
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
what are all the languages he found evidence of the h factor in
define construct validity
constrcut validity is the overall evidence that the test measures the intended variable- uses hypothetical abstractions called constrcuts
german, hungarian (but hungarian had the h factor as their 5th one, not a 6th), polish, italian, korean, french, dutch, croatian, english, greek, turkish
what is differen tbig 5 vs hexaco- need to knwo this from class!
what is situationism
if narrow facets, not broad factprs, are best for predictive validity, whatdo we need factors for
emotionality and agreeableness are different between the 2 models, as well as the addition of H
extraversion, conscientiousness and openess to experience are the same between hexaco and the big 5
situationism is what meschel advocated for- belief that all peronality diffs are actually just brought on by situational factors
we still need factors to summarize perosnalty efficiently and for predicting many criteria all at once
how are adjectives arranged differnetly in the studies of non english language
t or f- we have seen evidence of a 6th perosnality factor in english
look at each term individually, instead of group them together- this is why enlgish lanuages didnt find the commonlaity to begin with
true
who decides if a test has content validity or not
did kolar say self or observer reports are more valid
is MMPI empirical or rational
what did galton do
once we find the rs of the adjectives in a factor analysis, how can we interpret the adjectives
universal, unique, and intermediate ways of studying psych, and what type of psych studies each
sme/subject matter experts decide if a test has enough content validity
kolar said obsserver reports are slightly more valid
mmpi is empirical
galton did first suggestion for the lexical hypothesis
to figure out which of the highly correlated items have similar adjective menaings and then gorup them based on this
universal aspects of human nature- how people are similar in behaviior (ie. all people try to defend themselves if they are attacked)- common with social psych
unique- psych can look at what makes one person different from everyone else (ie. one person is why, one person is outgoing)- studied by philosophers, historians, poets, etc. and some personality psych
intermediate- explore how any given person is similar to some people yet different from others- looking at the spectrum of traits people can vary along and try to measure these characteristics (ie. how can we measure different levels of creativity)- between universal and unique ways of studying- this is the main one personality psych uses
idiographic vs nomothetic approach
- pros and cons of each
which indicates he origins of personality traits
idiographic- taking a unique apprach to personality psych- looking for what makes people different, and explaining what cuases these differences
- pros- insights into unique features of personality
give clues to origins of personality traits
inefficient- too much time and money to examine what makes each person unique in detail
- there is only a small segment of any one persons personality that is really unique to them
- no creating general laws about personality
nomothetic approach- studies certain persoanlity features of many people, and then compares them to find general rules about personality
- measuring variables between people and then finding how these variables are related
- can study hypothesized causes of behaviors related to personality- idiographic appraoch can allow us to study somebody who is consicientious and say that maybe it is due to a strict upbringing, but nomothetic approach allows us to say that this is for certain sicne we can see if a strict upbringing is acommon theme among all people who are consicentious)
- allows us to discover the laws of personality- can find causes of, and relationships between, personality traits
- this textbook uses the nomothetic approach
major challange to measuring psych characteristics
no absolute measures and no true measure of zero- cant measure somehting with a exact number like we can someones weight- if somebody gets a zero on an iq test, this doesnt necessairly mean the person has no intel like we would say somebthing has no weight if it weighs 0 pounds - due to this the ratios between measures are useless since saying somebody is twice as intelligent as somebody else isnt very accurate or helpful
what traits are the same and diff between hexaco and neo
all are the same except agreeableness and emotionality/neuroticism are diff between hexaco and neo
psychologists want to obtain scores that have meaningful...
differences- helps address the prob we see with rank roders when intervals are not consistent- we want interval scores, not ordinal ones
t or f- it is ok to use -30 as the benchmark for average assertiveness
yes- the benchmark doesnt matter and numbers you use for measurement dont matter, as long as the intervals between measurements are consistent- it doesnt matter as long as the diff between x and y is the same as the diff between y and z
- therefore, it also doesnt matter what units we use to measure it as long as these are consistent
what is the formula for standard score
false- we use standard scores/z scores to compare scores from different scales
relating scores on one scale to scores on another scale- a score of 50 on one test maymean soebody is average, but a score of 50 on another may mean they are in the top 1%
- allows us to compare levels of diff characteristics, or the levels of the same characteristics between different scales
- convert raw scores to standard scores:
1. take raw score and subtract mean score for the test- tells us if they are above avg (diff is pos) or below avg (if diff is neg)
2. divide the diff by the standard deviation- shows variability in scores
z/standard score=(your score-mean)/standard deviation
variability in scores
how the scores are distributed- 90% of people may get between 100 and 110, and 1% get between 120 and 130
avg and sd for standard score
aka. standard scores
- avg is exactly zero for a standard score
- standard deviation of a standard score scale is 1 (different for iq where average is 100 and sd is 15)
normal distribution produces what shape on a graph
a bell curve
somebody who scores the mean on a test has a score that is higher than...
50% of the people who took the test
r=-1, so if x is 1sd above the mean what is y
y would be 1 sd below the mean
how closely scores on one scale are related to scores on another- ie. how closely related iq and extraversion are
- symbol r
- +1- pos correlqtion
-1- neg correlation
0- no correlation
- a diff of 1 SD units on one variable is assoc with a diff of r standard deviation units on the other variable
- ie. r between x and y = +1, so when x is 1sd above the mean, y must also be 1sd above the mean- graph is bottom left to top right
ie. r=-1, if x is 1sd above the mean, y is 1sd below the mean- top left to bottom right
when r is not a perfect correlation (+ or -1), how do we correlate r to sd
use a large sample and see if you can find an average- if you find that the correlation is about 0.5, and many people are 2sd above the mean on variable x, they are likely 1sd above the mean on variable y
- can find a tendency, not a perfect correlation
if we do not take the square root when finding the standard deviation of scores...
fix this!
sizes for small vs large correlations
between -.20 to +.20- small
between -.20 to -.40, and .20 to .40 are moderate, and anything under -.4 or above .4 are large
- its very rare to find anything past .80/-.80
a good size for internal consistency is .7, but many people will accept .5 and above
if a personality trait correlates .25 with a variable like happiness, then people 2sd higher on this trait are how much higher above the mean for happiness
.5 sd above the mean for happiness (sd above one mean=sd above another meanxr between the 2 means)(sd= 2x0.25=.5)
if happiness and a personality trait are correlated by 0.25, then what is the sd between somebody who is 1sd above the mean for happiness, and somebody who is 1sd below the mean for happiness)
1sd above: 0.25x1=0.25
1sd below: 0.25x-1=-0.25
sd diff between them is 0.5
formula for finding correlation/r
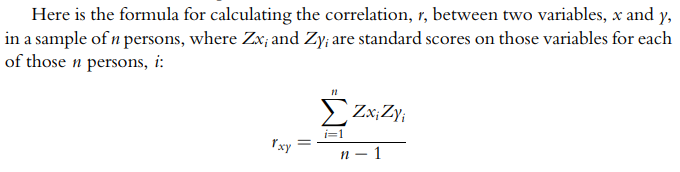
about how big should a sample be for us to get random chance types of repsonses and inc the averageness of repsonses
representativeness- the sample if representative of the population they want to learn about- cant look at political views in canada by using a sample of people at uofc since uofc students tend to be more liberal
sample is large- gets rid of differneces due to random chance and inc the averageness of responses- 250+ people in a sample is usually close to actual levels of something
reliability
extent to which a measurement is consistent with similar measures of the same characteristic
error vairance
the variance we get in what a test actually measures based on when the test was taken, what the specific items on the test were, who took th etest, etc.- variance caused due to something random other than the intended characteristic
the more reliable a test is, the less error variance it contains
true variance is variance in the test results due to a variation in the actual trait we want to measure. error variance is due to things like reprting errors, changes in mood between times taking the test, etc.
if we are trying to look at the diff between 2 peoples perosnality, low error variance and high true varinace means the differences in scores are due to actual differences in personlity, wheras error variance would mean the differences in scores are due to things like problems with the test design, problems with how the researcher recorded the data, etc.
3 types of reliability- internal consistency
1-reliability=error variance
internal consistency- error due to diff between items/parts of the measurement- each item on a test measures some part of what we are actually interesed in, and then somehting else (called the error variance)- if we can average a persons score accross many items the error assoc with any single item tends to be cancelled out- ie. a golfers score on any single hole is dep on hw good they are, but also random chance, but if we take their avg success accross 100 items or holes, we get a good indication of how good they are wihtout the element of randomness
amount of error left over after we sum the scores is dep on the number of items (the more items, the less error) and the correlation between the items (the more correlated the items, the more each item measures the characteristic we are interested in, and the lower the error will be- if people tend to get similar scores in gold between holes/items, the items have a high correlation, and thus are measuing ability more than random chance)
max reliability by having a large numbe rof items, and high correlation between items
reliabilty is between 0 and 1- shows the proportion of variance due to the common item- if we subtract reliability from 1, we get the proportion of viariance due to error/unique aspects of individual items- the more error we have coming from unique individual aspcects (true variance), and the less that comes from error variance, the more reliable our test is
t or f- a scale with low reliability can have high validity
false
acceptable levels of internal consistency reliability
about .70 or above (some people say .5 have a modest level)
2nd type of reliability- interrater/interobserver
-2 ways we inc it
the average rating demo…
the variance between the ratings demo…
inc by having more raters, and by having ratings that are closely correlated with one another
when we have multiple people rating/scoring somehting, even when they are using good practices, there is still some error/difference in their scores- it is expected that one person may rate person a as eing slightly better than b, and another rate b as being slightly better than a
average out the ratings to inc reliability of their assessments- the average rating depends on the common element of those ratings, and the diff between them depends on their error due to raters individual subjective assessments
inc when we have more raters
inc when raters ratings are closely correlated with one another
most common type of reliability measurement in perosnlaity psych
internal consistency reliability
3rd type of reliablity- test retest- is it typically high or low
contorls for error due to random fluctuations accross short periods of time
measure the same characteristic in the same group of individuals between 2 seperate occasions, usually several days or weeks
test retest reliability- how closely correlated the scores are between 2 diff instances
if there is too much time between the easurements, changes between scores may be due to changes in somehting like personality, not random fluctuations
test retest reliability tends ot be high since most measures show minimal fluctuations over time
can be low if we measure something like emotions if the uestions are phrased in a way where they measure current emotions, not overall long term emotions
if a psych administers 2 diff versions of a test to a person on 2 diff occassions, what reliability is measured
test retest- 2 occassions
2 diff versions-internal consistency- doing parallel forms- making sure the corelation between the 2 parallel tests is high to show the items are hung together
validity
extent to which a test measures the same characteristic it is supposed to assess
reliability- looks at how well measurements show menaingful characteristics
validity- which specific meaningful characteristics are being shown
validity is more specific and restrictive than reliability
reliability is consistency over time, validity is accuracy
reliability shows max…
validilty- soomething with low reliability cant have high validlity
t or f- a measurement with low validity can have moderately good reliabiility
yes- reliability restricts validity and validity is more specific- but something with low reliability could never have good validity
if we want to look at artistic ability and we only measure poetry writing talent, what is high and what is low
high internal consistency reliability- high correlation between the items
low content validity- not measuring all the relevant domains of artistic ability (similarly, if we looked at poetry skills and basketball skills, even though it is more diverse it would still be low content validity because now it is measuring somehing that is irrelevant)
internal consistency- do each of the items measure the same construct
content validity- are the items measuring all of the features of the concept we are interesed in, and none of the features of irrelevant concepts
extent to which items are relevant to characteristic they are supposed to measure
items should assess all features of relevant characteristic, and no features of irrelevant characteristics
if oyu want to measure how much people enjoy sports, you dont only ask them about hockey, but you also dont ask them how much they like reading
can be challanging to decide what type of content to include
can be challanging when we want high internal consistency reliability- if we try too hard ot get items that are highly correlated with eachother to inc internal consistency, we can select out items that would inc our content validity by excluding relevant characteristics (internal validity may be high if it only asks about hockey, but then content validity will be low)
construct validity
when somehting we measure is imagined, not concrete
ie. impulsivity, intelligence, sociability (stuff like mass, length, etc. are also constructs)(a phone is not a constrcut, the sun is not a construct)
constrcut validity is highh when the measurement assesses the same construct we are trying to assess
det by examinig correlation between measurement of the constrcut to other variables
size of correlation should dep on how similar the items are (look at convergent and divergent validity- should have high correlation with things that are related to the constuct, and low correlation with things that are unrelated to the construct)
convergent validity
part of construct validity
look at how strongly a scale correlates with variabes that measure characteristics very similar or very opposite from what the scale measures
- if the scale measures something opposite to what our scale should measure, there should be a strong negative correlation- shows divergent validity
if the scale has a weak positive correlation, then it should not measure something very similar to what our scale measures
if the scale has a high correlation to what we are measuring, it should show a high pos correlation to our scale- convergent valiidity
discriminant validity/divergent validity- t or f- we want disciminant validity to be close to 1
both discriminant and convergent valdity are demo with a r value/correlation coeff- if it is close to 1 it is high convergent and low divergent, and if it is close to 0 it is low convergent and high divergent
false- we want discriminant validity to be close to 0 which would mean they are uncorrelated (the construct is uncorrelated to other measures related to the trait)
a type of content validity
how strongly a scale correlates with variablees that measure characteristic unrelated to the one the scale is intended to measure
the closer discriminant validity is to zero, the better our scales assesses the construct it was designed to measure
criterion validity, and do we usually expect this to be high or low for personality related measures
what is it aka. as when it predicts something in the future
predictive validity- a type of criterion validity that predicts events in the future (concurrent is the type of criterion validity that predicts things now)- criterion validity is accuracy of a test or measure to predict a specific outcome
relating a measurement with an outcome/criterion variable that has practical significance
ie. how well a personality measurement can predict success in a job- when it is used to predict something in the future criterion validity is predictive validity
there are not often high correlations between criterion and the construct the scale measures- somebodys job success may depend on their perosnality, but it is also impacted by their boss, the task they have to do, etc.
self reports
ask people questions about their actions/thoughts/feelings
measurements are strcutred/objective- everyone gets the same questions, thre is a fixed set of possible responses (ie. can only answer with yes or no or rate it from 1 to 5)
most popular assessment method
cheap, efficient and accurate
accuracy depends on how knowledgeable people are of their own behaviors/feelings/thoughts, that people are willing to accurately report things
can either ask about feelings/behaviros nd thouhts and infer things about their perosnality based on these, or just ask them directly about their personality (asking directly about personality instead of inferring, like asking to rate how neurotic they are, may be better since it is more direct)
if people differ in understandings of hwat something like neuroticism means or looks like, then these reports can be quite inaccurate
reports ask about things like behaviors that can indicate elements of a trait, ratings ask peopeto directly talk about/rate themselves on the trait
report vs rating
report- used when we ask soembody to report a thouht/feeling/behavior and then infer somehting about personality
rating- when we ask somebody to directly rate something about their personality like how impulsive they are
___________ looked at childrens levels of altriusm. Who used these results to say perosnlaity doesnt exist, who disputed this, and who did it with uni students
harshorne and may looked at childrens levels of altriusm, walter mischel used this to say personality doesnt exist. this was disrupted by rushton annd colleauges/ jackson and others are responsible for looking at the same type of study with uni students and how to aggregate their results.
direct observations
when the psychologist observes the persons behavior direclty
can watch people in the natural enviornment where a perosnlaity trait manifests- ie. assess sociability by watching somebody interact with others
requires huge amounts of time and effort and can be expensive
can occur either in natural or artificial settings
very hard to use on a large scale
office of strategic services
example of the use of direct observation- WW2 method of selecting agents based on peronslity traits- would have the applicant be observed in a role playing scenario
this was renamed to the CIA
biodata/life outcome data- 1 pro (hint- the pro isnt that its easy to collect or anlaysze) and 1 con
obtain records of a persons life that seem relevant to that persons personality
ie. use time spent talking on phone as a measure of sociability
ie. use gpa as an indication of conscientiousness
good since they are objective measures
may not always be clear how well it represents personality- does talking on the phonoe mean you are sociable or bored
correlations between different measures of personality
high correlation between self report and observer reports of personality
high between direct observations and biodata
some people say direct obsrvation is the ideal method and a gold standard, but it is likely that self and observer reports are better measures (this is because it is so hard to obtain good amounts of data on observations about people)
personality trait definition
differences among individuals in a typical tendency to ___,___,___in _____ related ways, across a variety of _____ situations and accross a ________
differences among individuals in a typical tendency to behave, think or feel in concentpaully related ways, across a variety of relevant situations and accross a long period of time
differences among individuals- personality needs to tell us how people compare to others
typical tendency to think, behave or feel- likelihood of showing some behaviors or having some thoughts or feelings
in conceptually related ways- trait is expressed by behaviors, thoughts and feelings that share similarities to eachother- sometimes things like wearing flashy clothes, talking loudly, or sttaing extreme opinons all look different but are related since on a conceptual level they show the trait of extraversion
accross a variety of relevant situations- must occur in more than one situation- cant only be outgoing around your family to be considered outgoing
over a long period of time- must be an observable pattern over a long time, and not that the trait is due to a event- cant describe
t or f- somebodys level of cheerfulness dec for several weeks, has their trait level dec
no- for something to be a trait it has to be stable for a very long time- this could just be because something sad happened in their life
t or f- my levels or neuroticism are not a trait since threy have dec since i was a kid
false- traits can change over time, but the time span just has to be significant like several years
personality traits vs psych characteristics
mental abilities- psych characteristics- not typical was of thinking/feeling/behaving, but show max ability
beliefs and attitudes are not personality traits- focused on a specific thing, not general like personality traits
sexuality- not a personality trait
walter mischel
said that results of personality measures are of limited value for predicting behaviors
some studies showed that behaviors assoc with a trait were only weakly correlated accross situations
used hartshorne and may study to show that personality traits are less important that previously thought
said that individual behaviors depend heavily on the situation, not personality
hartshorne and may study
this was the study that walter mischel used
looked at childrens tendencies to be honest, altruistic, and self controlled in diff situations and accross time
only showed a weak tendency to be altriustic/honest/self controlled between situations and over time
led researchers to doubt that personality traits existed or could be used to predict behaviors
critiques of walter mischel
many said that when you aggregate behaviors over time, it does show consistency between personality traits and their predictive power on behaviors- said that perosnality traits are real and useful for predicting behaviors after all
he did several more studies, but the common critique is that he fails to aggregate the data he collects and thus doesnt identify any of the exiistent correlations between behaviors accross time and situations that demo perosnality traits
a conscientiousness scale asks “i always arrive on time” and “I never keep my room clean”- which of these is negatively keyed
the i never keep my room clean one is negatively keyed- asks about somehting that is opposite ot the trait being expressed so it will balance out
t or f- if i am outgoing in school, im also likely outgoing at home
false- its hard to predict behavior based on perosnlaity traits between 2 situations, since behavior depends heavily on the situation (maybe im scared of my parents and am introverted at home)- the predictive value of personality traits is for predicting behavior accross lots of situations- if i have the trait of outgoingness, im likely outgoing in many situations- you have to aggregate behavior to see if it is a perosnlaity trait or not
2 most common methods to assess personality
self and observer reports
structured personality inventories
how do they inc reliability and content validity
each item gets its own scale that somebody can answer along- this inc relliability and content validity
structured- people get a limited number of possible responses
(would be unstructred if it allowed people to respond freely)
most assess several diff personality traits
each trait is assessed with its own scale, which has several items- this inc reliability and content validity
ie. Consider as an example a scale that measures the trait of intellectual curiosity: Such a scale might contain items describing interests in history, in geography, in literature, in the arts, in life sciences, and in physical sciences. This scale would probably show good reliability, because the average response to these items would likely be a good indicator of the element that is common to those items (presumably, intellectual curiosity). This scale would also have good content validity, because the items describe a wide array of interests, all of which are intellectual interests.
negative keyed/reverse coded items and what is acquiesence
many agree responses are typically assoc with inc scores of the trait- ie. if you agree with “i often worry” your neuroticism score is higher, but sometimes agreeing with a statement dec the score
this is to control for the fact that diff people have diff tendencies to agree vs disagree with diff things- on a scale, many people find a few items they are stuck between 2 answers for, and their general tendency to agree vs disagree decides which way they swing— reverse key items control for this
tendency to agree vs disagree is acquiesence
By having roughly equal numbers of non-reverse-coded and reverse-coded items, the tendency to agree or disagree with statements in general is balanced out, with the result that higher scores on the scale really do indicate higher levels of the trait
3 strategies for constructing a personality inventory
empirical approach
factor analytic approach
rational approach
empirical approach- describe it
psych records a huge amount of possible behaviors/thoughts/ratings that could describe a perosnality trait, and then assesses people on these items as well as info unrelated to the items.
ie. to id. create a personalty inventory looking at achevement orientation, a psych may get info about peoples gpa and then select the items they created which have the highest correlation to a high gpa
not interesed in the content of an item- if we are assessing neuroticism, and decide that neuroticism can be measured based on cortisol level, annd find that people who have the highest cortisol also like the color green, then we would keep the question do you like green even though this seems like a stupid question to have in a personality inventory- this may be good because it makes it hard for people to try to fake their answers to get a certain result since iits unclear what scores the items are assoc with
4 problems with the empirical approach
may not generalize to other traits
strong association may not generalize between samples of people- just because an item shows strong assoc with a personality trait in one sample of people, doesnt mean it would show this assoc within all samples
sample has to be very large- at least a few huundred people- to acoid having selected items be related to the trait by chance
very different sets of items may be decided on depending on who the sample is made of
we will select different items based on which variable we chose- if we used hours spent studying, not gpa, as the basis for selecting items for the trait conscientiousness, then we may have wound up with a very different set of items
low face validity is a potential concern
how many traits does the neo-pi-r measure
2 ways to dec problems with the empircial method
measures 30 traits- 6/factor
1. use multiple samples of individual
2. select items on the basis of their correlation with several indicators
items can be selected on the basis of empirical relations that are observed within several samples of individuals
select items based on their correlation with several indicators of the trait, like gpa and hours spent studying
may be difficult to do these- hard to get large samples and expensive to get so much data
factor analytic strategy
psych starts with a large and diverse pool of items like empirical strategy, and administers them to a large group of people. then tries to id. groups of related items, so that each groups measures a different trait
helps sort correlated items into the same category/factor, and puts uncorrelated items into diff categories/factors
allows us to find out what personality trait is measured by each of the factors, and which items belong to each factor so that these items can be used to form the personality inventory
For example, imagine a very simple case in which the factor analysis shows only two factors, one of which contains items describing “risk-taking” behaviors, and the other of which contains items describing “energy level” behaviors. In the factor-analytic approach, the psychologist would select the items that clearly belong to the risk-taking factor and the items that clearly belong to the energy level factor, and would use those two sets of items to measure those two traits.
empirical vs factor analysis
in empirical, psych begins with a clear idea of which traits they want to measure, but in factor analysis the identity of the traits to be measured is completely based on what factors wind up being formed
rational strategy, and 2 ways we decide which of the items are best
this technique can also be appliied to an _______ pool of items
writes items specifically for the purpose of assessing each trait that needs to be measured. process of writing items to measures traits is done rationally in the sense that the psych tries to produce items that are relevant to the trait in question. then try to decide which items are best- can be done by asking experts their opinions, and to rate each item, or by administering the test to a large group of people and keeping items which are most cloely related to one another and based on how broad the items are (may try to keep items with dec correlation if they capture aspect of the trait that none of the other items can)
(can also be applied to an existing pool of items- psychologist would consider all of the items in such a pool, and select those that seemed theoretically most relevant to the trait)
empirical vs rational strategy
empirical- chooses items based on how correlated they are with an outside variable which is an indicator of the trait
rational- chooses items that are strongly related to one another
limit of rational approach
scales can only be as good as the sets of items the psych had written to measure the traits
items of rationally constructed scales may be so clearly relevant to their intended traits individuals can easily fake their way through the test
between emprical, factor analysis, and rational, which is the best strategy
several studies have suggested that rational is most reliable and valid, but one study showed that there is minimal diff between them
rational approach is much simpler and easier to implement
today, we msot often use the rational approach, or use several strategies in combo with each other
how can we verify results we gget from self reports
via observer reports (using the 2 together can also inc accuracy)
how to eval content validity of observer reports
correlation levels for people who know eachother well vs less well
examine the correlation between self reports and observer reports for the same trait
typically show high levels of correlation- high convergent validity (about .60 when they know eachother very well- ie. spouses and close family)(if they only know eachother moderately well, its about .30)
discriminant validity is also high to support the validity of scales- self rating on one scale is typically minimally correlated with observer ratings on another scale
alternative explanations for the high correlation between self reports and observer reports, and how do we test these
occurs because people develop a shared opinion about their personalities, but not because these opinions are accurate (test by using 2 sources of observer rating who do not know eachother to eval accuracy of self report- all 3 reports should have high convergent validity- if the observers dont know eachother, they cant agree on the behavior via previous discussion)(research study looking at this shows that the convergent validity is the same whether or not the observers have met eachother- the data is an accurate representation of personality traits)
how valid are personality inventories (how well do they predict behaviors) (give a number for both self and observer reports)
self reports have some validity, with an avg correlation of about .30, and observer reports have a slightly higher correlation of .35. (may be slightly more valid via observer, not self, reports)
averaging the reports will inc validity more than either can alone though
t or f- observer reports show inc vlaidity when done by somebody who doesnt know the participant well, so that they are less biased
false- the highest validity we can get from observer reports occurs when the observer is somebody close to the participant
biases in self reports and observer reports
some self reports, and some observer reports, do show biases where they are either overly favorable or overly unfavorable in their reporting
typically, the amount of distortion is small as long as the inventory is constructed properly
can dec bias if we use both self reports and observer data together
what does the h factor stand for, and what does it impact
the honest- humility factor of personality
(one of the 6 personlaity factors from the hexaco model)
h factor impacts…
approaches ot money, power and sex
odds of committing a crime
certain political and religious attitudes
choices of friends and spouse
big 6 vs hexaco
big 5 used ot be the leading model but this doesnt capture all of the dimensions of personlaity that including the H dimension can
what is the big 5 model
every perosnality trait, like absent mindedness to kindness to excitable, could be grouped into one of 5 categories or FACTORS- knowing a persons level of the big 5 could tell you everything about their personality
supposedly tells us the menaing of perosnality- by id. common element of the traits in each group, researchers could gather clues about what causes perosnality differences and why those differences matter
5 Factors:
extraversion
agreeableness (gentle vs harsh)
conscientiousness
neuroticism
openess to experince (creative vs conventional)
represent 5 groups of traits, not 5 types of people
inc ability to do systematic research on personality psych
developed a questionairre that measured the big 5 accurately- paul costa and robert mcrae
where did the big 5 model come from (list the steps)
costa and mcrae created it, but they didnt invent the tratis
the 5 factors had been established through a study of hundreds of different personality traits and how they related to one another
steps to discovering the big 5:
generate a lost of common traits- went through the dictionary and selected all personality descriptive adjectives they could find
measured people on the personality traits they identified (ask people to rate themselves in terms of the trait from 1-5)
determine how correlated each trait is with other ones, and then find main gorups of correlated items using factor analysis- they started to observe that no matter what sample they used to do a factor analysis on, they always wound up with the same 5 factors to gorup the traits into
for most perosnality traits, the number of people above and below each trait are…
about equal- same number of people who are high in extraversion is equal to the number of poeple who are low on extraversion
magnitude of correlation and meanning
small correlation- .10
medium- .30
large- .50
a correlation above .70/below -.70 is usually when the traits are extremely closely linked, or when we are measuring the same trait (remember both pos and neg sign of high magnitude can show convergent validity)
describe factor anlaysis
a stat technique that soorts traits into gorups accoridng to the correlations among the traits. id. traits that correlate with one another and puts them into the same gorup/factor
puts uncorrelated traits into different factors
each factor represents…
some influence that makes its traits correlate with one another
a factor can include traits that are ___ with other traits in that same factor
negatively- this means the factor has 2 opposite sides/poles
means that 2 opposite traits can still involve the same underlying dimension, and thus belong in the same factor
(ie. fast and slow, despite being opposites, still belong in the same factor because they involve speed)
2 problems with the big 5 model
done in english, so it was unclear if the traits could transfer cross culturally
based on a short list of traits- if we could analyze more traits, more than 5 factors may be found
however, studies trying to address these questions actually wound up finding the big 5 again and again (but these studies only looked at languages in europe- still no research on on western languages)
when prof did research on if the big 5 transfer to no western languages, he found…
that in korea, the same 5 factors seemed to emerge
however, when they asked the computer to do a factor analysis on more than 5 groups, it found that the results for 6 factors were large and easy to interpret- suggests that there were actually 6 personality factors (found that this 6th factor was also found in french, and in english)
this led to the HEXACO model- honesty/humility, emotionality, extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, openess to experince
low H, high E- give an example of hwo they manipulate people
low honesty/humility, high emotionality
inc fear, less status driven
typically treat people in a kinder way than low h low e
may try to exploit others, but in more subtle ways to avoid confrontation
sometimes described as a weasel or coward
may use their own weakness/exaggerations of their weakness to inc how many benefits they get from something (ie. somebody who exaggerates how sick they are to get extended time on their deadline for a assignment)
low h low e (what 2 things determine risk taking)
low h low e isnt necessairly enough to predict status driven risk taking- ____ and ____ factors also play a role
common scam assoc with this
risk taking is det by levels of greed and levels of fear
low honesty/low humility + low emotionality are high in greend and low in fear, which leads to high risk taking
status driven risk taking- likely to be tempted by high paying but dangerous jobs, people who get into street fights over status
men tend to be much lower in E and slightly lower in H- more low H low E are men than women
low h low e isnt necessairly enough to predict status driven risk taking- social and cultural factors also play a role- in a winnder takes all society like strong inequality, or is driven by status like socieities with polyyamory, then people are more likely to exhibit low h low e
cold and callous, low empathy and low pity
dont worry about hurting others in the pursuit of their goals
ie. sweetheart swindler scam- swimdler befriends an old man, pretends to fall in love with him, takes all his money, and leaves- not worried about the legal consequences of such an act (low e/low in neuroticism) and low in humility and honesty
low H, high x- do we often see them in positions of power
low honest/humility and high extravserion
seen with narcissists
see themselves as born leaders and think they should be the center of attention
want power and feel entitled to the things that they want
manipulative and crave status
can be very charismatic and attract followers
very often seen in positions of power
can eventaully be resented by the people around them
very seductive and inc sexually active- more likely to use sexual inneundos in their speech, wear revealing clothes (these behaviors dec as they age)- high exhibitionism
in sexual relationships, men often jsut want sex and women want wealth and status that the sex can bring
the international personality pool
not a perosnalty inventory, but a questionairre
has about 2000 items, annd has been developed sicne the 90s
the items are grouped into scales which can be used to assess diff aspects of perosnality, like the big 5
can be useful for developing self or observer reports- the nie thing about it is it is not copyyrighted like all the other personality inventoires like MBTI, CPI, etc. and thus can be used in any new research to further psyhology as a discipline
unlike most other, tests, this one will omit the word “I” at the start of the question- ie. instead od i pay attention to details, its pays attention to details
which combo of low h and what is seen with people who others view as stuck up
exploitative, but less charismatic so dec odds of becoming a leader
crave status, but dont necessairly enjoy being a leader- want a reclusive life of luxury
typically seen as stuck up due to a lack of interest in social interactions
which eprosnality combo is most likely to be seen as hypocritical
very difficult to get along with- inclined to manipulate others, and get angry when they dont get their way
very high in aggression and often involved in conflicts, and easily take offence to things
seen as hypocritical
very vengeful, and unlikely to forgive others (even more vengeful when they are also low in emotionality since then they arent concerned about the potential consequences of their revenge)
think people are as selfish as they are,so when they meet someone high in H they often think they are a liar or naive
people who can forgive and forget are high in
agreeableness
what personality combo uses ingriation
low h high a
still greedy and sneaky, but since they are even tempered and easy going they are easier to get along with
dont take things overly persoanlly and are less vengeful
will take advantage of other,s but arent overly upset when others take advantage of them
use ingiration (getting someone to like you so you can manipulate them later on)- allows them to tolerate unlikable people and hold their tongue
fake friendliness and flattery
low h low c
what 4 things are they inc likely to do
make very bad employees
no work ethic (no moral obligation to actually do a good job/try their best) and is very unorganized- little loyalty to employers and jobs
inc odds of stealing from work
inc odds of being involved in criminal activity
seen in psychopaths
inc odds of cheating on spouses (low H is dont feel morally obligated to be loyal, and low C is cant inhibit impulses)
inc odds of having a std, gambling addiction, and substance abuse problem
4 characteristics of psychopathy and define what it is
and what personality traits are assoc with it- CHE
tendency to commit immoral and antisocial acts without remorse
manipulative- low H
impulse and uncontorlled- low C
callous insensitivity- low E
chronic pattern of criminal activity
low H, low C, low E
general theory of crime- what trait does it not pay enough attention to
tries to explain odds of committing a crime based on personality traits, but doesnt pay enough attention to H and only looks at C
what personality type do we see white collar crime with
low h high c
selfish at heart, but control their impulses- think in terms of long term goals, so they are dec likely to break the law
type of people who look for legal loopholes ot meet their best interests
work hard and strive for goals, but its for the purposes of personal gain and not doing something altruistic
if their interests coencide with the interests of the company they are great workers, but when their interests and the companys interests dont align they arent such good workers
like order and strcture, and follow the rules
seen with things like white collar crime- these crimes are likely more harmful than the crimes committed by low H low c
low H high C and a high IQ can inc their odds of reaching a very powerful position that they can then exploit others from
seen with the guards in the standford prison experiment- in real life they had never committed a crime due to high C, but in the experiment their H was low enough that, when coupled with the promise of no consequences for their behavior, they were willing to explloit the prisoners without remorse
carnahan and macfarland- what wee the rates of personlity traits in tthe study
said standord prison expeirment wasnt a result fo the role of a prison guard, but that the people who signed up for the experiment were inc likely to have a personality low in H
experiment where they tested who signed up for a “psych experiment” vs who signed up for a “psych experiment about prison life”- found that peple who signed up for the prison one were below avg levels of H and A, but not overly low in C which means they had been able to contorl their antisocial behavior in contexts outside of the simulation where it might have a negative impact on their wellbeing
which perosnality type takes advantage of people who are different from them
shallow and superficial
interested in money and status
nature is only good for how much we can harvest from it, science is only good for making money, etc.
doing things like reading about philsophy and appreciating art is a waste of time
type of person to want the biggest mansion in the neighborhood
little respect for people who ahve accomplishments on the basis of high O like teachers- if you are so smart, why arent you rich
inclined to explloit others, and cant relate to people who have experiences different from their own- inc likely to take advantage of those who are different from them, but only if they think others wont look down on them for doing it
low h high o
like to show off, but do so with artistic flair
ie. the taj mahal- artistically very impressive but morally offensive when its surorunded by poverty
like to show off how cultured they are, use big words even when they dont make sense
very nonconformist- take pleasure in offending community standards and gaining a reputation for being nonconventional
would be the type to make a very offensive movie about drug use and rape that is supposed to be artistic