Monosaccharides
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
How are monosaccharides classified?
Based on the carbonyl group and the number of carbon atoms
What is the formula for monosaccharides?
CnH2nOn
What type of carbon chain do monosaccharides have?
Unbranched single bonded carbon chain
What is unique about the carbon atom in a monosaccharide?
One of the carbon atoms is double bonded to an oxygen making an carbonyl group, while the others have hydroxyl groups
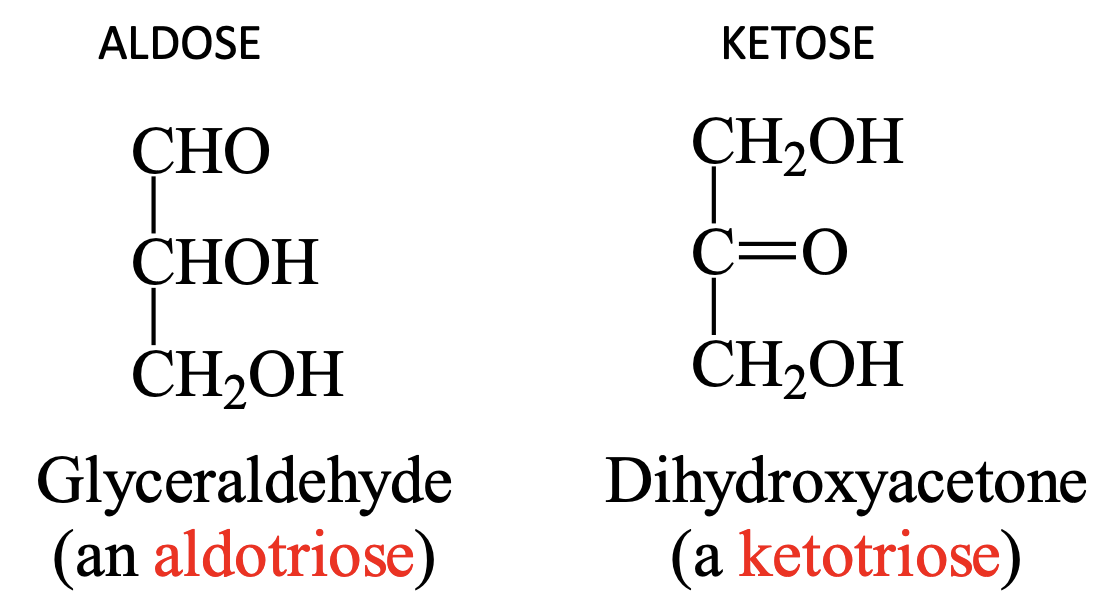
What is an aldose?
A monosaccharide with an aldehyde functional group (carbonyl at end of carbon chain)
What is an example of an aldose?
Glyceraldehyde which is an aldotriose
What is a ketose?
A monosaccharide with a ketose functional group (carbonyl at middle of chain)
What is an example of a ketose?
Dihydroxyacetone which is a ketotriose
What is the most abundant monosaccharide?
D-glucose
How are aldose and ketoses structurally different?
Aldose: Has carbonyl group at end of carbon chain (aldehyde)
Ketose: Has carbonyl group at middle of carbon chain (ketone)
Give the category name and examples for monosaccharides that have:
3 carbons
4 carbons
5 carbons
6 carbons
7 carbons
9 carbons
3 carbons:
Category name: Triose
Example:
Glyceraldehyde (aldo)
Dihydroxyacetone (keto)
4 carbons
Category name: Tetrose
Example:
D-Erythrose
Erthyrulose
5 carbons
Category name: Pentose
Example:
D-arabinose, D-ribose
D-ribulose
6 carbons
Category name: Hexose
Example:
D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose
D-fructose
7 carbons
Category name: Heptose
Example: D-sedoheptulose
9 carbons
Category name: Nonose
Example: Neuraminic acid (sialic acid)
Function of these main monosaccharides
D-glucose
D-fructose
D-galactose
D-mannose
D-sedoheptulose
D-glucose:
Major energy source
Sugar of blood
D-fructose: Sugar of seman, fetal blood, fruits
D-galactose: Sugar of milk
D-mannose: Composition of muscopolysaccharides
D-sedoheptulose: Intermediate in calvin cycle
What important function can monosaccharides do especially for diabetics?
Be sugar derivatives
Vitamin C as a monosaccharide
Why is it an necessary for our diet?
What animals can synthesise it?
Function
Lack in diet may cause
Necessary in diet: Because we cannot synthesize it
Animals that can synthesize vitamin C: Primates and guinea pigs
Function: Maintain health of dentine, cartilage, connective tissue and bone
Lack in diet may cause: Impairment of collagen formation