saunders
5.0(2)Studied by 14 people
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:22 PM on 2/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
1
New cards
coordinated sequence of involuntary, intermittent uterine contractions
Labor
2
New cards
4 major factors (4 Ps) interact during normal child birth; the 4 Ps are interrelated and depend on each other for a safe birth. What are the 4 Ps?
power
passageway
passenger
psyche
passageway
passenger
psyche
3
New cards
“Power”
uterine contractions
4
New cards
forces acting to expel the fetus
contractions
5
New cards
effacement
shortening and thinning of the cervix during the first stage of labor
6
New cards
dilation
enlargement of cervical os and cervical canal during the first stage of labor
7
New cards
“passenger”
the fetus, membranes, and placenta
8
New cards
“psyche”
A patients emotional structure that can determine their entire response to labor and influence physiological and psychological functioning; the pt may experience anxiety or fear
9
New cards
“attitude”
is the relationship of the fetal body parts to one another.
10
New cards
normal intrauterine attitude is ___________,__ in which the fetal back is _______ __, t__he head is forward on the chest, and the arms and legs are folded in against the body. The other attitude, extension, tends to present _________ fetal diameters.
flexion
rounded
larger
rounded
larger
11
New cards
“lie”
relationship of the spine of the fetus to the spine of the pregnant person.
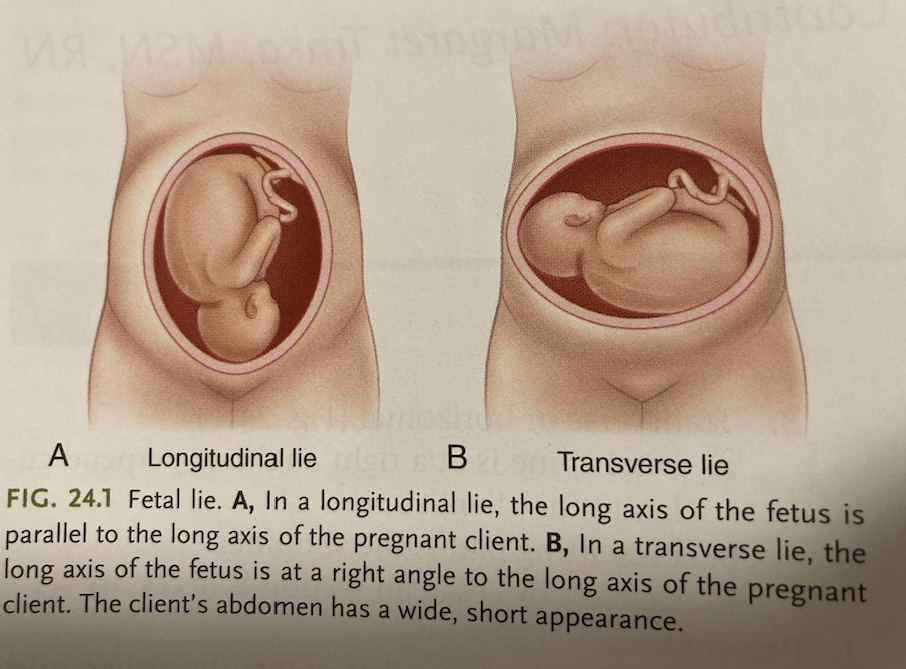
12
New cards
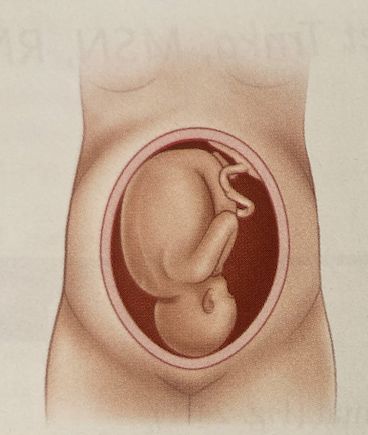
What lie is this
Longitudinal lie
13
New cards
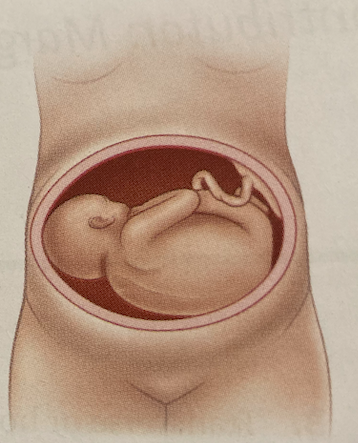
What lie is this
Transverse lie
14
New cards
Fetal spine is parallel to the clients spine.
Fetus is in cephalic or breech presentation.
Fetus is in cephalic or breech presentation.
Longitudinal or vertical
15
New cards
fetal spine is at right angle, or perpendicular, to patients spine.
presenting part is the shoulder.
delivery by cesarean section is necessary
presenting part is the shoulder.
delivery by cesarean section is necessary
Transverse or horizontal
16
New cards
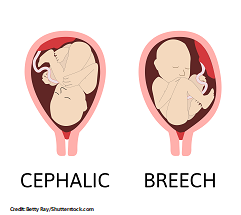
“presentation”
portion of the fetus that enters the pelvic inlet first.
\-cephalic (head first)
\-breech (buttocks first)
\-shoulder (arm, back, abdomen, or side first)
\-cephalic (head first)
\-breech (buttocks first)
\-shoulder (arm, back, abdomen, or side first)
17
New cards
lightening or dropping (aka engagement)
occurs when the fetus descends into the pelvis about 2 weeks before birth
18
New cards
The pregnant person may have a sudden burst of energy known as __________ , often 24-48 hours before on set of labor
nesting
19
New cards
prodromal labor
false labor
20
New cards
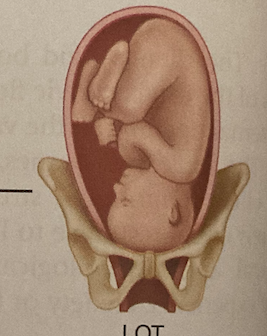
LOT
left occipitotransverse
left occipitotransverse
21
New cards
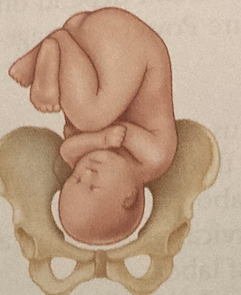
LOP
left occipitoposterior
left occipitoposterior
22
New cards
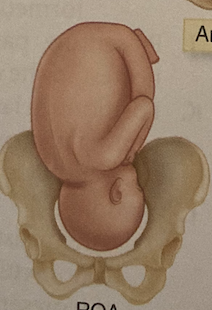
ROA
right occipitoanterior
right occipitoanterior
23
New cards
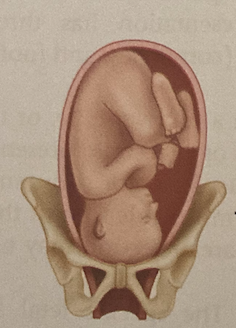
ROT
right occipitotransverse
right occipitotransverse
24
New cards
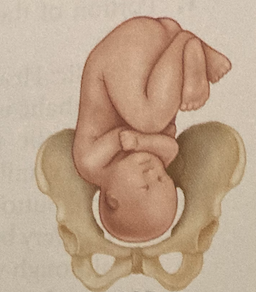
ROP
right occipitoposterior
right occipitoposterior
25
New cards
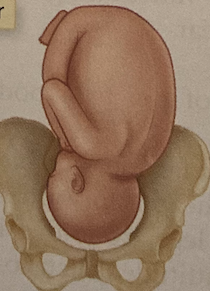
LOA
left occipitoanterior
left occipitoanterior
26
New cards
fetal vertex (occiput) positions
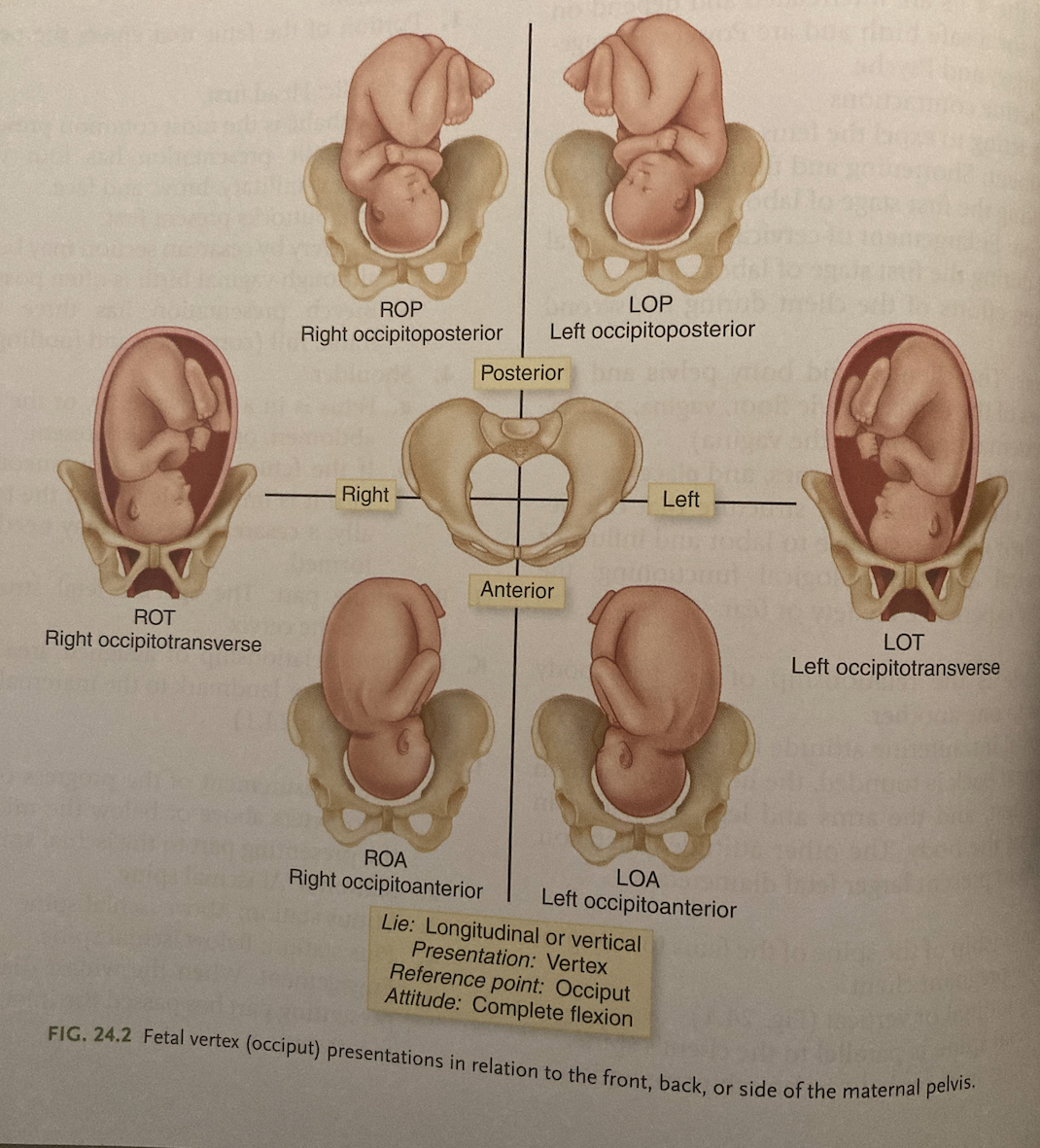
27
New cards
_____________ is the mechanism whereby the fetus nestles into the pelvis
engagement
28
New cards
engagement occurs when the presenting part reaches the level of the ?
ischial spines
29
New cards
________ is the process that the fetal head undergoes as it begins its journey through the pelvis
descent
30
New cards
descent is a continuous process, from before engagement until birth , and is assessed by the measurement called _________
station
31
New cards
mechanisms of labor
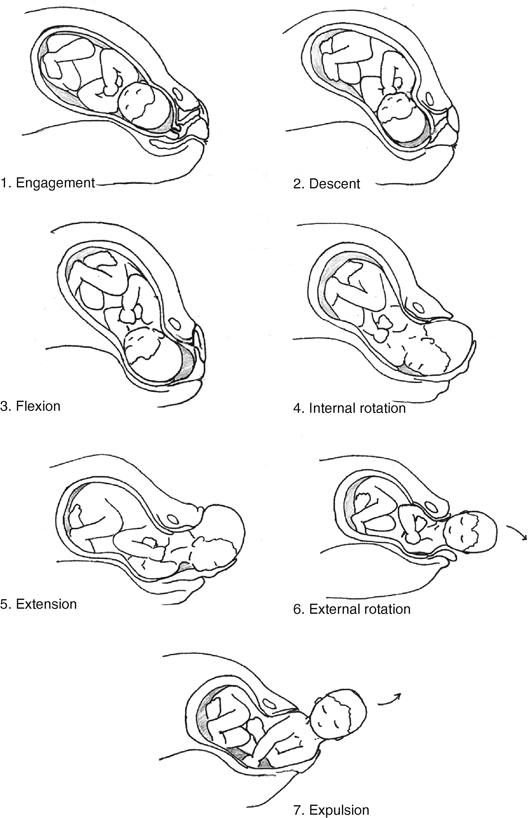
32
New cards
__________ is a process of nodding of the fetal head forward toward the fetal chest
flexion
33
New cards
__________ of the fetus occurs most commonly from the occipitotransverse position, assumed at engagement into the pelvis, to the occopitoanterior position while continuously descending
internal rotation
34
New cards
leopold’s maneuvers
\-methods of palpation to determine presentation and position of the fetus and aid in location of fetal heart sounds
35
New cards
Gestation is time from ______ of the ovum until the date of _______
fertilization.
delivery.
delivery.
36
New cards
the first preception of fetal movement by the pregnant individual may occur at the 16th to 20th week of gestation
quickening
37
New cards
changes to skin pigmentation such as linea nigra, melasa.
is this presumptive or probable sign
is this presumptive or probable sign
presumptive sign
38
New cards
what is the GTPAL ?
client is pregnant for the 4 th time. she had one elective abortion in first trimester, a child who was born at 40 weeks gestation, and a child born at 36 weeks gestation.
client is pregnant for the 4 th time. she had one elective abortion in first trimester, a child who was born at 40 weeks gestation, and a child born at 36 weeks gestation.
G4 T1 P1 A1 L2
39
New cards
rebounding of the fetus agaisnt the examiners fingers on palpation
ballottement
40
New cards
To measure fundal height, client will be _______ position
supine
41
New cards
fundal height is measured to evaluate the gestation ____ of the fetus
age
42
New cards
When assessing fundal height, monitor the client closely for supine ______ when placed in the supine position after 20 weeks gestation
hypotension
43
New cards
ask the client to ____ before measurement of fundal height
void
(because of possible uterine displacement from a full bladder)
(because of possible uterine displacement from a full bladder)
44
New cards
during pregnancy, circulating blood volume increases ( how much % ?)
40-50 %
45
New cards
premature rupture of the membranes is spontaneous rupture of the amniotic membranes before the onset of _________
labor
46
New cards
when the premature rupture of membranres is before term and birth will be delayed, ______ becomes a risk
infection
47
New cards
if the membranes are ruptured, ________ test is positive
nitrazine
48
New cards
prolapsed umbilical cord
umbilical cord is displaced between the presenting part and the amnion or protruding through the cervix, causing compression of the cord and compromising fetal circulation
49
New cards
prolapsed umbilical cord….. fetal heart rate may be ?
irregular and slow
50
New cards
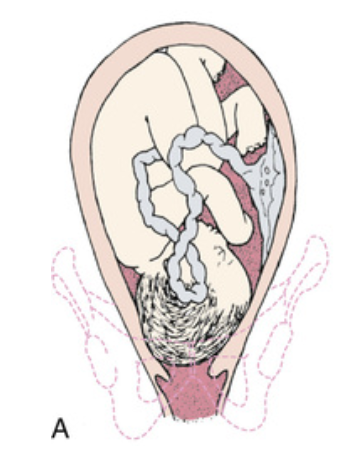
Prolapse of umbilical cord.
Occult (hidden) prolapse of cord.
Occult (hidden) prolapse of cord.
51
New cards
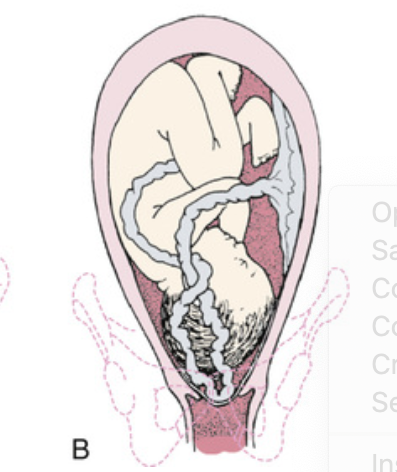
Prolapse of umbilical cord.
Complete prolapse of cord. Note that membranes are intact.
Complete prolapse of cord. Note that membranes are intact.
52
New cards
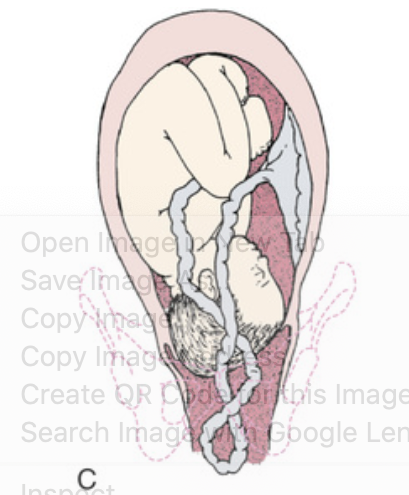
Prolapse of umbilical cord.
Cord presenting in front of fetal head may be seen in vagina.
Cord presenting in front of fetal head may be seen in vagina.
53
New cards
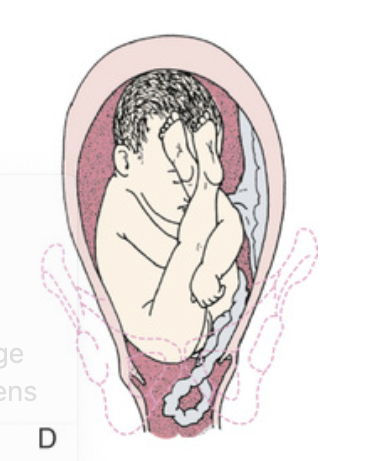
Prolapse of umbilical cord.
Frank breech presentation with prolapsed cord.
Frank breech presentation with prolapsed cord.
54
New cards
preterm labor occurs after the __ th week but before the _th week of gestation
20
37
37
55
New cards
precipitous labor and delivery
labor lasting less than 3 hours
56
New cards
encourage client to _____ between contractions
pant
57
New cards
Position for patient with prolapsed umbilical cord
extreme trendelenburg’s or modified left lateral position or knee-chest position
58
New cards
dystocia
difficult labor that is prolonged or more painful
59
New cards
Nurse is performing an assessment on a client who has just been told that her pregnancy test is positive. which woman is at risk for preterm labor?
\-35 y old primigravida
\-client has history of cardiac disease
\-clients hemoglobin is 135 mmol/d
\-20 y old primigravida of average weight and height
\-35 y old primigravida
\-client has history of cardiac disease
\-clients hemoglobin is 135 mmol/d
\-20 y old primigravida of average weight and height
\
\-client has history of cardiac disease.
\
\-client has history of cardiac disease.
\
60
New cards
A client is experiencing labor dystocia.
which risk factors in the clients history places them at risk for this complication?
\-age 45
\-bmi of 28
\-previous difficulty with fertility
\-administration of oxytocin for induction
\-potassium level of 3.6 mmol/L
which risk factors in the clients history places them at risk for this complication?
\-age 45
\-bmi of 28
\-previous difficulty with fertility
\-administration of oxytocin for induction
\-potassium level of 3.6 mmol/L
\-age 45
\-bmi of 28
\-previous difficulty with fertility
\-bmi of 28
\-previous difficulty with fertility
61
New cards
the nurse in a labor room is preparing to care for a client with hypertonic uterine contractions. the nurse is told that the client is experiencing uncoordinated contraction that are erratic in their frequency, duration, and intensity. what is the priority nursing action?
\-provide pain relief measures
\-prepare the client for an amniotomy
\-promote ambulation every 30 mins
\-monitor oxytocin infusion closely
\-provide pain relief measures
\-prepare the client for an amniotomy
\-promote ambulation every 30 mins
\-monitor oxytocin infusion closely
\-provide pain relief measures
62
New cards
the nurse has made a plan of care for a client experiencing dystocia and includes several nursing actions in the plan of care. what is the priority nursing action?
\-providing comfort measures
\-monitoring the fetal heart rate
\-changing clients position frequently
\-keeping significant other informed of the progress of the labor
\-providing comfort measures
\-monitoring the fetal heart rate
\-changing clients position frequently
\-keeping significant other informed of the progress of the labor
\-monitoring the fetal heart rate
63
New cards
________ are meds that produce uterine relaxation and suppress uterine activity
tocolytics
64
New cards
tocolytics are used for?
to halt uterine contractions and prevent preterm birth
65
New cards
fetal contraindications for the use of tocolytics
\-gestational age greater than 37 weeks
\-cervical dilation greater than 4cm
\-fetal demise (fetal death)
\-lethal fetal anomaly
\-chorioamnionitis
\-acute fetal distress
\-chronic intrauterine growth restriction
\-cervical dilation greater than 4cm
\-fetal demise (fetal death)
\-lethal fetal anomaly
\-chorioamnionitis
\-acute fetal distress
\-chronic intrauterine growth restriction
66
New cards
client contraindications for the use of tocolytics
\-severe preeclampsia and eclampsia
\-active vaginal bleeding
\-intrauterine infection
\-cardiac disease
\-placental abruption
\-poorly controlled diabetes
\-active vaginal bleeding
\-intrauterine infection
\-cardiac disease
\-placental abruption
\-poorly controlled diabetes
67
New cards
For a client receiving tocolytics, position them how
on the side to enhance placental perfusion and reduce pressure on the cervix
68
New cards
Indomethacin (type of tocolytic)
Relaxes uterine smooth muscle by inhibiting prostaglandins.
\
\
69
New cards
prostaglandins are used for
\-preinduction cervical ripening
induction of labor
\
induction of labor
\
70
New cards
oxytocin is used for
\-induces or augments labor
\-controls postpartum bleeding
\-controls postpartum bleeding
71
New cards
late decelerations vs early decelerations of fetal heart rate
late decelerations = fetal distress
early decelerations = reassuring sign and do not indicate fetal distress
early decelerations = reassuring sign and do not indicate fetal distress
72
New cards
_____ ________ is a poorly contracted uterus that does not adequately compress large open vessels at the placental site…. this can result in hemorrhage
uterine atony
73
New cards
uterine atony : assessment:
a soft (boggy) uterus noted on palpation of the uterine fundus
74
New cards
interventions for uterine atony
1. massage the uterus until firm
2. empty the patients bladder (void or catheterization) if that is contributing to the uterine atony
3. notify doctor
75
New cards
when is the greatest risk for postpartum hemorrhage?
4 hours immediately after delivery.
second greatest risk is 24 hours following delivery.
second greatest risk is 24 hours following delivery.
76
New cards
causes of postpartum hemorrhage
\-uterine atony
\-laceration of cervix or vagina
\-hematoma development
\-retained placenta fragments
\-obesity
\-laceration of cervix or vagina
\-hematoma development
\-retained placenta fragments
\-obesity
77
New cards
s/s of postpartum hemorrhage
\-significant bleeding (pad is soaked in 15 mins)
\-restlessness and increased pulse rate
\-rapid and shallow respirationss
\-decrease in blood pressure
\-cool clammy skin
\-ashen greyish skin
\-decreased urine output
\-change in loc
\-restlessness and increased pulse rate
\-rapid and shallow respirationss
\-decrease in blood pressure
\-cool clammy skin
\-ashen greyish skin
\-decreased urine output
\-change in loc
78
New cards
pt has endometriosis (infection of lining of the uterus in post partum)… what position should you put her in
fowlers position (to facilitate the drainage of lochia).
79
New cards
pt gets pulmonary embolism… an intervention is to administer ______
oxygen
80
New cards
Nurse is monitoring pt in the immediate postpartum period for signs of hemorrage. which sign would be an early sign of excessive blood loss?
a. temp of 38
b. increase in pulse from 88 to 102
c. blood pressure changes from 130/88 to 124/80
d. rr increases from 18 to 22 breaths per minn
\
a. temp of 38
b. increase in pulse from 88 to 102
c. blood pressure changes from 130/88 to 124/80
d. rr increases from 18 to 22 breaths per minn
\
b
81
New cards
nurse is assessing pt who delivered by c/s, for signs of superficial venous thrombosis. which sign would the nurse note if svt were present?
1. paleness of calf
2. coolness of calf
3. enlarged hardened veins
4. palpable dorsalis pedis pulses
1. paleness of calf
2. coolness of calf
3. enlarged hardened veins
4. palpable dorsalis pedis pulses
3,
82
New cards
Who is at most risk for hemorrage?
1. a primiparous who delivered 4 hours ago
2. a multiparous who delivered 6 hours ago
3. a multiparous who delivered a large baby after oxytocin induction
4. a primiparous who delivered 6 hours ago and had epidural anesthesia
1. a primiparous who delivered 4 hours ago
2. a multiparous who delivered 6 hours ago
3. a multiparous who delivered a large baby after oxytocin induction
4. a primiparous who delivered 6 hours ago and had epidural anesthesia
3
83
New cards
Bishops score
used to determine maternal readiness for labor and evaluates cervical status and fetal position
\-score of 8 or greater indicates that the chance of a successful vaginal delivery is good
\-score of 8 or greater indicates that the chance of a successful vaginal delivery is good
84
New cards
____________ is a deliberate initiation of uterine contractions that stimulates labor
induction
85
New cards
amniotomy
artificial rupture of the membranes
86
New cards
__________ is an incision made into the perineum to enlarge the vaginal outlet and facilitate birth
episiotomy
87
New cards
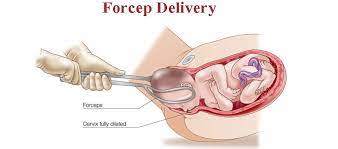
forceps delivery
used to assist in the delivery of the fetal head
88
New cards
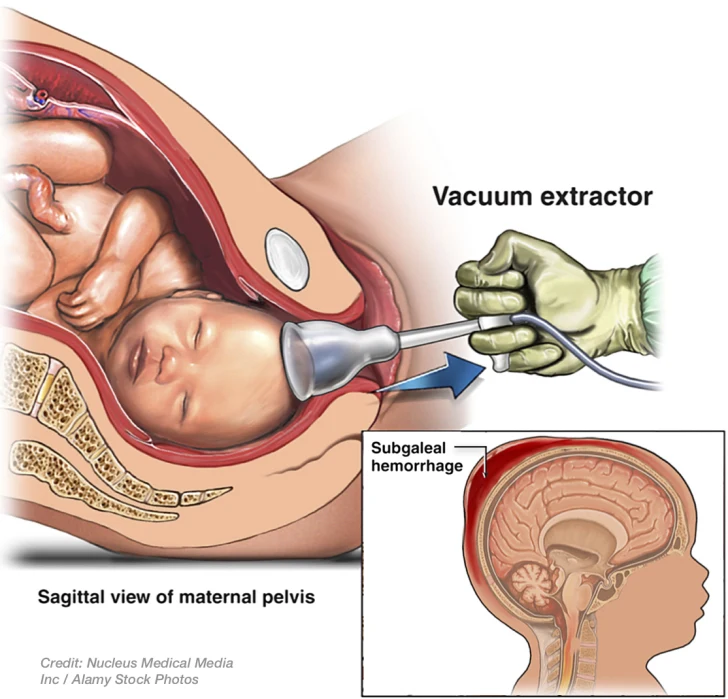
vacuum extraction
\-cap like suction device is applied to the fetal head to facilitate extraction
\
\
89
New cards
nurse is assessing a client who has a scheduled cesarean at 39 weeks. what assessment finding indicates you gotta call the doctor?
1. fetal heart rate of 180
2. maternal pulse of 85 beats
3. mother wants pizza
4. father wants pizza
1. fetal heart rate of 180
2. maternal pulse of 85 beats
3. mother wants pizza
4. father wants pizza
1. (normal fetal hr is 110-160)
90
New cards
a pt is brought to the delivery room and preped for a c section. the nurse would place patient in what position on the table?
supine with a wedge under the right hip.
\
\
91
New cards