Bio 112
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
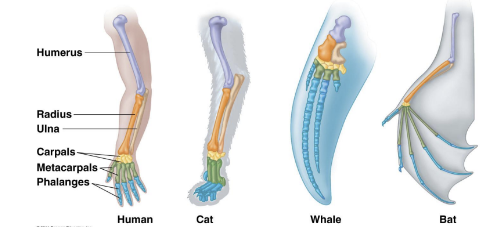
Homology (Homologous Structures)
* structures derived from a common ancestor but may be modified for different functions
2
New cards
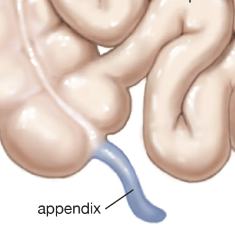
Vestigial Structures
* remnants of ancestral (homologous) structures with no present adaptive function
3
New cards
Cellular & Molecular homologies
* similarity of cell structures, proteins & DNA
4
New cards
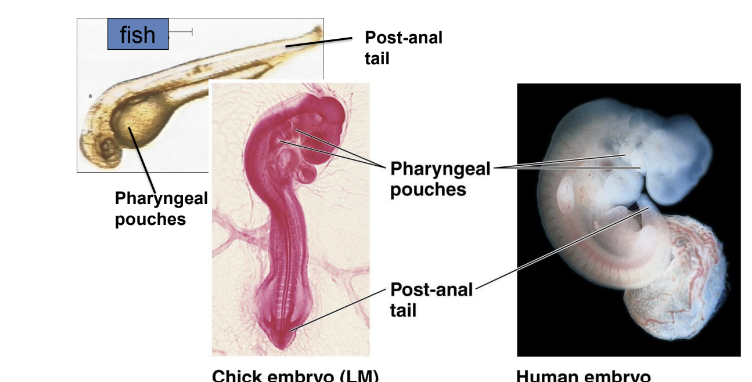
Developmental homologies
example) vertebrate embryos
5
New cards
Convergence
* unrelated species have similar adaptations (analogous structures) under similar environmental conditions

6
New cards
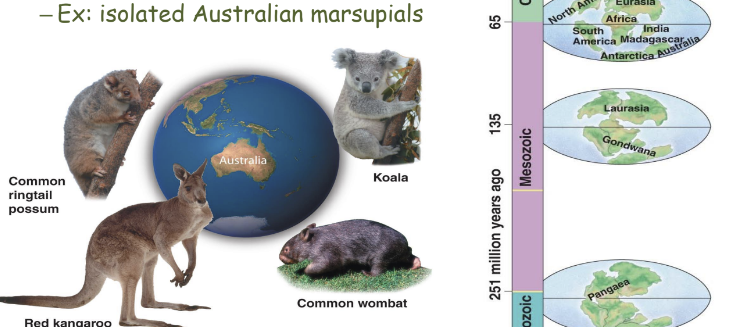
Biogeography
* distribution of species (corresponds to geographic history)
7
New cards
Scientific Theory
* broad, well-supported explanation with rich predictive value
8
New cards
Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
* explains both diversity and unity of life
* accounts for much of form and function
* can predict outcome of environmental change
* accounts for much of form and function
* can predict outcome of environmental change
9
New cards
Apomorphy
* derived characteristic or trait
10
New cards
Plesiomorphy
* ancestral characteristic or trait
11
New cards
Autapomorphy
* a derived but unique characteristic or trait
12
New cards
Synapomorphy
* a derived but shared characteristic or trait
13
New cards
Analogy
* a characteristic that is similar between organisms by convergent evolution, not due to the same evolutionary path.
14
New cards
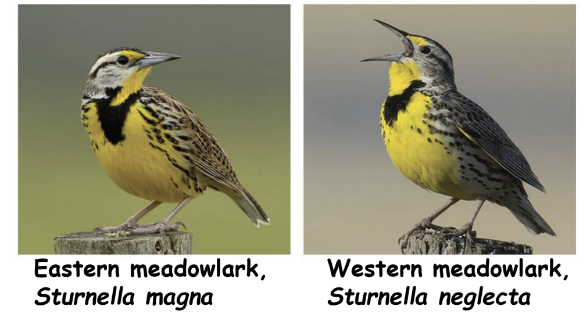
Morphological Species
* smallest set of organisms that look alike
15
New cards
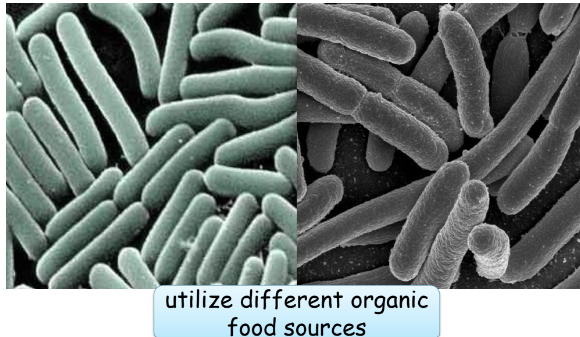
Ecological species
* a set of organisms adapted to a specific set of resources
16
New cards
Phylogenetic species
* smallest distinct set of organisms that share a common ancestor

17
New cards
Biological Species (our default)
* population whose members potentially interbreed in nature to produce fertile, viable young and do not successfully interbreed with other such groups.
18
New cards
Habitat isolation (prezygotic barriers)
* different species never meet b/c of habitats

19
New cards
temporal isolation (prezygotic barriers)
* different species are active at different times
20
New cards
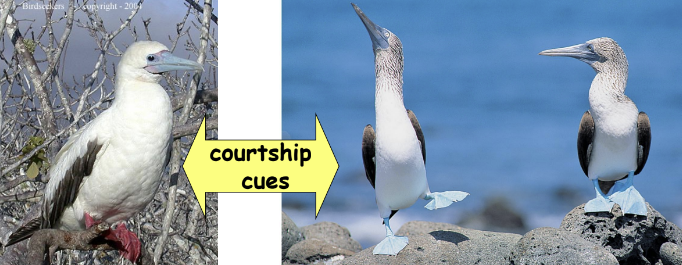
behavioral isolation (prezygotic barriers)
* courtship cues and other behaviors unique to a specie are effective barriers to mating (dances, songs, etc.)
21
New cards
mechanical isolation (prezygotic barriers)
* parts do not fit each other to “hook up”

22
New cards
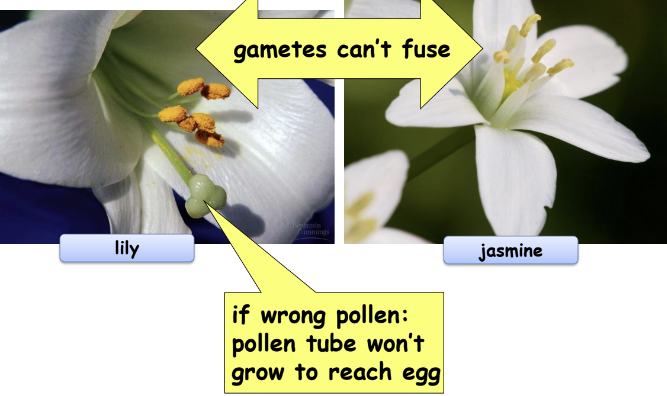
gametic isolation (prezygotic barriers)
* sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize eggs of another species
23
New cards
reduced hybrid viability (postzygotic barriers)
* embryo fails to develop or is weak
24
New cards
reduced hybrid fertility (postzygotic barriers)
* hybrid survives but is sterile ( or almost so)

25
New cards
hybrid breakdown (postzygotic barriers)
* 2nd generation hybrid are feeble or sterile
26
New cards
Speciation
* increases diversity of life
27
New cards
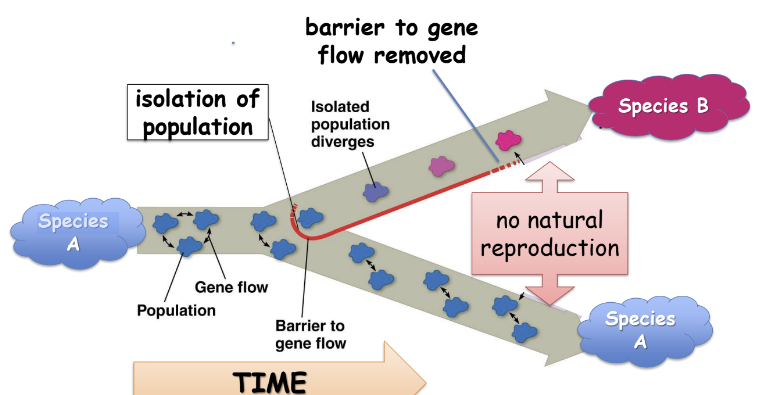
Allopatric Speciation
* geographic separation makes a new species
* physical barriers isolate one population and it diverges genetically due to natural selection and/or genetic drift
* biological reproductive barriers evolve, creating separate species
* physical barriers isolate one population and it diverges genetically due to natural selection and/or genetic drift
* biological reproductive barriers evolve, creating separate species
28
New cards
Adaptive radiation
* from one original species multiple others evolved each with its own distinctive characteristics
29
New cards
Sympatric Speciation
* speciation occurs in same geographical area
* (mating behavior & habitat differentiation)
* (mating behavior & habitat differentiation)
30
New cards
discrete genetic variation
* single gene locus (2 or more alleles)
31
New cards
continuous variation
* phenotypes produced by combined effects of 2 or more genes
32
New cards
Hardy-Weinberg Conditions
* no mutations
* mating is random
* no selection
* very large population size
* no gene flow in or out
* mating is random
* no selection
* very large population size
* no gene flow in or out
33
New cards
Natural Selection
* acts ono-randomly on phenotypes of individuals
* changes allelic & genotypic frequencies of populations non-randomly
* always leads to adaptation of population to current environment
* changes allelic & genotypic frequencies of populations non-randomly
* always leads to adaptation of population to current environment
34
New cards
Genetic Drift
* genetic frequency changes due to random events (often occurs in small populations)
* outcomes: reduces diversity, fixed allele
* outcomes: reduces diversity, fixed allele
35
New cards
Gene flow
* alleles move in/out of population (migration)
* outcomes: add diversity, reduces differences between populations
* outcomes: add diversity, reduces differences between populations
36
New cards
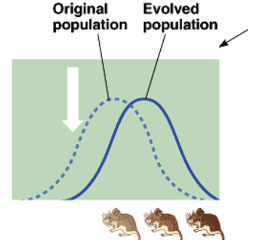
Directional selection
* shifts character’s mean value to one direction
37
New cards
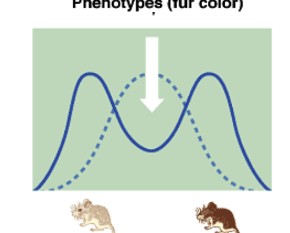
Disruptive Selection (Diversifying selection)
* intermediate (heterozygotes) are less fit than extremes (homozygotes)
* maintains diversity
* maintains diversity
38
New cards
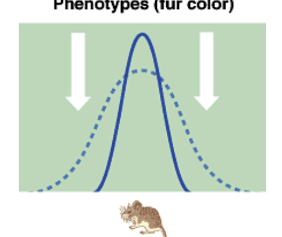
Stabilizing Selection
* intermediate (heterozygote) types more fit than extremes (homozygotes)
* variation reduced
* variation reduced
39
New cards
Sexual Selection
* success based on traits related to obtaining mates '
* leads to sexual dimorphism
* leads to sexual dimorphism
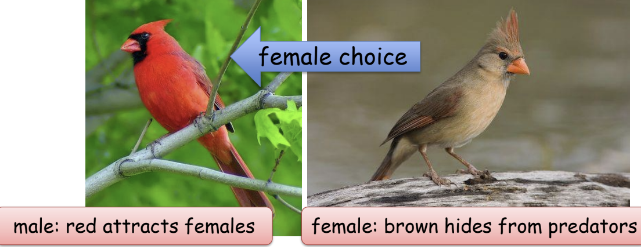
40
New cards
Diploidy
* less successful recessive alleles are hidden in herterozygotes
41
New cards
heterozygote advantage
* selection favors heterozygote over either homozygote, maintaining both alleles
42
New cards
frequency-dependent selection
* fitness of a phenotype decreases as its frequency increases in population
43
New cards
Binomial nomenclature
* scientific name by Linnaeus
44
New cards
Taxonomy
* grouping species together based on similarities & differences
45
New cards
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Daring King Phillip Cut Open Five Giant Snakes