APUSH Summer Reading Test (Chapter 1-7) (41 Questions)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
How did North America become settled by humans?
35,000 years ago glaciers formed over the world’s oceans
A land bridge connected Asia (Serbia) and North America (Alaska) over the Bering straight
Nomatic hunters moved over the bridge and traveled to the tip of South America, splitting into diffrent regions of the world (forming different cultures and native languages)
What was Native American life like before contact with Europeans?
Native culture (Language, lifestyle) was very diverse and varied across different regions
Different communities hunted/gathered differently based on region
Urban Dwellers, Hunter-Gatherers, Maritime Seafarers, and Farmers in all diffrent parts of North America
The most densely populated NA community was the pueblos of Mexico and South America, who grew and deeply relied on Mazie (Corn)
What were the reasons for European exploration of the “New World”
The Portuguese invented the caravel, a ship that could sail more closely into the wind (farther and better)
The Portuguese set up trading posts along the African coast. This allowed Portugal to profit from gold and ivory and use slaves, influencing them later on in the New World.
The Europeans desired silks, spices, and gold through new trade routes, bypassing the Muslims who controlled the middle trade routes
Explorers and monarchs wanted to spread Christianity
The Renaissance sparked optimism and adventure while eliminating false myths about sea travel
Define Columbian exchange
The Exchange of goods/ ideas/ diseases between the New World (North America), the Old World (Europe), and West Africa
When Christopher Columbus (Spainish) reached the West Indies in 1492
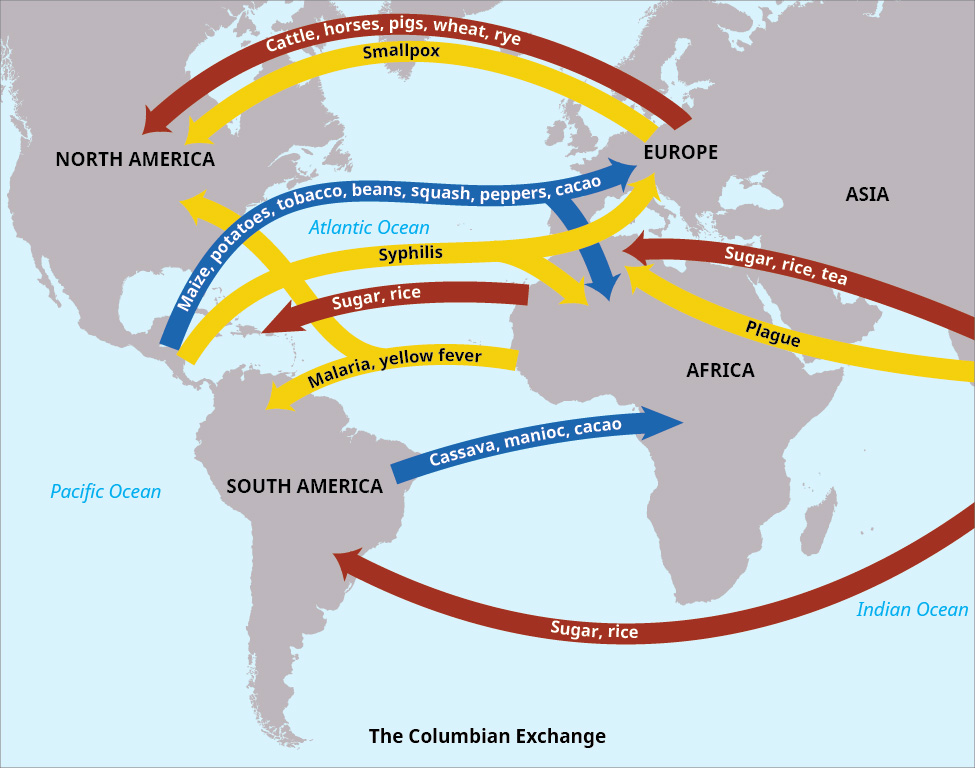
What were the effects of European contact on the native populations and Africans?
Natives:
The Spanish, after arriving, wiped out much of the Native population through enslavement, violence, but mostly through disease
The diseases (smallpox, measles, influenza, typhus) moved from Europe with Columbus, killing 90% of the native population
Africans
The Portuguese set up many trading posts on the African shore, which started a slave plantation system
40,000+ Africans forced out of their homes and into brutal labor on sugar plantations (Brazilian and Caribbean)
Who were the Spanish Conquistadores?
Between 1519 and 1540, conquistadores swept across America, defeating the powerful Inca and Aztec armies using Guns, horses, and germs
Most Famous Conquistadores: Hernan Cortez, and Francisco Pizarro
Took 10,000 men who completed private expeditions had to sign contracts with monarchs, raise money, and recruit armies
Goal: spread Christianity and bring more people under the Spanish flag
What was the encomienda system?
Allowed colonists to enslave Indians (farming and labor) in return for converting them to christianity, “protecting them.”
The system just led to harsh conditions for the natives and was used as an excuse to make slavery acepetable

What European nations colonized North America
Spanish - Sante Fe (1610)
French - Québec (1608)
British - Jamestown, Virgina
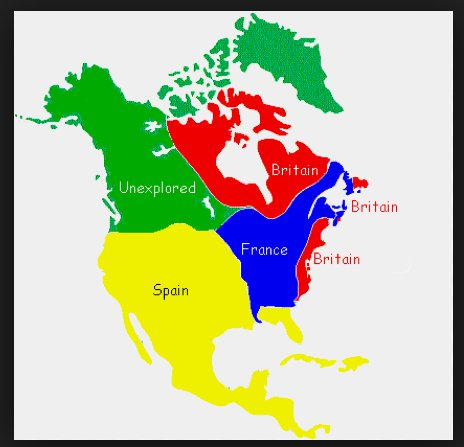
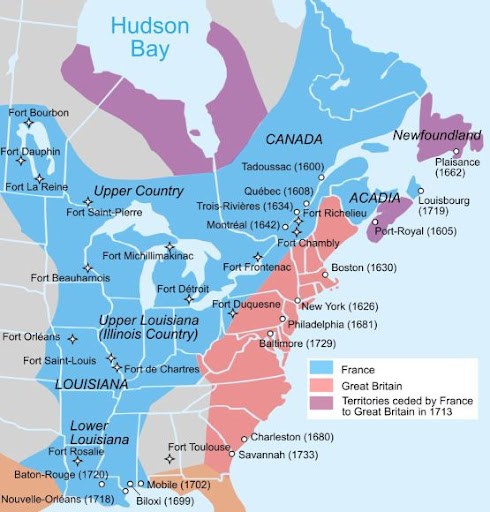
French Colony in North America (Canada)
Searched for beavers, causing the French to move further south
Semi-cooperative relationships with natives with a lot of fur-trading and a reiaence (on natives) with military, trade, and tried to spread Catholicism
Slow and small growing colony
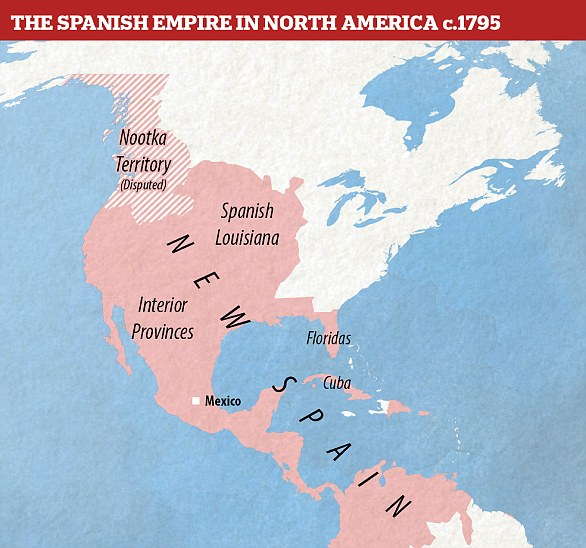
Spanish Colony in North America (Santa-Fe)
Sought wealth and power through natural resources (gold)
St Augustine, the first permanent European settlement in North America in 1565 (Florida)
Kept exploring and conquering North America, establishing New Mexico
Wanted to convert as many natives as possible to Christianity but were brutal to them
British Colony in North America (Jamestown)
In 1606, King James I sent a charter to the Virgina Company to go to the New World to make a profit
The charter enforced the settlers have the same rights as if they were in England, making sure they stayed “english” even when far away
Diverse motives (religious freedom, economic opportunity, land ownership, farming)
Varying relationships with Natives

Describe the early settlement at Jamestown
Located on the bank of the James River, making it easy to defend from a Spanish attack
At first, settlers did not want to work for their food, causing death and disease
Caption John Smith caused the English Settlers to work for their food, saying, “He who shall not work, shall not eat.”
The relationships with the natives were semi-peaceful because of Pocahontas’s saving of John Smith
The Colony still struggled, and many settlers continued to die (having to eat cats, rats, and mice).
Define “Cash Crops” and state the crop that saved Jamestown
Cash Crops: Grown for sale and profits rather than for local use. Exported generating income for the colony or the owner
Tobacco is the cash crop that saved Jamestown
John Rolfe (Father of the tobacco industry, saving/ Jamestown)
Tobacco was planted everywhere in Jamestown and cultivated in Europe (eliminating bitter tastes)
What was an indentured servant?
A person who agreed to work for a set period of time (4-7 years) in exchange for a free passage to America with support (clothes food) included.
Plantation life for the rich, white owners?
Imported millions of enslaved Africans to their plantations (sugar)
Sugar cultivation was very profitable if the owner was wealthy and could invest
Plantations were massive and owners had full control over slaves- allowed some religious tolerance
Plantation life for the enslaved people?
Brutal forced labor because sugar plantations were very labor-intensive
Viewed as property by owners (enslaved for life)
Barbados Slave Code: Denied slaves fundamental rights and gave owners full control + right to brutally punish slaves (Carolina adopted the code in 1696 when slaves from Barbados were already following the code)
What was the protestant reformation?
In 1517, Martin Luther denounced the authority of priests and popes (Catholic), sparking division across Europe. Priests and Popes made people pay as a way “to go to heaven”. Later, John Calvin built on the ideas of Martin Luther, saying that going to heaven was predestined.
Who were the Puritans?
Wanted to purify the church of England (getting rid of excess traditions) by moving away from Catholicism
Wanted to still work with the church of England
When the Church of England was not reforming, the Puritans moved to New England in the Great Migration (1630-1640)
Who were the Pilgrims (Separatists)?
A small group of Radical Puritans who wanted to fully break away from the church of England (corrupt) (Self-governing)
Faced intense persecution from the king and the church, causing a move to Holland (1608)
After turning too Dutch, the pilgrims took the Mayflower to Plymouth (1620)
Merged with Mass Bay Colony neighbors (1691)
Describe the development of the Mass Bay Colony
In 1629, Puritans, fearing for their faith and for England's future, secured a royal charter to form the Massachusetts Bay Colony
John Winthrop was named governor (served for 19 years)
Fur trading, Fishing, and shipbuilding became important industries
No democracy. Only “Freemen” (Male members of Puritan church) were able to vote in elections (for governor and general court)
Laws influenced by strict Puritan beliefs keeping people focused on hard work and minimizing pleasures
Who was Anne Hutchinson?
Extremely intelligent women whose views challenged the Puritan clergy and the integrity of the church
She believed those who were Puritan did not need to obey the law of god or man
Was banished from the Mass Bay Colony because of her challenges to the church
Who was Roger Williams?
A Salem Minister with radical ideas (extreme separatist)
Banished from the Mass Bay Colony, where in 1636 fled to the Rhode Island area
Created complete freedom of religion (even for Jews and Catholics) and challenged the legality of taking land from the Natives
Created the first Baptist church, making RH the most liberal and advanced colony
Many squatters came to RH due to religious freedom (Rhode Island Sewer)