AP geography unit 1:
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Absolute location
The precise point where a place is located on Earth.
Geographic information system (GIS)
A computer system which stores, organizes, and displays geographic data
Latitude
Distance north or south of the equator (line drawn around the earth)
Longitude
Distance east or west of prime meridian
Measured in degrees
Prime medium
Imaginary line drawn from, North Pole through Greenwich England, to the South Pole.
Place
Specific human and physical characteristics of a location
Site
The characteristics of a place (climate, soil type, human structures.)
Situation
The location of a place relative to other places and its surroundings
Toponym
Place name
Time-space compression
The shrinking of time distance between locations because of improved methods of transportation
Distance decay
Decline of activity or function with increasing distance from its point of origin
Density
Number of something in a specifically defined area. (Population density is a number of people per square miles)
Scale
The ratio between sizing of things in the real world and the size of those same things on a map
Projection
The system used to transfer locations from earths surface to a flat map
Diffusion
The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time
Formal region
An area which everybody shares in one or more distinctive characteristics
GPS
A system which determines accurately the precise position of something on Earth through satellite through tracking stations
Remote sensing
Process of gathering data about earth, from instruments far above the planets surface
Spatial analysis
The analysis of geographic data about a certain place
Reference map
Maps designed for people to refer to for general information about place
Choropleth map (thematic)
Uses various colors and shades of one color, to the show the location and distribution of data
Thematic map
A map that shows a particular theme (ex: choropleth, dot distribution, symbols)
Dot distribution map
A map where dots are used to demonstrate the intensity of a particular phenomenon
Isoline map
A thematic map with lines, that connect points of equal value
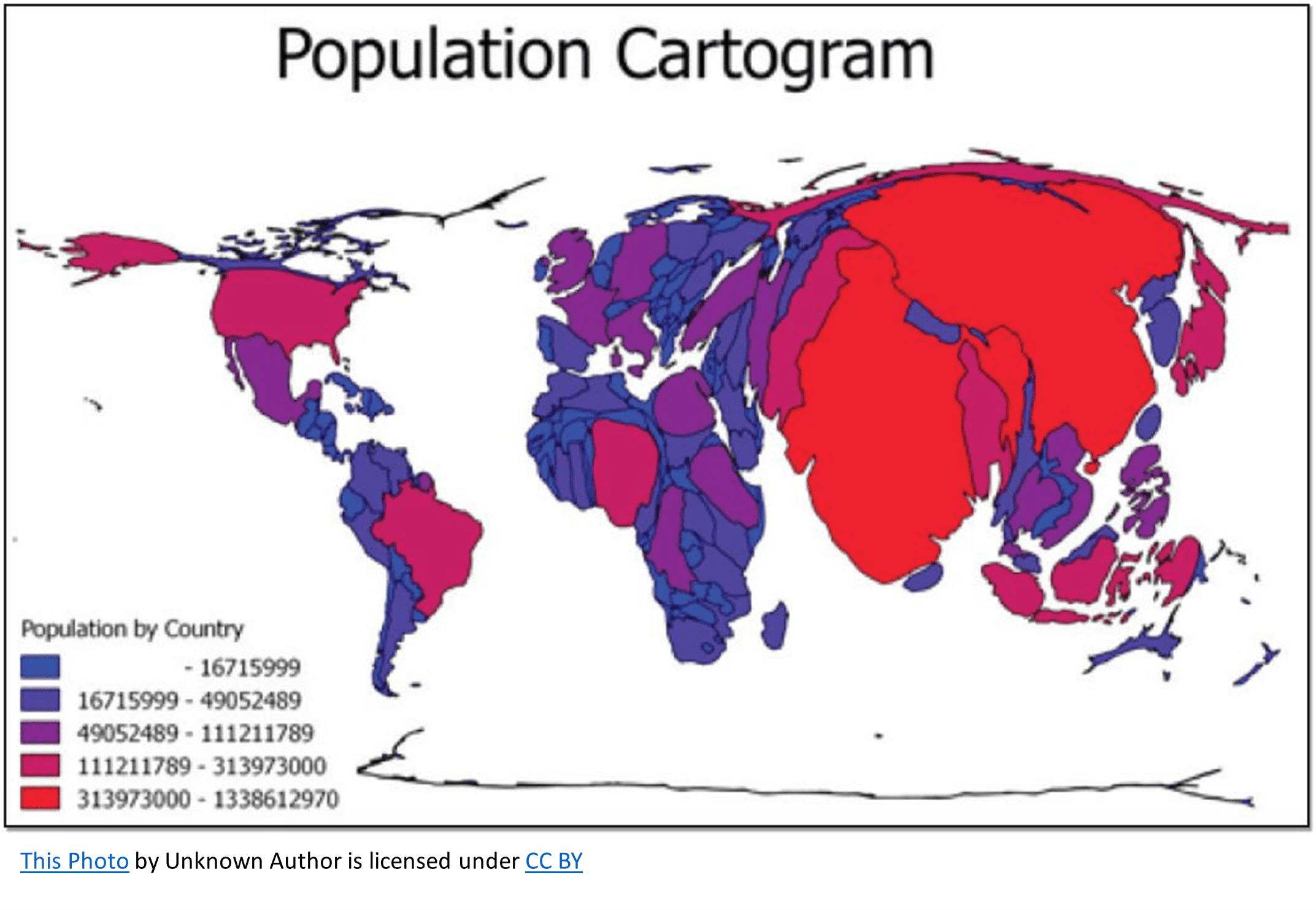
Cartogram (thematic)
The sizes of countries are shown in some specific statistic
Mercator projection
A projection of a map of the world into a cylinder in such a way that all the parallels of latitude have the same length (ex: used for marine charts
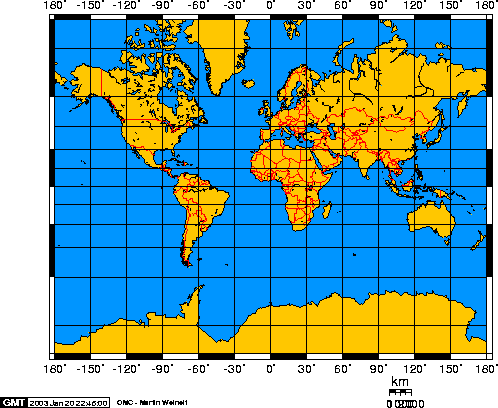
Petars projection
Focuses on keeping landmasses equal in area. As a result shapes are distorted and the map looks unfamiliar to viewers
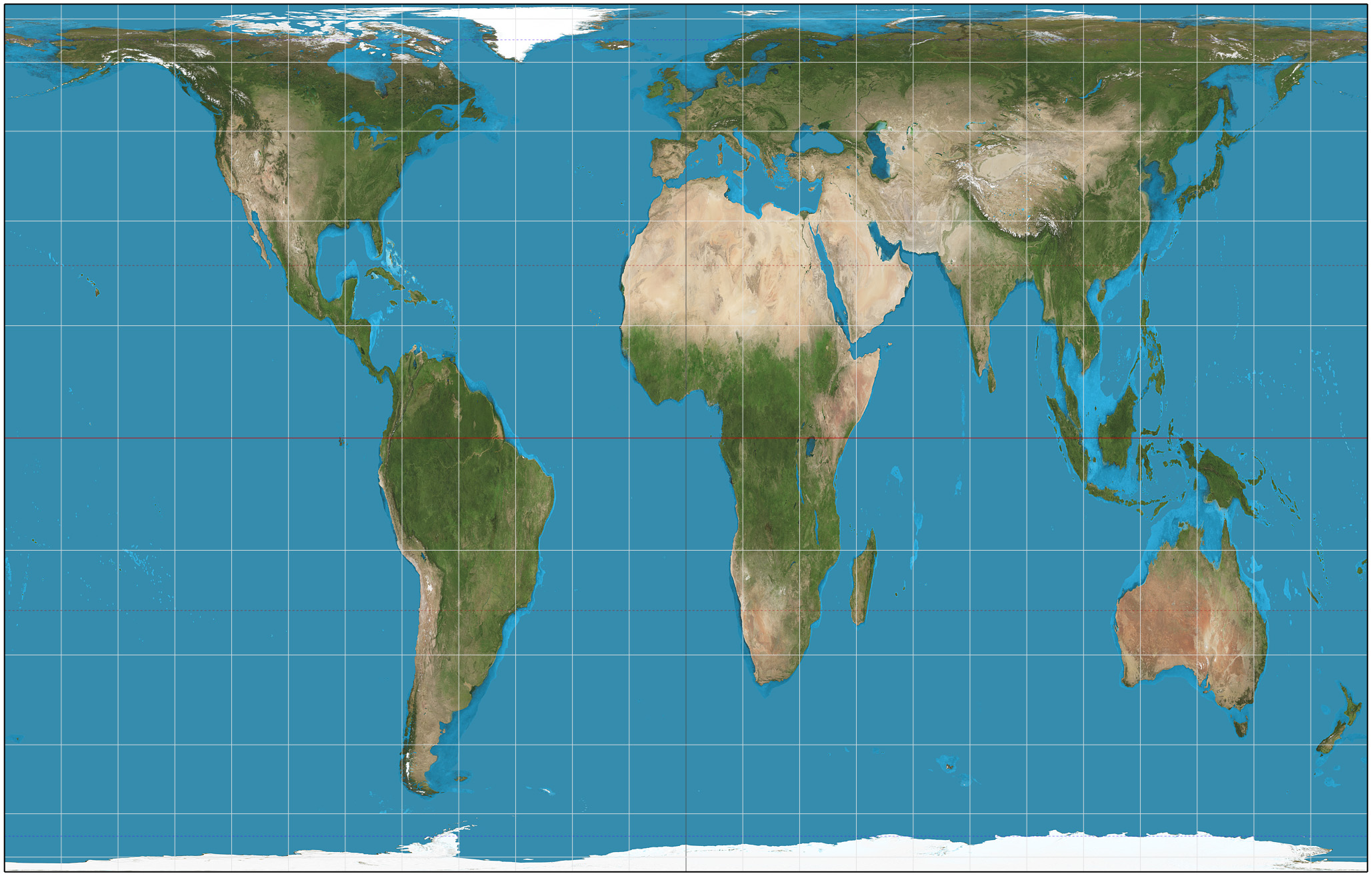
Robison projection
Projection that attempts to balance several possible projection errors. It does not maintain completely accurate area, shape or distance but it minimizes errors in each
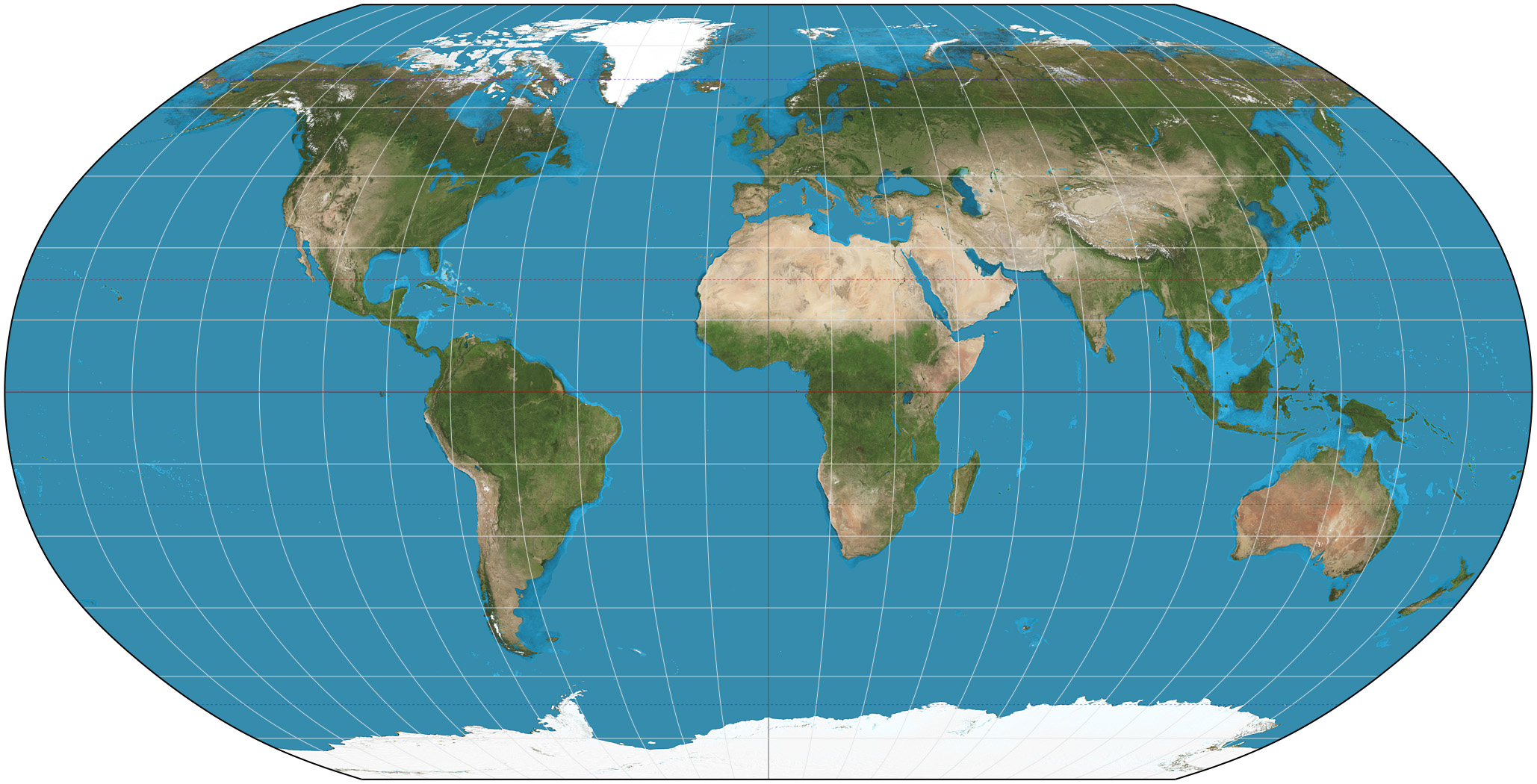
Mental map
Maps that people create in their minds based on experiences or knowledge
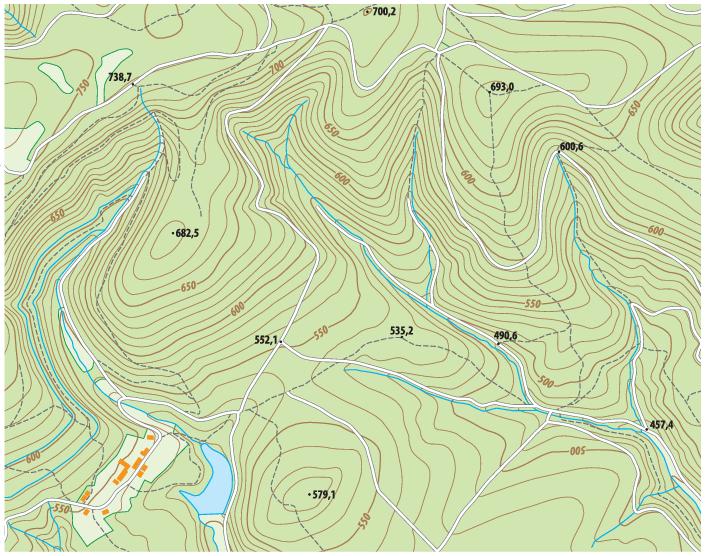
Topographic map
A map that shows the surface features of earth
Possibilism
Viewpoint that people, not environments, are dynamic forces of cultural development
Environmental determinism
The belief that physical environment determines potential for societal development
Sustainability
The use of earths renewable and nonrenewable natural resources in ways that do not constrain resource use in the future
Natural resources
Materials or substances such as minerals, forests, water, and fertile land that occur in nature that can be used for economic gain
Large-scale
Depicts a small area (such as downtown Iowa) with great detail
Small scale map
A map that shows a larger area without much detail
Clustered
Gathered closely together in a group
Land use
Various ways humans use the land, such as agricultural, industrial residential, or recreational