BIO12 - unit 3 - digestive system
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-add pictures!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
digestion def
+ how many functions
process of changing food into small soluble monomers that can be absorbed + used by your cells
-3 main functions:
digestion
mechanical
chemical
absorption
elimination
digestive SYSTEM functions
digestion
a. mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of food
b. chemical digestion
breaking of bonds in polymers to get similar monomers (hydrolysis)
absorption
movement of monomers/nutrients from digestive system into blood (circulatory) or lymph
elimination
expulsion (force smth out) of indigestive residues from body (poop)
digestion
2 types
mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of food
increases surface area to be able to attack
chemical digestion
breaking of bonds in polymers to get monomers (by hydrolysis)
absorption
movement of monomers/nutrients from digestive system into blood (circulatory) or lymph
elimination
expulsion (force smth out) of indigestive residues from body (poop)
stuff that has never been “in” our body since not absorbed; just gone thru our hole

why physical breakdown of food
to increase surface area so more places to be attacked
alimentary canal
tube that runs from mouth to anus
-food passes through the organs:
mouth
pharynx (throat?)
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
rectum
anus
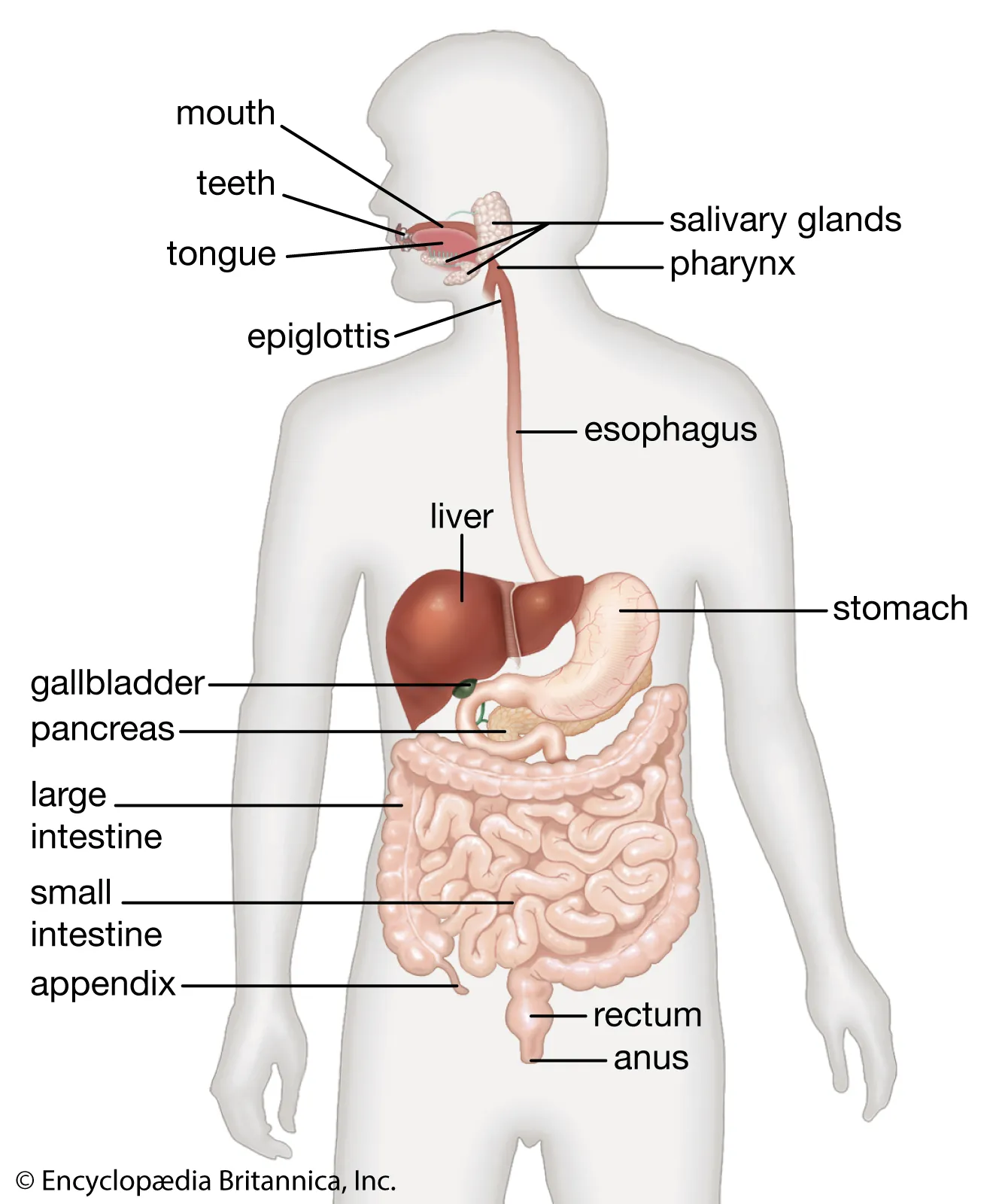
accessory organs
egs and how?
-the organs that assist but the food does not pass through them
eg. pancreas
eg. liver
mouth
-order
-type(s) of digestion
-first step
-mechanical digestion
teeth grinds cuts tears food
tongue + cheek holds food in to help mix w/ saliva
saliva
contains H2O, mucus for lubrication
-chemical digestion
saliva (comes from 3 sets of salivary glands)
salivary amylase (enzyme that breaks down starch)

salivary amylase
-what
-pH
-which type of digestion
-enzyme that breaks down starch
-pH of 7; same as mouth
-chemical
saliva
-contains
-comes from
-type of digestion(s?)
-contains
H2O
mucus
salivary amylase
-comes from 3 sets of salivary glands
-chemical digestion bc salivary amylase
-physical digestion bc lubricant
mouth
-order
-process
-first
teeth physical digestion by tear/cut
saliva breaks down starch (chem. digest.)
chewed food gets pushed to back of mouth (pharynx) by tongue (now called bolus) + gets swallowed
swallowed (3 steps)
a. soft palate moves back to cover opening of nose
b. epiglottis (trap door) covers the trachea (air tube/windpipe)
c. bolus enters the esophagus
how to swallow haha
3 steps
before:
chewed food (bolus) gets pushed to back of mouth (pharynx)
soft palate moves back to cover opening of nose
epiglottis (trap door) covers the trachea (air tube/windpipe)
bolus enters the esophagus

during mouth, what enzyme digests starch into
→ be specific and general
salivary amylase digests starch + H2O into maltose
→polysaccharide → disaccharide
(not into building blocks but rather smaller molecules)
does salivary amylase breaks down carbohydrates
yes, since starch is a carbohydrate
esophagus
-order
-what + contains
-function
-type(s) of digestion
-second (after mouth)
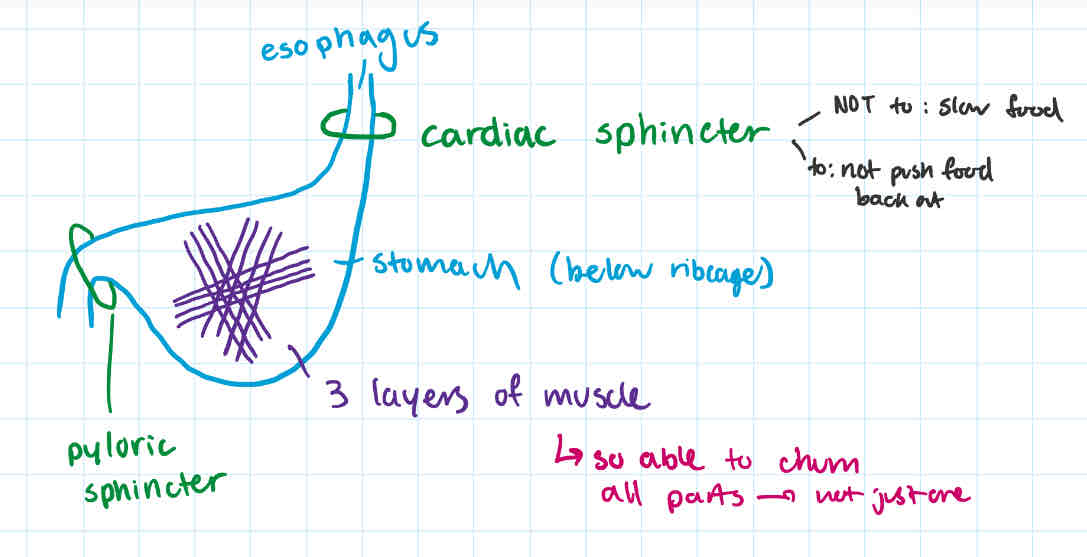
-long muscular tube extending from pharynx to stomach (stack of donuts) + contains cardiac sphincter
-transport
-produces mucus to allow food to travel more easily
-chemical digestion bc salivary amylase
esophagus
-order
-process
-type of digestion
-second (after mouth
-food moved along esophagus by involuntary muscle contractions (peristalsis)
-end of esophagus is cardiac sphincter (trap door)
muscle that opens to allow food into stomach + closed to prevent “back flow” of acidic stomach contents
peristalsis def
+ when
food (bolus) moving along esophagus by involuntary muscular contractions
heartburn
→ contains
burn in esophagus when there’s “back flow” of acidic stomach contents
→ HCl and pepsin
heartburn vs vomit
heartburn:
-HCl and pepsin in esophagus
-backflow of acid chyme
peristalsis
in esophagus, involuntary muscle contractions that moves food down
cardiac sphincter
-why called
-function
at end of esophagus,
-muscle that opens to allow food into stomach + closes to prevent back flow of acidic stomach contents
or else heartburn + vomiting
-closest sphincter to heart?
-NOT TO: slow down food, rather to not push food back up
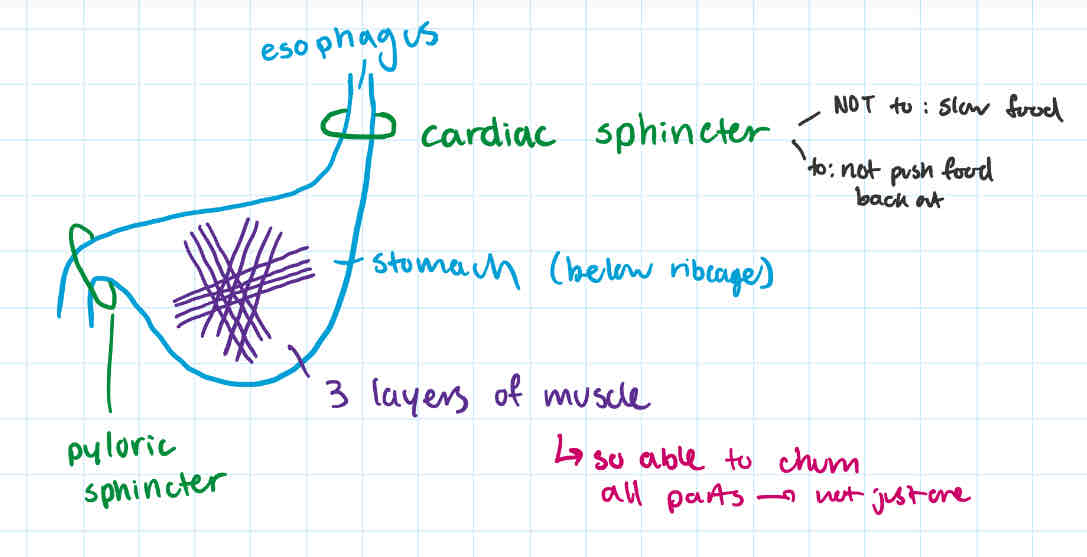
stomach
def
contains
types of digestion
order/location
-thick-walled
-J-shaped organ
-pH of 2 or 2.5 due to HCl
-acidic but won’t digest stomach because mucus (forms a thick protective layer)
-has 3 layers of muscle, running in diff directions to churn + mix
-mechanical digestion → the 3 muscles to churn + mix
→ not break down polymers yet
-chemical digestion of proteins if bolus contains proteins
if not protein, then no chem. digest.
-order: after esophagus + cardiac sphincter; below ribcage
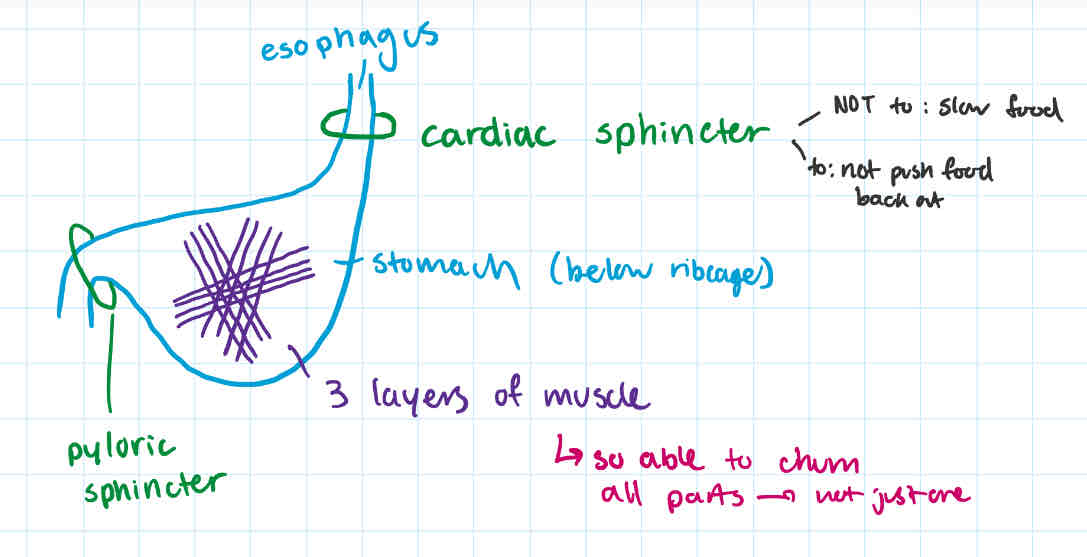
why does stomach have 3 layers of muscle running in diff directions
so able to churn all parts → not just one
→ physically digestion
stomach
order
process
afer esophagus + cardiac sphincter
-if bolus has peptides (proteins), causes stomach cells to secrete gastric juice (has pepsin; makes proteins into peptides)
-since acidic (pH of 2 or 2.5), kills bacteria + salivary amylase denatures (active site change so substrate can’t bind) + activates pepsin to digest protein
chem. digestio if protein only
-after food churn in stomach for 2-6 hours, pyloric sphincter opens
-bolus is released into duodenum (first part of small intestine) → bolus called acid chyme
secrete meaning
if cell make smth then cell dump out
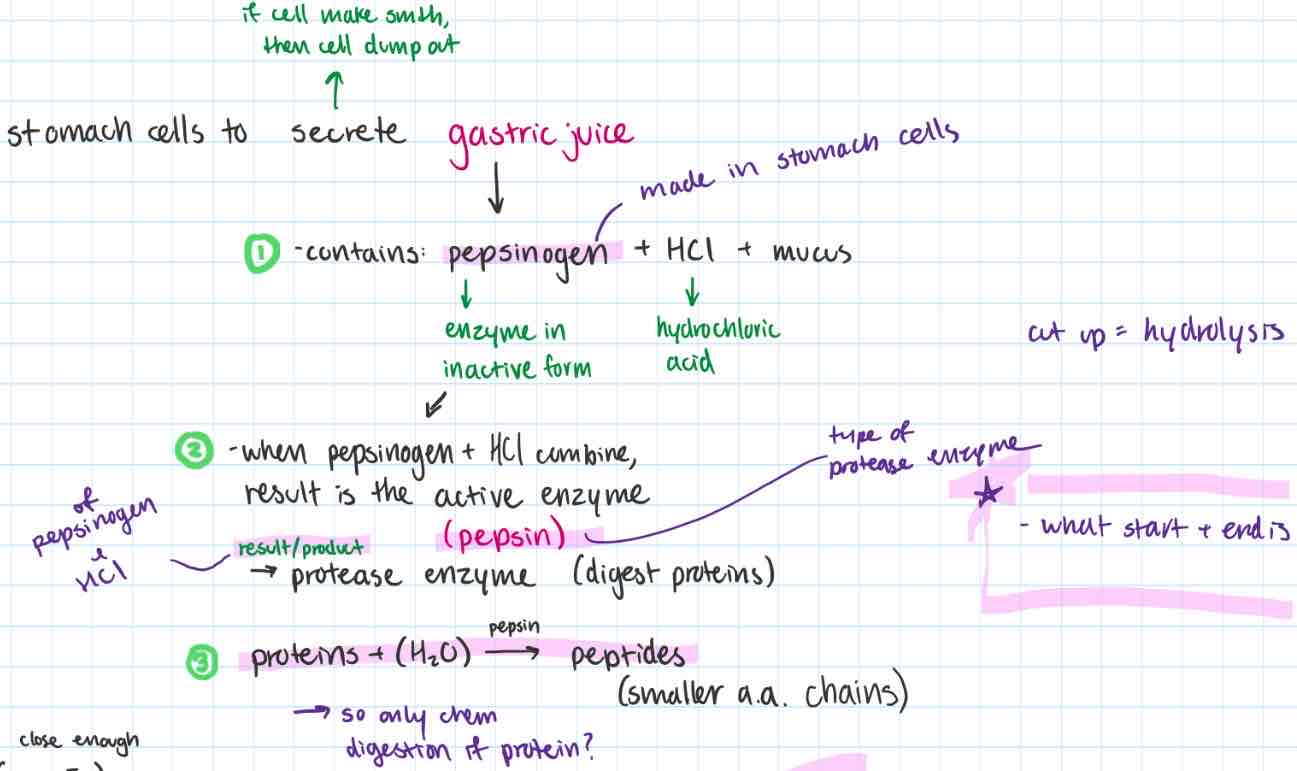
gastric juice
-where
-contains
-what
-secreted in stomach if bolus has proteins
-contains:
pepsinogen
enzyme in inactive form
HCl (hydrochloric acid)
mucus
-process:
when pepsinogen + HCl combine, result is the active enzyme
a type of protease enzyme (these digests proteins → peptides (smaller a.a. chains)
enzyme called: pepsin
what are protease enzymes
→ some examples of specific protease enzymes
-active
-these digests proteins
→ pepsin
what do enzymes do when break down/digests
a term
always forget what
hydrolysis
always forgets need to add water as reactant in order to cut
if mucus in stomach breaks, what happen
stomach ulcer
hole here
why called pyloric sphincter
close to pancreas
why stomach can stay in food for a big range
→ 2 to 6 hours
because depends on what food is
orange juice quicker bc liquid → less mechanical
steak longer → lots of protein → pepsin needed lots of time bc limited
what happens to salivary amylase goes from mouth to stomach
denatures (active site changes shape so substrate can’t bind) because pH of mouth 7 to stomach pH 2
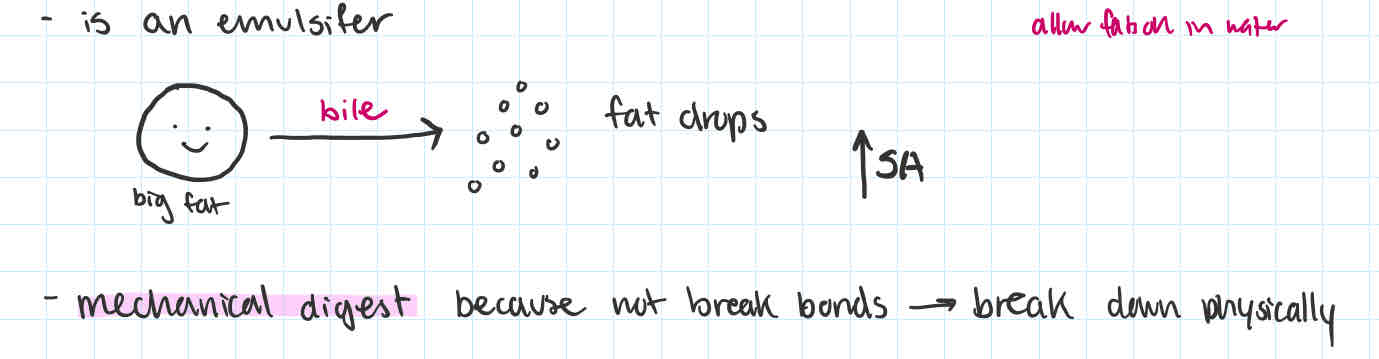
emulsify def
breakdown of fats
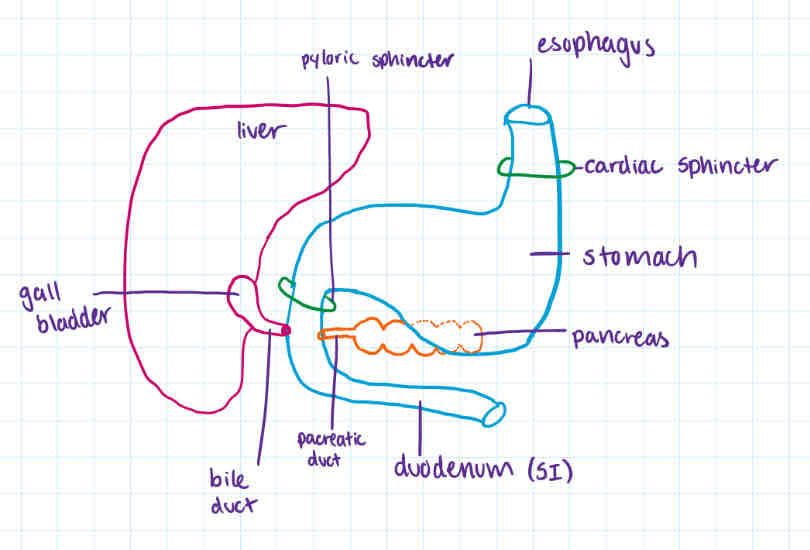
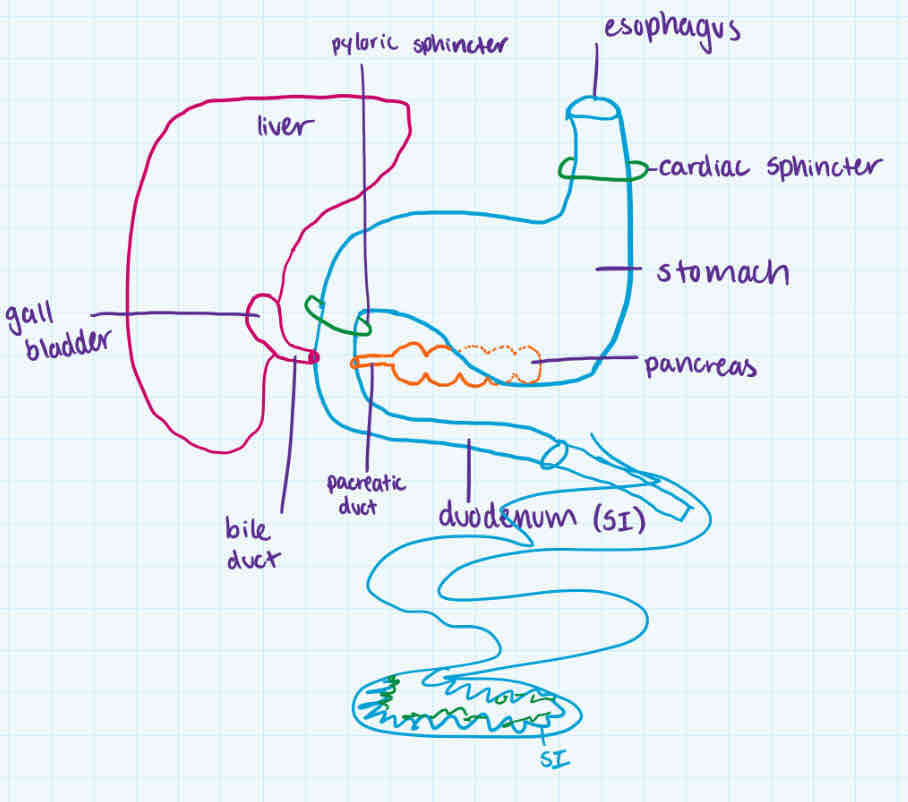
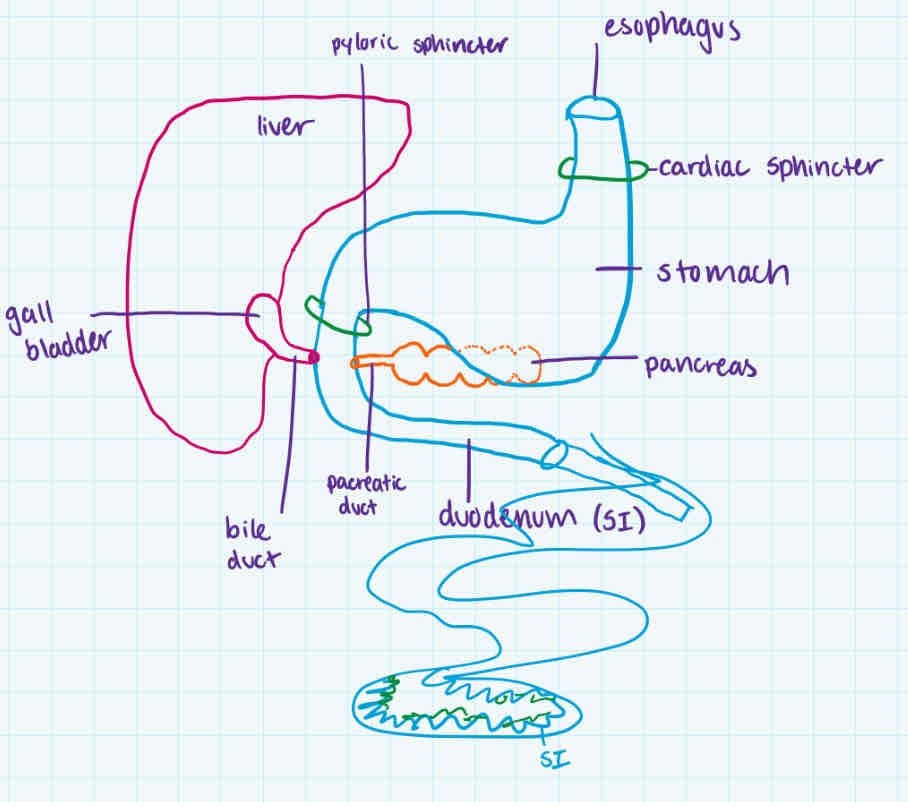
duodenum
order
accessory organs
def
contains
after stomach + pyloric sphincter
pancreas (and its duct) + gall bladder (with bile duct)
-most of digestion + absorption of nutrients (ehh into monomers)
-is the first 25cm of small intestine
-pH of 8.5 bc of sodium bicarbonate to neutralize stomach pH
-has pancreatic juice (containing sodium bicarbonate + 4 pancreatic enzymes which breaks into monomers)
-has bile (not enzyme), is emulsifier to do mechanical digestion
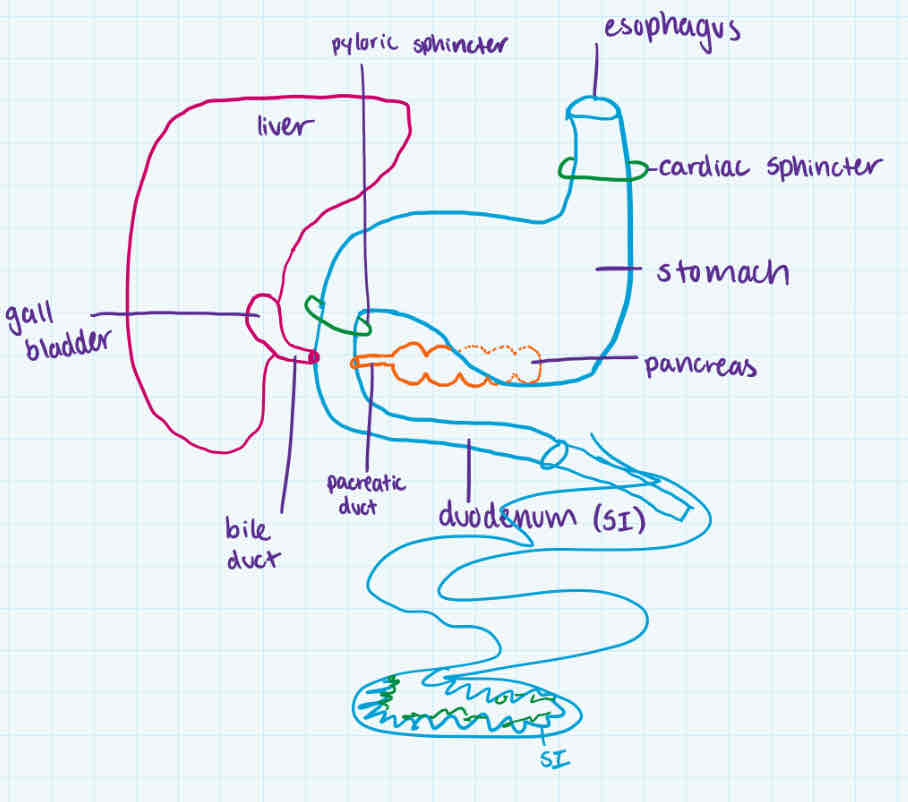
duodenum
order
process
type of digestion
after stomach + pyloric sphincter
-acid chyme enters duodenum
-stimulates pancreas to release pancreatic juice (neutralizes + breaks into monomers) thru pancreatic duct
-stimulates the gall bladder to release bile thru bile duct (mechanical digestion)
-goes to rest of small intestine
mechanical (bile) + chemical digestion (enzymes)
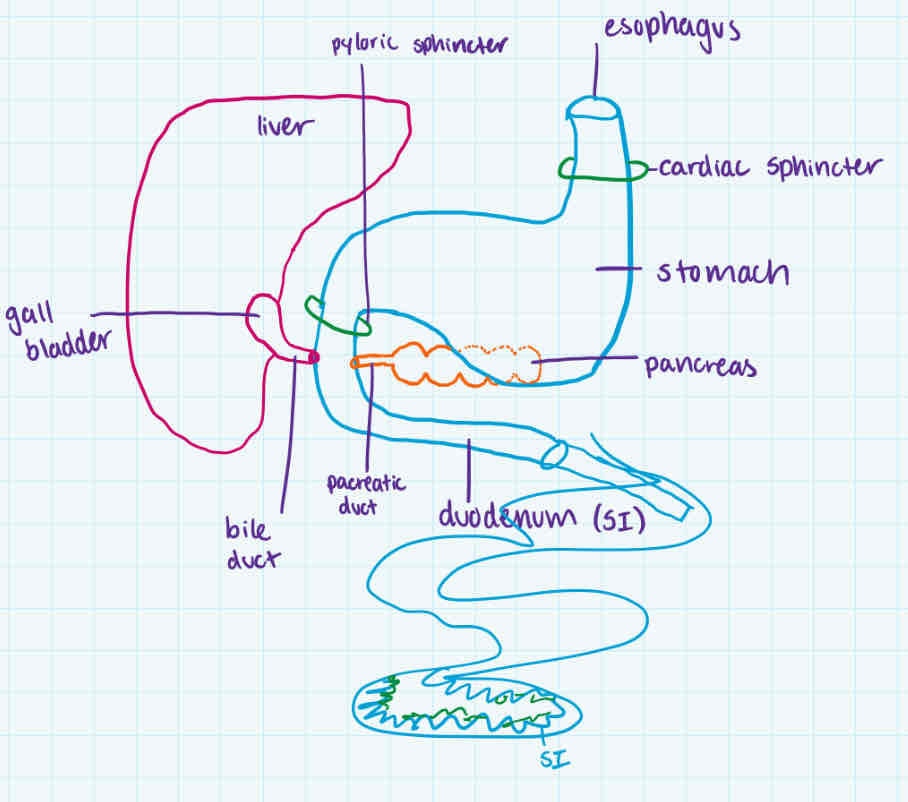
pancreatic juice
-made in + how release
-contains
-produced in pancreas, released into duodenum thru pancreatic duct
-has:
sodium bicardbonate (NaHCO3)
to prevent SI enzymes from being denatured (+…)
denatures pepsin
prevents bad stuff (see other)
4 pancreatic enzymes
pancreatic amylase (starch + H2O → maltose)
trypsin (peptides + H2O → smaller peptides)
lipase (fat droplets after bile breakdown + H2O → glycerol + fatty acids)
nuclease (DNA or RNA + H2O → nucleotides)
sodium bicarbonate
-chemical name
-made in
-helps in
-what happen if not enough
-NaHCO3
-made in pancreas bc its in pancreatic juice
-helps in duodenum (small intestine)
-prevents:
digesting the small intestine
duodenum ulcer
denaturing (active site change → can’t bind substrate)
4 pancreatic enzyme
-pH of all
all have pH of 8.5 (or 8-9)
-pancreatic amylase (works on starch - long chain of glucose)
starch + H2O → maltose (disaccharide)
-trypsin (works on bigger peptides)
peptides + H2O → smaller peptides
-lipase (works on lipids) (time: after bile breakdown) (fully digested bc into monomers)
fat droplets + H2O → glycerol (think HOHOHO) + fatty acids
fat droplets are bile breaks down
-nuclease (works on DNA/RNA from foods)(even tho monomers, still has smaller pieces)
DNA or RNA + H2O → nucleotides
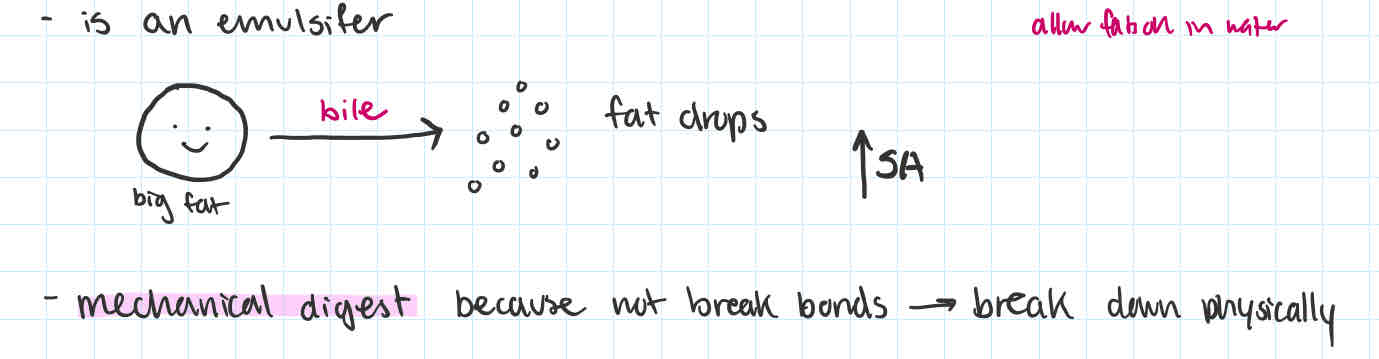
bile
-made in + why/places been in
-function
produced in liver as a result of RBC destruction
stores + released from gall bladder through bile duct
-is an emulsifier (big fat → fat droplets)
→ increase surface area → easier to be coated in pancreatic juice + access lipase
-NOT break down bonds
-mechanical digestion
acid chyme
-descr
-where called
where is this
-acidic
-liquid-y
-has: polypeptide + disaccharide from salivary amylase + full form fats
this is when entering to duodenum
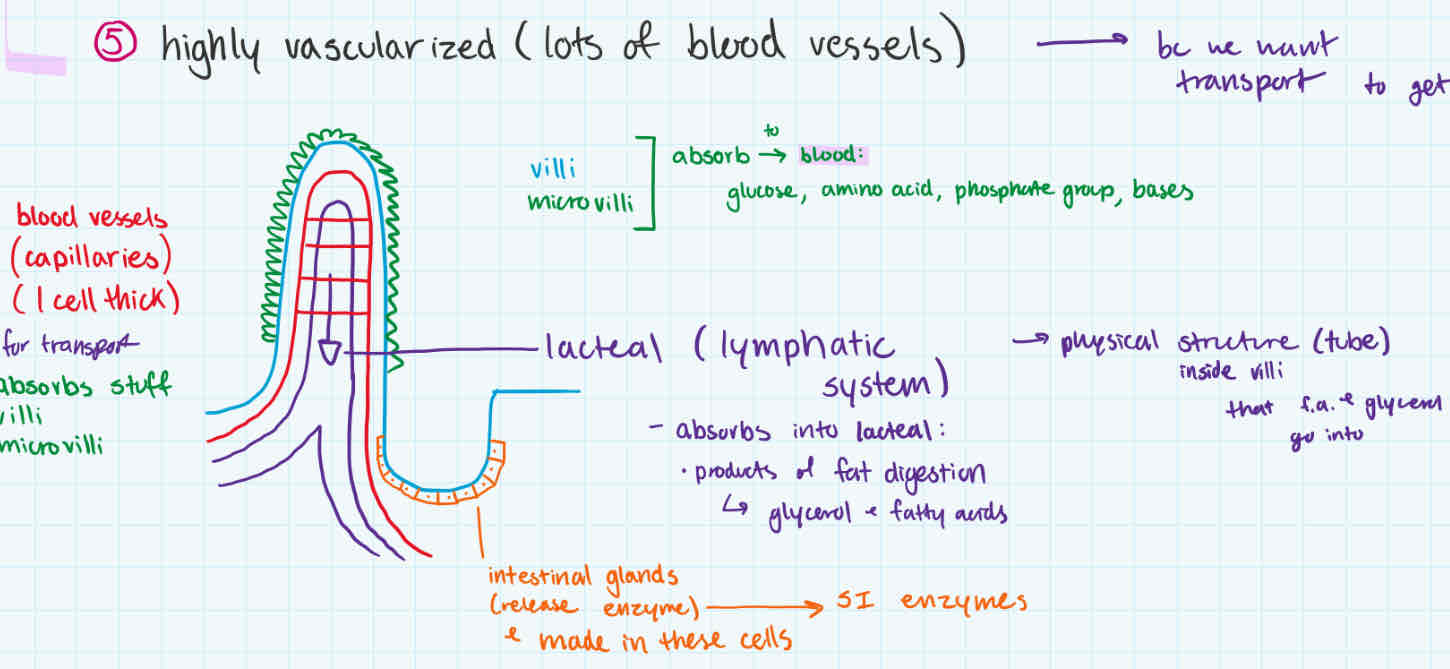
small intestine (second part)
order
how long
what makes it small
what
contains
type of digestion
after stomach + after duodenum
6-7m long (including duodenum)
lumen of it is small
-rest of small intestine after duodenum
-absorption of nutrients
-walls of the SI, secrete 4 enzymes to complete chem digestion by hydrolysis
-walls contain:
villi
microvilli on villi
both absorb glucose, amino acid, phosphate group, bases to go in blood
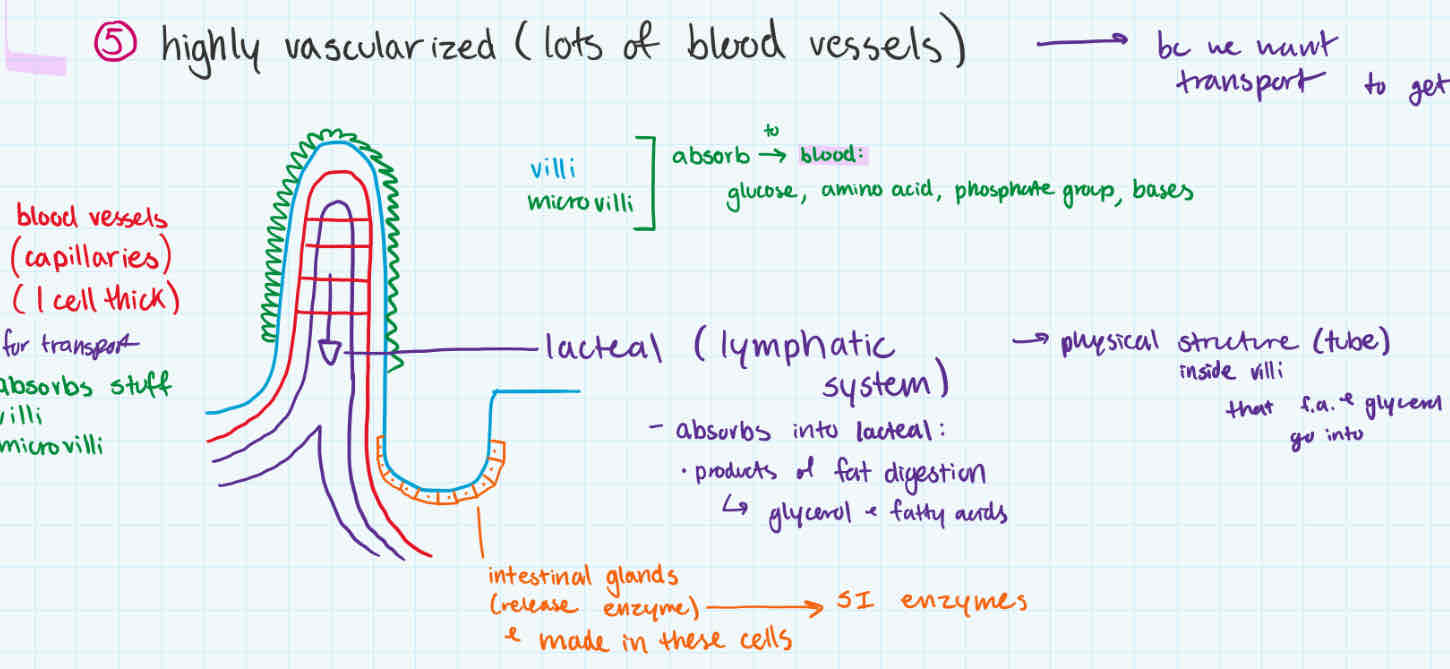
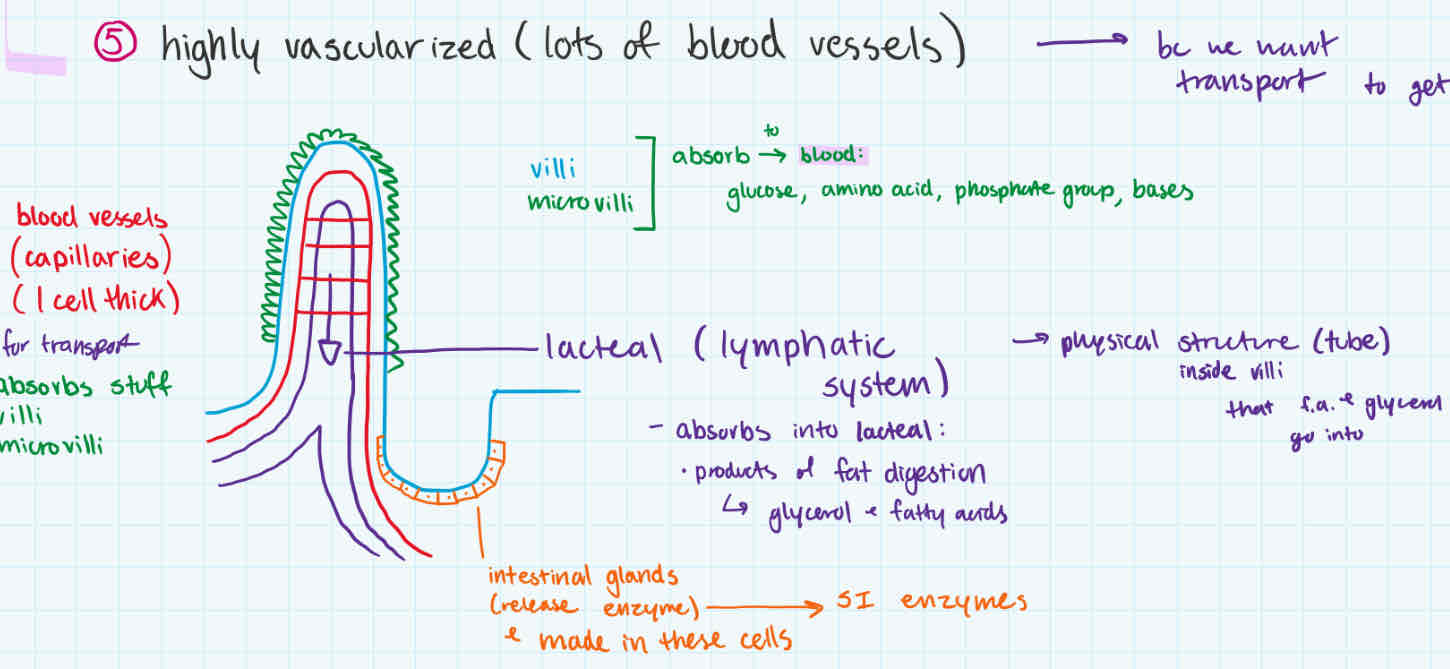
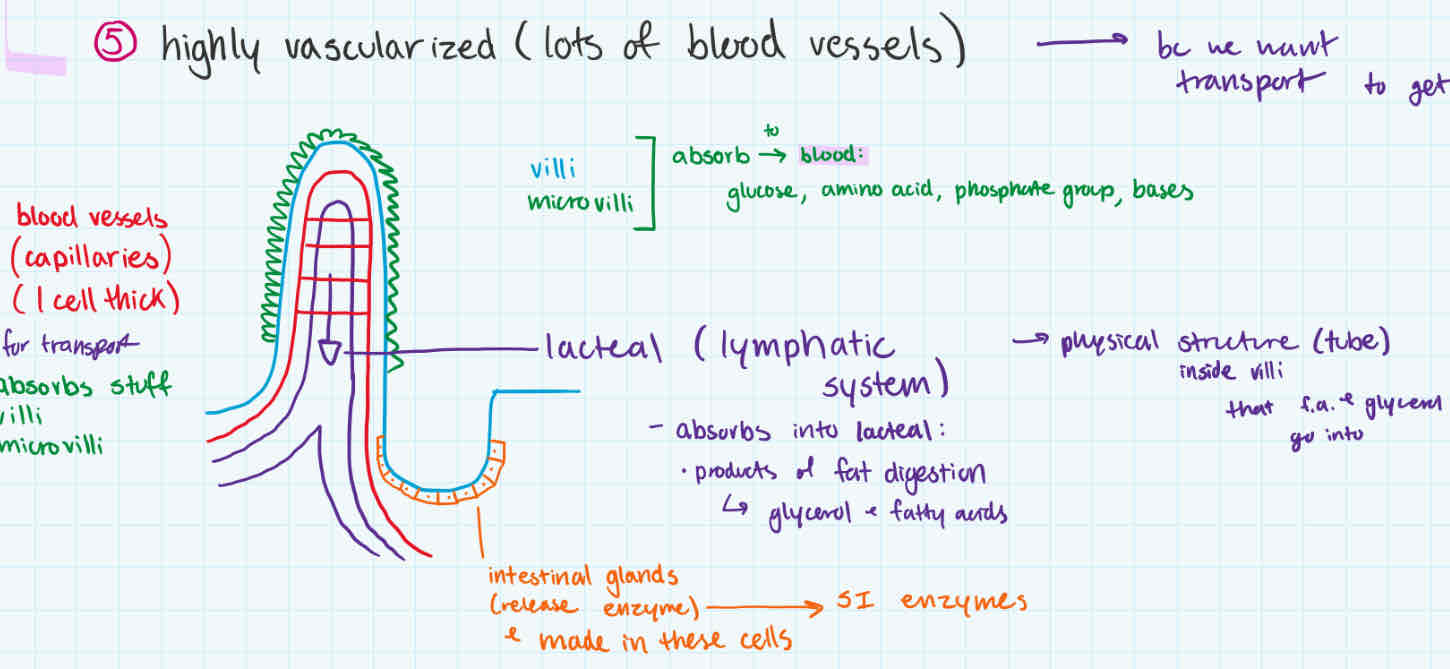
has lots of blood vessels/capillaries within (vascularized)
intestinal glands (makes SI enzymes)
lacteal
absorbs products of fat digestion (fatty acids + glycerol)
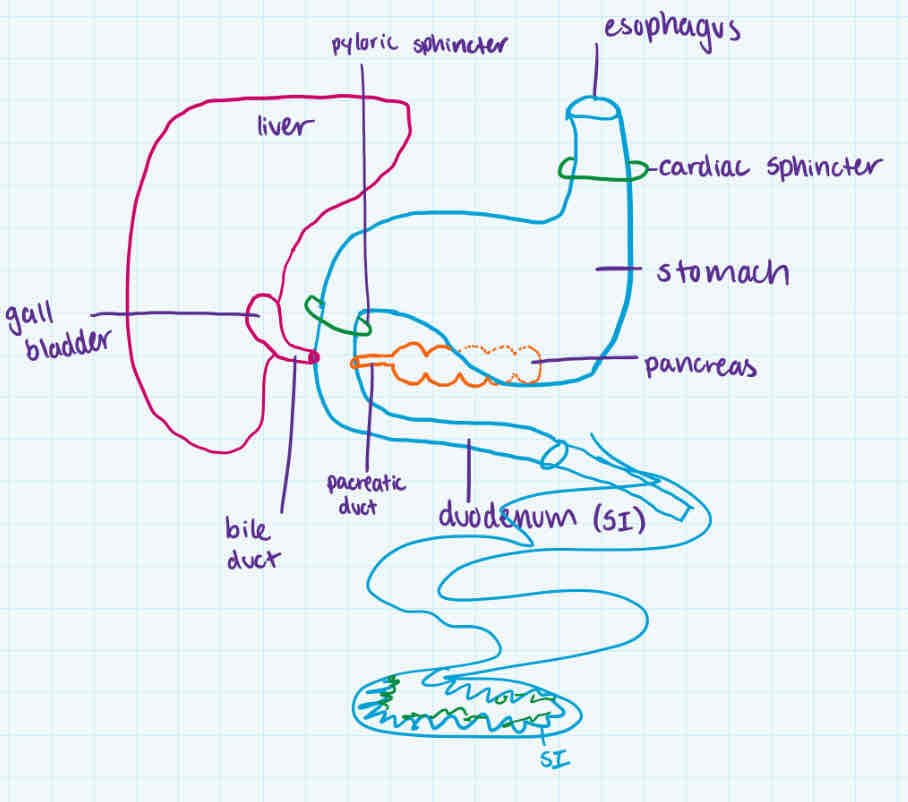
small intestine (after duodenum)
order
process
after stomach and after duodenum
-nutrients absorbed by walls of SI (secretes 4 enzymes to complete all chemical digestion by hydrolysis):
-maltase (works on maltose)
maltose + H2O → glucose
-lactase (works on lactose)
lactose + H2O → glucose
-peptidase (works on small pepsides)
small peptides + H2O → amino acids
-nucleotidase (works on nucleotides)
nucleotides + H2O → phosphate group, sugar, nitrogen-base
enzymes are pH of 8.5
where are biomolcules fully done digesting (breaking down)
-lipids/fats → in duodenum
-rest in small intestine after duodenum
where nutrients are absorbed?
which nutrients absorbed by x and which by y
walls of small intestine
non-fat nutrients absorbed by villi + microvilli to go to blood
fat products (glycerol + fatty acids) absorbed into lacteal (lymphatic system)
if broken pancreas, what happens/how affect
no pancreatic juice
sodium bicarbonate not released
not neutralize
denatures the enzymes
4 enzymes won’t work
-not break down to get nutrients, stops at:
starch
big peptides
fat droplets
DNA or RNA
pancreas produces hormones
no or lower production of insulin + glucagon
→ no homeostasis
if liver broken, what happens/how affect
-won’t make bile
→ big fat won’t be broken down into fat droplets
lipase can’t break them down into glycerol + fatty acids → can’t digest → nutrients not absorbed by lacteal
-food goes into appendix + rots (appendicitis)
-if burst, waste spread to liver area, bad
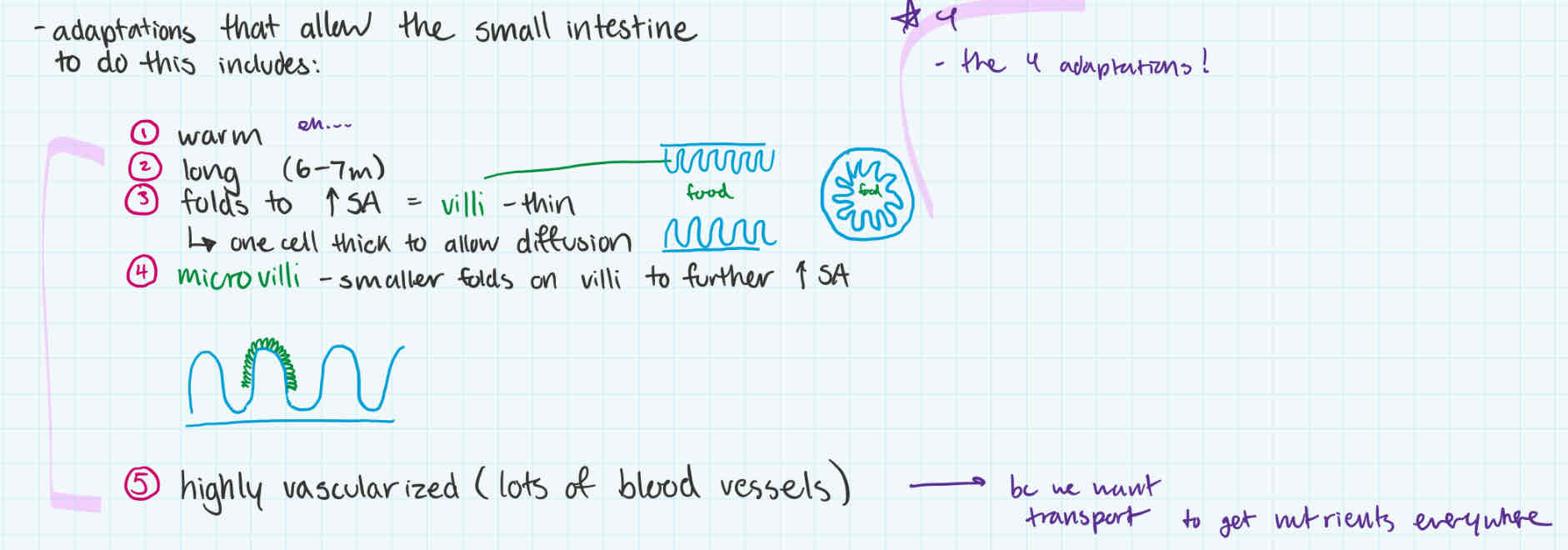
what allows the small intestine (after duodenum) to do big job
(adaptations)
warm
long (6-7m)
folds to increase surface area = villi (very thin → one cell thin so can diffuse easily)
microvilli to increase surface area
highly vascularized (lots fo blood vessels/capillaries) → to transport to get nutrients everywhere
small intestine wall
parts
functions
villi
microvilli
both absorb glucose, amino acid, phosphate group, bases go into blood
lacteal (lymphatic system)
absorbs products of fat digestion (glycerol + fatty acids) into inside villi tube
intestinal glands
make SI enzymes + releases them
blood vessels/capillaries
for transport, so absorbed nutrients can go into blood
liver
what role in digestion
functions
-an accessory organ
production of bile (then stored in gallbladder)
1.5 L / day
production of blood proteins from amino acid
produces urea from breakdown of amino acids
removing the very toxic amino group from body by converting it to urea (NH2 → urea)
converts hemoglobin (quaternary protein; 4 poly-pep; RBC, carry oxygen) from old red blood cells to bile pigments
gives bile its greenish-yellow colour)
detoxifies blood by removing + metabolizing poisonous substances (eg. alcohol)
stores glucose as glycogen after eating + breaks down glycogen into glucose to maintain blood glucose concentration between meals
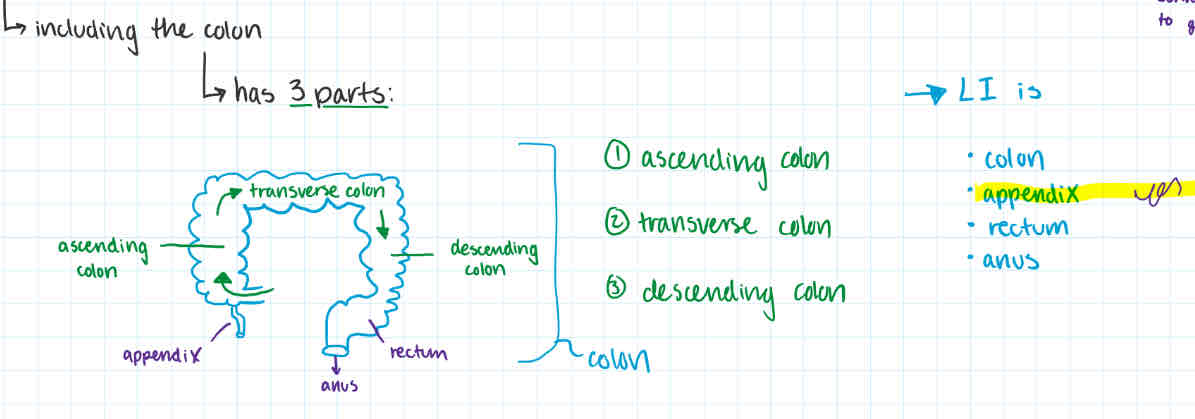
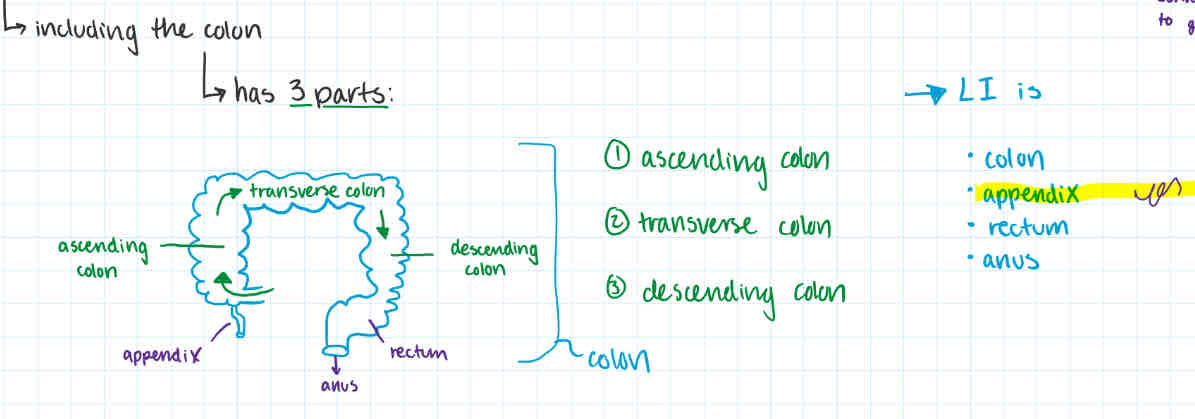
large intestine
order
made of? / made of
size
after duodenum + rest of small intestine
-consists of:
appendix
colon
ascending colon
transverse colon
descending colon
rectum
anus
bacteria
bacteria (eg. e-coli) are v important for proper functioning of LI
-larger in diameter than small intestine (larger lumen)
6.5 cm vs. 2.5cm in diameter
1.5 - 2 m vs. 6-7m in length
large intestine
functions
process
-functions:
absorbs water + any soluble nutrients
stores non-digestible material unit until is defeated at anus
-process
when acid chyme first enters LI, it encounters the appendix
→ function of organ not clear, + subject to inflammation (appendicitis)
peristalsis, which began in esophagus occurs along the entire digestion tract
moving it along
poops
feces contains
nondigestive remains (eg. got cellulose-fiber)
Bile pigment (colours) - liver makes it
large quantities of bacteria (swells)
functions of bacteria in large instestine
-bacteria (eg. E.coli) are very important for the proper functioning of your LI
help breakdown starch (fibre → glucose)
eats/reduce your amount of feces
produce usable vitamins, minerals, and amino acids
diarrhea and constipation
what
-watery fees (diarrhea)
often caused by infection (food poisonings, contaminated water) that causes small intestine wall to become irritated and increase peristalsis
→ poop more often
→ leads to dehydration +death bc less absorption of water
constipation
what
-hard., dry feces, - hard to pass
often caused by ignoring the need to “go”
can cause. hemorrhoids
how is blood sugar regulated
-by pancreas producing 2 hormones (insulin and glucagon)
-they work together to maintain blood glucose levels = homeostasis
pancreas
-diff types
2 types of cells
produces pancreatic juice
(cell called islets of Langerhans) produces two hormones
insulin
glucagon
hormone def
made in one place, travels to another and acts on the other place
feedback inhibition of insulin
-process
-so what
after eating, you have high blood sugar
pancreas insulin in response
insulin travels in blood + targets the liver
liver will convert glucose → glycogen and stores it
lowers blood sugar since convert glucose to smth else
lower blood sugar = inhibits insulin bc pancreas won’t need response
feedback inhibition of glucagon
-process
-so what
low blood sugar (after fasting)
pancreas responds by releasing glucagon
glucagon (a trigger) travels in blood to liver
in liver, glycogen → glucose
increase blood sugar since smth converted to glucose (sugar)
blood sugar increase = inhibits glucagon bc pancreas won’t respond
ppl with diabetes (high blood sugar)
-inject insulin to lower blood sugar (glucose → glycogen) since turn sugar into smth else
the diff types of enzymes
in duodenum..
sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) will neutralize acid chyme to prevent enzymes from denature
will denature pepsin to protect duodenum
4 pancreatic enzymes work by hydrolysis (using H2O to cut)
pH of 8.5
pancreatic amylase
starch + H2O → maltose (disaccharide)
trypsin
peptides + H2O
some alr digested in stomach
peptides + H2O → smaller peptides
lipase
first bile (non-enzyme) helps mech. digest. big fat → fat droplets
fat droplets + H2O → glycerol + fatty acids
digestion of fats done!
nuclease
DNA/RNA + H2O → nucleotides
protein’s second chance at digestion
fat complete digestion
in small intestine…
digestion + absorbption
4 SI enzymes work by hydrolysis
pH of 8.5
maltase
maltose + H2O → glucose
lactase
lactase + H2O → glucose
peptidase
smaller peptides + H2O → animo acids
nucleotidase
nucleotides + H2O → phosphate group, sugar, nitrogen base
absorption happens in SI walls:
villi + microvilli absorb:
non-fat nutrients
lacteal/lympthatic system absorb:
fat products (glycerol + fatty acids)