Exchange Rates
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are ER?
the cost of one currency in comparison to another
The market for currency is called the….
foreign exchange market (FOREX)
What is Appreciation (stronger currency)?
An increase in the value of a currency against another
meaning your £ can buy more $ and therefore more goods and services.
What does appreciation do to Xs and Ms?
Ms = cheaper
Xs = expensive
What is depreciation (weaker currency)?
A decrease in the value of a currency against another
meaning your £ can buy fewer $ and therefore fewer goods and services.
What does depreciation do to Xs and Ms?
Ms = expensive
Xs = cheaper
Mnemonic to remember appreciation & depreciation

What factors could cause an appreciation in a currency?
➢ A current account surplus on BOP
➢ Strong inward investment inflows and portfolio flows
➢ Relatively high interest rates
➢ Speculative currency demand
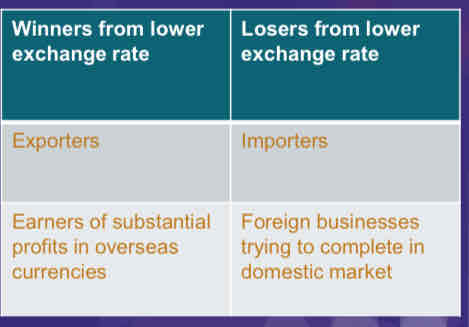
Impacts on businesses of changing ER
➢ Price of exports in international markets
➢ Costs of imports
➢ Revenues & profits earned overseas
➢ Converting cash receipts from customers overseas
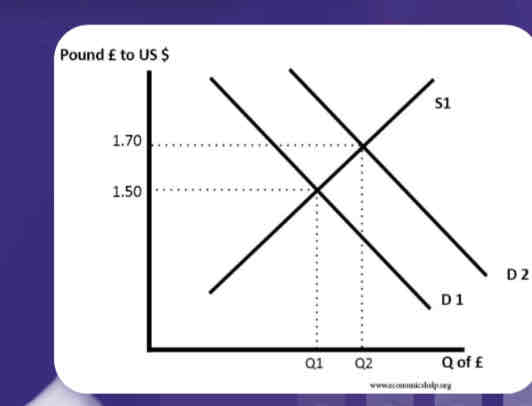
Show changing ER diagram
What is a free floating exchange rate, (clean or pure float)?
determined by market forces of demand/supply of foreign/domestic currency
Central banks/government do not intervene.
What is a fixed exchange rate?
rate that ties the country's official exchange rate to another country's currency/price of gold
How can governments artificially fix the exchange rate?
buying/selling currency on the forex market
adjust their bank rate
The government or central bank set a floor and ceiling price for the currency. As long as market forces keep the currency within this band, everything is fine.
If the equilibrium strays too close to the ceiling or floor then the government/central bank get involved to artificially adjust the exchange rate...
A boom in exports causes the demand for the £ to push the equilibrium just outside of the ceiling (D2).
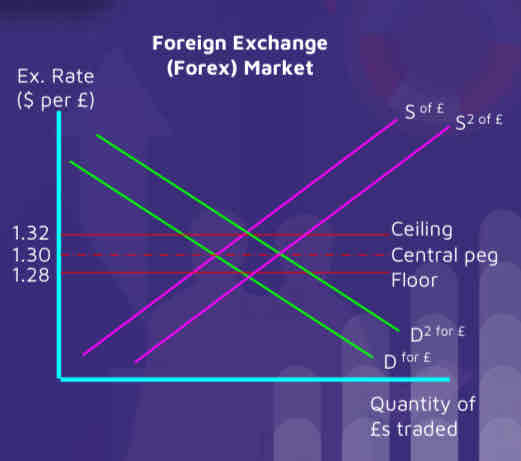
How does the government increase the supply of the currency to S2?
1. Selling lots of their currency, by buying more of the dollar… flooding the forex market with £.
2. Decreasing the bank rate causing international savers to move their money out of the £ and into another currency
What is the adjustable peg?
central bank will devalue/revalue currency from time to time.
move the central peg, ceiling and floor to a different point...and then continue to fix at that point.
What is dirty floating?
countries maintain free floating exchange rates but get involved to soften the dips of the exchange rate.
aim to ensure that shocks do not turn into economic disasters.
2015 Chinese devaluation
On August 11, 2015, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) surprised markets with three consecutive devaluations of the yuan, knocking over 3% off its value.
Since 2005, China’s currency had appreciated 33% against the U.S. dollar, and the first devaluation marked the most significant single drop in 20 years.
Chinese devaluation - Reasons
lowered the price of its exports and gained a competitive advantage in the international markets.
China still manages the exchange rate within a range against the dollar. When the U.S. dollar rises rapidly against world currencies
market-oriented reforms.
SDR is an international reserve asset that IMF members can use to purchase domestic currency in foreign exchange markets to maintain exchange rates
Chinese devaluation - Impacts
