Lec 3: Neuro III (anesthesia)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
anesthesia def
sedation of a pt for the purposes of a medical procedure/intervention
what are the diff types of anesthesia
local
general
monitored anesthesia care (MAC)
localized anesthesia general def (use)
localized effect=loss of sensation in a focused body area or region (regional anesthesia) = nerve block
local anesthetics used
used for minor procedures ex sutures to a laceration
used for some major procedures ex oral surgery, labor & delivery
general anesthesia def (use)
systemic effect=loss of consciousness
combines many drugs for optimal effect
used for major procedures ex abdominal surgery
Monitored anesthesia care (MAC) general def
systemic effect
sedation at lower levels to maintain VS without intubation (ET tube)
3 types (level of sedation dependent): ex conscious sedation
=sleepy, able to awaken, able to respond when prompted, maintains VS without assistance
what is the drug class and MOA for local anesthesia
sodium channel blockers
no Na influx into neurons=> no action potential => no cellular depolarization = no communication of sensory info to cerebral cortex
what areas are affected with local anesthesia
NS pathways affected: efferent & afferent
sensory & motor
drug specificity
what drugs are part of the sodium channel blockers for local anesthesia
lidocaine
prilocaine
bupivacaine
ropivacaine
what is the onset and duration of the sodium channel blockers for local anesthesia
onset=<2 min
duration=drug dependent, dose dependent
ex lidocaine & prilocaine = 1-2 hrs
bupivacaine = 2-4 hrs
ok for longer duration, allows for PO analgesia
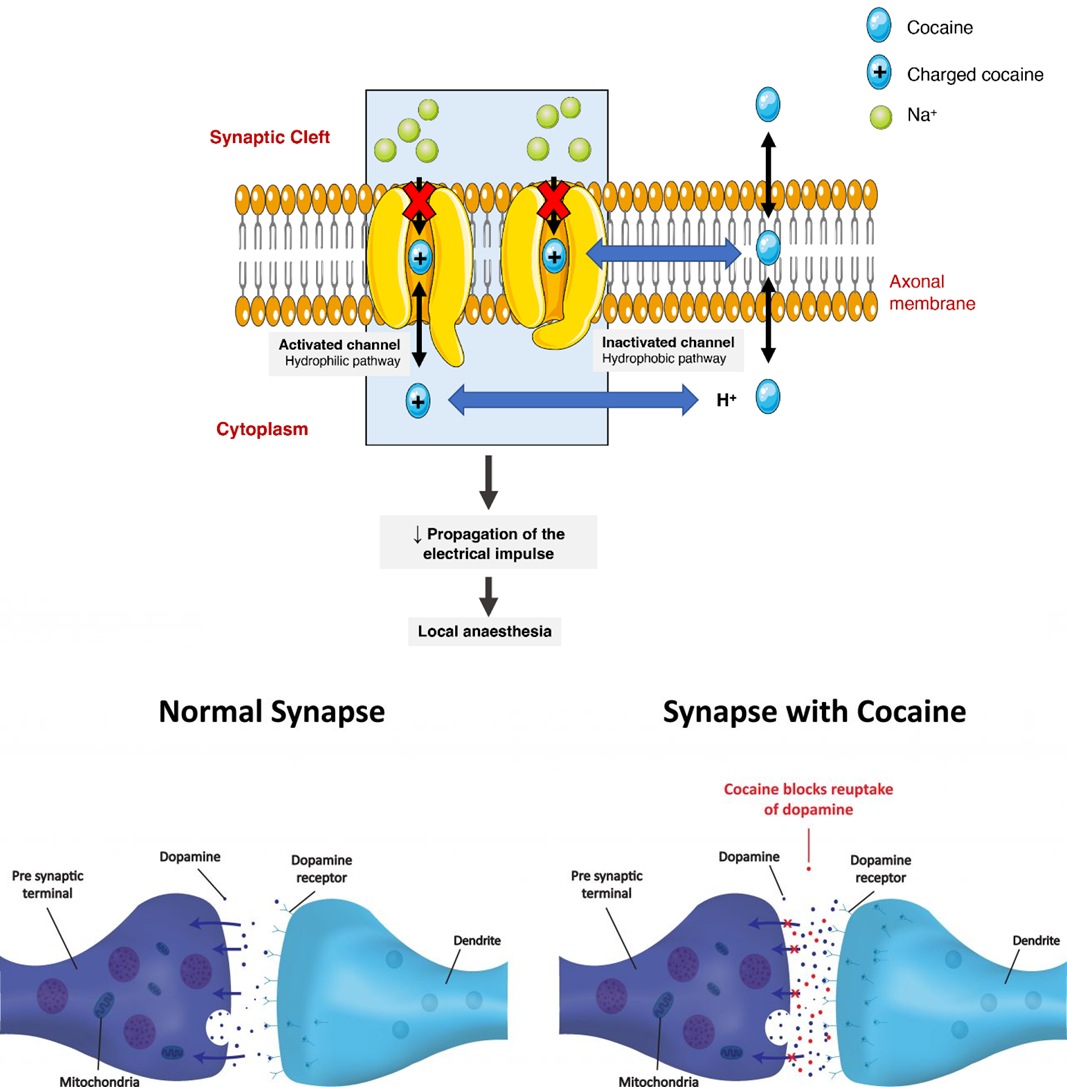
what is cocaine’s drug class
sodium channel blocker (for local anesthesia)
not commonly used
high addiction risk
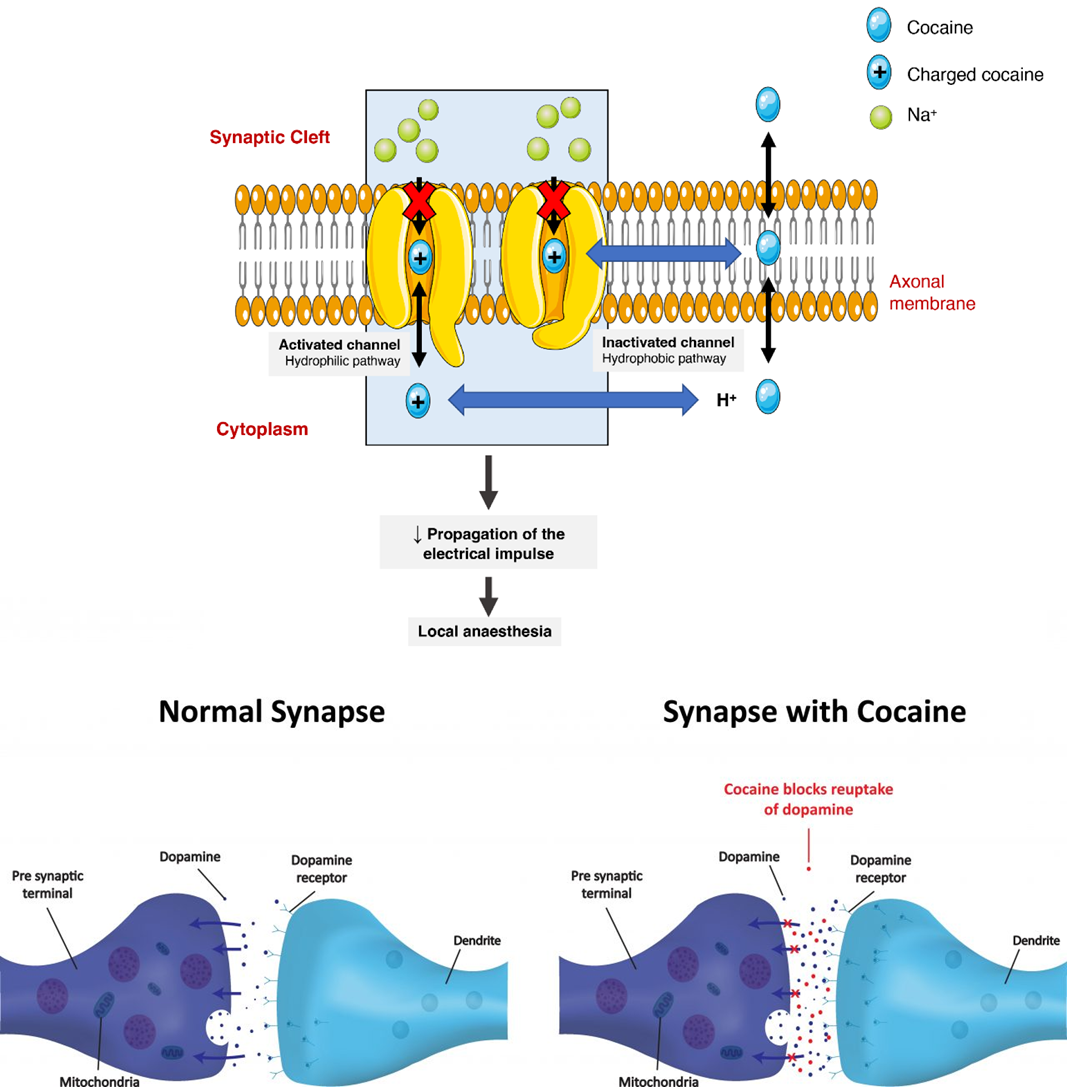
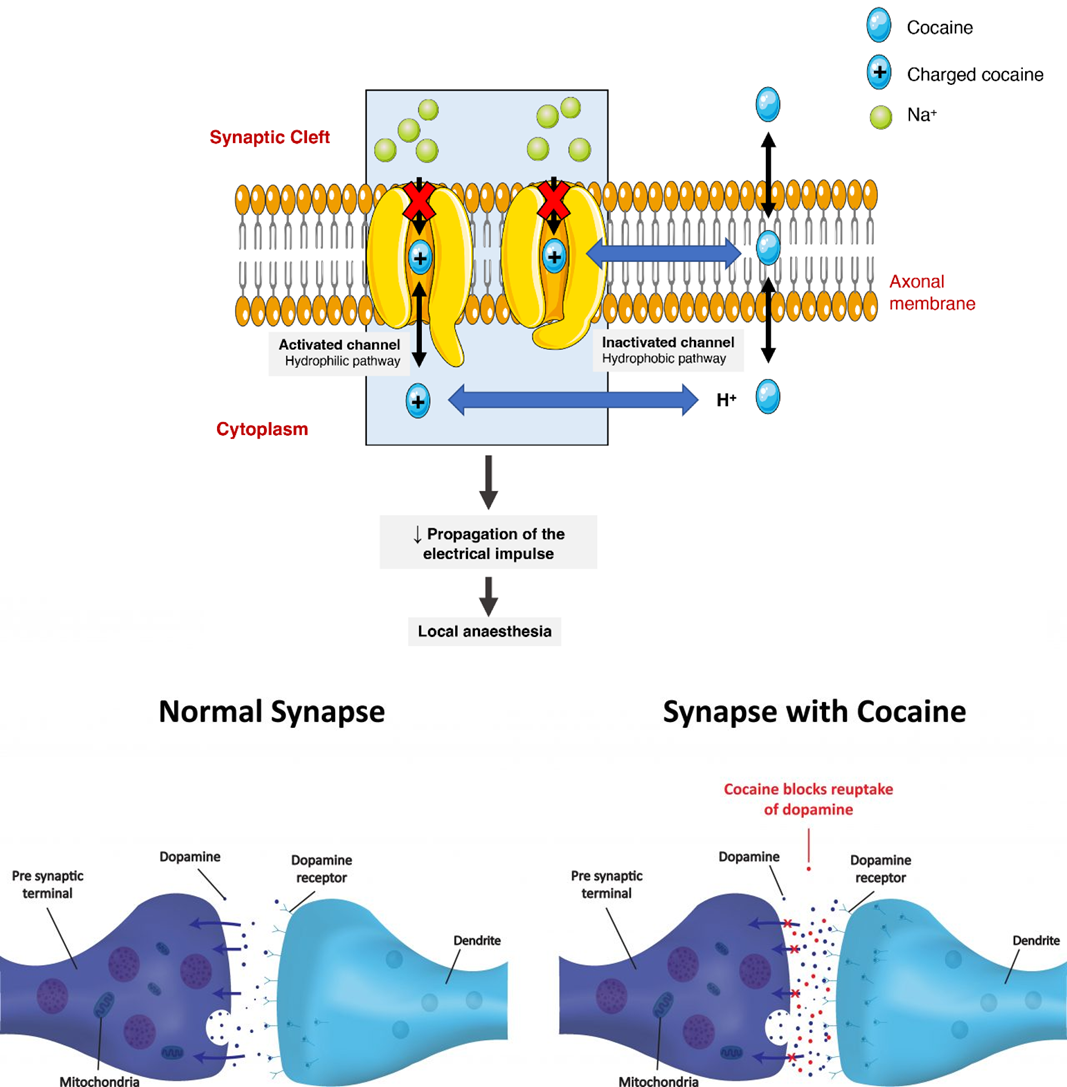
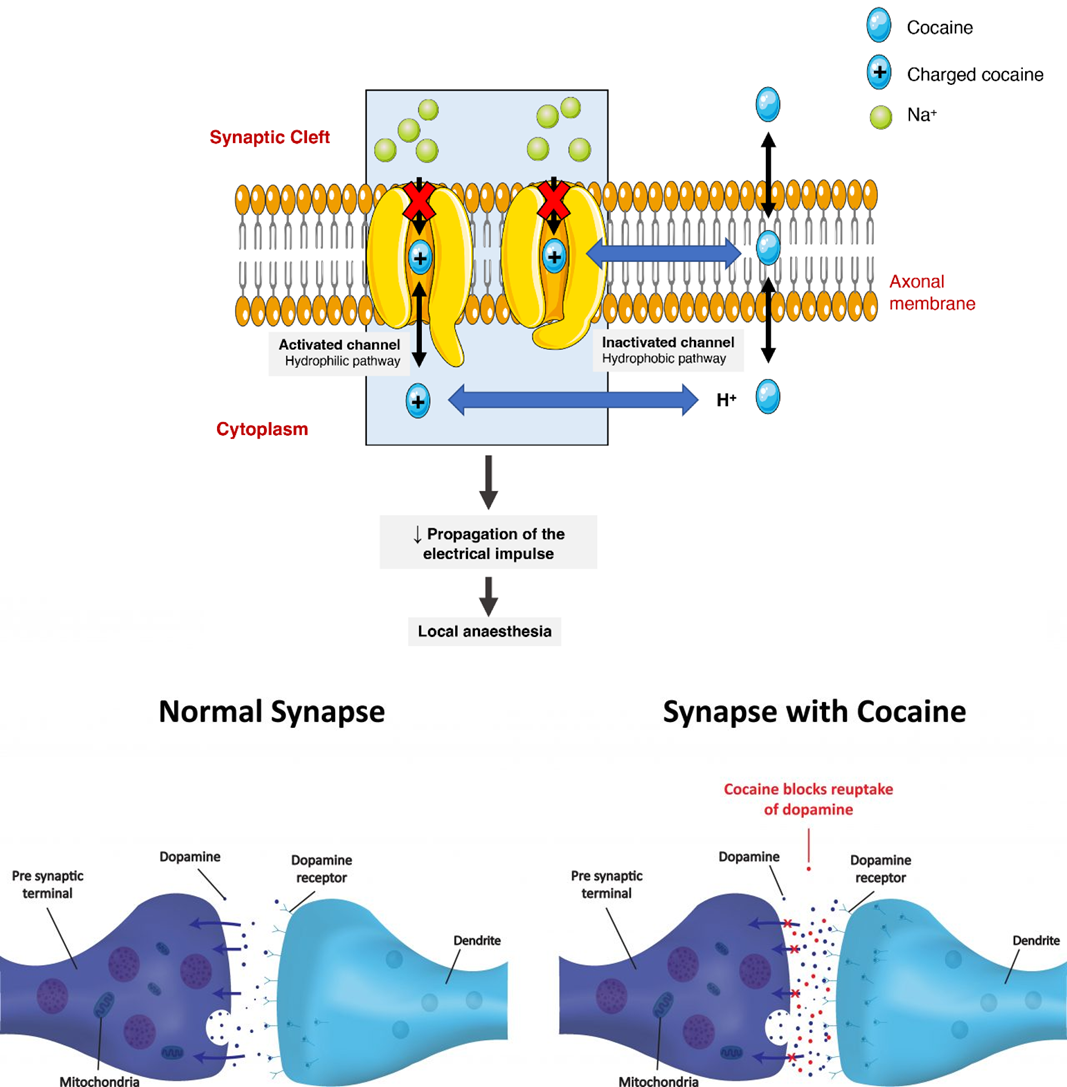
cocaine PKPD (distribution areas)
local action ex intranasal route = nasal mucosa numbness
CNS distribution=dopamine & reward system agonist
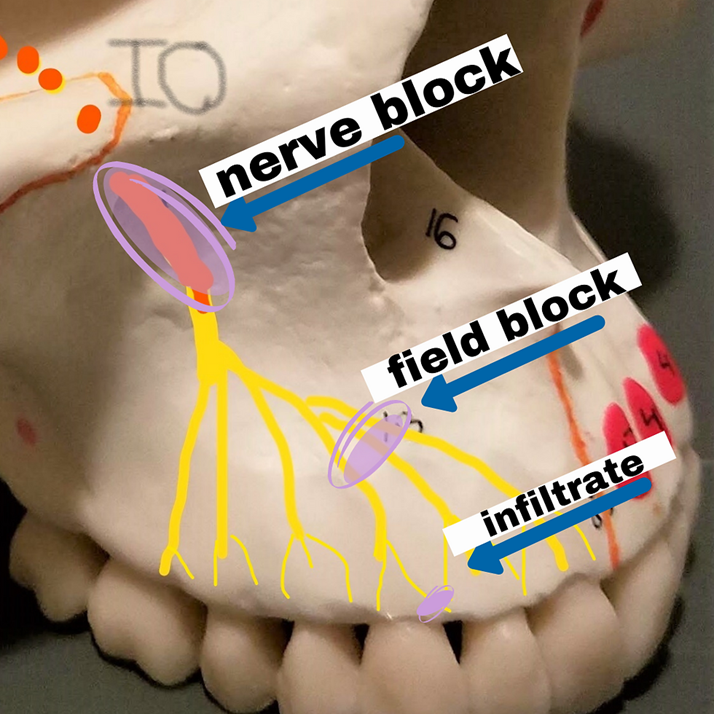
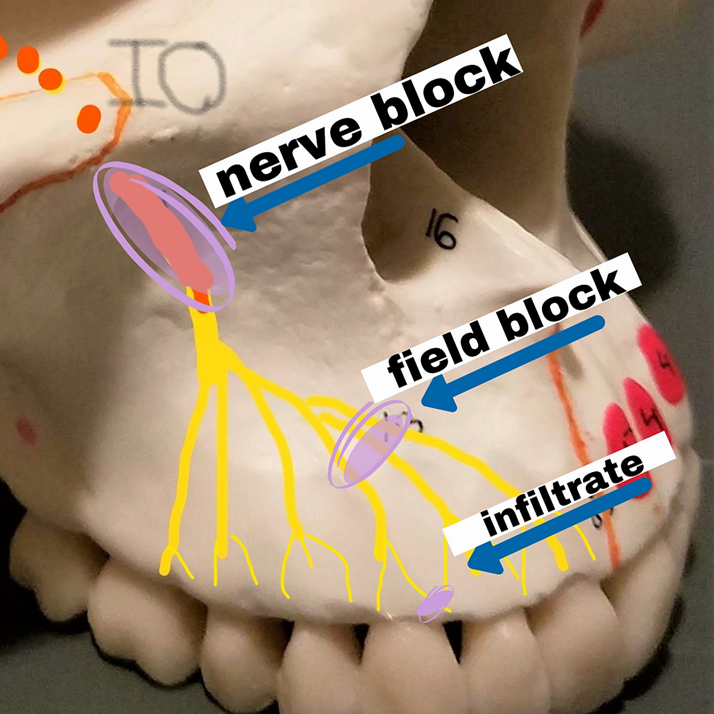
what routes do we use for local anesthesia
application near the procedure site
topical=on the surface ex cream, spray
infiltration=SC injection into the tissue near nerve ending
nerve block=injection near a large nerve
what synergy drugs do we use for local anesthesia
epinephrine (adrenalin)= localized vasoconstriction =bleeding control, increased DOA of anesthetic
sodium bicarbonate=alkalization of the tissue in case of bacterial infection (bacterial acid)
opioids, NSAIDS, tylenol=adjunct analgesia PRN, once anesthesia wears off
epidural local anesthesia route (what does it do/effects)
into epidural space
location ensured by no CSF return in needle
anesthetic bathes the spinal nerve
disruption of impulse transmission to/from CNS
assess sensory & motor ability (ex prior to mobilizing pt)
what locations can we do an epidural for local anesthetic (injection site or catheter placement at a specific location:)
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
what is the onset of a local anesthesia epidural (route)
20-30 mins
continuous infusion via an indwelling catheter
drug dosage = higher for epidural route than for spinal route
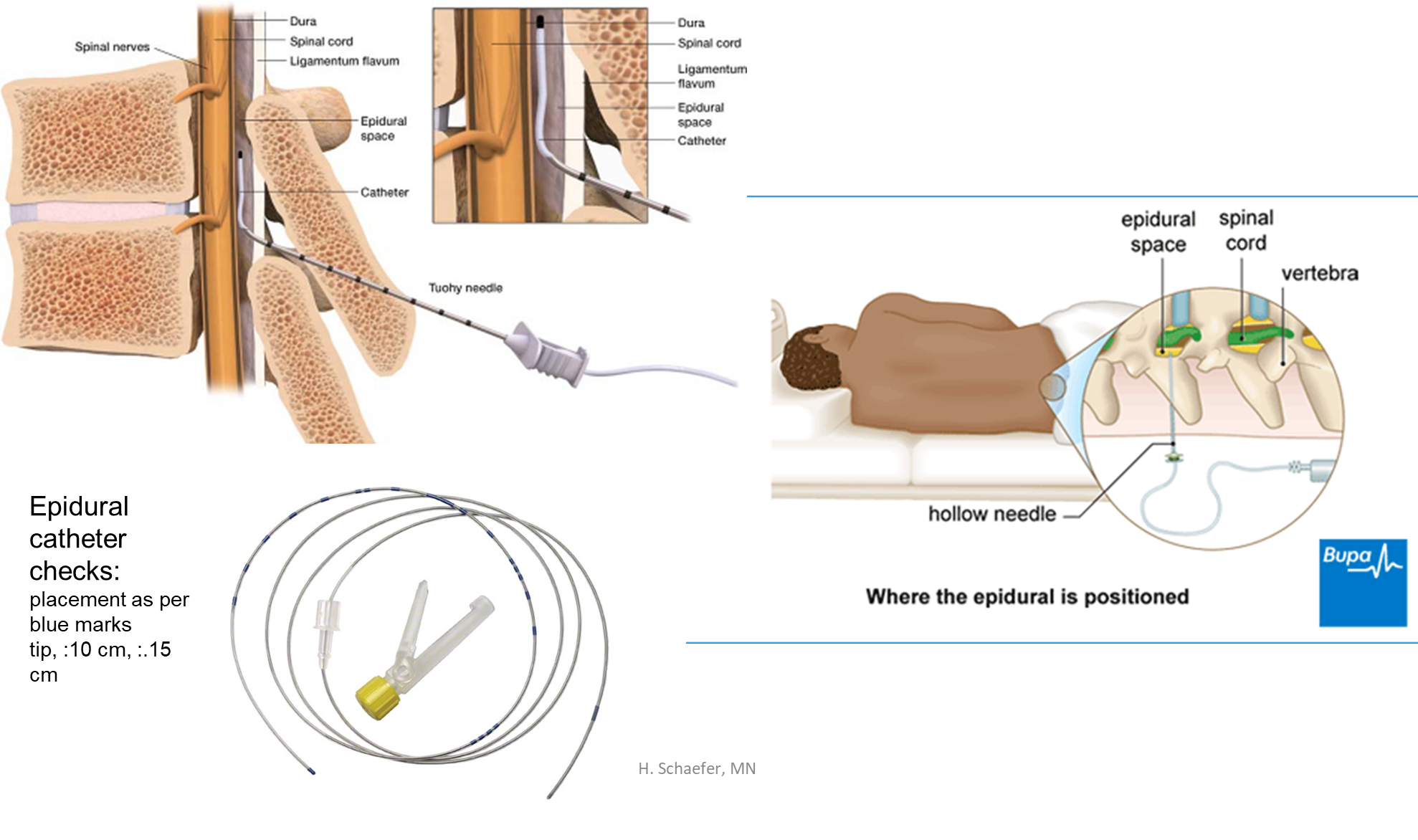
Epidural catheter checks, where do we place it
placement as per blue marks
tip :10 cm
:.15 cm
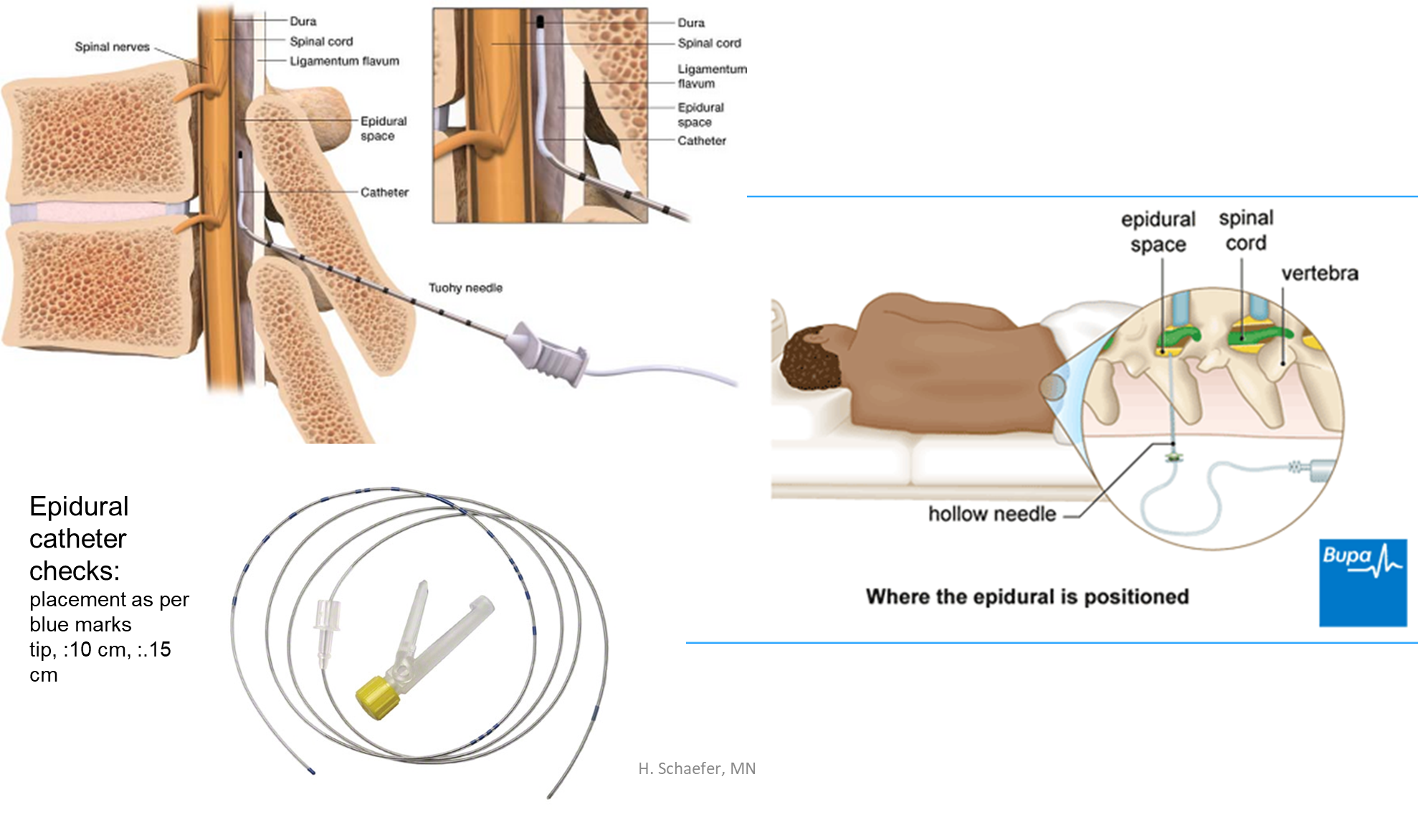
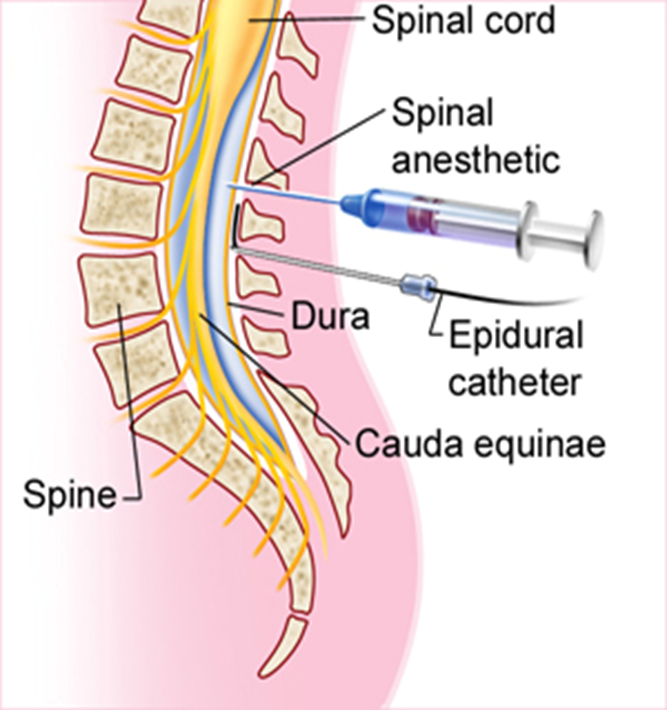
Local anesthesia: spinal “intrathecal” route (where is it done)
directly into CSF (intrathecal space/subarachnoid space)
1x dose injected
always below L2 (avoids spinal cord damage)
needle position verification => CSF present in needle
quick onset
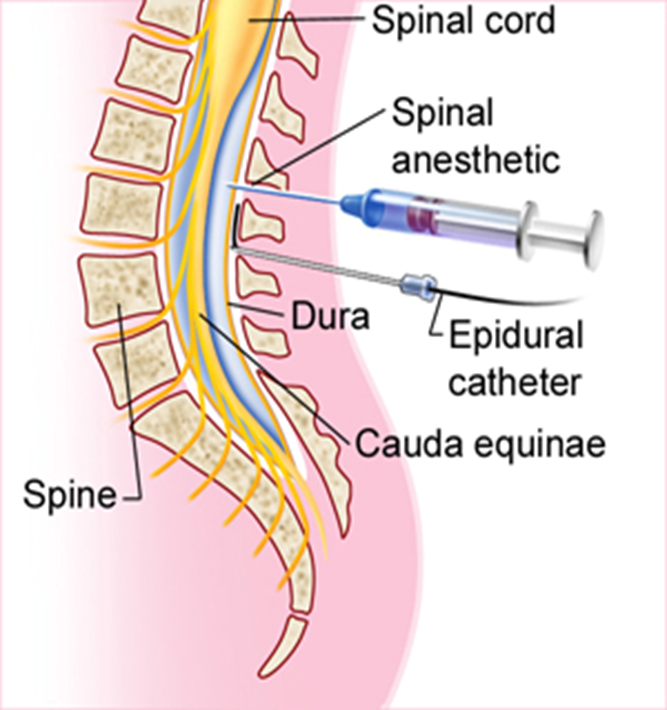
what alters the effect location for a spinal “intrathecal” route
tonicity of solution effects location of action
pt positioning effects location of action
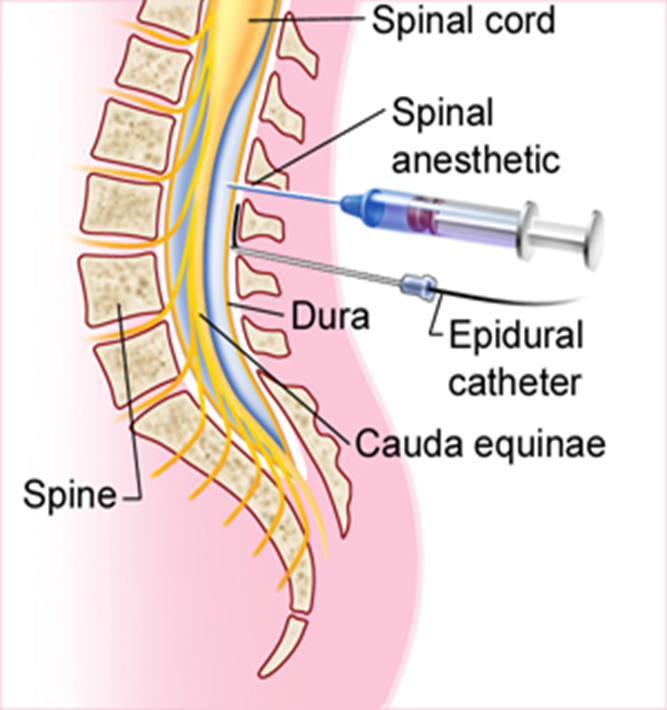
what are the most common procedures done with the spinal “intrathecal” route
abdominal
pelvic
risk of resp depression if diaphragm affected
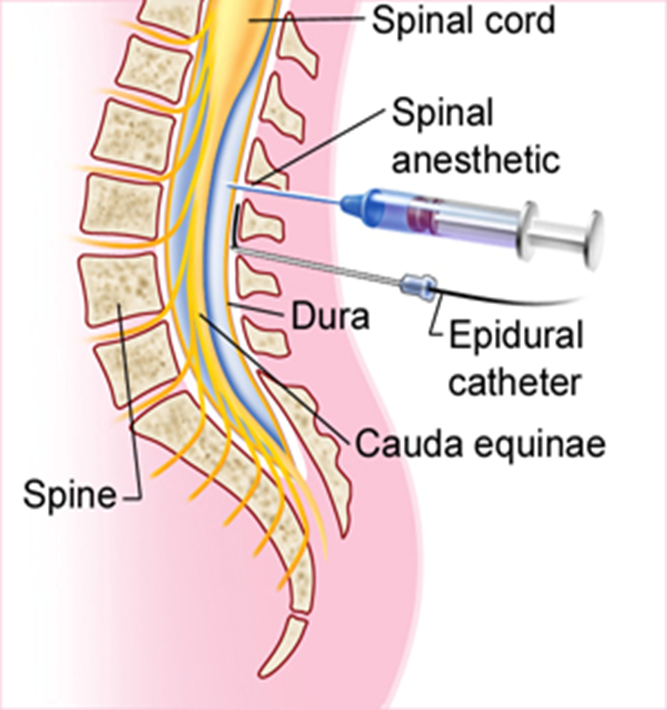
Side effects of anesthesia & nursing assessment
monitor VS (RR!) esp. with spinal anesthesia=hypotension, resp depression
test sensation & motor function, during & post
site hematoma
site infection
catheter migration (epidural catheter)
backache
urinary retention (location of effect dependent)
spinal cord injury
wrongful CSF infiltration! (if epidural migrates into spinal, the dose is higher!)
general anesthesia def (SIMPLE DEF)
drug induced loss of consciousness, pts are not rousable even by painful stimulation
what are the tx goals of general anesthesia
analgesia
unconsciousness (& amnesia)
loss of reflexes (procedure dependent)
what general anesthesia drugs do we use for analgesia
opioids, IV ex fentanyl, morphine
induction/maintenance def
what general anesthesia drugs do we use for maintenance of unconsciousness (process of unconsciousness)
induction=beginning of the loss of consciousness
maintenance=of above for purpose of deep sedation aka surgical anesthesia
inhaled &/or IV general anesthetics
other ex benzodiazepines, ketamine
what general anesthesia drugs do we use for loss of reflexes
neuromuscular blocking agents, IV aka anticholinergics, paralytics
Inhaled general anesthetics drugs and MOA
nitrous oxide, halothane, isoflurane
decrease action potentials, increase GABA, other CNS effects
list Intravenous anesthetics drug and MOA
barbiturate-like drug=propofol (diprivan)
increases GABA, other unknown CNS effects
rapid onset of action
short t1/2, continuous infusion for effect
dose dependent: intubation necessary, VS support (ex hypotension)
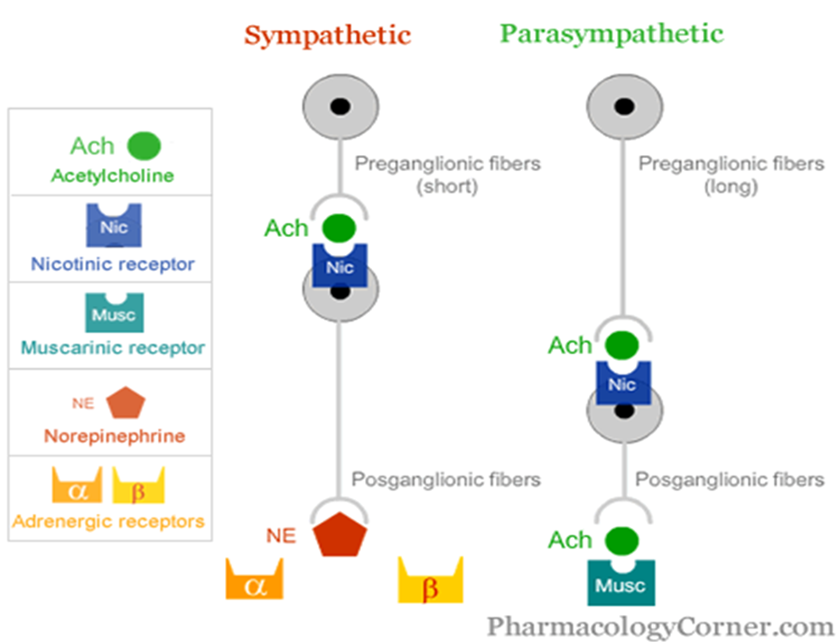
what drug class do we use as neuromuscular blocking agents and their MOA
anticholinergics
block Ach binding at nicotinic receptors (SNS, PNS, Somatic)
=no BBB penetration
=muscle paralysis, including diaphragm (paralytics, ventilation required)
ideal for complex procedures
rapid onset, continuous IV infusion
list the neuromuscular blocking drugs (anticholinergics)
vecuronium
rocuronium
pancuronium
succinylcholine (short t1/2)
MAC def
combo of sedative & analgesic meds used to induce a depression of consciousness, while able to maintain an airway & be awakened
conscious sedation
what drugs do we use for MAC
ketamine (note: higher doses than for depression tx)
benzodiazepine ex midazolam (Versed)
adjunct meds= opioids
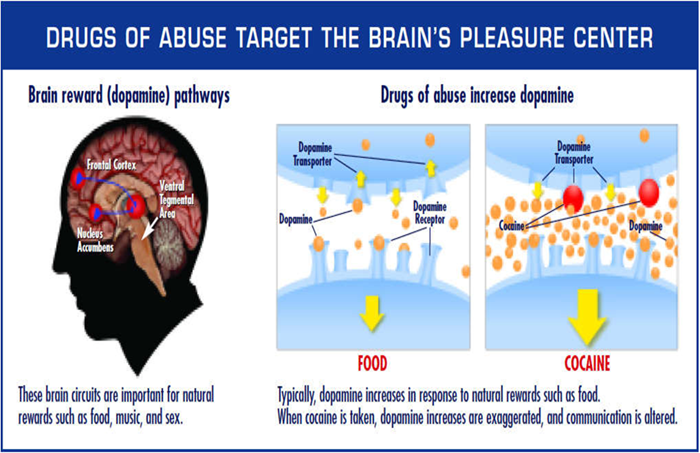
CNS drugs – cautions, things to keep in mind
do not consume with other CNS drugs ex ETOH
drug-drug interactions
additive effects
risk of toxicity
assess for effect, titrate dose PRN
evaluate if CNS effects/side effects seriously interfere with ADLs
risk of addiction
risk of overdose
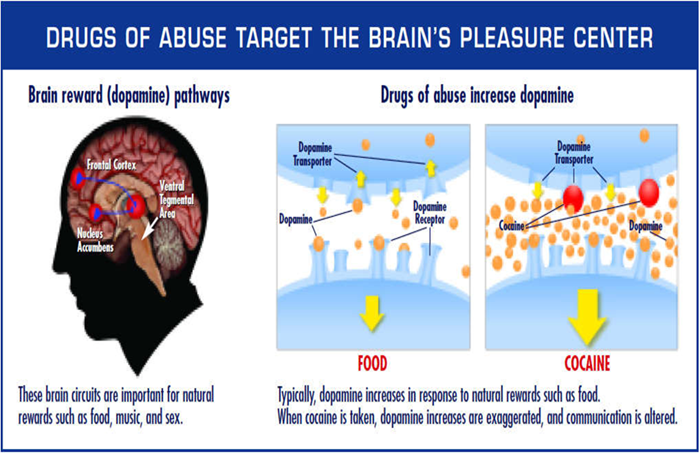
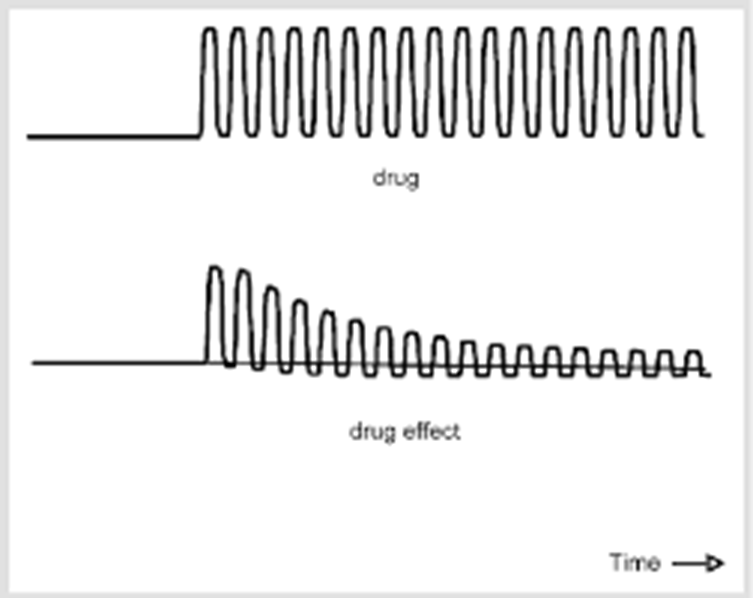
physical dependence on a drug def and effects
body adapts to the presence of a drug
creates tolerance (requiring higher doses to yield the same effect)
creates withdrawal symptoms if abruptly stopped (2-4 weeks duration)
withdrawal weaning protocols carefully observed
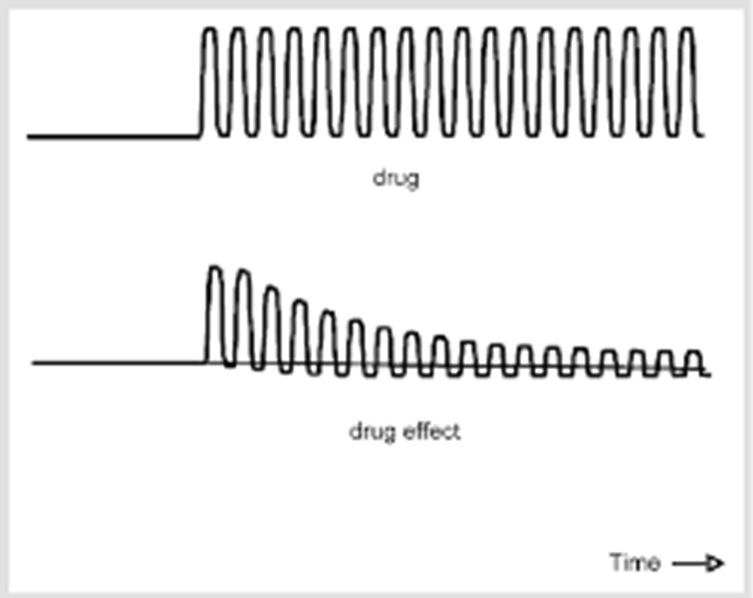
what SNS effects/withdrawal symptoms occur when physical dependence is in play
VS changes
blurred vision
loss of appetite
what other effects/withdrawal symptoms occur when physical dependence is in play
fever
psychosis, agitation, anxiety, panic
seizures
disorientation, impaired memory & focus
what must occur do be diagnosed with drug Abuse & Psychological Dependence according to the DSM-5
3 or more, occurring at any time in the same 12 month period:
spending a great deal of time acquiring, using and recovering from use of the substance
disruption of important activities because of substance use
using more than intended
compulsive use despite harm
unsuccessful efforts to cut down
tolerance=requiring more drug over time
withdrawal symptoms if without drug (note: physical dependence is present)