Chapter 3 - sugars (polysaccharides)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what are polysaccharides?
long chain polymers of sugars and sugar derivatives
function: in structure and storage
consist of a single kind of repeating unit or sometimes an alternating pattern of two kinds
oligosaccharides
short polymers sometimes attached to cell surface proteins
identification tag (glycoprotein)
what are the monomers of sugars
monosaccharides
what can a sugar be? two types
aldehyde (aldosugars) — terminal carbonyl group
ketone (ketosugars) — with an internal carbonyl group
(named based on how many carbon atoms they contain)
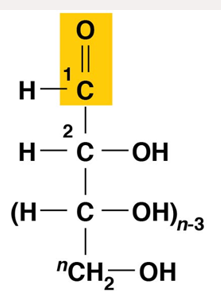
aldosugar
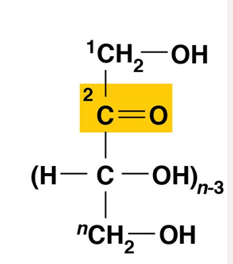
ketosugar
classification of sugars
most sugars have bn 3 and 7 carbons:
trioses (3 C)
tetroses (4 C)
pentoses (5 C)
hexoses (6 C)
heptoses (7 C)
What is glucose?
most common monosaccharide is aldohexose D-glucose (c6h12o6)
formula for sugars and its name
CnH2nOn
carbohydrate
how are carbons of glucose numbered?
from the more oxidized, carbonyl end
for every molecule of ___ incorporated into a sugar, one ___ molecule is consumed
CO2; H2O
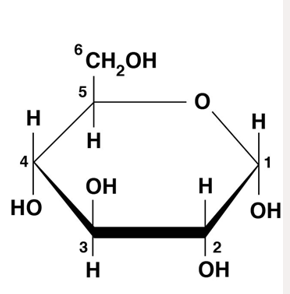
structure of alpha D-Glucose
repeating unit of starch and glycogen
what is the 2 alternative forms of the ring of D-glucose? why do they happen?
depend on spatial orientation of the hydroxyl group of carbon number 1
forms designated (alpha if pointed downward) or beta (hydroxyl group upward)
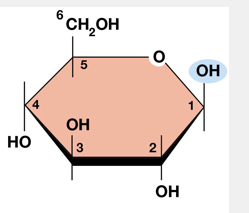
beta glucose
repeating unit in cellulose
disaccharides and bond type
two monosaccharides are covalently linked
linkage of disac glycosidic bond
formed bn 2 monos by the elimination of water
alpha form of bond called: alpha glycosidic bonds (maltose)
beta form of bond called: beta glycosidic bonds (lactose)
what is the most familiar storage polysaccharides? what is the bond type?
starch in plant cells
glycogen in animal cells and bacteria
consist of alpha D-glucose units linked by alpha glycosidic bonds, involving 1→4
sometimes alpha(1→6) bonds may form, allowing for branching!
glycogen and branching and location
HIGHLY BRANCHED
occurs every 8-10 glucose units along the backbone
mainly stored in liver (as a source of glucose) and muscle tissue (as a fuel source for muscle contractions) of animals
bacteria store glycogen as glucose reserve
starch and branching
glucose reserve found in plant tissues
can be
unbranched = amylose (10-30% of time)
branched = amylopectin (70-90% of time)
amylopectin branching
has alpha 1→6 branches once every 12-25 glucose units
has longer side chains than glycogen
starch storage
stored as starch grains within plastids
chloroplasts: the sites of carbon fixation and sugar synthesis in photosynthesis
amyloplasts: specialized for starch storage
both are membrane bound organelles
cellulose
the best known structural polysaccharide
found in plant cell walls
composed of repeating monomers of beta-D-glucose, which is v abundant in plants
mammals cannot digest cellulose “insoluble fiber”
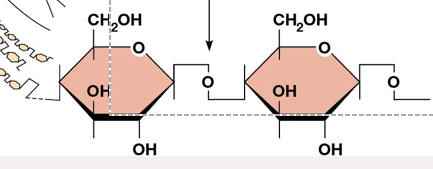
beta (1→4) bond
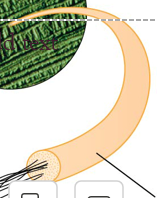
microfibrils — made of many long, unbranched cellulose chains
each chain made up of beta D-glucose molecules arranged in linear manner and linked by beta (1 to 4) glycosidic bonds
how does the cellulose of fungal walls differ from that of plants?
they may contain either beta(1-4) or beta(1-3) linkages
what kind of sugars does bacterial cell walls contain?
GlcNAc and MurNAc
both are derivatives of beta-glucosamine and are linked alternatively in cell walls
Chitin
a polysaccharide
consists of GlcNAc units only, joined by beta(1-4) bonds
found in insect exoskeletons, crustacean shells, and fungal cell walls
what does polysaccharide structure depend on?
the type of glycosidic bonds involved
alpha and beta glycosidic bonds are associated with ___ ___ ___
marked structural differences
what do starch and glycogen form?
they are alpha polysaccharides
form loose helices that aren’t highly ordered bc of side chains
cellulose forms what kind of linkages? what is structure?
beta linkages
exists as rigid linear rods that aggregate into microfibrils, about 5-20 nm in diameter
what contains the rigid microfibrils? what other things do they contain?
plant and fungal cell walls in a noncellulose matrix
contains other polymers (hemicellulose and pectin)
and a protein called extensin (glycoprotein)