Carbohydrates
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Monosaccharides
monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made
Monosaccharide Examples
-glucose
-galactose
-fructose
Glycosidic bonds form when -
a condensation reaction occurs between two monosaccharides
Disaccharides
formed by condensation of two monosaccharides
maltose
condensation of two glucose molecules
sucrose
condensation of a glucose & fructose molecule
lactose
condensation of glucose & galactose molecule
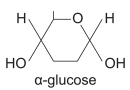
a-glucose (isomer of glucose)
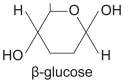
b-glucose (isomer of glucose)
polysaccharides →
formed by condensation of many glucose units
condensation of a-glucose →
glycogen & starch
condensation of b-glucose →
cellulose
monosaccharide attributes
-sweet tasting
-soluble
-(CH2O)n
glucose use -
main substrate for respiration
Glycogen structure -
many molecules of alpha glucose joined together by 1,4 & 1,6 glycosidic bonds
glycogen structure - large no. of side branches
energy can be released quickly → enzymes can act simultaneously on branches
glycogen structure - large but compact molecule
maximises amount of energy it can store
glycogen structure - insoluble
doesn’t affect water potential of cells & cannot diffuse out of cells
Starch →
-stores energy in plants
-mixture of 2 polysaccharides (amylose & amylopectin)
Amylose
unbranched chain of glucose molecules joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds →coiled structure, compact molecule →stores a lot of energy
Amylopectin
branched & made up of glucose molecules joined by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds →side branches = acted upon simultaneosly by enzymes →broken down to release energy
Starch Properties - insoluble
doesn’t affect cell water potential
Starch Properties - compact
a lot of energy can be stored in a small space & when hydrolysed released alpha glucose can be transported easily
Cellulose - component of cell walls
composed of long & unbranched chains of b-glucose, joined by glycosidic bonds
Microfibrils
strong threads made of long cellulose chains running parallel to eachother →joined together by hydrogen bonds forming strong cross linkages
Cellulose Function
stops cell wall bursting under osmotic pressure →exerts inward pressure that stops influx of water →cell stays turgid & rigid →maximises surface area of plants for photosynthesis
Benedicts Reagant
test for reducing sugars →sugars that can donate an electron to Benedicts
Reducing Sugars =
all monosaccharides & some disaccharides (maltose)
Benedicts reagant =
alkaline solution of Copper (II) Sulfate
Benedicts Reagant Reaction
addition of a reducing sugar + heat →insoluble red precipitate (copper (I) oxide)
Benedicts Test
add 2cm3 of food sample to be tested (liquid)
add 2cm3 of Benedict’s Reagant
heat mixture gently in water bath for 5 minutes
brick red = positive
non-reducing sugars
polysaccharides & some disaccharides
Non-reducing Sugar test
2cm3 of food sample (liquid) & 2cm3 of Benedicts placed in hot water bath for 5 minutes
No colour change (blue →brick red) leads to
add 2cm3 of same food sample & 2cm3 of dilute HCl
place test tube in water bath for 5 minutes (dilute HCl will hydrolyse disaccharides + polysaccharides to their constitutent monosaccharides)
add sodium hydrogencarbonate to neutralise test tube (benedicts X work in acidic conditions) & use pH paper to check solution is neutral
retest solution by adding 2cm3 Benedict’s Reagant and placing in water bath for 5 minutes
positive = blue benedicts →brick red
Starch Test
iodine/potassium iodide = orange/brown →blue/black