E139 Week 1 Forces (Lecture 2)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
newton’s first law
a body maintains a constant velocity if the net force acting on it is 0
newton’s second law
net force = mass x acceleration
F = MA
newton’s third law
to every force, there is an equal and opposite force
types of forces
gravitational force
inertial force
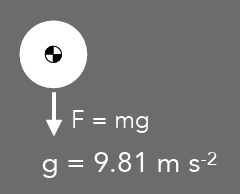
gravitational force
F = mg
g = 9.81 m/s²
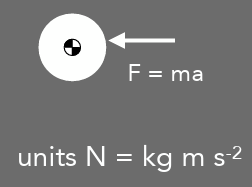
inertial force
F = ma
units = N
newtons
kg m /s²
energy
potential and kinetic energy
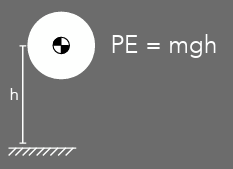
potential energy
PE = mgh
units = J
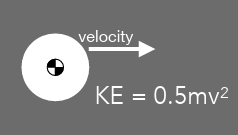
kinetic energy
velocity
KE = 0.5mv²
units = J
joules
Nm = kg m²/s²
momentum
p = mv
conservation of momentum
applies 3rd law
F1 = -F2
t1 = t2
F1t1 = -F2t2
applies 2nd law
m1a1t1 = -m2a2t2
m1v1 = m2v2
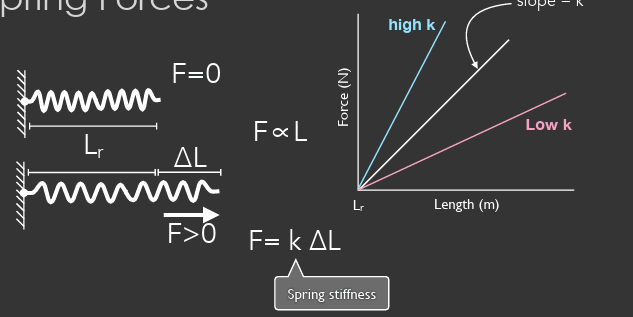
spring stiffness
k = spring constant
△L
length that the spring is stretched from rest
spring force
F = k△L
force and length relationship
proportional
high k = high stiffness = lower length with more force
low k = low stiffness = greater length with less force
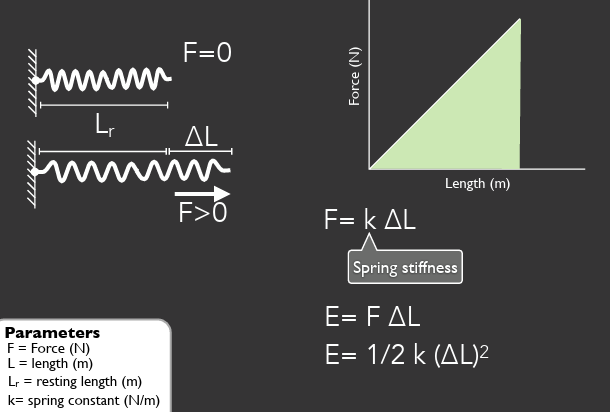
elastic strain energy
E = F△L
E = ½ k (△L)²
area under the curve
steps for calculations
sketch picture to define variables
define governing equations
solve for variable of interest
define knowns
plug in using consistent units and solve
write the answer in a sentence
state any assumptions made