A&P TEST II
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
What are the functions of skeleton system?
Provide structural support and point of attachment for tendons and ligaments
Protect internal organs
Assist body movements
Store and release salts and calcium and phosphorus
Participate in blood cell production
Store triglycerides in adipose cells of yellow marrow
Is bone vascularized?
Yes, highly. With a hard extracellular matrix.
What are the two types of bone?
Compact and spongey
What are the tissues of the skeletal system?
Bone and cartilage, which are associated with ligaments, tendons, and joints.
Is bone dynamic?
Yes. It is always remodeling (building up and breaking down).
What is compact bone good for?
Providing protection and support.
Strongest.
It makes up the diaphysis of the long bones,
Makes up external layer of all bones.
What is the spongey bone good for?
Lightweight and provides tissue support
Also called trabecular or cancellous bone
Forms epiphysis and medullary cavity
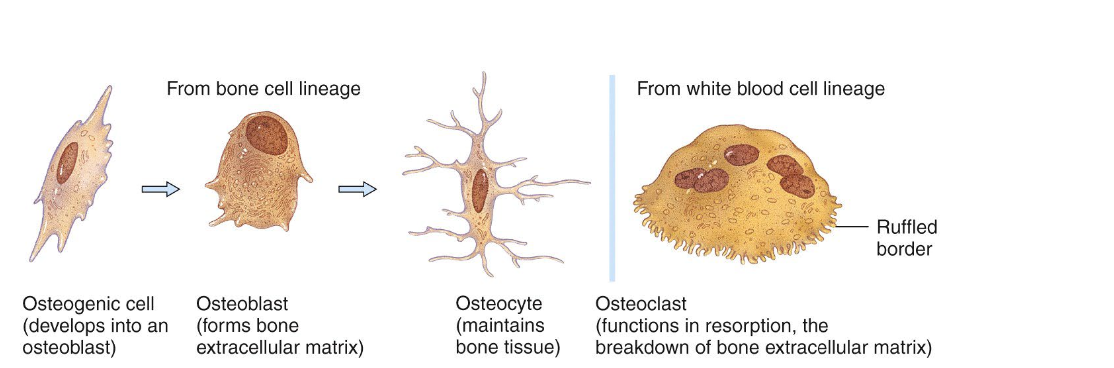
What are the bone cells?
Osteoprogenitor cells: stem cells which differentiate into other types
Osteoblasts: bone building, synthesize and secrete collagen
Osteocytes: mature osteoblasts (maintenance)
Osteoclasts: remodel bones and cause them to release calcium; bone resorption
What other tissues does the skeletal system consist of?
Endothelium form capillary walls
nerves
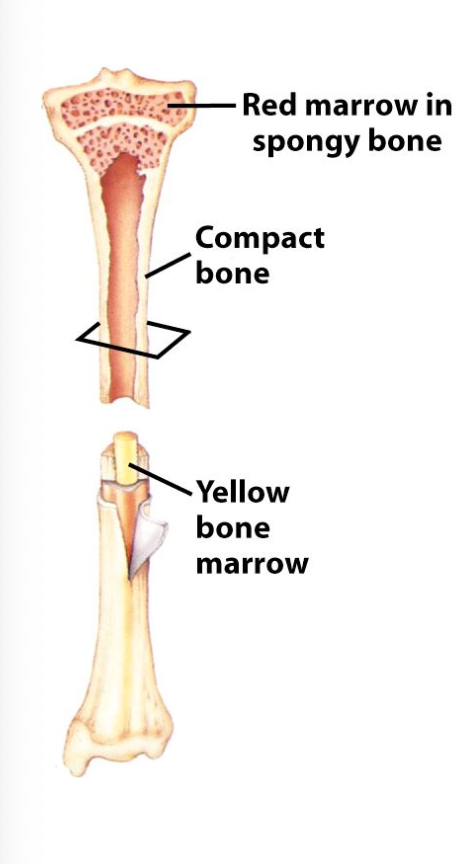
red marrow (hematopoiesis)
yellow marrow (fat storage)
What is the chemical constituent of bone?
25% water, 25% organic proteins, 50% mineral salts (hydroxyapatite crystals).
Organic constitutions include collagen fibers which provide flexibility, tensile, and strength
Inorganic hydroxyapatite crystals are calcium phosphate, calcium carbonate, and other trace elements of magnesium, fluoride, and sulfate
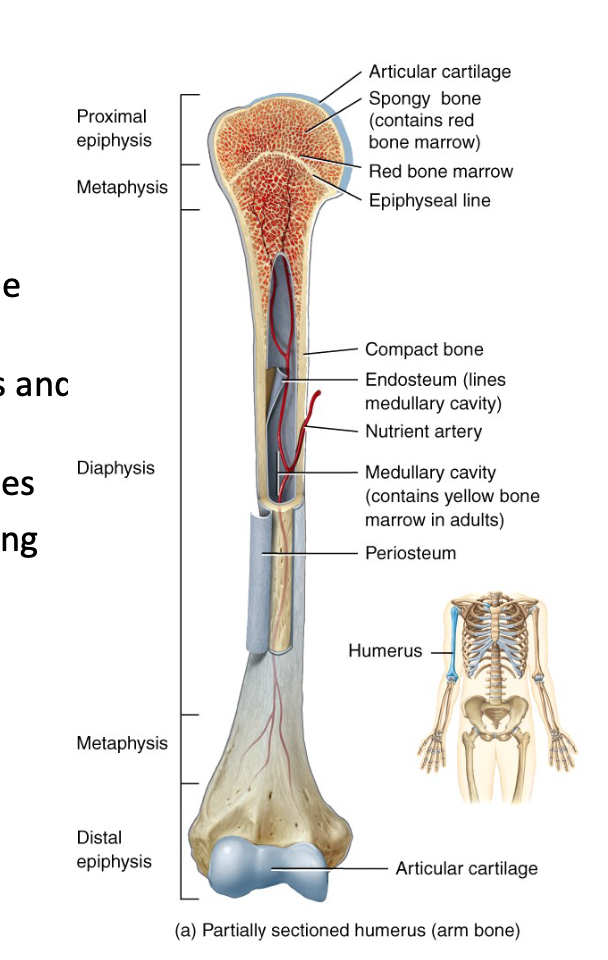
What is the structure of the long bone?
Diaphysis (shaft)
2 epiphysis (both ends)
2 metaphases/growth plates (between diaphysis and epiphysis)
Articular/hyaline cartilage covering epiphyses
Periosteum (connective tissue surrounding diaphysis)
Medullary cavity (hollow space within diaphysis)
Endosteum (thin membrane lining medullary cavity)
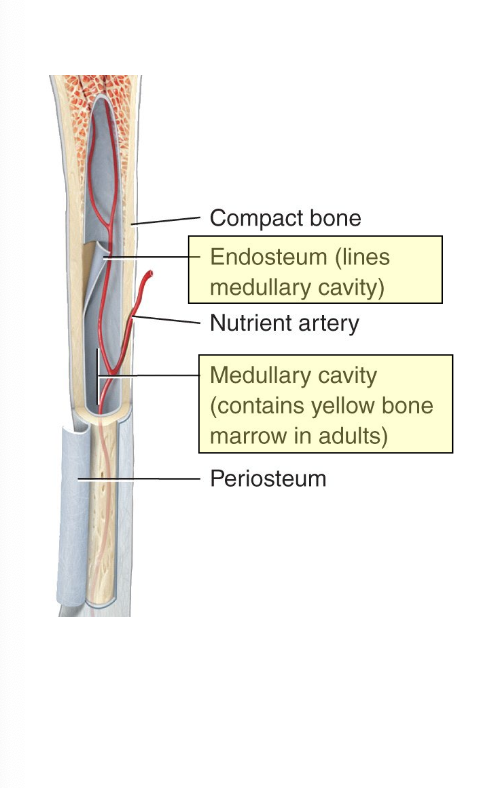
What is the medullary cavity of the bone?
Space within the diaphysis which contains fatty yellow bone marrow in adults.
The endosteum lines the medullary cavity and is composed of dense irregular connective tissue and contains osteoclasts and osteoblasts
What is the articular cartilage of the bone?
Thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the epiphysis of long bones.
Found where bone forms an articular (joint) surface - one bone moves against another
What is the growth called for bone thickness?
Appositional growth
What is the perichondrium?
Dense irregular CT that surrounds cartilage.
Chondrocytes are cells that form cartilage.
What is the periosteum?
Tough sheath of dense irregular CT.
Contains osteoblasts
Assists with fracture repair and serves as an attachment point for tendons and ligaments
What is the epiphyseal line/growth plate?
Growth plate is hyaline cartilage which actively divides and causes bone to elongate.
Growth plate turns into epiphyseal line in adulthood (calcified)
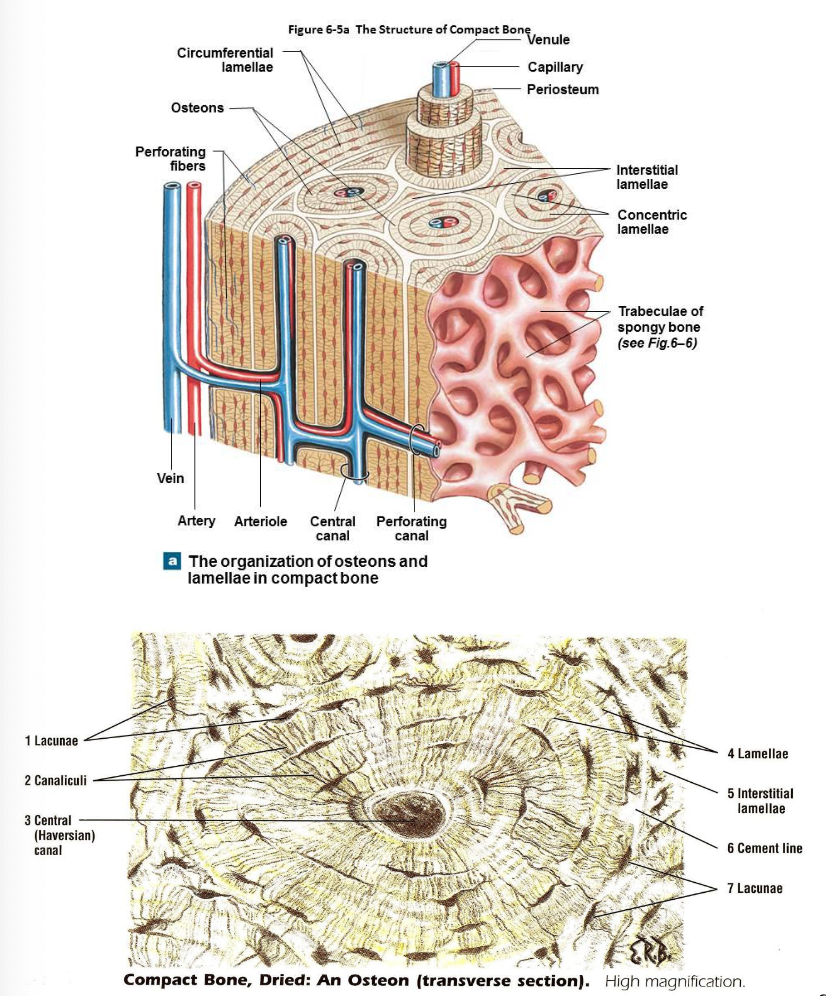
What is the histology of compact bone?
Units of osteons or Haversian systems forming concentric lamellae.
Interstitial lamellae are between osteons which are leftover fragments of old osteons
Outer circumferential lamellae encircle bone beneath periosteum
Inner circumferential lamellae encircle medullary cavity
Lacunae are small spaces between lamellae which house osteocytes
Canaliculi are small channels filled with extracellular fluid counting lacunae
Blood and lymphatic vessels are found in central canal/haversian
Volkmann’s canal allow transit of vessels to outer cortex of bone
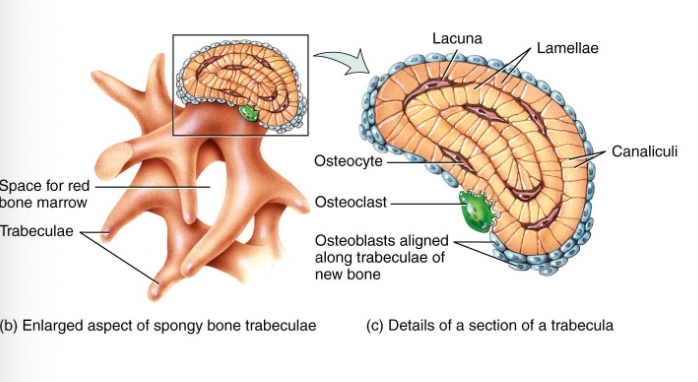
What does spongy bone have instead of osteons?
Trabecular.
Offer support and protect red bone marrow and oriented along lines of stress (resist breaking)
Lacunae are located in each trabecular which contain the osteocytes to nourish mature bone tissue
What is the interior of long bones primarily made up of?
Spongy bone
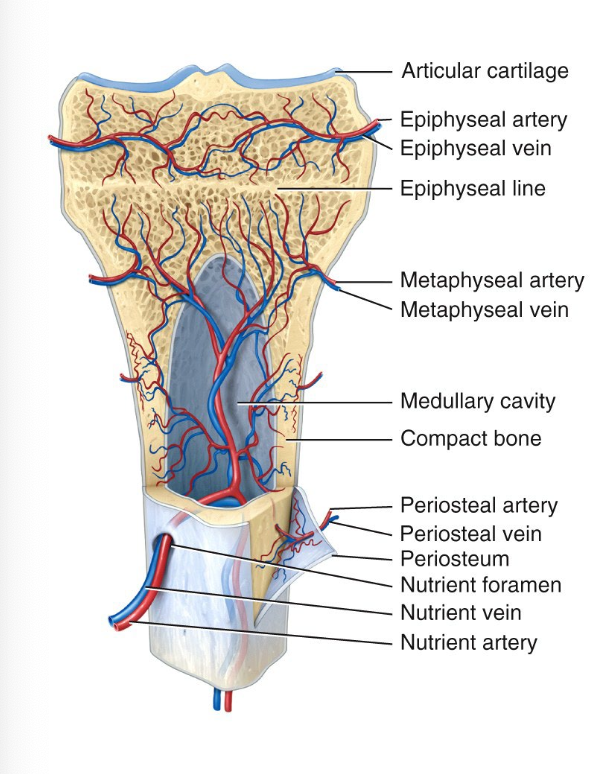
What makes up blood supply of bone?
Periosteal arteries enter diaphysis through Volkmann’s canal and are accompanied by periosteal veins
Nutrient arteries enter the center of diaphysis through nutrient foramen. Exist via same canal
Nerves accompany blood vessels (periosteum is rich in nerves)
What is formation of bone tissue?
Ossification or osteogenesis.
When does ossification occur?
Formation of bone in embryo
Growth of bones until adulthood
Remodeling of bone
Repair of fractures
What are the two methods of ossification?
Intra-membraneous ossification produces spongy bone. It may be remodeled to form compact bone
Endochondral ossification is process whereby cartilage is replaced by bone. Forms both compact and spongey.
What bones use intra-membraneous ossification?
All bones of skull and clavicle
Which is the primary method of ossification?
Endochondral ossification
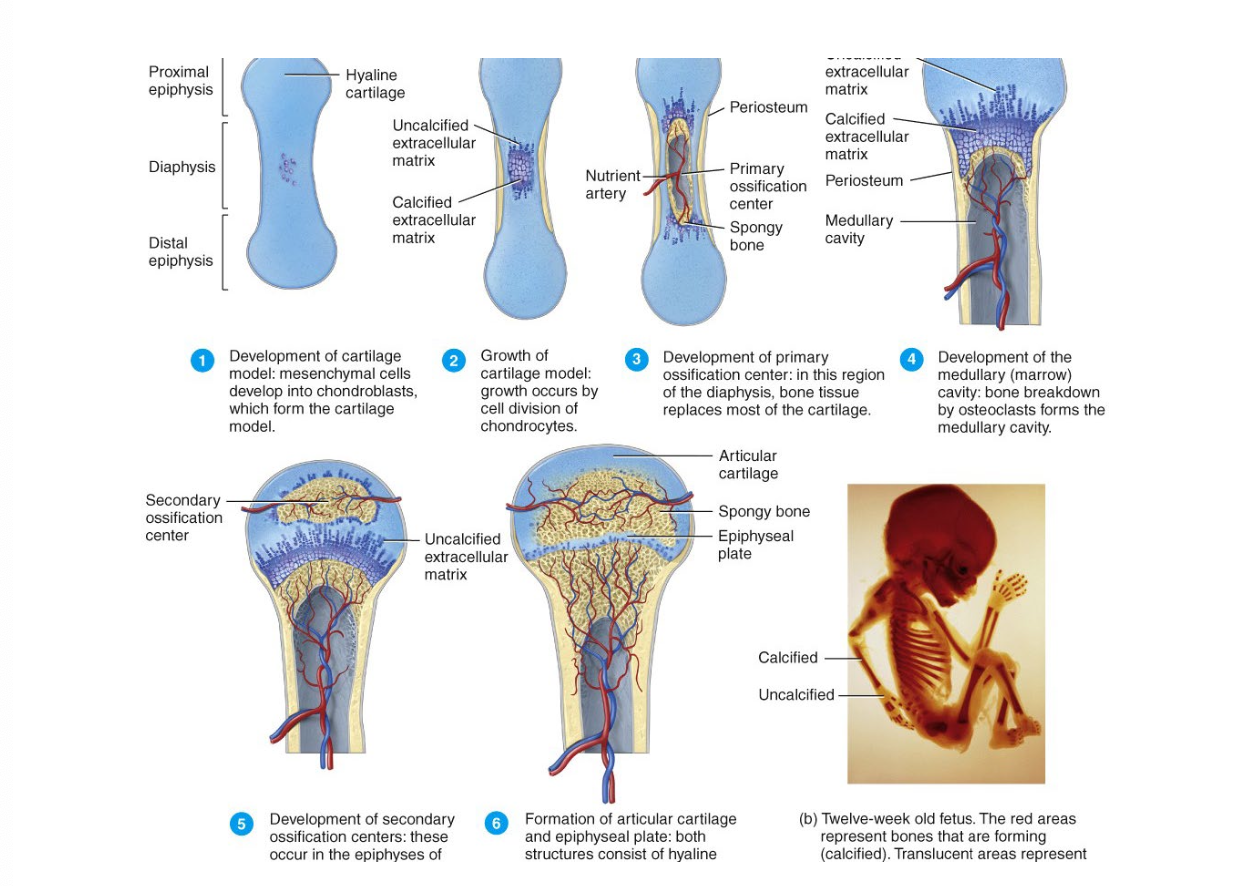
What are the zones/layers of the epiphyseal growth plate?
Zone of resting cartilage which are scattered chondrocytes that do not function for bone growth
Zone of proliferating cartilage are larger chondrocytes which undergo interstitial growth as they divide and secrete extracellular matrix
Zone of hypertrophic cartilage which is chondrocytes in columns
Zone of calcified cartilage is lysis of chondrocytes and osteoblasts lay down matrix. This zone becomes new diaphysis.
Does the epiphysis ever increase in length?
No
What is growth in length?
Interstitial
Define bone deposition
Addition of minerals and collagen fibers to bone by osteoblasts
What is bone resorption
Removal of minerals and collagen fibers from bone by osteoclasts.
What causes Acromegaly?
New tissue formed due to excessive growth hormone after growth plate is closed
What causes Gigantism?
New tissue rapidly formed before closing of the growth plate due to excessive growth hormone
What hormone is responsible for growth of growth plate?
Growth hormone
What is osteomalacia?
Vitamin D deficiency causes soft bones.
Its called rickets in children.
Vitamin factors of bone growth
Vitamin A: stimulates osteoblasts
Vitamin C: synthesis of collagen
Vitamin D: promotes abosprtion of calcium
Vitamins K and B12 are needed for synthesis of bone proteins
Hormones affecting bone growth:
Human Growth Hormone (hGH): Secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland; promotes general growth of all body tissues, including bone by stimulating insulin growth factors
Insulin Growth Factors (IGFs): Secreted by liver, bones, and other tissues on the stimulation by growth hormone; promotes normal bone growth by stimulating osteoblasts and by increasing the synthesis of proteins needed to build new bone
Thyroid hormones: Secreted by thyroid gland; promote normal bone growth by stimulating osteoblasts
Insulin secreted by pancreas; promotes normal bone growth b increasing synthesis of bone proteins
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): secreted by parathyroid glands and promotes resorption of osteoclasts and enhances recovery of calcium ions from urine. Promotes formation of Vitamin D.
Calcitonin (Thyrocalcitonin): Secreted by thyroid gland and inhibits bone resorption of osteoclasts.
Sex hormones of bone growth:
Estrogen secreted by women and testosterone by men
Stimulates osteoblasts and promote growth spurt in teenage years
Shown down growth when 18-21
Contribute to bone remodeling during adulthood
What contributes to calcium homeostasis?
PTH stimulates osteoclastic and raises calcium level
Calcitonin and hGH (lesser extent) stimulate osteoblastic activity and lower serum calcium level
Vitamin D is needed for absorption of Ca and PO4 ions from small intestine and reabsorption of those same ions in kidneys
What is the bone’s role in calcium homeostasis?
Bone stores 99% of calcium. PTH is secreted when calcium levels drop, which stimulates osteoclasts to increase bone resorption and calcium is released. PTH also stimulates calcitriol production in kidneys to increase calcium absorption.
What is a complete fracture?
Fracture all the way through bone
What is closed fracture?
Simple
What is open fracture?
Fracture punctures skin
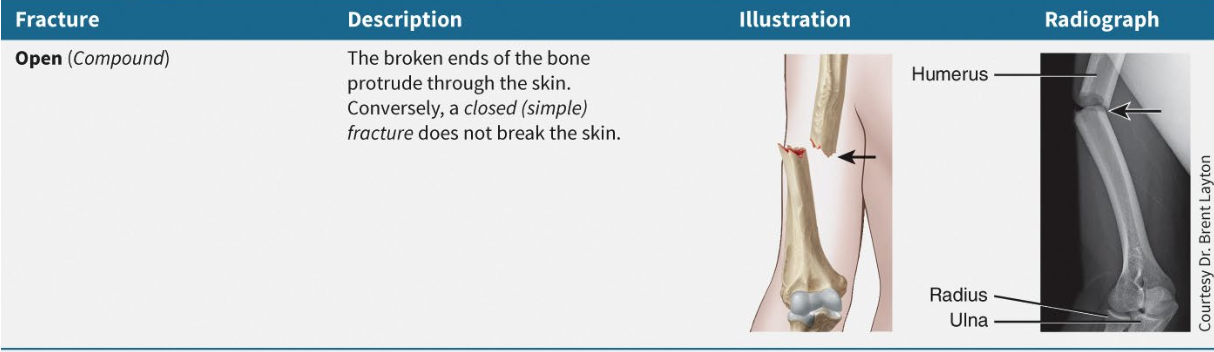
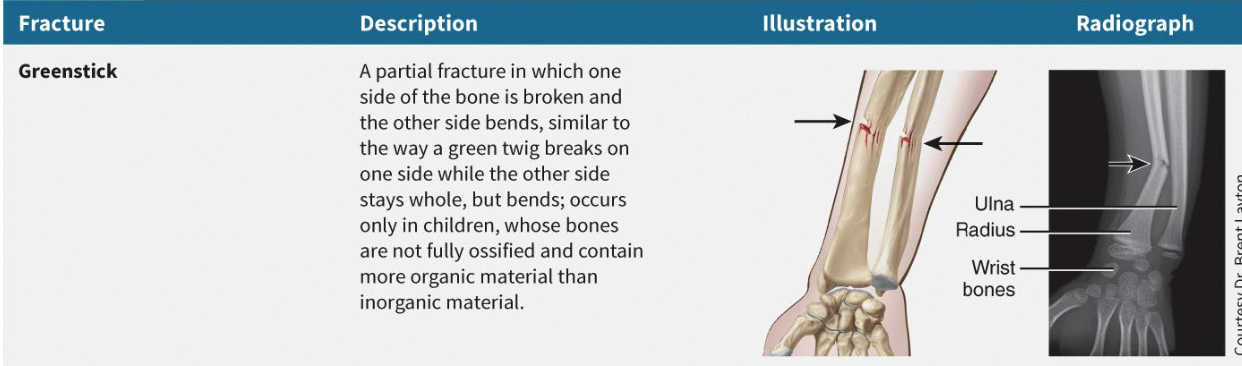
What is green stick fracture?
Small linear break in bone cortex
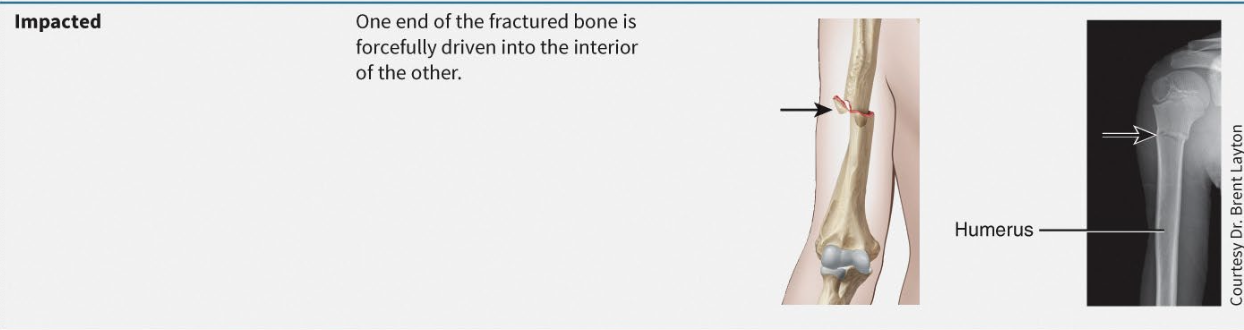
What is impacted fracture?
One part is shoved up into another
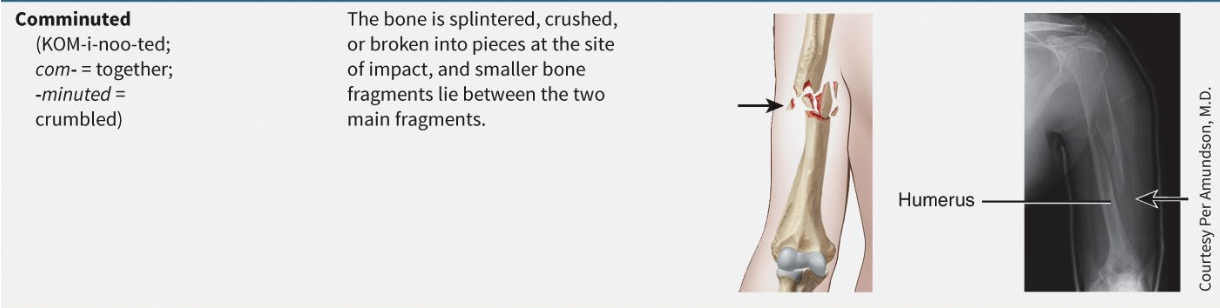
What is comminuted fracture?
Multiple fragments due to crash injury
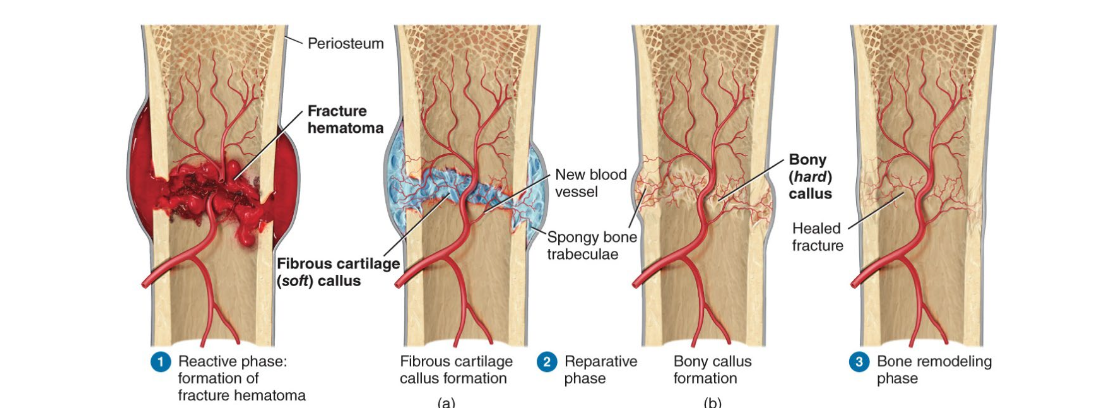
What is the healing process of fractures?
Reactive phase is early inflammatory phase
Reparative phase includes formation of fibrocartilaginous callus first and a bony callus second
Bone remodeling phase is last step as the bony callus is remodeled
What is the axial skeleton?
Skull, auditory ossicles, hyoid bone, ribs, sternum, bones of vertebral column
What is the appendicular skeleton?
The bones of the upper and lower limbs and bones forming pectoral and pelvic girdles that connect the limbs to the axial skeleton
What is long bone?
Long bones
What is short bone?
Short and cube shaped (wrist and ankle)
What is flat bone?
Thin layers of parallel plates (skull/sternum/scapulae)
What is irregular bone?
Complex shapes (vertebra)
What is sesamoid bone?
Sesame seed shaped (patella)
What are sutural bones?
Also known as Wormian. They are the cranial bones.
What do depressions and openings in bone do?
Form joints and allow passage of blood vessels and nerves
What is condyle process and example?
Projections or outgrowths that form joints and serve as attachment points for ligaments and tendons
Ex. Lateral condyle of femur
What is a fissure and an example?
Narrow slit between adjacent parts of bones where blood vessels or nerves pass.
An example is superior orbital fissure of sphenoid bone
What is a foramen and example?
Opening for blood vessels, nerves, or ligaments.
Ex. Optic canal of sphenoid bone
What is fossa and example?
Shallow depression.
Ex. Coronoid fossa of humerus
What is sulcus and example?
Furrow along bone surface that accommodates blood vessel, nerve, or tendon?
Ex. inter tubercular sulcus of humerus
What is meatus and example?
Tubelike opening.
Ex. External acoustic meatus of temporal bone
What is facet process and example?
Smooth, flat slightly concave or convex articular surface.
Ex. Superior articular facet of vertebra
What is head process and example?
Rounded articular projection supported on neck of bone
Ex. head of femur
What is crest process and example?
Ridge or elongated projection.
Ex. Iliac rest of hip bone
Epicondyle process and example?
Roughened projection above condyle.
Ex. Medial epicondyle of femur
Line process and example?
Long narrow ridge or border
Ex. Linea aspera of femur
Spinous process and example?
Sharp, slender projection
Ex. spinous process of vertebra
Trochanter process and example?
Large projection
Ex. Greater trochanter of femur
Tubercle process and example?
Greater tubercle of humerus
Tuberosity process and example?
Variably sized projection with rough, bumpy surface
Ex. Ischial tuberosity of hip bone
How many bones are in axial skeleton?
80
Two categories of skull bones?
Cranial (8) and facial bones (14)
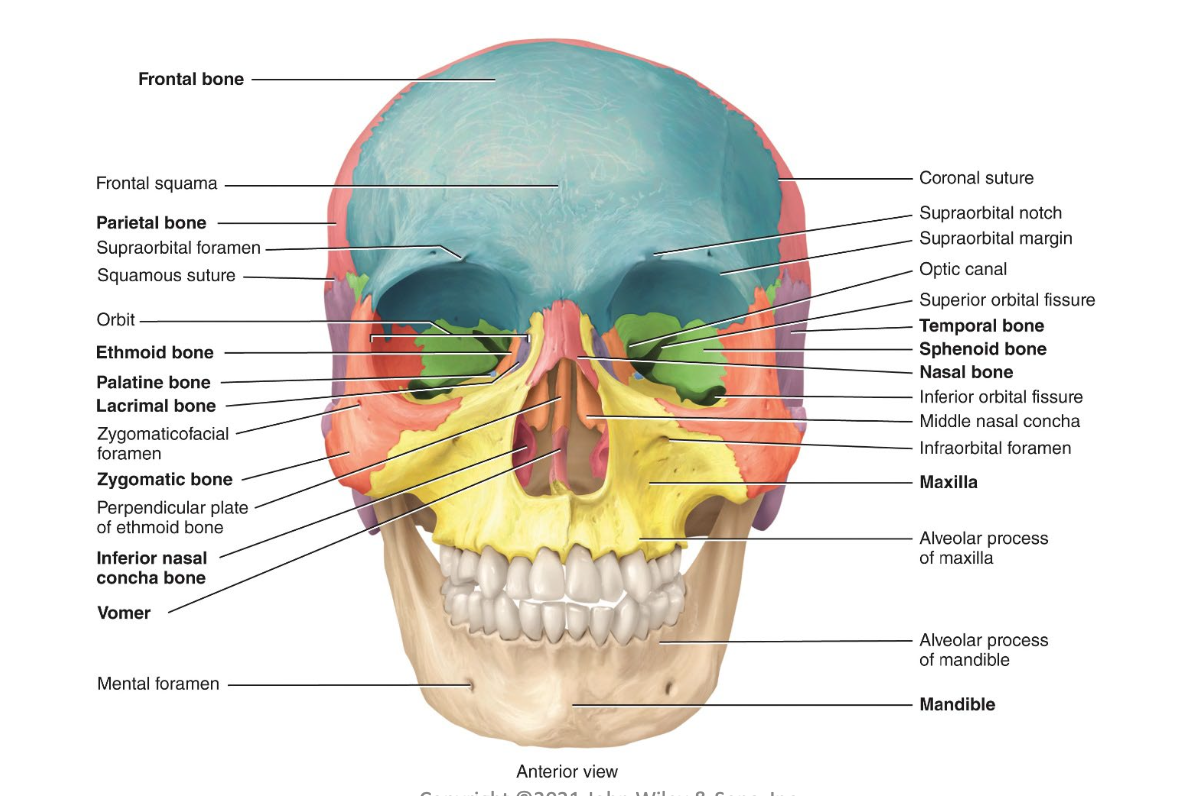
What is a suture in the skull?
A “seam” or immovable joint between bones of the skull
What are fontanels?
They are found in babies and are unossified mesenchyme filled spaces between cranial bones.
They ossify between 19-24 months and become sutural joints
Allow expansion of brain after birth and easy birth of baby
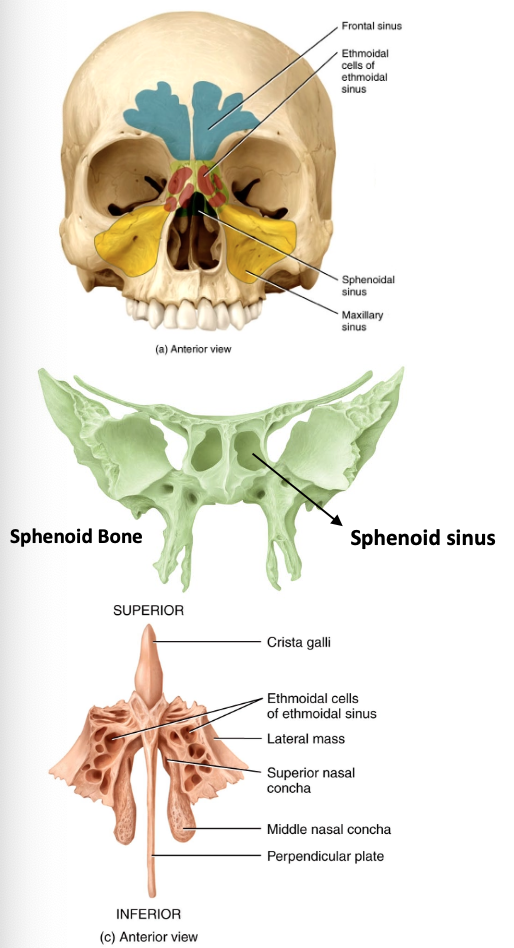
What are paranasal sinuses?
Prominent features of frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary bones
Lined with mucuous membrane that humidify and warm air
Reduce weight of skull
Help resonate sound of our voice
What is temporomandibular joint dysfunction
Dull pain around ear, tender jaw muscles, clicking noise with mouth
Caused by improperly aligned teeth, grinding of teeth, trauma to the head, arthritis
Treatment includes moist heat or ice, soft foods and pain relievers
Function of hyoid bone
Supports tongue and provides attachment for muscles of neck and pharynx
Does not articulate with any other bone
How many bones and regions in the vertebral column?
26 vertebrae and 5 regions
Are the cervical and lumbar curves convex or concave?
Convex
Are the thoracic and sacral curves convex or concave?
Concave
What cartilage makes up intervertebral disc
Fibrocartilage
What does spinal cord travel through
Vertebral foramen?
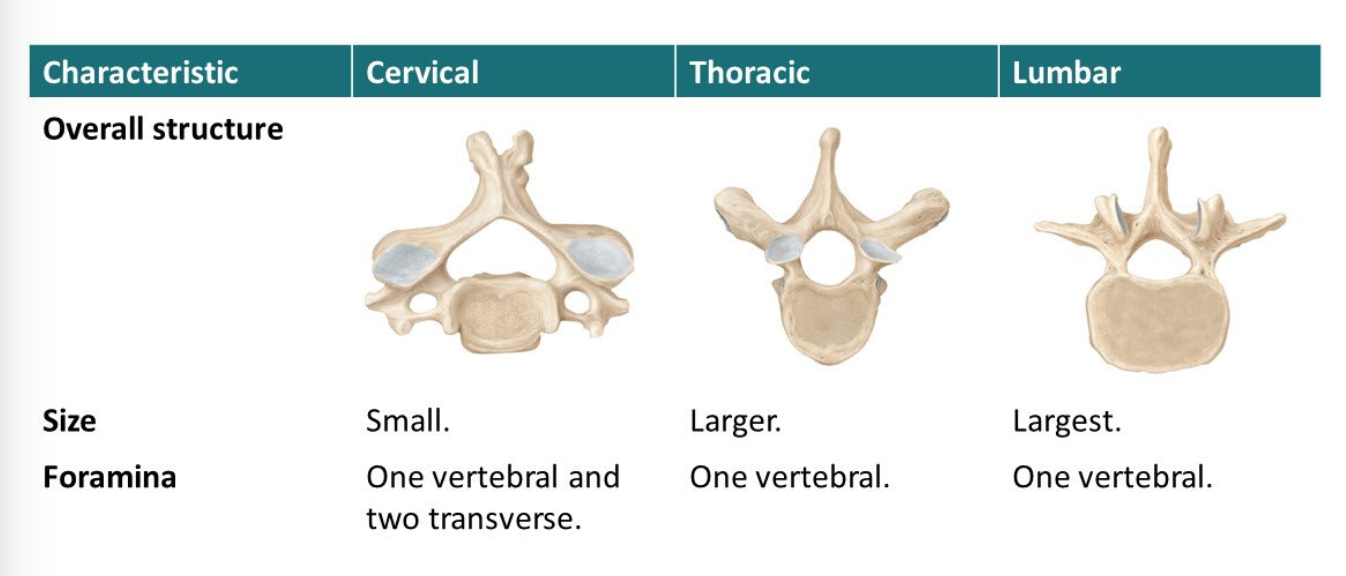
Characteristics of cervical vertebrae?
C1 is atlas and holds up head
C2 is Axis because it allows head to pivot
Characteristics of thoracic vertebra
12 vertebrae form thoracic cage
Characteristics of lumbar vertebra
Largest and strongest
No special structures
Anatomy of vertebrae
Consist of a body (weight bearing) and vertebral arch (pedicle and laminate).
Several processes (attachments for muscle)
Function of thoracic cage
Enclose and protect organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities
Play a role in breathing and supports bones of upper limbs
Markings of Thorax
True ribs (upper 7 - attach to sternum)
False ribs (bottom 5 8th to 12)
Floating ribs (11th and 12th pairs - do not attach)
What are costal cartilages?
Hyaline cartilage connecting sternum to the ribs
What is scoliosis
Increased lateral curve
What is kyphosis
Increased thoracic curve
What is lordosis
Increased lumbar curve
What is spina bifida
Laminae of vertebral column did not develop normally
Where do fractures of vertebral column most often occur?
C1, C2, C4-T, and T12-L2.
What are bones held together by dense collagen?
Fibrous
What are bones held together by cartilage
Cartilaginous
What are joints held together by ligaments?
Synovial
What is an immovable joint?
Synarthrosis
What is a SLIGHTLY moveable joint?
Amiphiarthrosis