Cog Psych 200 Exam 2
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Attention
process of focusing on specific features of the environment or on certain thoughts or activities
Covert
directing focus without moving your eyes
Overt
moving your eyes to what you’re focusing on
Selective attention
ability to focus on one message and ignore all others
Dichotic listening
One message is presented to the left ear and another to the right ear
Cocktail party effect
recognizing your name in another conversation
Broadbent’s early selection model
Filters message before incoming information is analyzed for meaning
McKay’s late selection
Attending ear heard ambiguous sentence; Unattending ear heard biasing words
Treisman’s attenuation theory
Attended message is let through attenuator at full strength while unattended is let through with much weaker strength
Dictionary unit
contains words, each of which have thresholds for being activated; uncommon words have HIGH threshold
Divided attention
Practice enables people to simultaneously do two things that were difficult at first
Spelke
After hours of practice, participants could read and categorize dictated words
Schneider & Shiffrin
Divide attention by remembering target and monitoring rapidly presented stimuli; Memory set and test frames (3 is target with letters)
Consistent mapping condition
target would be numbers and distractors would be letters
Automatic processing
occurs without intention and only uses some of a person’s cognitive resources
Stroop effect
Name of the word interferes with the color of the word
Varied mapping condition
rules change from trial to trial; Overtime participants never achieved automatic processing
Controlled processing
participants paid close attention and their search was slow and controlled
Inattentional blindness
a stimulus that is not attended is not perceived, even though a person might be looking directly at it
Stimulus salience
areas that stand out and capture attention; Color and motion are highly salient
Scene schema
knowledge about what is contained in typical scenes
Location-based
moving attention from one place to another
Precueing
directing attention without moving the eyes
Object-based
attention being directed to one place on an object
Egly
participants saw two rectangles followed by a target cue; Reaction time fastest when target appeared where indicated
Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
Preattentive stage and Focused attention stage; Treisman and Schmidt tested this
Preattentive stage
Automatic, no effort or attention, unaware of process
Focused attention stage
Attention plays key role, features are combined
Memory
a collection of processes involved in retaining, retrieving, and using information about stimuli after the original information is no longer present
Modal Model of Memory (Atkinson & Shiffrin)
Computer used as a model for human cognition
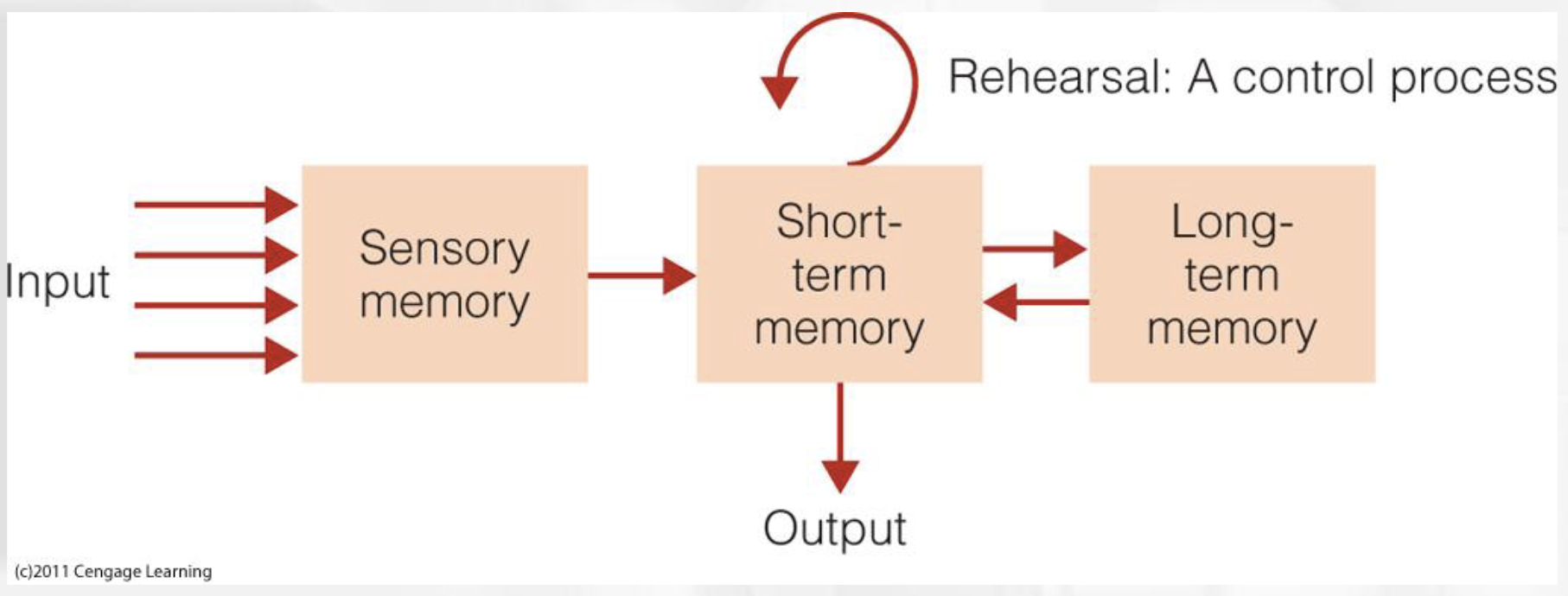
Control processes
active processes that can be controlled by the person; ex. Rehearsal
Sensory memory
registers all or most information that hits our visual receptors; Holds a large amount of information for a short period of time
Persistence of vision
retention of the perception of light
Sperling
measured the capacity and duration of sensory memory; Array of letters flashed across the screen and participants had to recall as many as possible
Whole report
participants asked to report as many as could be seen
Partial report
participants heard tone that told them which row of letters to report
Delayed partial report
presentation of tone for a fraction of a second after the letters were extinguished
Short-term memory
Stores small amounts of information for a brief duration; Includes new information from sensory stores and information recalled from long-term memory
Proactive interference
when information learned previously interferes with learning new information
Chunking
small units can be combined into larger meaningful units
Ericcson
Trained a college student with average memory ability to use chunking; S.F. could remember up to 79 digits after 230 hours of training sessions
Chase & Simon
Memory for chess pieces on a board; When the pieces were randomly placed, they were equal
Coding
the way information is represented
Physiological
how stimulus is represented by the firing of neurons
Mental
how stimulus or experience is represented in the mind
Auditory coding (Conrad)
Participants saw target letters and were asked to write them down after a short delay; Errors most often occurred by letters that sounded alike
Visual coding (Della Sala)
Presented visual information that is difficult to verbalize
Digit span
how many digits can you remember; usually 5-8 items
Semantic coding (Wickens)
Participants listened to three words, counted backwards for 15 seconds, and attempted to recall the three words; On trial 4 he changed the category of words
Working memory
Limited capacity system for temporary storage and manipulation of information for complex tasks such as comprehension, learning, and reasoning
Phonological loop
Composed of 2 sub-systems; Baddeley formed this
Phonological memory store
Holds traces of acoustic or speech-based material with limited time capacity
Articulatory subvocal rehearsal
Maintains phonological memory traces; Translates visual information by subvocal naming; silently repeat yourself
Auditory (phonological) input
Info: Sensory memory → Central executive → Phonological memory store; Trace kept active using articulatory subvocal rehearsal unit; 2 sec
Visual/Visuospatial unit
Info: Sensory memory → Central executive → Visuospatial sketchpad; Input then transferred to phonological memory store
Word length (Baddeley, Thomson, & Buchanan)
Serial recall; 4-8 words & 1 vs 5 syllables; Words appear to be coded by temporal duration and not in meaningful units
Articulatory suppression (Baddeley, Thomson, & Buchanan)
word length effect should occur in conditions where rehearsal is allowed; Suppression eliminated the word length effect because material not coded phonologically
Visuospatial sketchpad
Brooks ran experiments and concluded if the task and response are the same WM component, performance is worse
The Central Executive
Attention controller: focus, divide, switch attention; Vogel ran experiments with red and blue rectangles
Prefrontal cortex
responsible for integrating incoming visual and auditory information
Long term memory structure
“Archive” of information of past events and knowledge learned
Clive Wearing & H.M.
Could have functioning STM but cannot form new LTM’s
K.F.
Could have poor STM but functioning LTM
Murdock
Tested with free recall test and serial position curve
Primacy effect
Earlier words can be rehearsed more; Number of rehearsals correlates to recall performance
Recency effect
No time to rehearse; Number of rehearsals unrelated to performance
Glanzer & Cunitz
Tested delay and spacing with free recall tests
Results
delay prevents recency; spacing influences primacy
Explicit/declarative memory
personal events/episodes; facts knowledge
implicit/non-declarative memory
procedural (like riding a bike); priming
Episodic memory
specific events, personal events, Remembering
Semantic memory
General fact/meaning, not tied to experience, Knowing
K.C.
No episodic memory, cannot relive any events of his past, but semantic memory intact
Italian woman
Impaired semantic memory; Episodic memory for past events was preserved
Tulving, Schacter & Stark
Word completion/standard recognition tasks
Repetition priming effect
When the same stimulus reappears, processing is faster; Slow decline over time; Does not rely on explicit memory
Types of implicit memory
Procedural, priming, classical conditioning, non associative learning
Neath
classification of memory tests
Depth of processing experiment (Jacoby & Dallas)
3 orienting tasks and 2 different tasks; No relationship between depth and implicit memory; Strong relationship between depth and explicit memory
Retrograde amnesia
forgetting past memories
Anterograde amnesia
not able to create new memories
Korsakoff
Both amnesias
Graf, Squire & Mandler
Cued recall: use the 3 letter cue to form a word from the list (direct test); Stem completion
Propaganda effect
more likely to rate statements read or heard before as being true