chapters 11 & 20 - atomic and molecular mass spectrometry
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
mass spectrometry
the separation of molecular and atomic species according to the mass to electrical charge ratio (m/z)
info we obtain via MS includes molecular weight, molecular formula, structure, isotopic distribution, and protein sequencing
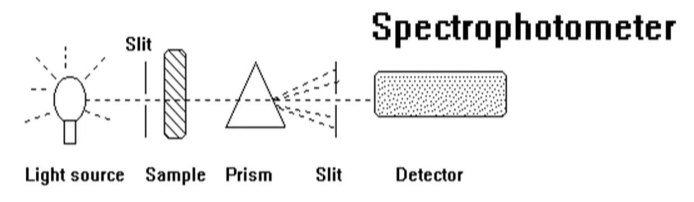
be able to draw a block diagram of a spectrophotometer
light source → slit → sample → prism → slit → detector
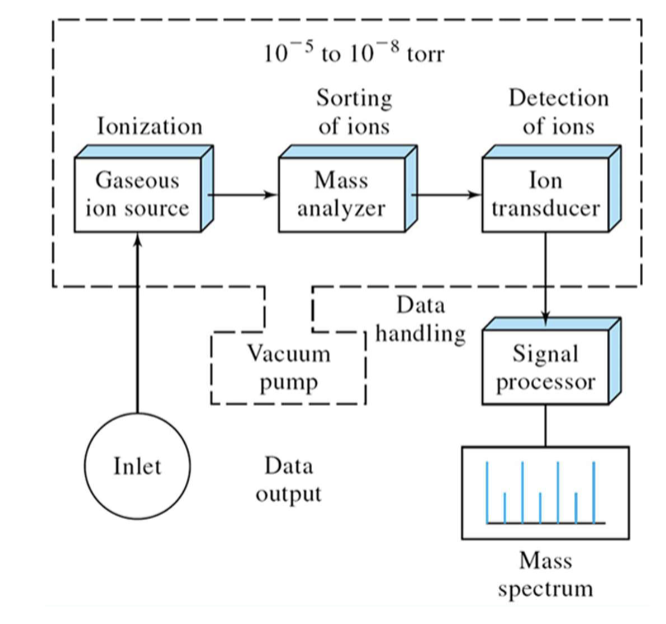
be able to draw a block diagram of a mass spectrometer
inlet → gaseous ion source → mass analyzer → ion transducer → signal processor → mass spectrum
advantages of atomic mass spectrometry
detection limits that are as great as three orders of magnitude better than optical methods
remarkably simple spectra that are usually inique and often easily interpretable
the ability to measure atomic isotopic ratios
disadvantages of atomic mass spectroscopy
expensive instrument costs (2-3 times that of optical atomic instruments
certain types of interference effects
instrument drift that can be as high as 5-10% per hour
what are the steps of atomic mass spectrometric analysis?
atomization
conversion of a substantial fract on the atoms to a stream of ions (usually positively charged)
separating the ions formed in step 2 on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z)
counting the number of ions in each type or measuring the ion current produced when the ions formed from the sample strike a suitable transducer
average mass
weighted average of the atomic masses of the different isotopes of each element in the molecule
nominal mass
predominant isotopes of each element rounded to the earest integer value that corresponds to the mass number
monoiosotopic mass
exact mass of the most abundance isotope for each constituent element
scaled mass “frequency”
what the y-axis on the mass spectrum graph is; shows “how many” of that type of atom there is, or how frequently that type of atom/molecule fragment occurs
what is the equation for resolution?
R = m/∆m
∆m = mass difference of two adjacent resolved peaks
m = avg mass of the two peaks
what is the effect of isotopes on mass spec?
isotopic patterns can sometimes simplify identifying a spectrum; different isotopes of an element will show up differently on a spectrum
how many decimal places do m/z measurements need?
at least 4; many molecules will round up to be the same number so decimal places are needed to accurately identify
fragmentation
parts of the molecule that are measured for relative abundance in mass spec; fragments are rationalized by experts..they rationalize the starting molecular ion-s structures as well as the final fragment structure
inlet
introduces a micro amount of sample into the ion source where the components of the sample are converted into gaseous sions by bombardment with electrons, photons ions or molecules
batch inlet
leak some gas into a vacuum from an external source (GC column)
direct probe inlet
sample is introduced through a holder via an interlock so that you do not lose vacuum
ionization source
converts the sample into ions
gas phase ionization source
typically starts with molecules in the gas phase; typically with thermally stable compounds with boiling points less than 500°C and molecular weights less than 1000
desorption sources
a liquid or solid sample must first convert to gas
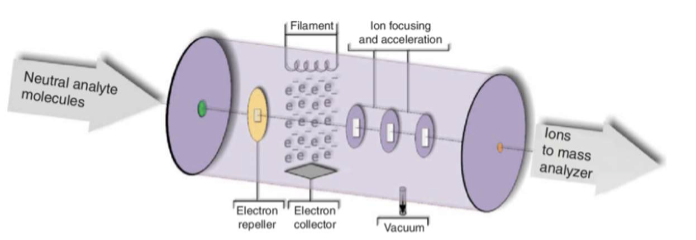
electron impact (EI) ionization
is designed to produce gaseous ions; the electrons come form a tungsten filament, and the electrons and molecules collide. singly charged positive ions are extracted by a small potential through a slit.
when the electrons approach a molecule, the molecule undergoes rovibrational excitation; a transfer of energy to the molecule occurs; interaction with an electron beam ultimately ionized to molecule but also leaves that molecule in a highly excited vibrational and rotational state
relaxation occurs by extensive fragmentation giving a large number of positive ions that are less than the mass of the molecular ion
advantages of EI ionization
easy to use and gives a large number of ions
gives a complex mass spectra with fragment ions, which is useful for structural identification
many search libraries exist for EI
disadvantages of EI ionization
can produce too much fragmentation, frequently leading to no molecular ions, which makes structural identification difficult
the sample must be a stable gas
is a low pressure technique
chemical ionization (CI)
a form of ionization that uses gas-phase chemistry; it is less energetic; usually involves proton transfer reactions; it can have both positive and negative ions
what are the differences between EI and CI?
EI is more energetic and results in a hard ionization (meaning there are more lines and the resolution is higher. CI is less energetic and results in a softer ionization with less lines
atmospheric pressure CI (APCI)
involves using the liquid effluent in a spray chamber (typically a liquid chromatograph); this operates at high pressures, outside the vacuum MS regions. it utilizes nickel 63 or a corona discharge at several kV. ionized reagent gas (nitrogen or oxygen) acts as the primary reactant ions, forming secondary ions with the analytes
electrospray ionization (ESI)
there is a flow of solution through an electrically-conductive capillary held at a high voltage; the solution flows out of the capillary and experiences the voltage; charges build up on the nebulizer droplets, which then begin to evaporate
Rayleigh limit
when the repulsion of the charges overcomes the surface tension of the solution
what is a possible mechanism for ESI?
droplets pass through a capillary, then become charge while they also start to shrink as the droplets evaporate. this increases the charge density on the droplet. as this happens, the desorption of the ions into the gas phase occurs resulting in some, but not a lot of fragmentation. most of the molecules are multiply charged so the m/z ratio is lower
what is a reason for ion suppression in ESI?
the ions that are surface active will be preferentially ionized
which two techniques are complementary to each other? why?
ESI and APCI
ESI has soft ionization and can ionize thermally labile sample. ions are formed in solution. it involves singly and multiply charged ions
APCI requires some sample volatility (with a nebulizer). ions are formed in the gas phase. it involves singly charged ions.
MALDI (matrix assisted laser desorption)
desorbs a sample with a laser while preventing degradation. the sample is mixed with a radiation absorbing matrix to help it ionize while it volatilizes.
is good for very large molecules
mass analyzer
measures the m/z using a high vacuum system, similar to how a monochromator selects wavelengths; it contains a transducer that converts the beam of ions into an electrical signal that can then be processed then stored or displayed.
what all components of a mass spectrometer require connection to the vacuum pump?
ionization source, mass analyzer, ion transducer
time of flight (TOF) mass analyzer
ions are introduced into a chamber (drift tube) by a pulse of accelerating current
these ions are all given the same kinetic energy, and their velocities vary inversely with their mass during their drift
fast electronics are needed for this instrument
quadrupole mass analyzers
the most common mass analyzer; can generate an entire spectrum in 0.1 seconds, is inexpensive and robust
there are two pairs of rods in which ions are accelerated into; the ions with a limited m/z range reach the transducer
what is the typical detector for mass spectrometry?
electron multipliers
electron multiplier
like a PMT tube; ions strike a surface and cause electron emission. each successive impact releases more electrons. has low noise and a good dynamic range
how is MS coupled with other techniques?
you can run a MS as a doctor on LC or GC
tandem MS (MS-MS)
ions from one mS are subjected to conditions that further fragment that one specific fragment, then are passed to a second MS for additional analysis
is good for sequencing proteins, drug metabolism, environmental samples, complex unknowns, and conformational studies
ion mobility spectrometry (IMS)
ion source → drift tube → detector
advantages: no vacuum pumps, room temp with air as the drift gas, smaller
disadvantages: no overlaps in flight times, low information content
applications: airport security, military defense, anti-counterfeiting, pharmaceutical