Primate Intestinal Protozoan Parasitology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
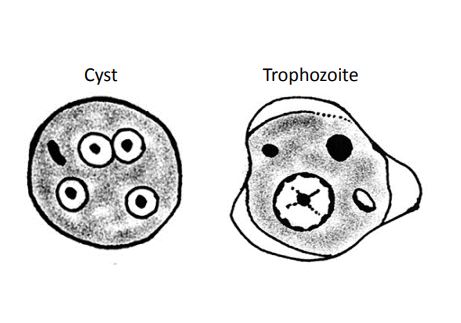
Entamoeba histolytica
Cysts:
• Size: 10-20µm spherical (typically 12-15µm)
• Nucleus: 1, 4 and occasionally 8, 1N >5µm, 2N ~ 3.5 - 5µm, 4N ~ 2 - 2.5µm
• Chromatin: fine, uniform
• Karyosome: small, central
• Cytoplasm: rounded or oval chromatoidal bars
Trophozoites:
• Size: 12-60µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~3.5 - 5µm
• Chromatin: fine, uniform
• Karyosome: small, round and central
• Cytoplasm: ground glass clean appearance • Inclusions: RBC’s
• Pathogenic
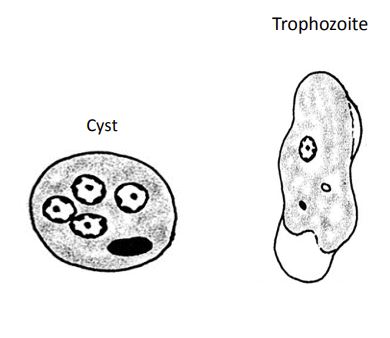
Entamoeba hartmanni
Cysts:
• Size: 5-10µm
• Nucleus: 1, 2 or 4 (2 are common), 4N ~1.5-2.5µm
• Chromatin: even distribution
• Karyosome: centrally located, small and compact
• Cytoplasm: fine granular, chromatoid bodies are “cigar” shaped
Trophozoites:
• Size: 5-12µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~2 - 2.5µm
• Chromatin: fine and even
• Karyosome: small, eccentric or centrally located
• Cytoplasm: fine granular appearance
• Non-pathogenic
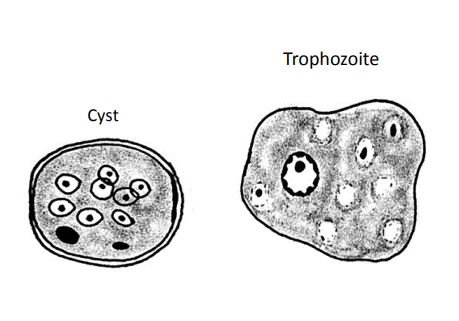
Entamoeba coli
Cyst:
• Size: 10-35µm, spherical
• Nucleus: 2-8 nuclei, 2N ~ ≥8µm, 4N ~ 5 - 6µm, 8N ~ 2.5 - 3µm
• Chromatin: uneven
• Karyosome: large, eccentric
• Cytoplasm: splinter shaped chromatoid bars, sometimes large vacuoles
Trophozoites:
• Size: 15-50µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~3.0-4.5µm
• Chromatin: irregular and uneven
Nebulous Border “Floppy Pancake”
• Karyosome: large, off centered
• Cytoplasm: course and often with large food vacuoles. Can see RBC’s and WBC’s as well as yeast
• Non-pathogenic
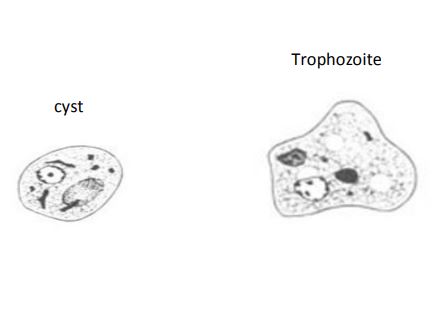
Entamoeba chattoni/E. polecki
Cyst:
• Size: 5-20µm
• Nucleus: 1 large circular (occasionally 2), ~ 5 - 8µm
• Chromatin: fine and even
• Karyosome: small and central, may not be visible
• Cytoplasm: granular, often will contain several small chromatoid bodies
Trophozoite:
• Size: 10-30µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~2.5-3.5µm
• Chromatin: fine and even
• Karyosome: small, and central, may be absent
• Cytoplasm: granular
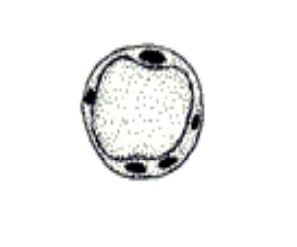
Blastocystis
• Unique protozoan
• Pleomorphic features
• Controversial pathological effects
• Size: 2-200µm, with a thin outer shell of cytoplasm
• Nucleus: 1 or more (usually 2)
• Inner vacuole with storage droplet
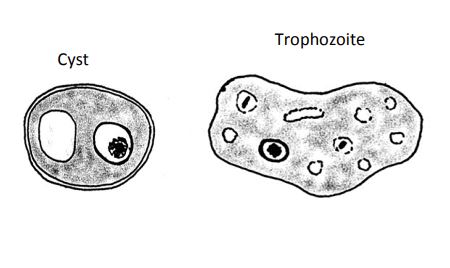
Iodamoeba buetschlii
Cyst:
• Size: 5-20µm, ovoid
• Nucleus: 1, elliptical
• Achromatic granules
• Karyosome large (if present)
• Cytoplasm: almost always has a glycogen vacuole
Trophozoite:
• Size: 8-20µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~2.5-3.0µm
• Chromatin: fine, granular, “fuzzy” appearance
• Karyosome: large
• Cytoplasm: fine, granular with small food vacuoles
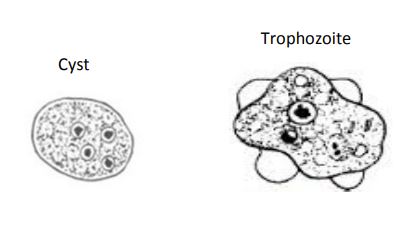
Endolimax nana
Cyst:
• Size: 8-15µm, usually ovoid
• Nucleus: 4
• Chromatin: thin to none
• Karyosome: large
• Cytoplasm: granular with a large vacuole and a few thin chromatoid bodies
Trophozoite:
• Size: 5-15µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~1.5-2.5µm
• Chromatin: thin
• Karyosome: large
• Cytoplasm: granular
• Non-pathogenic
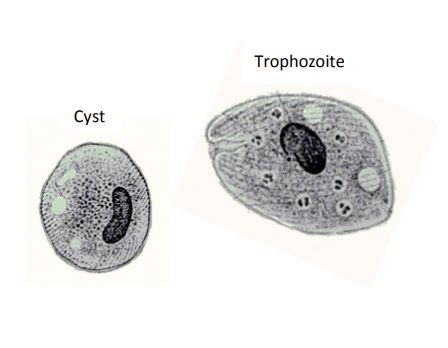
Balantidium coli
Cyst:
• Size: 40-65µm
• Nucleus: 1 Macronucleus
• Cilia visible under cyst wall in young forms
Trophozoite:
• Size: 50-100µm, spheroid to pear shaped
• Large bar shaped or dumbbell shaped macronucleus
• Micronucleus may be obscured
• Prominent oral groove and cytopyge
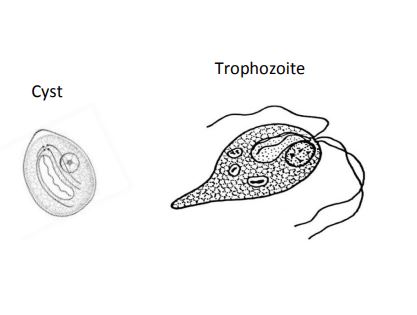
Chilomastix mesnili
Cyst:
• Size: 6-10µm, lemon shaped with “knob”
• Nucleus: 1 (not distinct) • Cytoplasm: contain curved fibers
Trophozoite:
• Size: 5-20µm, pear shaped with tail
• Nucleus: 1, ~1.5-3.5µm
• Karyosome: small and variable
• Chromatin: can be solid, diffuse or fragmented
• Cytoplasm: course with large food vacuole
• Non-pathogenic
“Swimming Tuna”
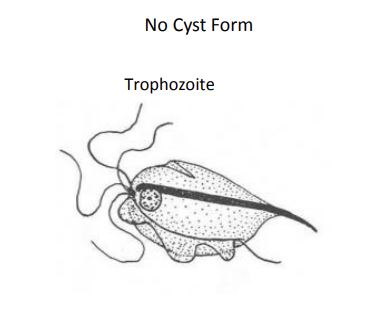
Pentatrichomonas hominis
• Size: 5-15µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~1.5-2.5µm
• Cytoplasm: smooth to fine granular, undulating membrane is often visible
“Smiling Whale”
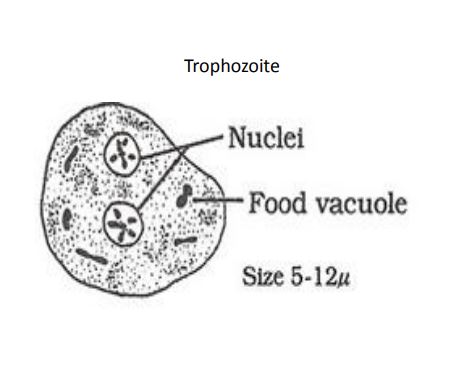
Dientamoeba fragalis
• Size: 5-25µm
• Nucleus: 1 - 2, ~1.5-2µm often bi-nucleated.
• Karyosome: is fragmented into small granules in stained preps
• Cytoplasm: pale staining with numerous small food vacuoles
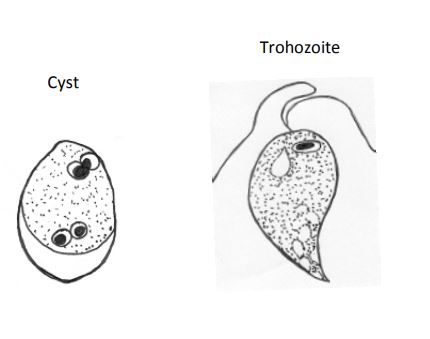
Enteromonas hominis
Cyst:
• Size: 4-8µm, ovoid
• Nucleus: 2 or 4 bipolar
Trophozoite:
• Size: 4-10µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~0.7-1.5µm, tiny and usually pushed up against on end of the cell (resembles a small E. hartmanni or Endolimax nucleus)
• Cytoplasm: smooth with a large glycogen vacuole
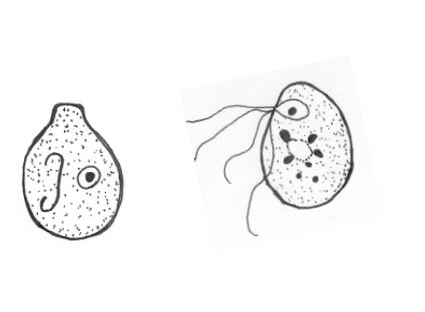
Retortamonas intestinalis
Cyst:
• Size: 4-8µm, ovoid
• Nucleus: 1
• Characteristic “knob”, resembles a very small Chilomastix cyst
Trophozoite:
• Size: 4-10µm
• Nucleus: 1, ~0.7-1.5µm, tiny and usually pushed up against on end of the cell (resembles a small E. hartmanni or Endolimax nucleus)
• Cytoplasm: smooth with a large glycogen vacuole
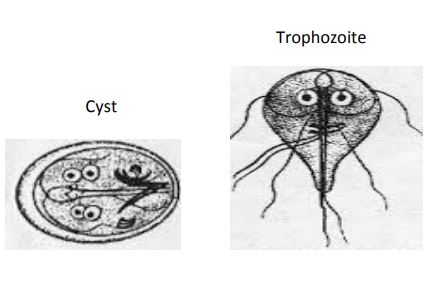
Giardia
Cyst:
• Size: 8-15µm
• Nucleus: 2-4 usually located on one end
• Karyosome: central
• Cytoplasm: contains median bodies and flagella
Trophozoite:
• Size: 10-20µm
• Nucleus: 2, ~1.5-2.0µm
• Karyosome: central
• Cytoplasm: large central sucker disc with 8 flagella
• Pathogenic
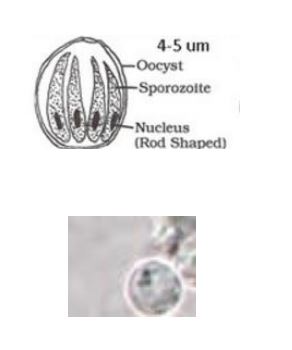
Cryptosporidium
• Size: 4-6µm
• Thin walled, spherical to oval shape
• 4 sporozoites
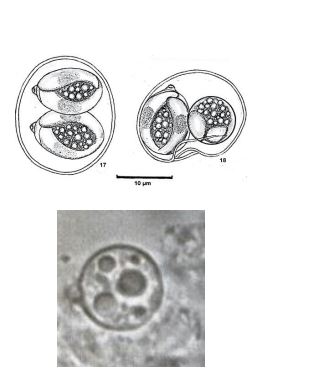
Cyclospora cayetanensis
• Size: 8-10µm
• Thin walled, spherical
• Single sporoblast containing several refractile bodies when passed
• 2 sporocysts with 2 sporozoites
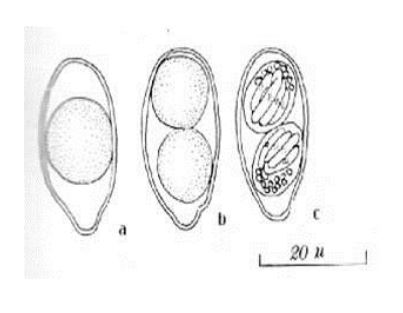
Cystioisospora (Isospora) belli
• Size:20-30µm
• Thin walled, ovoid with tapered ends
• Mature oocysts contain 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites each

Sarcocystis
• Size:10-15µm
• Infection from eating muscle of intermediate host
• Usually not pathogenic in definitive host
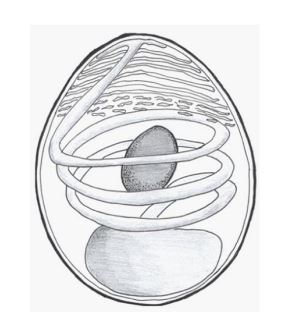
Microsoporidia
• Size: 3-6µm long depending on species
• Spores can be ovoid, spheroid or cylindrical
• Trilaminar spore wall is visible by electron microscopy
• Contains infective sporoplasm and coiled polar tube with accessory structures to allow it to emerge rapidly and infect a host cell
• Some are facultative parasites in immunosuppressed animals-Enterocytozoon bieneusi
• Encephalitozoon intestinalis, various Nosema and Pleistophora species can cause severe diarrhea
• Difficult to detect without proper staining