Plant Science Lab Final
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Research
systematic inquiry into a subject to discover new facts or principles.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research
Qualitative research is subjective and assesses attitudes, opinions, behaviors, etc. Whereas, quantitative research is objective and asses more concrete observations and data
Please list the 6 basic components or steps, in order, of conducting research according to the scientific method
1. Ask a question.
2. Do background research.
3. Construct a hypothesis.
4. Test your hypothesis.
5. Analyze your data and draw a conclusion.
6. Communicate your results.
ecology
The study of the relationship of organisms and their environment or ecosystem
the 5 levles of ecological organization
a. Biosphere, the global sum of all ecosystems and living organisms and their interactions.
b. An ecosystem consists of a community of interacting and interdependent populations of plants, animals, and microorganisms and their physical environment.
c. A community consists of all the populations of plants, animals, and microorganisms that share the same habitat and interact directly or indirectly with one another.
d. Population is a group of individuals of the same species that occupies a distinct space and possess characteristics that are unique to the group.
e. Individuals are locally interacting, interbreeding groups of individuals of the same species that forms populations.
climate
refers to the temperature, humidity, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions over a long period of time
define competition
when more than one organism draws on a resource that is in short supply
What is unique about legumes and what do they contribute to an ecosystem
Legumes can fix nitrogen in the soil by the symbiotic relationship with Rhizobium bacteria which can enrich the soil with nitrogen and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers
Why did we, as the scientific community, classify plants? Consider the concepts of common vs botanical names.
a. The botanical names are uniform and accepted internationally that classifies the plants, while the common names can vary depending on the geographical location. Common names are not uniform and can vary from person to person.
How does a dichotomous key work
a. A dichotomous key works as a process of elimination by making yes or no decisions to characteristics offered in the key. As you make the decisions, you eliminate the alternative and thus move forward to the next pair of choices.
what is a cotyledon
leaflike structure at the first node of the seedling stem.
monocotyledon
parallel venation
dicotyledon has what type of venation
complex
simple vs compound
a. Simple leaves feature a single, undivided or slightly incised leaf blade, whereas compound leaves consist of multiple leaflets arranged on one leaf blade.
5 components of leaf division
shapes, bases, apices, margins, arrangements

identify the parts of the leaf
apex
vein
midvein/midrib
margin
base
petiole
blade
difference between complete and an incomplete flower
a. A complete flower contains four parts: sepals, petals, stamen, and the pistil.
b. An incomplete flower lacks one or more of the four parts: sepals, petals, stamen, and the pistil.
difference between perfect and imperfect flowers
a. A perfect flower contains a stamen and a pistil.
b. imperfect flowers are missing either the stamen (containing only pistils) or the pistil (containing only stamen).
monoecious vs dioecious
a. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts in their flowers on the same plant.
b. Dioecious plants have a male plant separate from the female plant. Male and female flowers are on different plants.
determinate growth
Determinate, or bush, types of plants produce a full crop all at once and reach a specific height before ceasing growth. These plants are typically favored by commercial growers who aim to harvest an entire field simultaneously.
indeterminate growth
a. develop vines that never cease growing and continue producing fruit until they are killed by frost. These plants keep growing and producing along the stems throughout the entire growing season and usually require a trellis or support system. Most heirloom tomatoes exhibit indeterminate growth.
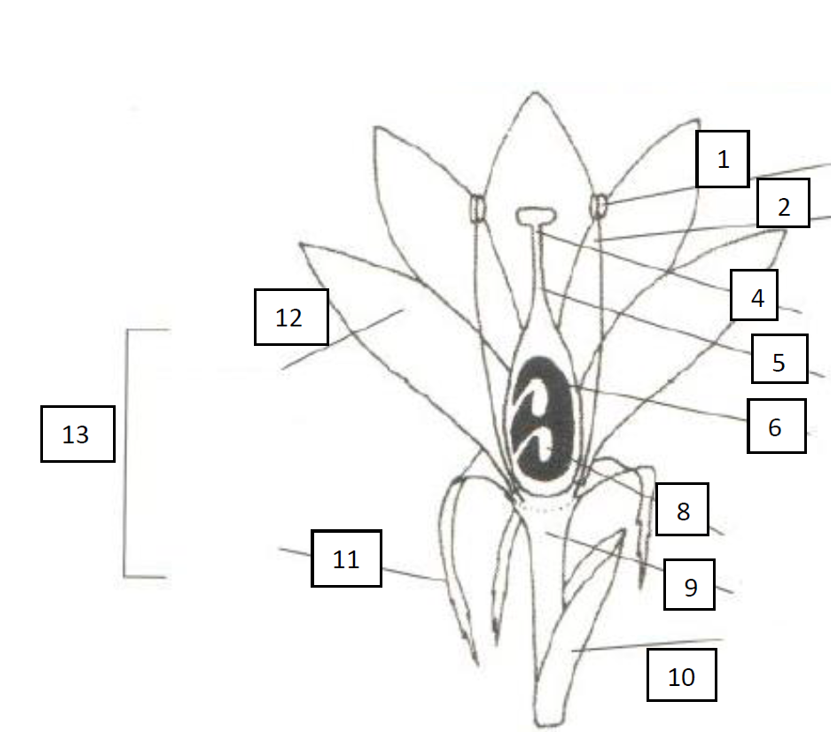
identify the numbered flower components in the above diagram
anther
filament
stamen
stigma
style
ovary
pistil
ovule
receptacle
bract
sepal
petal
perianth
what is a seed
a mature ovule with 3 basic parts
3 basic parts of a seed
embryo
food storage tissue
seed coat
difference between fruit and a vegetable
fruit is a seed bearing structure that develops from the ovary of a flowering plant
a vegetable contains roots, stems, and or leaves
APHIS
animal and plant health inspection service
this service protects animal agriculture from pests and diseases and regulate biotechnology products that could pose a risk
EPA
environmental protection agency
This agency regulates sale, distribution, and use of all pesticides. They also set tolerance limits for residues of pesticides on and in food and animal feed.
FDA
food and drug administration
The FDA oversees safety and proper labeling of all plant-derived food and feed (including GM), and they make sure all food meets the same standards.
If you or your family performed large-scale agriculture production, would you choose a GE crop over a non-GE crop? Why or why not?
The reason why I would choose a GE crop over a non-GE crop depends on several factors. These include: many GE crops are often designed to be more resistant to pests, diseases and adverse weather conditions which can help increase the yield of crops. GE crops can also reduce the use of chemical pesticides and herbicides which can benefit soil and water quality.
3 fates of light
reflected
transmitted
absorbed
wavelength range in nm that plants absorb
400 nm to 700 nm
phototropism
growth of plants and their parts towards (or away) from a light source
two unique abilities that plants posses to adjust for phototropism
acclimation which is the increase in plant stress tolerance due to exposure in prior stress and could involve changes in gene expression
plasticity which is the ability to adjust morphologically, physiologically, and biochemically in response to the changes in the environment
photoperiodism
regulation of biological processes according to relative lengths of day and night
grouping of photperiodism
short day
long day
day neutral
lumens
the total amount of light emitted by the light source. It indicates how efficiently the light source converts power into visible light. Bulbs usually have ratings
lux
the amount of light output in a given area. The total amount of visible light present and the intensity of the illumination on a surface
PAR
photosynthetic active radiation (quality or type). The band of wavelengths between 400 nm and 700 nm. Plants use this range of electromagnetic radiation to preform photosynthesis
PPFD
photosynthetic photon flux density (quantity). A measure of the PAR photons that are actually hitting the plant. PPFD measures how many photons are hitting an area per second. Reported in micromoles per square meter per second
2 locations photosynthesis takes place
thylakoid membrane (in chloroplasts)
chloroplast stroma
6 factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis
light quality
light intensity
CO2 concentration
heat
water availability
plant development and source-sink relationship
how does light intensity affect the foliage of plants
light intensity affects photosynthesis efficiency, leaf size and thickness, growth patterns, and pigmentation of the individual leaves
2 forms or types of plant propagation
sexual which involves a seed
asexual which involves vegetative tissue such as roots, stems, and leaves
list and describe 2 primary activities used to enhance seed germination and/or break seed dormancy
scarification: physical modification of the seed coat
stratification: cold treatment
3 reasons why we might want to graft a plant
pest resistance
improve root system
enhance vigor or growth
most important factor affecting success of grafting and budding
must properly match cambium layers
pest
organism that reduces the availability, quality, or value of a human resource
integrated pest managment (IPM)
a. An integrated ecosystem-based strategy that focuses on long-term prevention of pests and their damage thorough a combination of techniques such as biological control, habitat manipulation, modification of cultural practices, and use of resistant varieties.
3 essential component for disease to develop
susceptible host, pathogen, favorable environment
3 general strategies in IPM
preventative:pest free seeds
cultural: cultivation to prevent weedy growth
suppressive: use of biological control
tolerable injury
amount of pest damage can be tolerated without significantly affecting yield
treatment threshold
point at which pest populations or damage levels reach where intervention is required to prevent economic loss
how to distinguish abiotic disorder from biotic damage
abiotic: not contagious and does not spread to other plants
biotic: results from living organisms that can spread between plants often affecting specific species