S1.7 Reproductive System
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is Gonads
Gonads 性腺 are the primary reproductive organs in humans and other animals.
🔹 Definition:
Gonads are organs that produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete sex hormones.
🔹 Types of gonads:
Testes (singular: testis) in males
Produce sperm (male gametes)
Secrete testosterone
Ovaries in females
Produce eggs (ova) (female gametes)
Secrete estrogen and progesterone
What is a Gametes
What is the gametes cell in man/women
🔹 Definition:
Gametes are haploid cells (contain half the number of chromosomes compared to normal body cells) that fuse during fertilization to form a zygote.
🔹 Types of gametes:
Male gamete: Sperm cell
Small, motile cell produced by the testes.
Female gamete: Egg cell (ovum)
Large, non-motile cell produced by the ovaries.
🔑 Key points:
Haploid (n): Contains 23 chromosomes in humans.
Fertilization: When a sperm (n) and egg (n) combine, they form a zygote (2n) with a full set of chromosomes (46 in humans).
What is a Haploid & Diploid
Haploid refers to a cell that has only one set of chromosomes.
🔹 Definition:
A haploid cell (n) contains half the number of chromosomes found in normal body (somatic) cells.
🔹 In humans:
Haploid number (n) = 23 chromosomes.
Found in gametes (sperm and egg cells).
🔹 Why is it important?
During fertilization, two haploid gametes (sperm and egg) combine to form a diploid (2n) zygote with a complete set of chromosomes (46 in humans).
🔑 Key summary:
Haploid (n) = 23 chromosomes in humans (sex cells).
Diploid (2n) = 46 chromosomes in humans (body cells).
Let me know if you want a table comparing haploid, diploid, and p
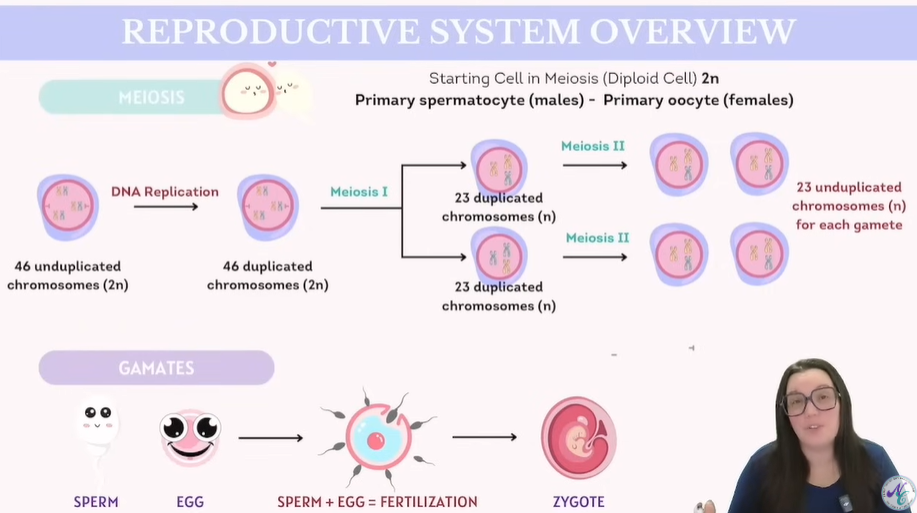
What are the Accessory organs in the Reproductive system?
Glands
Ducts
External Genitalia
What is a Zygote
A zygote is the first cell formed after fertilization.
🔹 Definition:
A zygote is a diploid cell (2n) formed when a male gamete (sperm) fuses with a female gamete (egg/ovum).
🔹 Key points:
Contains a full set of chromosomes (46 in humans), half from the father (sperm) and half from the mother (egg).
It is the beginning of a new organism.
Undergoes rapid cell division (mitosis) to develop into an embryo.
🔑 In simple words:
Sperm + Egg = Zygote, which then grows into an embryo and later a fetus.
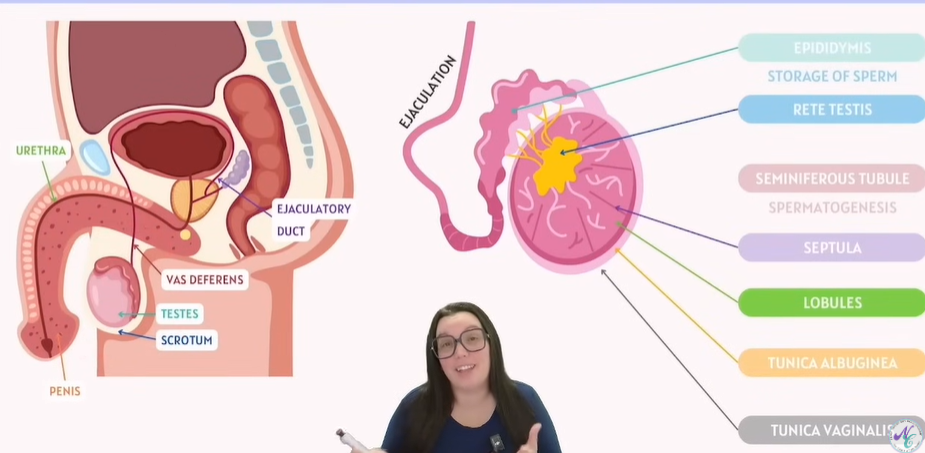
Male Reproductive System Anatomy
1. Urethra
The tube that carries urine and semen out of the body through the penis.
2. Vas deferens
Transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct during ejaculation.
3. Testes
Male gonads that produce:
Sperm (spermatogenesis)
Testosterone (male sex hormone).
4. Scrotum
Sac of skin that holds and protects the testes, maintaining a temperature slightly cooler than body temperature for sperm production.
5. Penis
The external organ that delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract and also carries urine out.
6. Ejaculatory duct
Formed by the joining of vas deferens and seminal vesicle duct; it carries semen to the urethra.
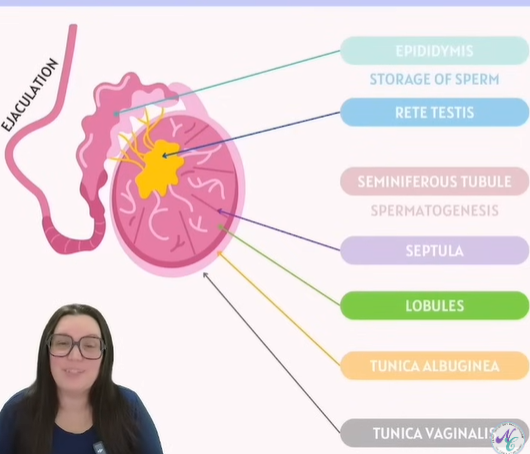
Testicular internal structures:
Part | Function |
|---|---|
Epididymis | Stores and matures sperm before ejaculation. |
Rete testis | Network of tubules that collect sperm from seminiferous tubules and channel it to the epididymis. |
Seminiferous tubule | Tiny coiled tubes where spermatogenesis (sperm production) occurs. |
Septula | Connective tissue walls that divide the testis into lobules. |
Lobules | Compartments within the testis containing seminiferous tubules. |
Tunica albuginea | Tough fibrous covering (inner) around the testis, giving it structure. |
Tunica vaginalis | The outer protective serous membrane covering the testis. |
What do each of the Testicular internal structures do? |
|---|
Epididymis |
Rete testis |
Seminiferous tubule |
Septula |
Lobules |
Tunica albuginea |
Tunica vaginalis |
Testicular internal structures:
Part | Function |
|---|---|
Epididymis | Stores and matures sperm before ejaculation. |
Rete testis | Network of tubules that collect sperm from seminiferous tubules and channel it to the epididymis. |
Seminiferous tubule | Tiny coiled tubes where spermatogenesis (sperm production) occurs. |
Septula | Connective tissue walls that divide the testis into lobules. |
Lobules | Compartments within the testis contain seminiferous tubules. |
Tunica albuginea | Tough fibrous covering (inner) around the testis, giving it structure. |
Tunica vaginalis | The outer protective serous membrane covers the testis. |
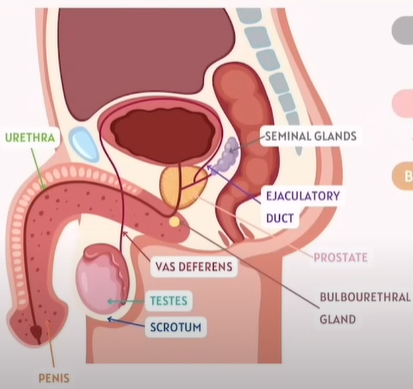
Accessory Glands in Male ?
Gland (English) | 中文名称 (Chinese) | Function (English) |
|---|---|---|
Seminal glands | 精囊 | Produce the fluids that will turn into semen (Produces semen) Sperm plays an important role, it enhances sperm mobility and provides a nutrient-rich environment that suppresses the immune response in female body. |
Prostate | 前列腺 | Produces fluid for semen and surrounds the urethra (Activates the sperm) |
Bulbourethral gland (Cowper’s gland) | 尿道球腺 (库珀腺) | Discharges a component of seminal fluid into the urethra that lubricates the glans penis |
Note: Semen does not contain sperm cells. Instead, it is mixed with sperm cell during ejaculation. cells
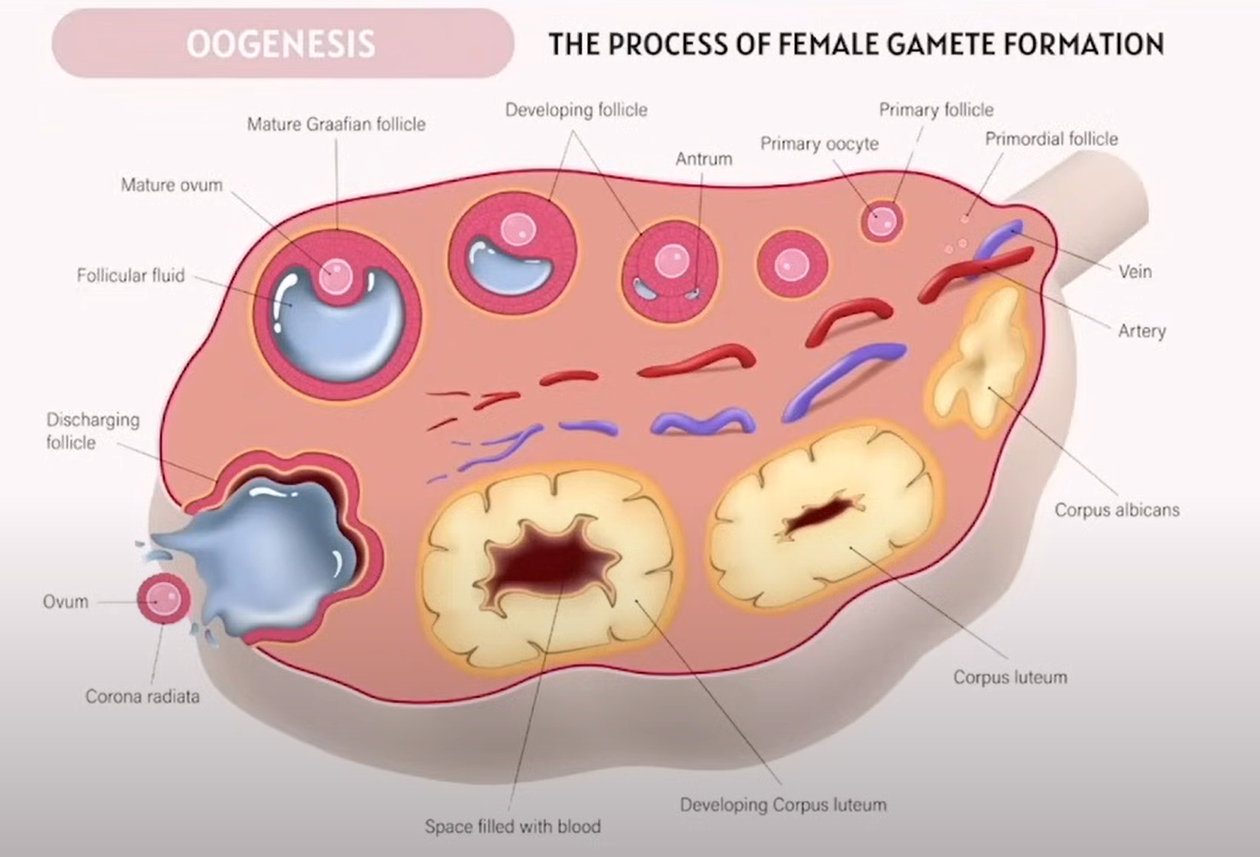
Female Reproductive system
What do they each do?
Term |
|---|
Primordial follicle |
Primary follicle |
Primary oocyte |
Developing follicle |
Antrum |
Mature Graafian follicle |
Mature ovum |
Discharging follicle |
Ovum |
Corona radiata |
Term | Function |
|---|---|
Primordial follicle | The earliest and most immature stage of the follicle; contains a primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of flat cells. |
Primary follicle | Slightly more developed follicle with a primary oocyte and a layer of cuboidal granulosa cells. |
Primary oocyte | Immature egg cell arrested in prophase I of meiosis until puberty; present in primordial and primary follicles. |
Developing follicle | Intermediate stage of follicular development as granulosa cells multiply and fluid-filled spaces begin to form. |
Antrum | The fluid-filled cavity that forms within the follicle as it matures; helps expand the follicle and prepare it for ovulation. |
Mature Graafian follicle | A fully developed follicle containing a secondary oocyte, ready to be released during ovulation. |
Mature ovum | The egg that is released during ovulation (technically still a secondary oocyte until fertilized). |
Discharging follicle | The follicle that is releasing the ovum during ovulation. |
Ovum | The female gamete (egg cell) released into the fallopian tube for possible fertilization. |
Corona radiata | Layer of cells surrounding the ovum, which provide nutrients and support as it travels through the reproductive tract. |
What is Oogenesis
Oogenesis is the development and maturation of the female sex cells (ova) from primordial germ cells through a series of stages including mitosis, meiosis, and cellular differentiation.
What is an oocyte & ovum
An oocyte is an immature female gamete, or egg cell, involved in reproduction. It is the precursor to the mature egg, and it develops within the ovary during the process of oogenesis.
oocyte = immature female gamet
ovum = mature egg

Female Reproductive System Anatomy
Identify the function of each part.
Structure |
|---|
Ovaries (What hormones do Ovaries produce) |
Fallopian Tubes |
Uterus (Womb) |
Cervix |
Vagina |
Structure | Function (English) | 中文名称 (Chinese) |
|---|---|---|
Ovaries | Oval-shaped glands where eggs (ova) form and hormones estrogen and progesterone are produced. | 卵巢 (luǎn cháo) |
Fallopian Tubes | Tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus; site of fertilization. | 输卵管 (shū luǎn guǎn) |
Uterus (Womb) | Hormone-responsive organ where implantation, gestation 妊娠, menstruation, and labor occur. | 子宫 (zǐ gōng) |
Cervix | Lower, narrow part of the uterus that connects it to the vagina. | 子宫颈 (zǐ gōng jǐng) |
Vagina | Muscular canal that connects the uterus to the outside of the body; birth canal and site of sexual intercourse. | 阴道 (yīn dào) |

What are estrogen and progesterone and what they do?
🔄 Summary Table:
Hormone | Main Role | Cycle Phase | Produced By |
|---|---|---|---|
Estrogen | Growth of uterine lining, puberty | Follicular phase | Ovaries |
Progesterone | Prepares uterus for implantation | Luteal phase (after ovulation) | Corpus luteum (ovary) |
雌激素(Estrogen)和孕激素(Progesterone)
🌸 1. Estrogen 🔹 What is it?
Estrogen is a group of hormones (mainly estradiol) that regulate female sexual development and reproductive function.
🔹 Where is it produced?
Mainly in the ovaries
Also in the adrenal glands and fat tissue (in small amounts)
🔹 Main Functions:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
Sexual development | Triggers the development of secondary sex characteristics (e.g., breasts, wider hips) during puberty. |
Menstrual cycle | Thickens the endometrial lining of the uterus during the first half of the cycle. |
Bone health | Helps maintain bone density. |
Skin and hair | Supports skin elasticity and hair growth. |
🌙 2. Progesterone 🔹 What is it?
Progesterone is a hormone that prepares the body for pregnancy and helps maintain it in early stages.
🔹 Where is it produced?
Corpus luteum in the ovary (after ovulation)
Placenta (during pregnancy)
🔹 Main Functions:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
Prepares uterus | Maintains and thickens the endometrial lining for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. |
Supports pregnancy | Prevents uterine contractions and supports early embryo growth. |
Regulates cycle | Works with estrogen to control the second half of the menstrual cycle. |
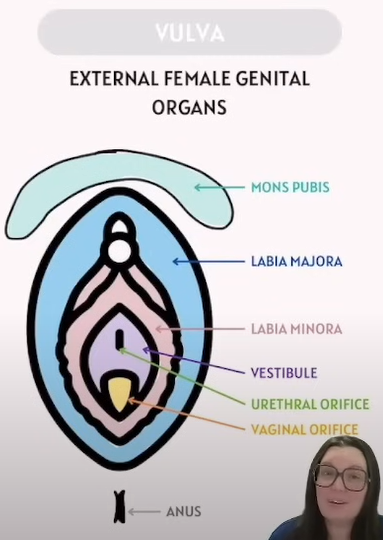
The anatomy of the Vulva
Structure | Description / Function |
|---|---|
Mons Pubis | Area of fatty tissue that covers the pubic bone. “Mons Pubis” 在中文里通常翻译为 阴阜 (yīn fù). 它指的是女性外阴部,耻骨联合前方隆起,呈丘状,由皮肤和脂肪层构成. 青春期后,阴阜上开始长出阴毛,呈倒三角形分布. |
Labia Majora | Fleshy folds of tissue (outer/larger lips) that extend from the mons pubis to the perineum. |
Labia Minora | Two inner folds of skin (inner/smaller lips) that surround the opening of the vaginal vestibule. |
Vestibule 阴道前庭 | Space between the labia minora housing the urethral orifice and vaginal orifice. |
Urethral Orifice 尿道口 | Opening through which urine is discharged from the body. |
Vaginal Orifice 阴道口 | Slit below and behind the urethra; opening for menstrual flow and childbirth. |
Anus | Opening of the rectum; passage for solid waste to exit the body. |
How the Endocrine & Reproductive system work together?
sperm and semen difference
Sperm and semen are related but distinct components of male reproductive fluids. Sperm are the individual male reproductive cells, while semen is the fluid that carries and protects sperm. Essentially, sperm are a component of semen.