Midterm review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/146
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
1
New cards
gametes
sex cells (sperm or egg)
2
New cards
meiosis
process that makes gametes
3
New cards
haploid
1 set of chromosomes (sex cells)
4
New cards
diploid
2 sets of chromosomes (somatic cells)
5
New cards
crossing over
exchange of genetic info between homologous chromosomes (during prophase 1)
6
New cards
fertilization
combination of sperm and egg
7
New cards
ATP
universal energy molecule
8
New cards
cell respiration
Glucose is broke down to produce 38 ATP molecules. Oxygen is used in this process and carbon dioxide is given off.
9
New cards
glycolysis
1st step of cell respiration, splits glucose in half
10
New cards
Electron Transport Chain
Series of reactions that make the most ATP
11
New cards
aerobic
oxygen needed
12
New cards
anaerobic mean
-oxygen is not needed
13
New cards
Lactic acid fermentation
type of anaerobic respiration that occurs in animals cells when oxygen isn't available. makes 2 ATP and lactic acid
14
New cards
Alcoholic fermentation
type of anaerobic respiration done by yeast and some bacteria. makes 2ATP, ethyl alcohol and CO2
15
New cards
cell division
process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells
16
New cards
mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
17
New cards
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm during cell division
18
New cards
chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
19
New cards
centromere
area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
20
New cards
interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions
21
New cards
cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
22
New cards
prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus
23
New cards
centriole
tiny structures in animal cells that spindle fibers radiate out from.
24
New cards
spindle
microtubule protein fibers that help separate the chromosomes during mitosis
25
New cards
metaphase
second phase of mitosis during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
26
New cards
anaphase
the third phase of mitosis during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
27
New cards
telophase
fourth and final phase of mitosis during which the chromosomes begin to disperse into a tangle of dense materials
28
New cards
cancer
disorder in which some of the body's own cells lose the ability to control growth
29
New cards
chromatin
un-condensed version of chromosomes
30
New cards
G1
growth and activity period during Interphase
31
New cards
S phase
Stage of interphase where DNA is copied, "synthesis"
32
New cards
G2
last phase of interphase, preparation for mitosis
33
New cards
somatic cells
body cells, all cell except sperm and egg
34
New cards
homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes, one from each parent
35
New cards
METAPHASE
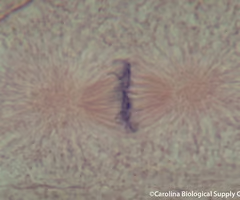
36
New cards
ANAPHASE
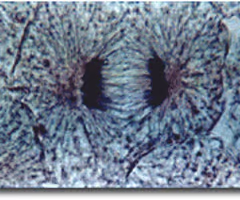
37
New cards
PROPHASE
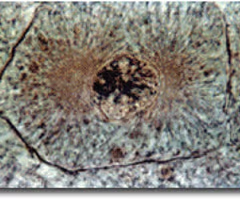
38
New cards
TELOPHASE
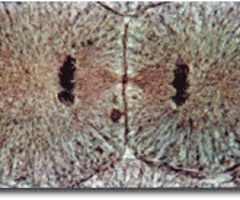
39
New cards
heterotrophs
organisms that obtain food by consuming other living things
40
New cards
autotrophs
organisms that make their own food (photosynthesis)
41
New cards
photosynthesis
the process by which autotrophs use the energy of sunlight to produce high-energy sugars (glucose) that can be used as food\`
42
New cards
pigments
light-absorbing molecules that capture energy from sunlight
43
New cards
chlorophyll
plants' principal pigment
44
New cards
thylakoids
disc shaped membranes inside chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll
45
New cards
NADP+
an electron carrier molecule
46
New cards
light-dependent reactions
sunlight trapped by light absorbing pigments
47
New cards
Calvin cycle
reactions that make glucose (another name for the light-independent cycle)
48
New cards
guard cells
specialized cells in epidermis (mostly lower layer) that regulate openings in leaf
49
New cards
stomata
openings in leaf to allow CO2 to enter and O2 to leave
50
New cards
epidermis
upper and lower layers of leaf cells, each 1 cell layer thick
51
New cards
palisade cells
tightly packed columns of cells in mesophyll, most photosynthesis happens here
52
New cards
spongy cells
loosely packed cells in mesophyll layer to allow gas exchange, some photosynthesis
53
New cards
xylem
vascular tissue that transports water up from roots throughout the plant
54
New cards
phloem
vascular tissue that transports "food" (glucose) throughout the plant
55
New cards
cuticle
waxy covering that allows leaves to minimize water loss
56
New cards
photosynthesis:
process that converts sunlight into chemical energy (glucose)
57
New cards
diffusion
The process by which molecules of a substance move from an area higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. ex: CO2 and O2. Passive.
58
New cards
phagocytosis
"cell eating". Kind of endocytosis in which extensions of cytoplasm surround a particle and package it within a food vacuole. Amoebas and white blood cells.
59
New cards
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of molecules outside the cell is lower than inside.
60
New cards
osmosis
The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Passive
61
New cards
hypertonic solution
A solution in which there is a higher concentration of molecules outside the cell than inside.
62
New cards
facilitated diffusion
The process by which molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels. Glucose, uses membrane proteins. Passive
63
New cards
endocytosis
Process of a cell taking in material by means of enfolding the cell membrane. The pocket that results breaks loose from outer portion of cell membrane. It forms a vesicle within cytoplasm. types: Pinocytosis and phagocytosis. Active.
64
New cards
equilibrium
Diffusion continues until the concentration of molecules is equal throughout the space.
65
New cards
active transport
1. substances move from LOW to HIGH
66
New cards
2. requires energy (ATP)
67
New cards
concentration gradient
The difference in the concentration of molecules across a space.
68
New cards
passive transport
1. molecules move from High to Low.
69
New cards
2. Does not require energy to move molecules.
70
New cards
protein channel
Membrane proteins that help move larger molecules or ions across membranes.
71
New cards
selectively permeable
A membrane that lets certain molecules pass through and not others.
72
New cards
pinocytosis
A kind of endocytosis for liquids "cell drinking". active.
73
New cards
exocytosis
Expels unwanted material outside the cell. Active.
74
New cards
isotonic
Solution of molecules is the same inside and outside of a cell.
75
New cards
plasmolysis
The shrinking of a plant cell membrane away from the cell wall when placed in a hypertonic solution.
76
New cards
homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal conditions.
77
New cards
fluid mosaic model
description of cell membrane because it is made of many different molecules (lipids, carbs, proteins) AND can move around - "fluid", not "fixed"
78
New cards
phosphate head
polar part of cell membrane
79
New cards
fatty acids tails
non polar part of cell membrane
80
New cards
explain "like dissolves like"
polar substances dissolve other polar substance and non-polar dissolves non-polar
81
New cards
Cell
Basic unit of life
82
New cards
Cell theory
Fundamental concept of biology that states 1. all living things are composed of cells, 2. cells are basic structure and function, 3. new cells are formed from existing cells
83
New cards
Cell membrane
Thin flexible barrier surrounding cell, selectively permeable, made primarily of phospholipids
84
New cards
Nucleus
"director" of cell activity, Large membrane enclosed structure that holds genetic info (DNA)
85
New cards
Eukaryote
Cell with a nucleus
86
New cards
Prokaryote
Cell without a nucleus
87
New cards
Cytoplasm
fluid like solution inside cell
88
New cards
Organelle
"Little organs" within the cell, perform important cellular functions
89
New cards
Vacuole
Cell organelle stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbs
90
New cards
Lysosomes
Organelle which contains digestive enzymes, and breaks down lipids carbs and proteins into small molecules for use around the cell
91
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments which give the cell structure, internal organization, and sometimes movement
92
New cards
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis; most numerous of all organelles and is found in EVERY cell, even prokaryotes
93
New cards
Endoplasmic reticulum
"highways of cell"; narrow channels for transport, also manufactures lipid components of cell membrane
94
New cards
Golgi body
Organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials
95
New cards
Chloroplast
Organelle in plant cells that converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy (site of photosynthesis)
96
New cards
Cell wall
made of cellulose in plant cells. Strong supporting layer surrounding the membrane
97
New cards
cell (plasma) membrane
surrounds and protects all cells, made of phospholipids, flexible structure that acts as a gate keeper to regulate what enters/leaves the cell.
98
New cards
Tissue
Group of similar cells with similar tasks
99
New cards
Organ
Group of tissues which work together
100
New cards
Organ system
Groups of organs work together to live