IB Biology - Ecology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Population
A group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the same time.

Community
A group of populations living and interacting with each other in an area

Photoautotroph
organism that uses energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water to carbon compounds

Mixotroph
organism that can obtain nutrition by autotrophic or heterotrophic means
Saprotrophs
heterotrophs that obtain organic nutrients from dead organic material by external digestion.
Chemoautotroph
Builds organic molecules from oxidation of inorganic chemicals

Stats: What is a negative association between species?
If two species tend NOT to occur within the same habitat
Give an example of a reason that leads to negative association between organisms
Driving out or extincting an organism through competition (for same "niche")

Stats: What data must be collected in a Chi Sampling test for Association?
The number of quadrats with:
Both species present
Both absent
One present: One absent
Stats: What hypotheses must be made in a Chi Sampling test for Association?
Null Hypothesis: There is no association
Alternative Hypothesis: There is a association (positive OR negative)

Stats: What happens to your hypotheses is the Chi squared value is greater than the table value?
Alternative Hypothesis (Null hypothesis s rejected)
Does biomass increase or decrease as you go up trophic levels and why? (2)
Decrease --> Loss of carbon dioxide, water and other waste products, such as urea. Also not as much energy for generating living material / growth

What is the main difference between nutrients and energy within ecosystems?
energy is lost ie can't be recycled wheras

Plant --> Rabbit --> Fox
In this example, what is the rabbit in terms of trophic status?
Primary consumer (eats producer)

Why is only 10% of energy (and biomass) passed on from trophic levels? (3)
1) Respiration produces heat
2) Some egested as feces (not assimilated)
3) Unconsumed portions of foods (eg grasses vs rabbits)

Obligate aerobes
require O2 for cellular respiration
Obligate anaerobes
carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2
Facultative anaerobes
Can make enough ATP to survive using using fermentation or respiration. Yeast is a good example
Tropical Rainforest Biome
A biome that is hot, humid with high rainfall.

Desert Biome
a biome that has little or no plant life, long periods without rain, and extreme temperatures; usually found in hot climates

Tundra Biome
Very low temperatures, very little rainfall, mostly as snow. Very small trees, a few herbs, mosses and lichens.

Taiga Biome
coniferous forests that have long, cold winters. the trees have needles instead of broad leaves.

Temperate Forest Biome
A biome that has four seasons with deciduous. trees.

Grassland Biome
land biome characterized by moderate rainfall, fields of grasses, and few trees

Exponential phase of population growth
Rapid increase in population growth, natality exceeds mortality, abundant resources, rare diseases and predators
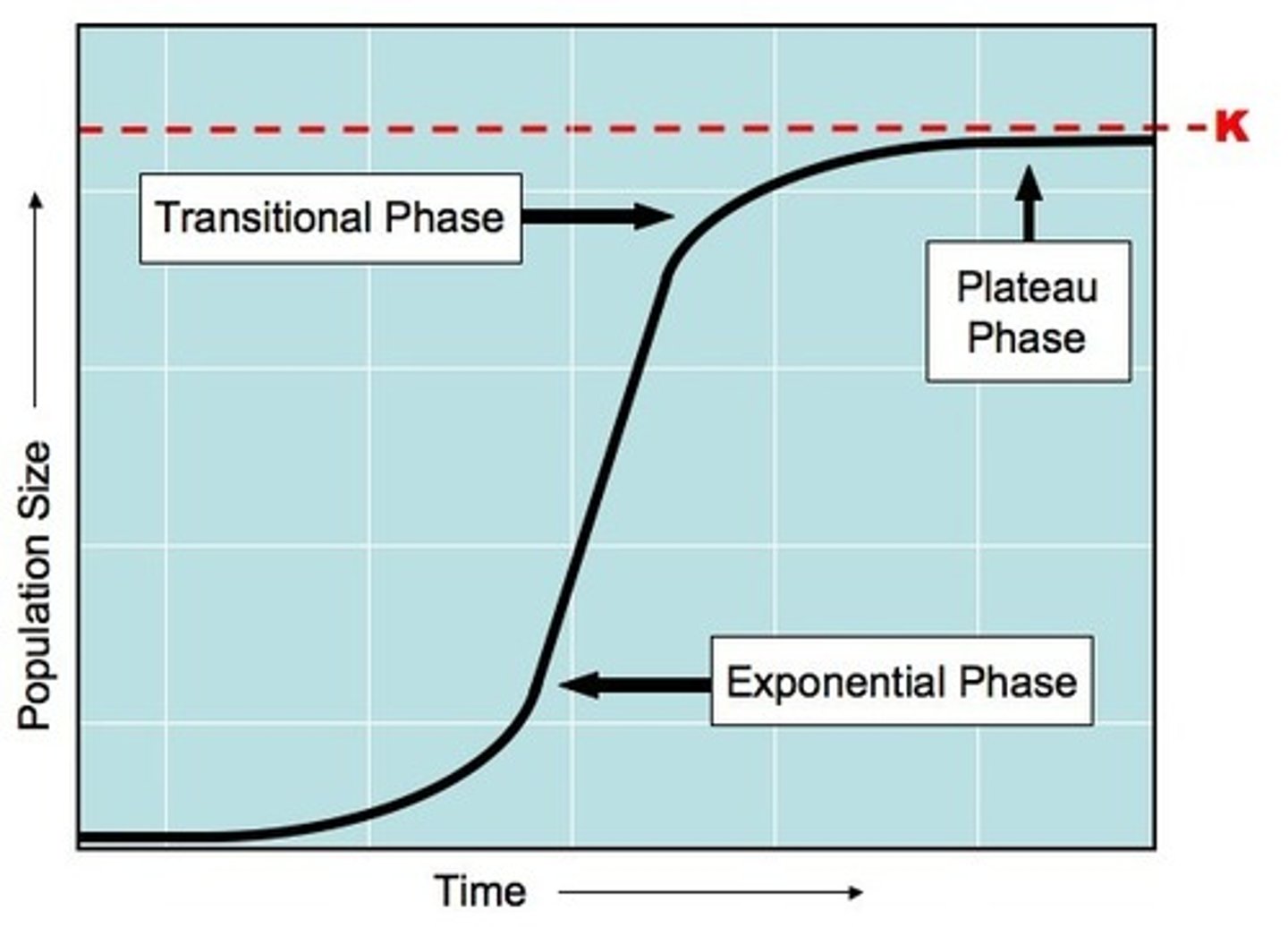
Transitional Phase of population growth
When density dependent limiting factors start to impose TOP DOWN control on the size of the population
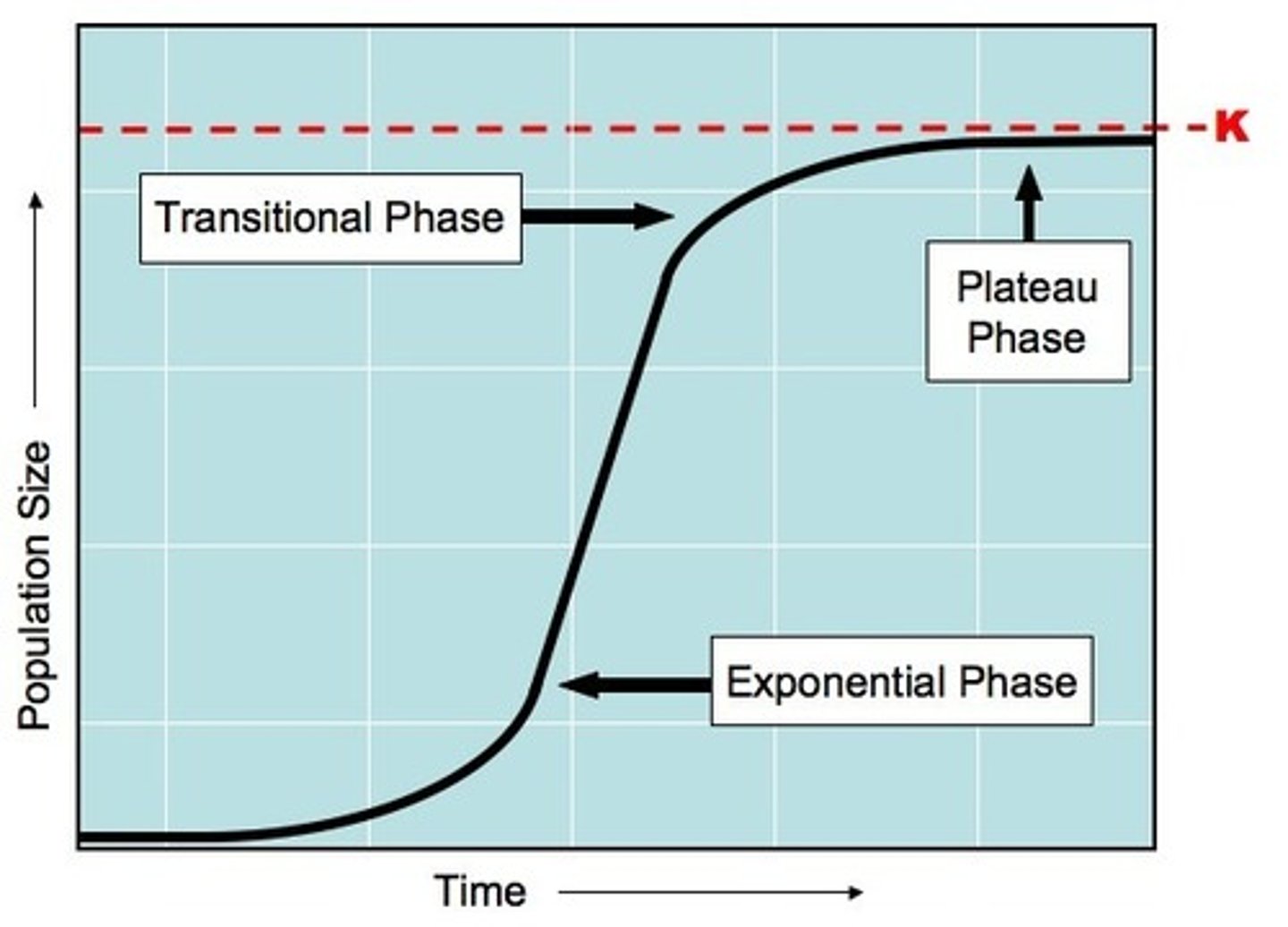
Plateau Phase of population growth
No more population growth, population has reached carrying capacity, limited resources and common predators and diseases
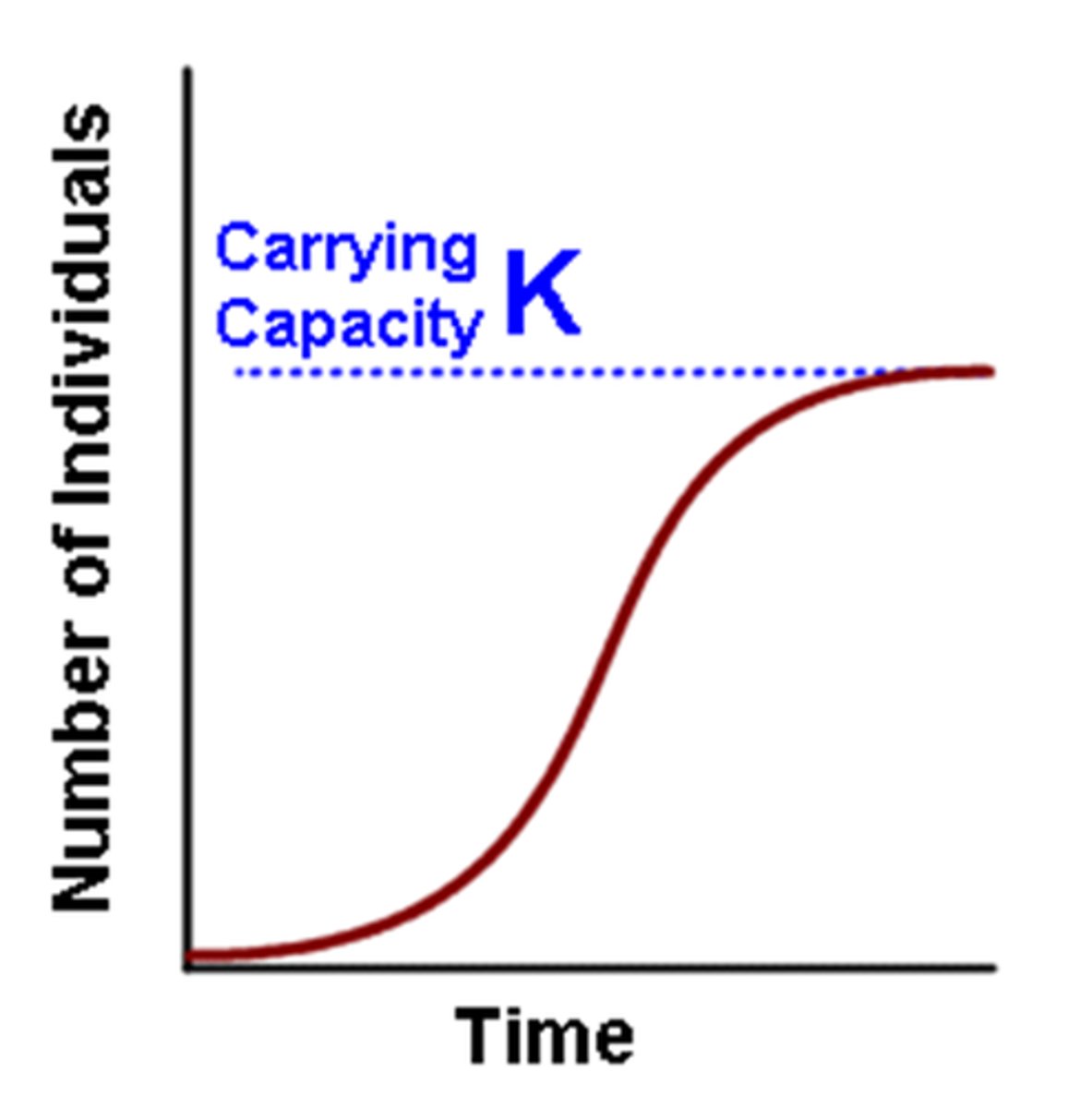
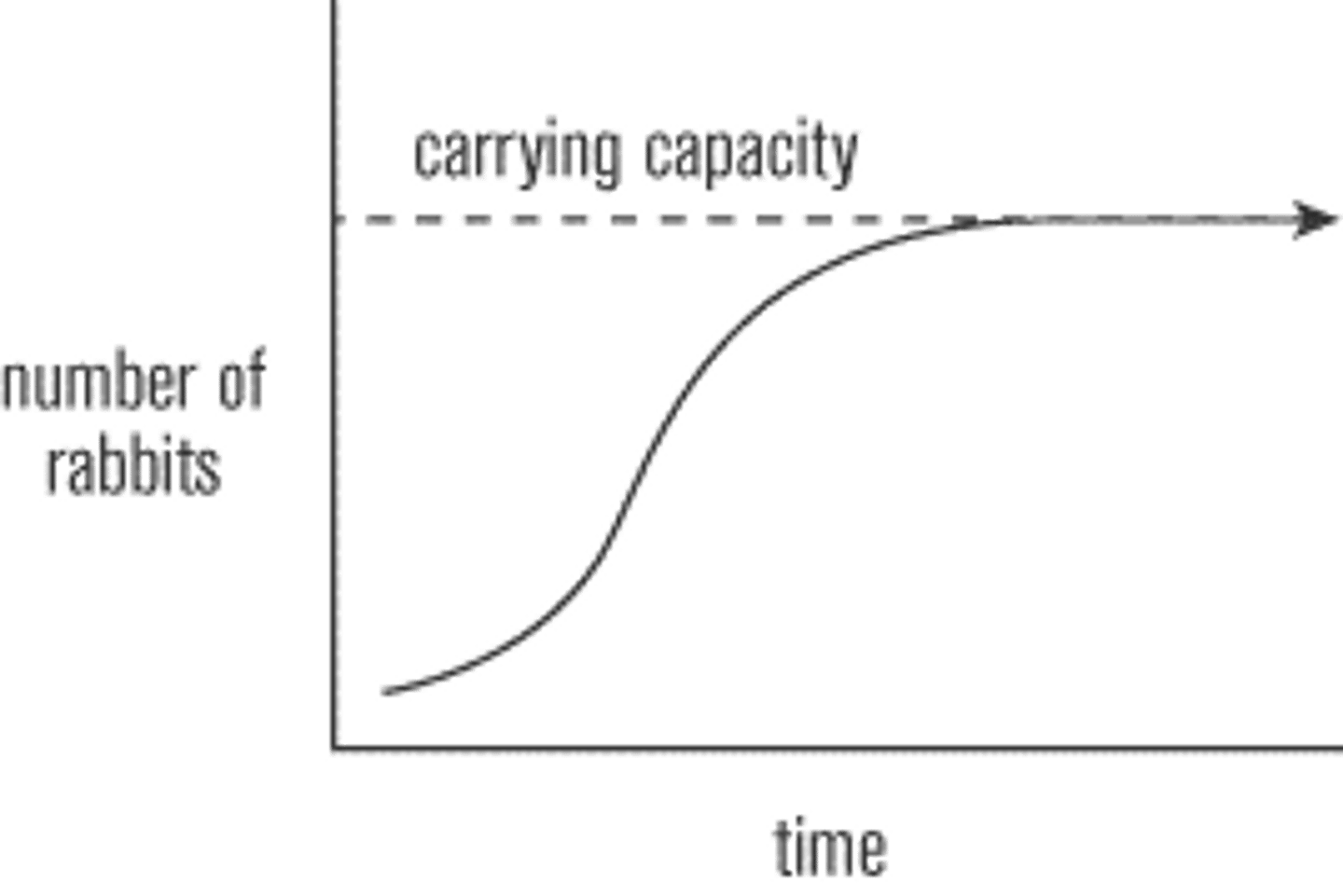
Carrying Capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
Density Dependent Limiting Factors
limiting factor that increases its impact as population density increases. This is a negative feedback, the higher the population goes, the more intense the TOP DOWN restriction is. (disease, food availability, space, competition, predation)

Density Independent Limiting Factors
limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size (temperature, sunlight, pH, natural disasters, climate change, pollution, forest fire

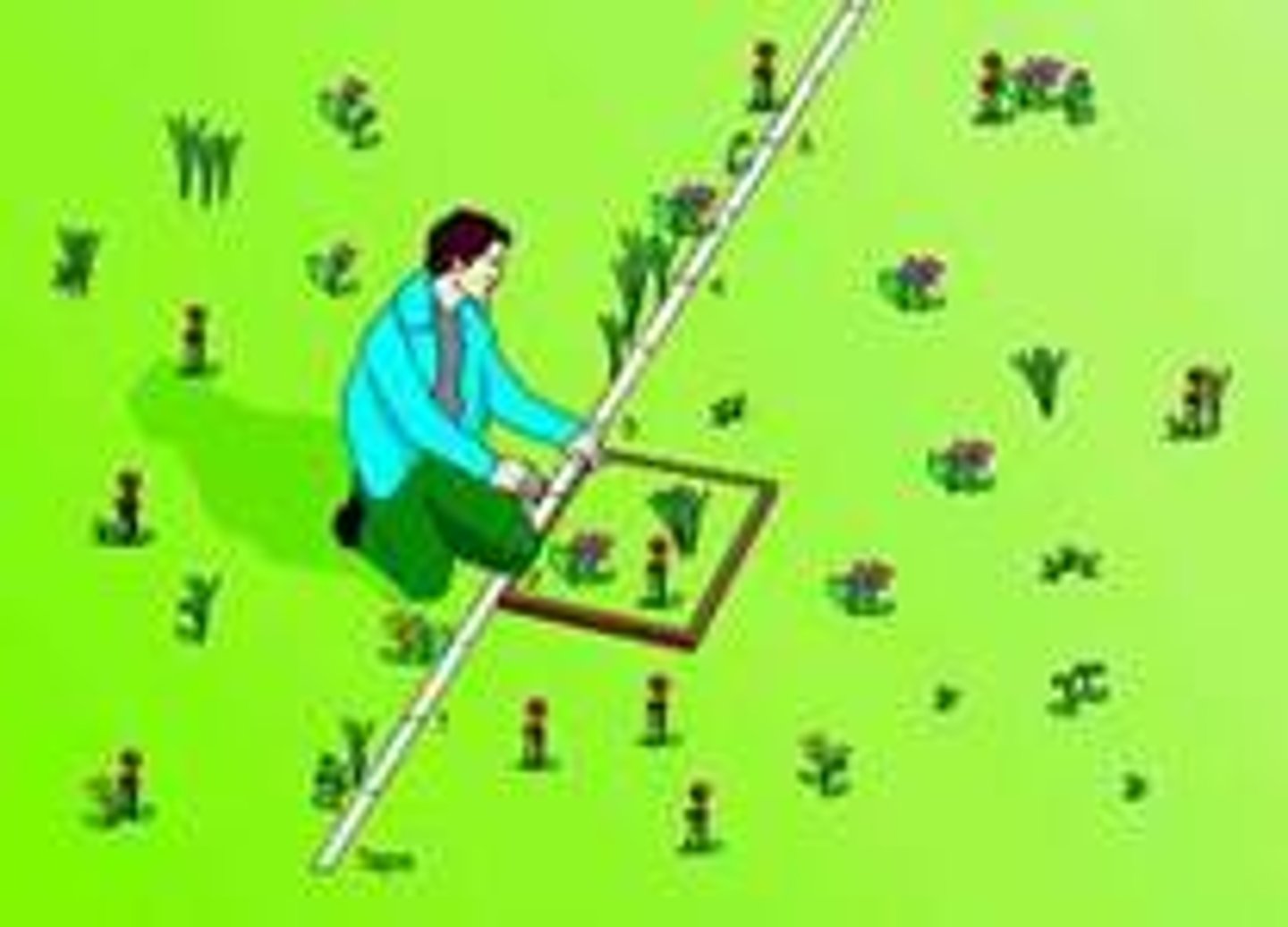
Quadrat Sampling
Using a known small area at random to count organisms within that area. The number of organisms within that area can give an approximate estimate of the population of that particular species in a larger area.

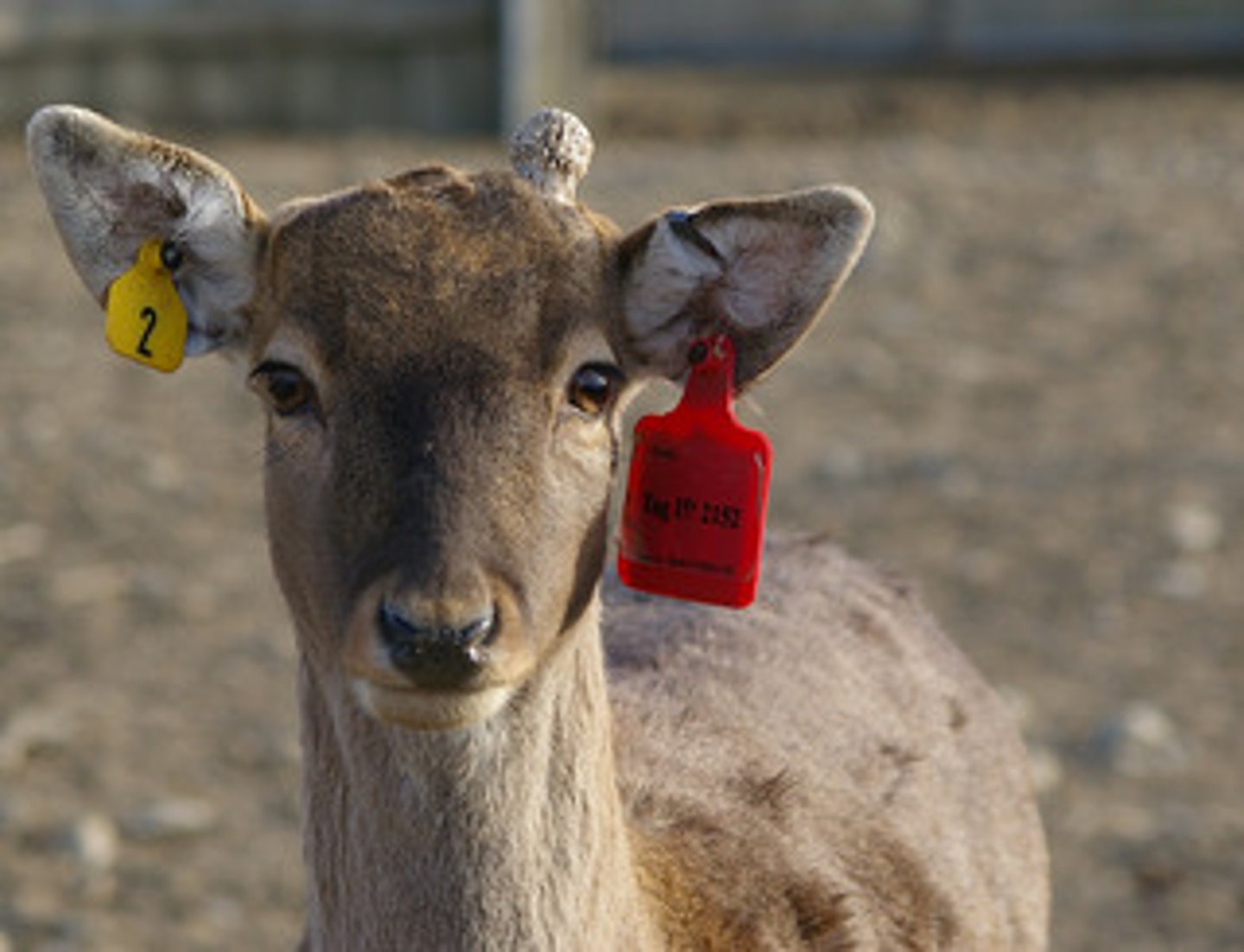
Mark Recapture Method
A sampling technique used to estimate the size of animal populations.

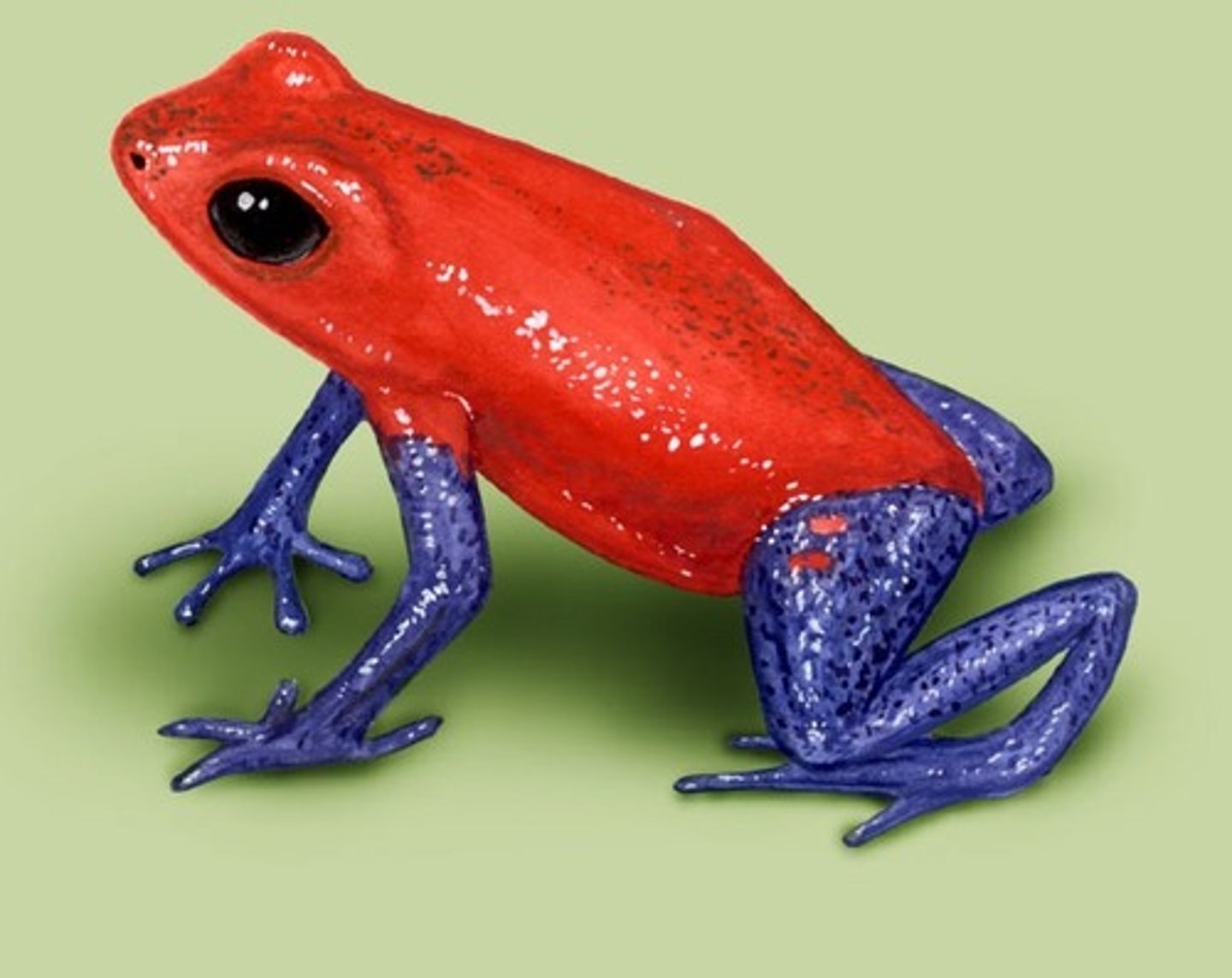
Adaptations of Poison Dart Frog
They have toxins in their skin to kill predators.
Laying their eggs in little pools of water inside leaves to avoid their young being in the water unprotected

Adaptations of Kapok Tree
buttress roots that are above the soil to give the tree support but also to obtain nutrients from the very poor nutrient soil.
Adaptations of the Fennec Fox
Large ears help radiate out excess heat
Active at night to avoid hea
Make very concentrated urine / low frequency of urination
Adaptations of Saguaro Cactus
1. thick stem to store water
2. small number of stomata that open at night
3. deep root
Mycorrhizae fungus & Plant Roots
Fungus increases the surface area of the roots so that plant can absorb more water & minerals
The plant provides carbohydrates made by photosynthesis to the fungus
Nitrogen fixing bacteria & Plant roots
Convert N2 from atmosphere to a form that plants can use.
Bacteria receive carbohydrates from the plant.
Bacteria live in specialized nodules on the roots.
Coral polyps & Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae (small symbiotic algae) provides carbohydrates to the corals
The corals provide protection (calcium carbonate shell) and also CO2 for photosynthesis
Fundamental Niche
The full potential range of the physical, chemical, and biological factors a species can use if there is no competition from other species.
Realized Niche
The niche species actually occupies as a result of competition
Photosynthesis in Carbon Cycle
plants capture CO2 from the atmosphere and use it to make carbohydrates
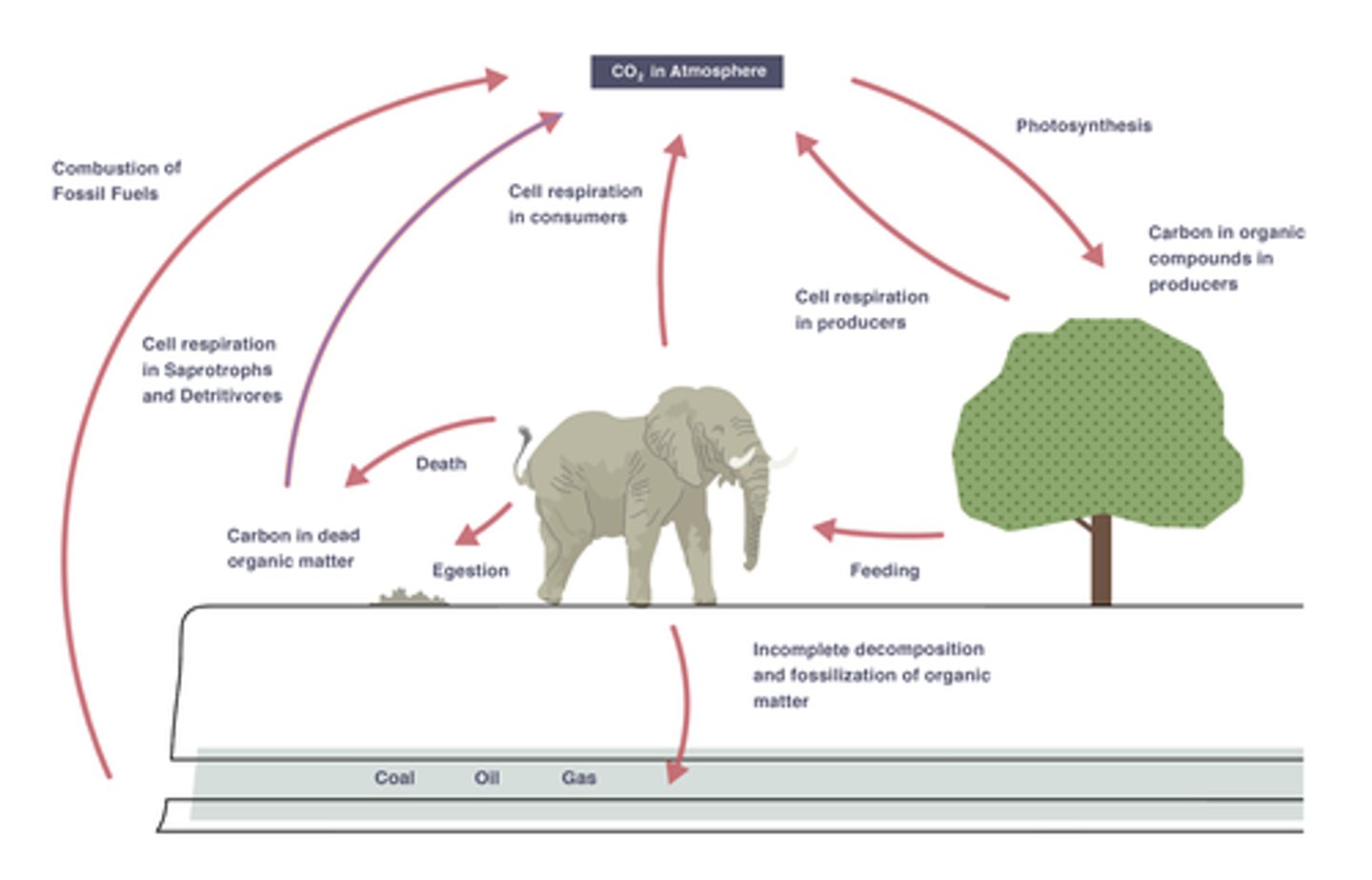
Feeding in the Carbon Cycle
moves carbon in the form of organic (carbon-containing) molecules along the food chain
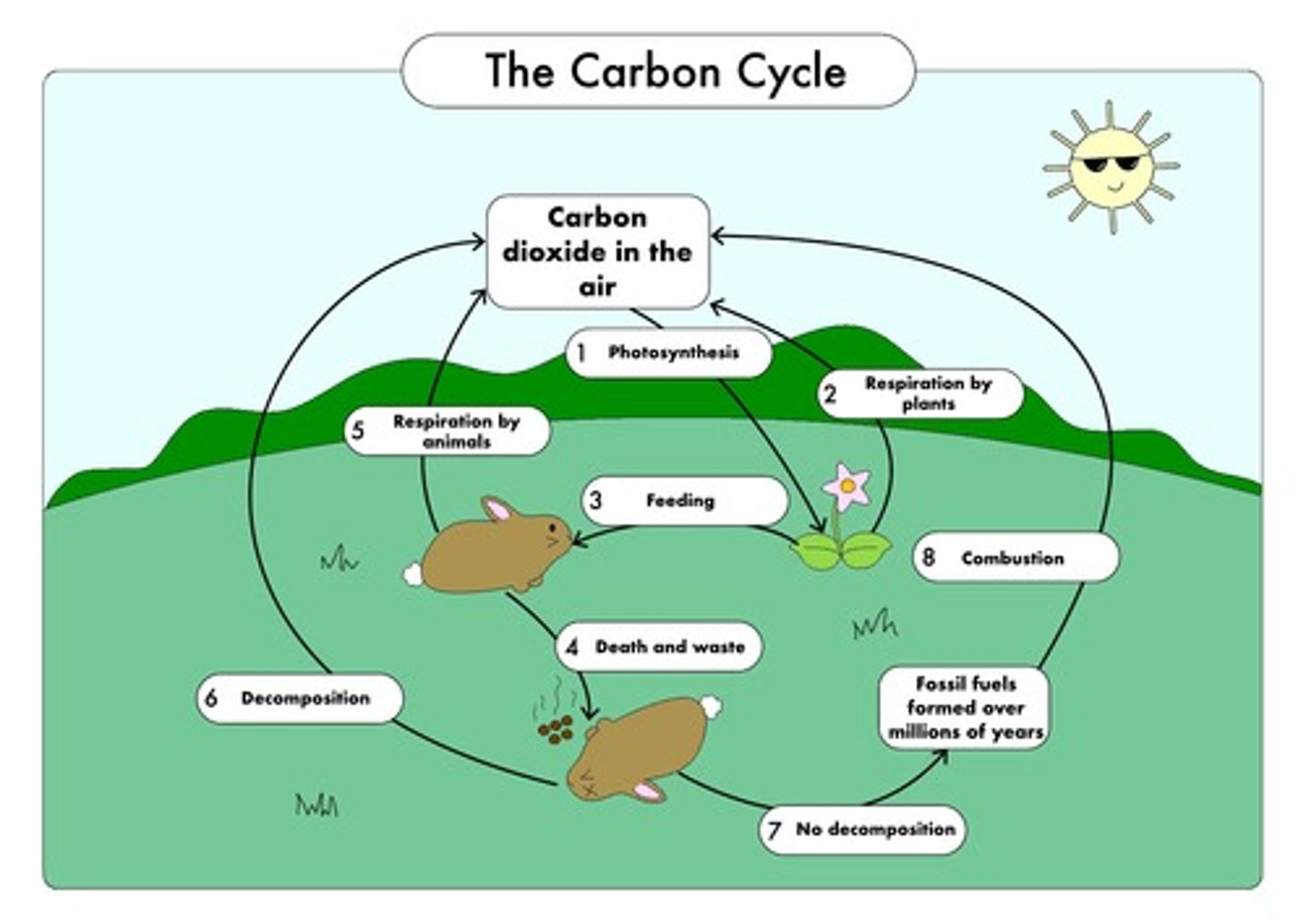
Respiration in the Carbon Cycle
The release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere by humans and animals; taking in oxygen too.
Combustion in the Carbon Cycle
When organic matter, such as wood, oil or coal is burned, carbon dioxide is given off into the atmoshphere