ib econ- 3.6: fiscal policy
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/macroeconomics/3-6-fiscal-policy/goals-and-tools-of-fiscal-policy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
what is fiscal policy?
the use of taxation and government expenditure to influence the level of economic activity in order to achieve macroeconomic objectives
what are examples of government revenues?
direct and indirect taxation: income, inheritance, sales, carbon
sale of goods and services from state owned enterprises: most governments own some companies, which provide revenue
sale of governmental assets: by selling state run businesses like the postal service the government makes money - this can only happen once per business though
what are some examples of government expenditures?
current expenditures: spending on goods and services within the current year, such as healthcare and education
capital expenditures: long term investments by the government (e.g. a new airport)
transfer payments: payments sent to people without any return (e.g. unemployment benefits)
what are the goals of fiscal policy?
low and stable inflation
low unemployment
promote a stable economic environment for long term growth
reduce business cycle fluctuations
ensure an equitable distribution of income
ensure an external balance
what is expansionary fiscal policy?
the use of increased government spending and/or reduced taxes to stimulate economic activity and achieve macroeconomic objectives. used when trying to close recessionary/deflationary/negative output gaps
what are the two methods of expansionary fiscal policy?
cut taxes: means people and businesses will take home more money, incentivising more consumption/investment
increase gov. spending: since G is a part of measuring rGDP (C+I+G+(X-M)), an increase in G will increase economic activity
what is contractionary fiscal policy?
the use of decreased government spending and/or increased taxes to reduce the level of economic activity and achieve macroeconomic objectives. used when the government wants to close inflationary gaps.
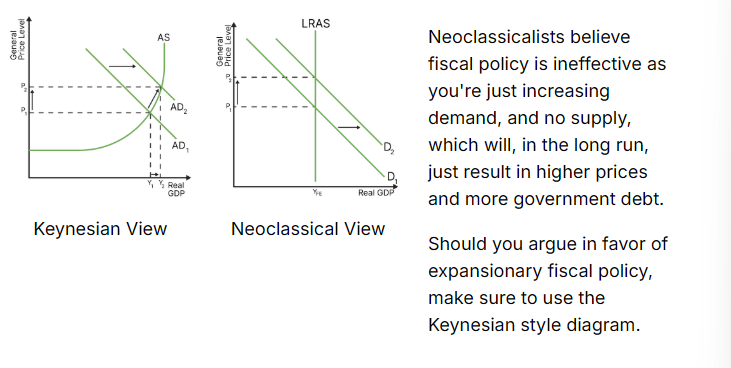
draw the diagram for expansionary fiscal policy (neoclassical and keynesian)
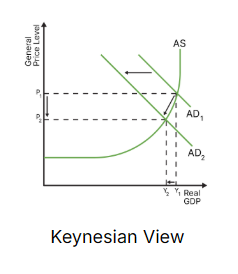
draw the diagram for contractionary fiscal policy
what are the strengths of fiscal policy?
it can target specific economic sectors
gov. spending is effective in recessions (boosts confidence easily)
what are the weaknesses of fiscal policy?
political pressure: it is dependent on the government, and requires political support
time lags: bureaucracy and injection of money take time
increases government debt (not sustainable in the long run)