividing
No mitochondria
Phagocytosis (PAMPs and PRRs)
Pattern Recognition
PAMPs: pathogen associated molecular patterns
PRRs: pathogen recognition receptors
How does a phagosome form?
pseudopodia extend out, actin myosin close, phagosome forms
2 Types of fusion and killing
oxygen-independcent (other mechanisms and enzymes)
oxygen-dependent (using bunch of intermediates)
Compliment system of Phagocytosis
Contact > Formyl Methionyl peptides attracts leukocytes (chemotaxis) > Compliment proteins
Compliment system
product > catalyst of next
C followed by # (ex C3)
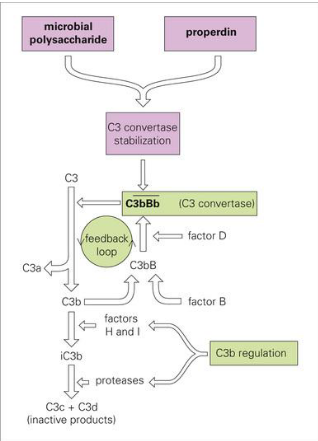
Explain the C3 complement system
C3 to C3a & C3b
C3b > C3bB > C3bBb (c3 convertase)
More pathogen, more stabilized and breakdown occurs more
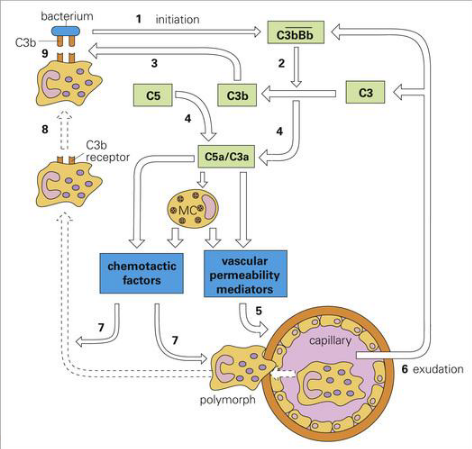
Alternative Complement Pathway (C5 C3 pathway)
C3b bind to bacteria (marks bacteria)
C5 forms complex with C3a
chemotactic factors (attracts bacterial cell)
vascular permeability mediatiors (allows macrophage travel)
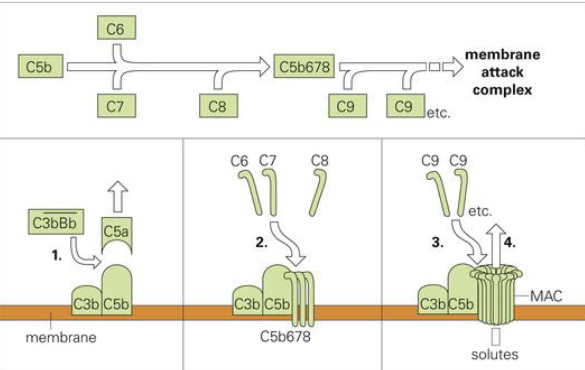
Poking hole pathway
MAC: membrane attack complex
C3bBb makes C5a leave (later forms complex with C3a)
C3b and C5b left, recruit C6-8 then C9
creates hole
Acute Phase Proteins
Increase in concentrations in response to injury and inflammation
Not specific, used as indications
Antimicrobial Factors
Act in phagocytic cells and in fluids
Tears and Saliva (Lysozyme)
Lactoferrin (blood, iron binding compound sapping iron from pathogens)
Interferons
Cells infected resistant to superinfection
Secrete interferons, which bind to other cell receptors, leading to producing antiviral proteins to limit spread.
Natural Killer Cells
Bind to receptors of cell, cell release granules like MAC (membrane attack complex)
Allows entry of granzyme B, leading to apoptosis
Eosinophils
Combat large parasites (since too large to be engulfed)
Bind to C3b to activate, toxic compounds released.
Antigen
any molecule that reacts with Ab or Ag receptor
Immunogen
Ag that can induce IR
Antigenic/immunogenic
Relative ability of Ag to induce IR, how good or strong it induces it.
Antigenic determinants = epitopes
Regions of Ag molecule recognized by adaptive immune response
10 or more aa, antigenic structure
thats why mutations are tricky, just need to change the sequence of 10 amino acids
Antibody
produced by b-lymphocytes (b-cells) which produce only one specificity
Neutralizes
In response to Ag divides and differentiates
some to memory cells some to antibodies
Antibody Structure
Two regions (2 arms and stem)
Arms bind
Stem tags for destruction (creates link)
What is antibody made of? (tell me the two and the classes)
Light Chain: either lambda (λ) or kappa (k) since both are identical. Lλ or Lk
Heavy Chain: 5 types, giving the class
μ (mew)=IgM
Y (gamma)= IgG
α (alpha)= IgA
δ (delta) = IgD
ε (epsilon)= IgE
IgG
Y (gamma)
monomeric, 75% of antibodies
4 subclasses based on aa of heavy chain c regions
IgG1-4, IgG1 most
Functions:
Opsonization (marking for death)
Neutralizes
Secondary response
Crosses placenta (w mom)
IgM
μ (mew)
Monomeric (attached to b cell) pentameric in serum held by j chain
Functions:
First Ab during primary response (indicate if been exposed)
Ag receptor on b cell
activate part of innate
clumps particulate antigen (e.g bacteria)
IgD
δ (delta)
monomeric, <2%
\Serum and B cell surface
Unknown Function
IgA
α (alpha)= IgA
monomeric but dimeric in sercretions, low amount
Primary Ab of mucous membranes
Secondary Ab in mucosal secretions (resistant to lac protease, in saliva)
Functions:
Prevent mucous membrane attachment
Passive immunity - breast milk (w mom)
IgE
ε (epsilon)= IgE
monomeric form, low levels
On mast cells (tissues) and basophils (blood)
Functions:
Anaphylactic Hypersensitivity (alergies, can lead to anaphylactic shock)
Antibody mediated complement pathway
Ab Ag complex trigger C4 > C4b > C4b2 > C4b2a (like C3bBb but for adaptive, breaks down c3)
Shows that they are tightly integrated
Antibody uses
Activate phagocytic cells (trigger phagocytosis)
Neutralization
blocks virus binding
blocks bacterium from getting nutrients
blocks toxic binding
Cell mediated immunity
using Tcells
Ag must be on cell, can’t be free
Its receptor binds to complex of MHC and peptide (taken from pathogen)
T-lymphocytes activate and kill with macrophages (also activated via macrophage activating factors IFNy)
Two major functional population of Tcells
Cytotoxic Tcells:
Tc, infected or cancerous cells CD8
Helper Tcell:
Th, activate b cells and macrophages CD4 (this down=aids)
Th1 Macrophage
Th2 B cells
look at ag presented by MHC class 2
What can T-lymphocytes do?
help macrophages, inhibit intracellular replication
Difference between B and T cells
difference in surface markers (CD). Mature at diff places (not in notes)
B cells
Surface immunoglobin
T cell
Tcell receptors
Clonal selection and expansion of B-lymphocytes, also why does this happen?
We would need so many Ag and epitopes since it is 1 to 1, not possible.
Correct B-cells (needed Ab) bind to Ag “clonal selection”
Then, “clonal expansion”
Somatic mutations for further tuning
Clonal selection and expansion of T-lymphocytes
No somatic mutations
after expansion some to memory cells
Memory Cells
More readily available and stimulated by Ag
Better combining power, why?
Bcells, somatic mutations
Tcells increased expression
Basis for Vaccines
Why are vaccines tricky in regard to toxicity?
Need to keep immunogenicity but cant keep toxicity in. Tricky to deactivate without ruining.
Cytokines
Communication factors
Role:
control of infection
ex. Interferon
Interferon
Infected cell release IFN, attach to uninfected, release antiviral molecules (degrade viral mRNA, Inhibit protein synthesis)
What else do cytokines do in regard to counterbalancing?
help control population of helper T cells
Host-Pathogen relationship
ability to cause disease vs host ability to eliminate
Adaptation of host and pathogen (length of relationship)
longer the relationship=less damage
myxoma in rabbits
Types of microbial infections
attachment and penetration
biting arthropod
skin wound
Steps of infection
Attachment
Spread (local)
Multiplication
Evasion
Shedding
Damage (not always)
Koch postulates
Suspect germ
Isolated and grown
put into healthy to see if disease
same germ must be reisolated
Challenges of kochs postulates:
Unculturable organisms
Host immunologic factors
More than one pathogen
if only in humans
Molecular evolution of kochs postulates
Virulence trait should be associated with pathogenic strain
Inactivation of that gene should decrease pathogenicity
Replacement of gene with norm should restore pathogenicity
Gene should be expressed at one point
Abs or immune should directed at it should protect
Biological response gradient (severity)
Depends on:
Dose and route (some routes, like skin and gi track need more)
Age (bimodal, young and old)
Sex
Nutritional status
Genetic background
Microbiome
Microbiota + structural elements, metabolites, env conditions
For every human gene how many microbial genes in our body?
350
Role of micorbiota
Nutrient extraction
Metabolism
Immunity (yeast infection)
Making bioactive molecules (vitamins, lipids, aa’s)
Skim microbiota
Lots of variation (oiliness, sweatiness, hairiness, env exposure)
gram + and -
Oily skin: actinobacteria
Moist areas: staphylococcaceae
Dyer: diverse
Most dependant on environment than individual
Vaginal microbiota (transient vs colonizers)
Colonizers (stay)
Lactobacillus acidophillus
Transient (come and go, sexual activity etc)
Staphylococcus epidermis
E.coli
Candida
Enterococcus faecalis
What influences the vag microbiota makeup?
Sex
Diabetes
Antibiotics
Age
Hormones
Oral microbiota
heavily colonized (2nd to colon)
Tongue: lactobacilli
Exposed tooth: streptoccoci
What microbe is inversely related to asthma? Why?
H. Pylori. cagA+ induces an immune response of balancing and preventing over response
Obesity and Microbiota
Antibiotics > microbiota with higher metabolism > extract higher amount (especially foods that were relatively indigestible)
Growth promotion, also thinner intestinal walls (more extraction)
Height and microbiota
Height is increasing in countries that use antibiotics more, correlation not causation. Children with less diarrhea, taller and heavier.
Edward Jenner
Founder of modern vaccination
Small pox vaccine (from cow pox, noticed milk maids didnt get)
Term coined by pasteur in honor, Vacca (latin,cow)