Medical Terminology Chapter 3- Skeletal System (Extended)
1/269
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
270 Terms
Bone, Bone Marrow, Cartilage, Joints, Ligaments, Synovial Membranes, Synovial Fluid, And Bursae
Skeletal System consists of…
Calcium
What does the bones store for normal nerve function?
Fontanelle
The soft undeveloped part of the skull in a infant that closes after 18 months.
Ossification
The process of turning fragile membranes and cartilage into bones. Starts at 3 moths of age and continues through out ones lifetime repairing minor and major injuries.
Osteoclast cells
Cells that break down old or damaged bone
Osteoblast cells
Cells that rebuild the bone
Second Hardest (after Dental enamel)
Bone is the ___ hardest tissue in the body
Periosteum (Peri- surrounding)
A tough fibrous tissue that forms the outermost covering of a bone
Compact Bone/Cortical bone
A dense, hard, and strong bone that forms the protective outer layer of bones . It accounts for 75% of the body’s bone matter.
Spongy Bone/Cancellous bone
A porous bone which is lighter and weaker then compact bone.
Red Bone Marrow
A marrow located in the spongy bone on the ends and inner portions of the long bones. This marrow creates erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Marrow found in the medullary cavity that stores fat. Starts out as red before half are turn to █████ Marrow.
Long bones
Femur, Humerus, ect
Short bones
Metacarpals, Tarsals, ect. Cubic shape made up of spongy bone covered in compact bone
Medullary cavity
The central cavity located in the shaft of long bones were it is surrounded by compact bone. Red and Yellow marrow are stored here.
Endosteum
The tissue that lines the medullary cavity
Hematopoietic
pertaining to the formation of blood cells
Cartilage
A smooth, rubbery, blue-white connective tissue that acts as a shock absorber between bones. It is more elastic than bone, also makes up the flexible parts of the skeleton such as the outer ear and the tip of the nose.
Articular Cartilage
Cartilage that covers the surface of bones were they articulate and allows smooth joint movements.
Articulate
To come together to form joints
Meniscus
A curved fibrous cartilage found in some joints such as the knee and temporomandibular joint in the jaw
Diaphysis
Shaft of the bone
Epiphyses (Epiphysis) (Proximal and Distal)
Wider ends of the long bones which are covered in articular cartilage.
Foramen
A opening in a bone which blood vessels, nerves, and ligaments pass through. The █████ magnum is located in the occipital bone at the base of the skull
Process
A normal projection on the surface of a bone that most commonly serves as an attachment for a muscle or tendon. For example, the mastoid ____ is the bony projection located on the temporal bones just behind the ears.
Articulations
Joints
Fibrous Joints
Inflexible layers of dense connective tissue that holds bones tightly together. Allows little or no movement. In adults its known as sutures
Cartilaginous Joints
Joints that only allow slight movement and consist of bones connected entirely by cartilage. Ex:
Coastal cartilage connects to the ribs and allow slight movement in breathing
Pubic symphysis allows movement to facilitate childbirth.
Pubic symphysis
A joint that allows some movement to facilitate childbirth. This joint is located between the pubic bones in the anterior (front) of the pelvis
Synovial Joints
A joint where two bones articulate to permit a variety of motions.
Ball-and-socket joints
Joints found in the hips and shoulders, allow a wide range of movement in many directions
Hinge Joints
Joints found in the knees and elbows, are synovial joints that allow movement primarily in one direction or plan
Synovial Capsule
The outermost layer of strong fibrous tissues that resembles a sleeve as it surrounds the █████ joint
Synovial Membrane
A membrane that lines the █████ capsule and secretes █████ fluid
Synovial Fluid
Fluid which flows in the █████ cavity and acts as a lubricant to allow smooth movement of the joints.
Ligaments
bands of fibrous tissue that from joints by connecting bone to bone or bone to cartilage.
Bursa
Fibrous sac that acts as a cushion to ease movements in areas prone to fiction (such as where a tendon passes over a bone).
206 bones
The typical human body has ___ bones
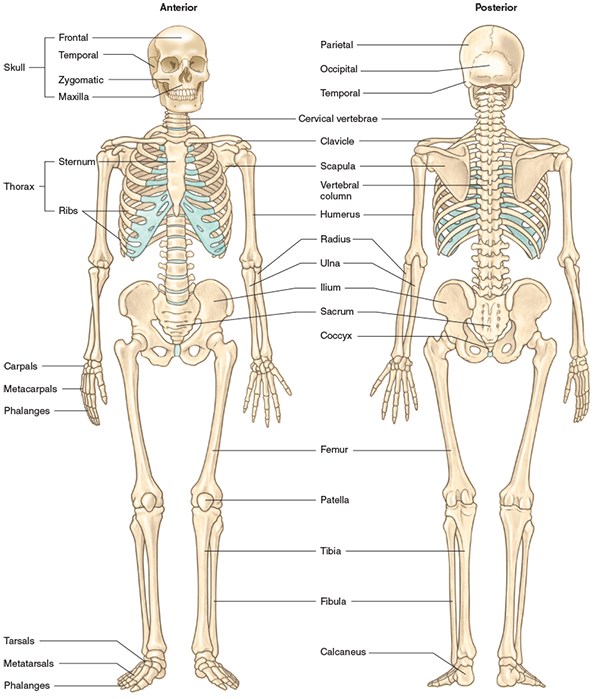
Name the bones of the body

Axial Skeleton
80 bones of the head and body
Skull
Ossicles of the middle ear
Hyoid Bone
Rib Cage
Vertebral Column
Appendicular Skeleton
126 bones of the
Upper extremities
Lower extremities
Appendage (appendicular)
Anything that is attached to a major part of the body
Extremity
Terminal end of a body part
8 bones form the cranium, 14 form the face, 6 form the middle ear.
What number of bones composes the cranium, face, and middle ear of the skull.
Frontal Bone
Anterior portion of the cranium that forms the forehead. This bone houses the frontal sinuses and forms the roof of the ethmoid sinuses, the nose and part of the socket that protects the eyeball.
Parietal Bones
Two of the largest bones of the skull. Together they form most of the roof and upper sides of the cranium.
Occipital Bone
A bone that forms the back part of the skull and the base of the cranium.
Temporal Bones
2 bones that form the sides and base of the cranium
External auditory meatus
The opening of the external auditory canal of the outer ear. This canal is located within the temporal bone on each side of the skull.
Sphenoid Bone
An irregular, wedge-shaped bone at the base of the skull. This bone makes contact with all of the other cranial bones and helps form the base of the cranium, the sides of the skull, and the floors and sides of the eye sockets.
Ethmoid Bone
The light, spongy bone located at the roof and sides of the nose. Here it separates the nasal cavity from the brain, and it also forms a portion of each orbit.
Orbit
Bony socket that surrounds and protects each eyeball
Auditory Ossicles
Three tiny bones in the ear
Malleus, incus, stapes
What are the auditory ossicles
Nasal Bones
Two bones that form the upper part of the bridge of the nose
Zygomatic Bones/ Cheekbones
Bones that articulate with the frontal bone that makes up the forehead (Cheeks)
Maxillary bones (Maxilla)
Bone that forms the upper jaw
Palatine Bones
Two bones that form the anterior part of the hard palate of the mouth and the floor of the nose.
Lacrimal Bones
Two bones that make up part of the orbit in at the inner angle
Inferior Conchae (concha)
Two thin, scroll-like bones that form part of the interior of the nose
Vomer Bone
This bone forms the base for the nasal septum
Nasal Septum
The cartilage wall that divides the two nasal cavities
Mandible/Jawbone
The only movable bone of the skull attached at the temporomandibular joint.
Thoracic Cavity
The bony structure/cavity that protects the heart and lungs. It consists of the ribs, sternum, and upper portion of the spinal column extending from the neck to the diaphragm, but not including the arms.
Costals
Ribs
7 true ribs(directly attach) , 3 false ribs (Indirectly attached by costal cartilage) , 2 floating ribs (not attached at all)
What types of ribs are there?
Sternum/Breast Bone
Dagger shaped bone located in the middle of the chest were the ribs attach to
Manubrium
Bony structure that forms the top of the sternum
Gladiolus
Middle body of the sternum
Xiphoid process
The tip of the sternum made of cartilage
Pectoral girdle/ Shoulder girdle
The shoulders form the █████ girdle which supports the arms and hands
Clavicle/ Collarbone
slender bone that connects the manubrium to the scapula
Scapula
Shoulder bone is known as the
Acromion process
Extension of the scapula that forms the high point of the shoulder.
Humerus
Bone of the upper arm
Radius (radii)
The shorter bone of the forearm that runs up the thumb side
Ulna (ulnae)
The longer bone of the forearm that runs up the pinky side and articulates with the distal end of the humerus.
Olecranon/ Funny bone
proximal tip of the ulna that forms the point of the elbow. There is an exposed nerve which tingles when struck.
Carpals (Carpal)
8 bones that form the wrist
Carpal tunnel
The wrist bones form a narrow bony passage which the median nerve and tendons pass through.
Metacarpals
5 bones of the palms of the hand
Phalanges (phalanx)
14 bones of the fingers and toes
Distal, Middle, Proximal phalanges/phalanx (for the fingers and toes)
Distal and Proximal Phalanx (for the thumb and big toe)
The name of the bones of the fingers from outermost to innermost
Vertebral Column
Spinal column also known as the…
26 vertebrae (singular vertebra)
How many bony units in the spinal column
Cervical vertebrae (C1-C7)
Thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12)
Lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5)
Sacrum
Coccyx
How many vertebra are in each section of the spinal column
Body of vertebra
Anterior portion of the vertebra that is solid to provide strength
Lamina
Posterior portion of the vertebra were the transverse and spinous processes extend from to serve as attachment points for muscles and tendons.
Vertebral Foramen
Opening in the middle of the vertebra which allows the spinal cord to pass through.
Intervertebral disks
Disks made of cartilage and pads of tissue which separate and cushion the vertebrae from each other and allow movement of the spine.
Nucleus Pulposus
The inner core of the intervertebral disks is made up of a soft gelatinous material which allows the disks to act as shock absorbers.
Ilium
Blade shape bone that forms the back and sides of the pelvis
Ischium
Lower posterior portion of the pelvis which the weight of the body is bared.
Sacroiliac (sacr/o— sacrum, ili— ilium)
the slightly movable articulation between the sacrum and posterior portion of the ilium
Pubis
Anterior portion of the pelvis located inferior to the urinary bladder
Pubic symphysis
cartilaginous joint that unites the left and right pubic bones
symphysis
a place where two bones are closely joined
Acetabulum
A large circular cavity where the head of the femur articulates with the pelvis to form the hip joint
Femur
Largest bone in the body
Head of the femur
What part of the femur articulates with the acetabulum