A-Z NAVLE study guide part 1
1/680
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
681 Terms
IN which species and at white time relative to parturition are LDA and RDA most common?
Cattle, 1 month pre/postpartum
What is the primary underlying cause leading to abomasal atony in LDA/RDA cases?
Hypocalcemia
Describe the metabolic abnormalities that result form abomasal sequestrum of contents in RDA and LDA
Metabolic alkalosis, hypochloremia, hypokalemia
Which side is more commonly affected and approximately how much for DA?
Left (5-10x more likely)
Where would you expect to find a ping on PE for an LDA and RDA
LDA → Ribs 9-13
RDA → Right side
What are common CS of LDA, besides the ping?
Normal TPR, anorexia, decreased prod., diarrhea (poor prognosis indicator)
Is diarrhea a good or poor prognostic sign in LDA?
Poor prognostic indicator
What are treatment options for LDA and what is the likehood of recurrence w/rolling?
Rolling the cow (likely to reoccur), omentopexy or abomasopexy
What surgical methods are mentioned for correcting LDA?
Omentopexy or abomasopexy
What is a sig. risk associated with an RDA if not treated promptly?
Abomasal volvulus
In which species and stage or production is RAV typically seen?
Dairy cows near parturition with decrease in milk
How do CS of RAV compare to LDA/RDA and why?
Very sick (more severe), R sided ping
What PE findings is characteristic of RAV and can be palpable?
R sided ping, palpable
What is the primary treatment for RAV and what is the prognosis?
Surgical treatment, POOR prognosis
In which animals and stage of production are abomasal ulcers most common?
High producing dairy cows in first 6 weeks of production
How does stress contribute to ulcer formation?
Stress decreases prostaglandin
Where do ulcers typically form in abomasum?
Ventral portion of the fundic region of the greater curvature
What CS are suggestive of abomasal ulcers?
Melenia, anorexia, occult blood, abdominal pain
What is a sig. cause of bleeding ulcer in older cattle?
LSA
Describe the difference in between bleeding ulcers and perforating ulcers, especially in relation to calves?
Perforating ulcers don’t bleed, common in calves
Bleeding ulcers do not perforate
In which animals and under what conditions is abomasal impaction most common?
Pregnant beef cattle in winter w/ poor quality feed
Besides LDA what other conditions can cause left-sided ping?
Pneumoperitoneum, atonic rumen
Besides RDA and RAV, what other structures or conditions can cause a right sided ping, and which of these might be palpable?
Spiral colon, rectum/colon, RDA, RAV (palpable)
List common herd problems that cause abortion in cattle?
IBR, BVD, brucellosis, lepto, campy, Trich, anaplasmosis, ureaplasmas, mycoplasmas
List common sporadic causes of abortion in cattle
Mycotic (Aspergillus, Mucor)
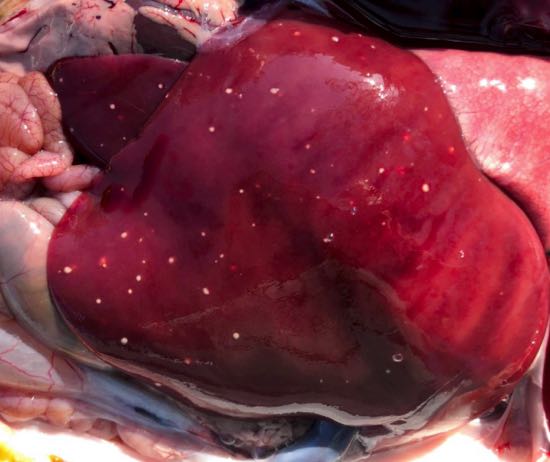
In mycotic abortions, how do the organisms reach the uterus, when do they typically cause abortion, how is fetus affected, and how is the placenta affected? How is this diagnosed?
Reach uterus hematogenously. Fetus may be unaffected or ringworm lesions, placenta has necrosis of the cotyledons. Diagnosed of fetal membranes
List specific infectious agents as causes of abortion in cattle?
Listeria, haemophilus, Corynebacterium pyogenes, Staph, Bluetongue
List non-infectious (toxins/plants) mentioned for abortion in cattle?
Lupine, nitrates, locoweeds, mycotoxins
What is the most common infectious cause of abortion in horses, and when does it typically occur during gestation?
Equine Herpes-1 in the last trimester
Name another viral cause of abortion in mares mentioned. Are vaccines available for these viral causes.
Equine viral arteritis is a less common cause. Vaccines are available for EHV-1 and EVA
List specific bacterial species mentioned as sporadic causes of abortion in mares
Strep zooepidemicus, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Psuedomonia aeruginosa, Staph aureus, R. equi, Actinobacillus equuli
How do these bacterial equine abortions typically occur?
Typically ascending infections from the cervix
What common non-infectious factor often results in abortion in mares? What management techinique is suggested for this?
Twins → Crush the smaller twin @ 22-25 days
What is the most common cause of abortion in sheep?
Campy
Describe the transmission, characteristic of aborted fetus and liver, and how carrier sheep contribute to the spread of Campylobacteriosis. How is it diagnosed and prevented?
Transmitted via ingestion of organisms
Edematous fetus & gray foci on liver
Carrier sheep shed Campy in their excretions
Culture campy from abomasal fluids
Vaccinate ewes @ breeding and booster @ 2nd month of gestation
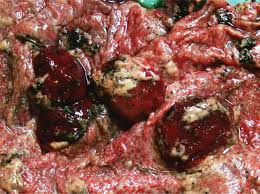
For Toxoplasma gondii, what type of organism is it, and what animal completes its life cycle? What are the signs seen in aborted sheep fetuses?
Toxoplasma is a protozoa with LC completed in cats
White foci in cotyledons, leukoencephalomalacia
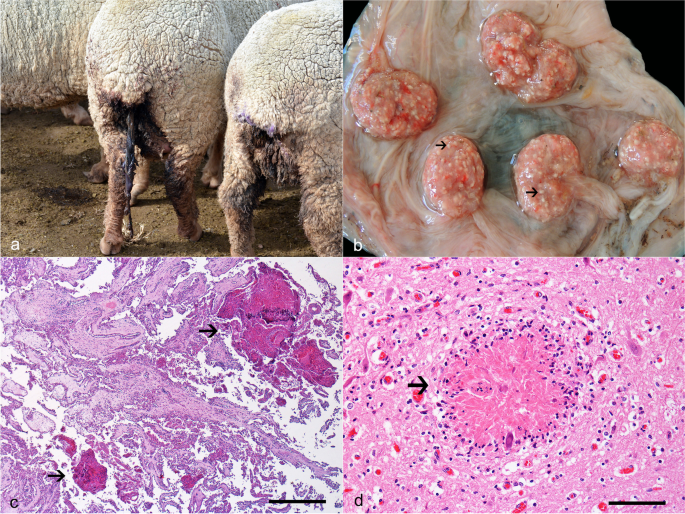
For Chlamydia psittaci, what are the potential routes or exposure? What is the common finding in the aborted fetus and placenta?
Exposure via ingestion, inhalation, or veneral
Placenitis (most common), fetus is well preserved of mummified
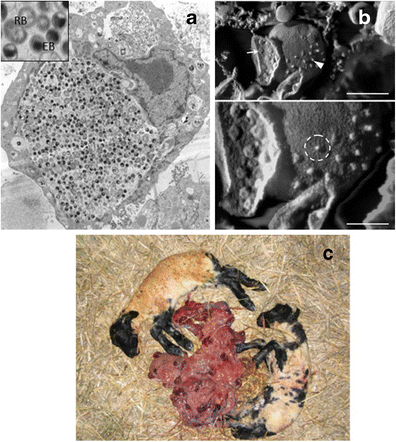
What are typical signs of Listerosis-induced abortion in sheep fetuses? Can humans be affected?
Late-term abortion
Weak @ birth
Autolysis of fetus, fluid in serous cavities, necrotic foci on liver, lung, spleen. Erosions of mucosa
People can be affected
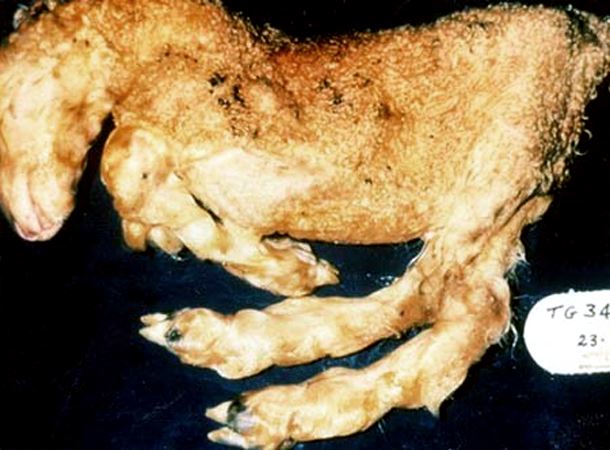
What fetal abnormalities are associated with Akabane virus disease?
Arthrogryposis, hydrancephaly
List viral diseases that can affect repro performance in pigs?
Parvovirus, pseudorabies, enterovirus
Besides vaccination, what management practice is suggested to allow natural exposure to endemic pathogens like parvovirus and enteroviruses?
Expose 21 days post breeding for endemic pathogens
What are the repro consequences of Parvo in pigs? How does maternal immunity gilts relate to timing of exposure?
Early fetal resorption, decrease litter size, mummies
Maternal immunity interferes w/ gilts until maturity. Must expose @ breeding time
What are the repro systemic signs of Pseudorabies in pigs?
Abortion, stillbirths, mummies, weak piglets, fever, respiratory signs, nervous signs
How is Brucellosis transmitted in pigs?
Venereal
Which species of leptospirosis in a common cause of repro failure? Which species is associated w/ late-term abortion? Which species is commonly associated with abortion?
L. interrogans most commonly causes repro failure
L. pomona is associated with late term abortions
L. Bratislava is seen in serology but is NOT associated w/ abortion
What drug can be used to induce abortion/parturtion in cows up to the 4th month of gestation?
PGF2a
What combination of drug used in parturition in cattle for months 5-8?
PGF2a & Dexmethasone
What is a common complication of induced parturition in cows?
Retained placentas
If induced w/in 0-14 days pre-term, what is the expected viability and IgG status of the calves?
Normal
What drug is used for inducing abortion in mares?
Prostaglandins
What might be required regarding to the dose and frequency after the 4th month in mares?
Must double dose or repeat dose @ 48 hr intervals of Prostaglandings
What other methods works for inducing abortion in mares at any stage?
Douching of uterus
When can be Oxytocin be used to induce parturition for a live foal?
Only after the cervix has begun relaxing
Is inducing parturtion considered safe in SA?
No!
What drug can be used for abortion after day 40 in SAs?
PGF2a
What are the effects of Dex over 10 days for pregnancy termination in small animals?
Fetal death and resorption
What class of drug is Acepromazine?
Phenothiazine tranquiler
Describe Acepromazine MOA in CNS
Blocks release and uptake and dopamine
List Acepromazine’s other pharmological effects
Anticholingeric, antihistamine, antispasmodic, alpha-adrenergic blocking effects
How can atropine be used in conjuction w/ Acepromazine
Atropine counteracts bradycardiac effects
List the potential adverse effects of Acepromazine?
Seizures, decreased RR/arterial BP, increased CVP, bradycardia, sinoatrial arrest, bradycardia, extrusion of penis of large animal males
Does Acepromazine provide pain relief?
No analgesic effects
What are some positive affects of Acepromazine particularly regarding arrythmias and malignant hyperthermia in pigs?
Antidysrhythmic effects, inhibit arrhythmias inducted by barbituates, reduces halothane-malignant hyperthermia
What conditions should dose of Acepromazine by decreased?
With hepatic dysfunction or cardiac disease
In what specific patient conditions is Acepromazine contrainidcated?
Hypovolemia, shock, tetanus, strychinine
What is another name for Acetaminohpen
Tylenol
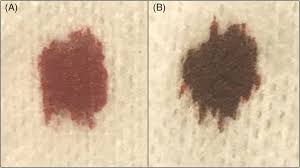
Describe the CS of Acetraminophen poisoning, including effects on blood, urine, liver, and overall demeanor
Hemolytic anemia, methemoglobinemia, dark-colored urine, icterus, facial edema, lethargy
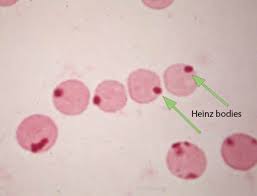
What key findings would you expect on clin path with Acetaminophen toxicity?
Heinz body anemia, hemolysis, hemoglobinuria
What is the recommended therapy for Acetaminophen poisoining?
N-acetylcysteine (mucomist)
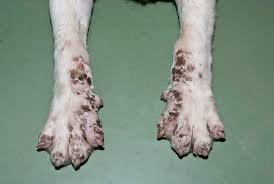
What is the underlying cause of Acrdodermatitis?
Lethal famial zinc deficiency
What specific breed is affected by Acrodermatitis?
White Bull Terriers

Describe the CS of Acrodermatitis?
Retarded growth, progressive, acral, hyperkeratotic dermatitis, pustular dermatitis at mucocutaneous junctions
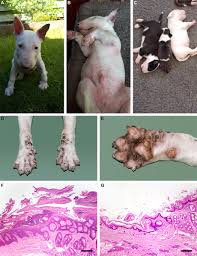
What is the typical prognosis and age of death of Acrodermatitis?
Poor, 2 year of age is typical age of death
Describe the general presentation of an animal with Acute Abdomen Syndrome
Acute presentation of systemic signs, abdominal pain, distended, ventrodorsal weakness
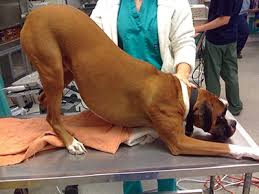
What are the major categories of underlying causes of Acute Abdomen syndrome?
Bacterial sepsis, obstruction/perforation, ischemia/thrombosis
What is ID as the fundamental question and that needs to be addressed when evaluating an acute abdomen case?
Medical or surgical treatment
Regarding septic peritonitis, what principle guides the treatment, and what procedures are involved?
Dilution is the solution to the pollution → Exploratory and lavage
What is the common name of hypoadrenocorticism?
Addison’s disease
What are the main causes of hypoadrenocorticism?
Immune-mediated or iatrogenic adrenocortical insufficiency
What hormones are deficient in hypoadrenocorticism?
Glucocortcoids and mineralocorticoids
What animals is typically seen with Addison’s disease?Is there a familial predisposition in any breed?
Young-middle aged animals, sometimes horses
Predisposition in Standard poodles

Explain how the lack of aldosterone secretion leads to characteristics electrolyte imbalances in Addison’s disease? What is the typical Na:K ratio finding?
Results in impaired ability to conserve Na+ and excrete K+ → hyponatremia and hyperkalemia (Na:K <25:1)
Explain how hyponatremia affects animals with Addison’s and can lead to prerenal azotemia?
Leads to hypotension, decreased CO, hypovolemia leading to prerenal azotemia
What CS are associated with lack of cortisol secretion?
GI signs, lethargy, and impaired stress response
What specific findings might be present on a CBC in an animal w/ Addison’s? What about blood glucose and calcium?
Normocytic, normochromic anemia
Absolute eosinophilia
Hypoglycemia (dt decreased glucose production)
Hypercalcemia (occasionally)
What is the definitive test for Addison’s disease?
ACTH stim test
Describe treatment approach, initial stabilization and long term medication options for Addison’s?
Fluid replacement and electrolyte assessment for stabilization
Prednisone (glucocortcoid) and DOCP/Florinef (mineralcorticoid)
What are the 2 main parts of adrenal gland?
Cortex and medulla
Regarding the adrenal cortex, name the 3 zones and primary steroid hormone secreted by each?
Zona glomerulosa → Mineralcorticoids
Zona fasiculta → Glucocorticoids
Zona reticularis → sex steriods
What is the function of accessory cortical tissue sometimes seen in older dogs?
Small nodules that are nonfunctional and normal
Regarding the adrenal medulla, what is its origin, and what hormones does it secrete? What is its role and body?
Origin: Modified sympathetic system ganglion
Hormones: Epi and norepi
Role: An important role in responding to stress or hypoglycemia
What is the name for tumor of adrenal medullar, and what hormones might it secrete?
Pheochromcytoma → Epi or norepinephrine
Explain the primary function of mineralocorticoids, specifically aldosterone. How does aldosterone affect electrolyte and water balance, plasma volume, and blood pressure? What stimulates aldosterone secretion?
Aldosterone regulates ion transport of epithelial cells, resulting in excretion of K+ and conservation of Na
Explain the primary function of glucocorticoids. How do they affect metabolism? How do they impact inflammatory and immune response? What negative effect do they have on wound healing?
Regulate carbs, protein, lipid metabolism resulting in sparing glucose and lipolysis. Suppresses inflammatory and immunologic responses. Can have negative effects on wound healing due to inhibition of fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis
List types of sex hormones secreted by adrenal cortex
P4, estrogens, and androgens
What species does Aeluostrongylus abstrusus affect, and what is its common name?
Affects cats, also known as cat lungworm

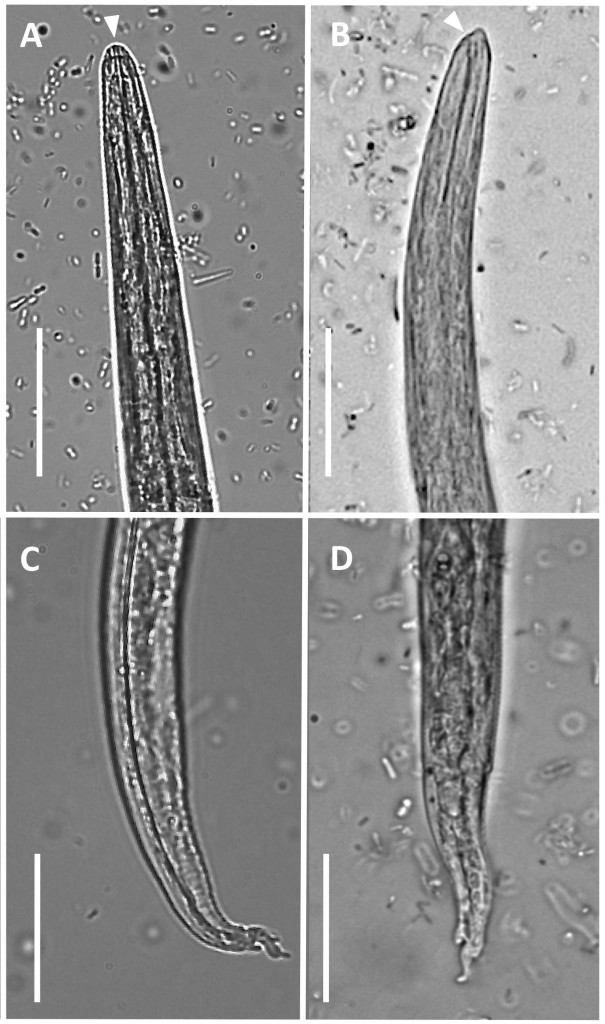
Describe the LC including the first intermediate host and examples of transport hosts for Aerlurostrongylus abstrus
Snail (1st host) → Vector (frog, lizard, bird, rodent) for encysted larvae → Cat eats vector → larvae migrates from stomach to lungs → Embedded in lung tissue → Egg in nodule → larvae coughed up and passed in feces
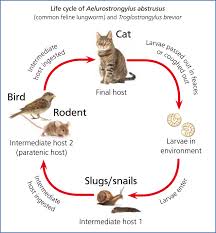
Once cats eat a transport host, where do Aelurostrongylus abstrusus larvae migrate and embed?
Lung tissue
Where are Aerulostronglyus abstrusus eggs forms, how do larvae hatch, and how are they passed out of the cat?
Eggs form in alveolar ducts
Larvae hatch
Coughed up and passed in feces
What is the characteristics morphological feature of the Aerulostrongylus abstrusus larvae seen in feces?
Dorsal spined tails