week 05
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Last updated 1:16 AM on 4/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
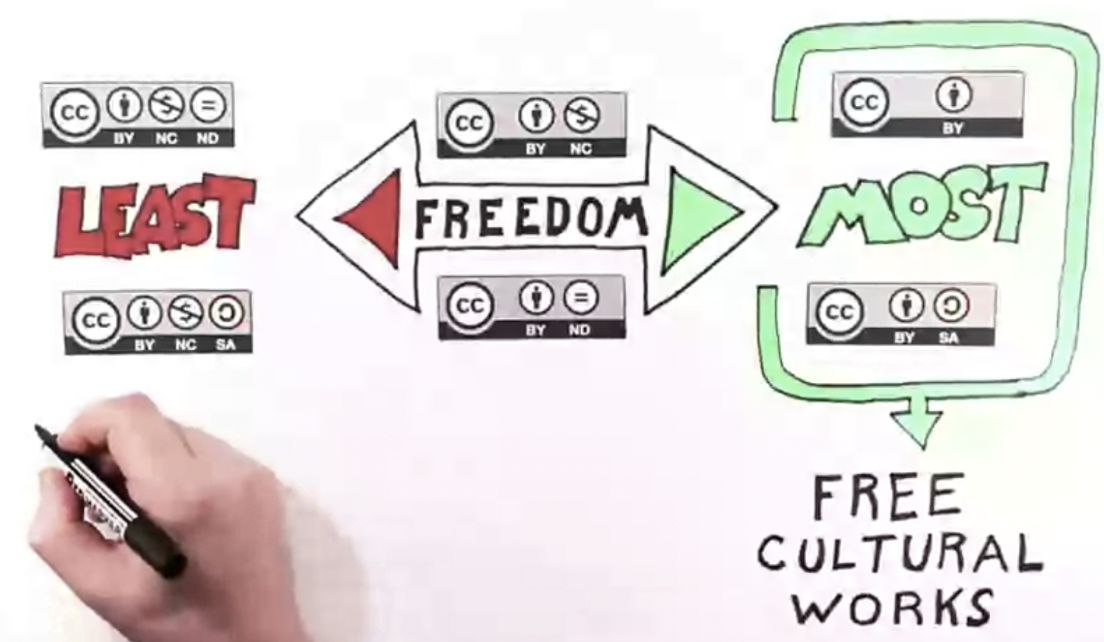
creative commons
* provides free licensing tools
* allows others to use your work
* allows others to use your work
2
New cards
creative commons: attribution
acknowledgement (only CC that is mandatory)

3
New cards
creative commons: non-commercial
no one can make money

4
New cards
creative commons: no derivatives
cannot change original work

5
New cards
creative commons: share alike
must have all the same license

6
New cards
copyright
* right to control your works of creative expression
* if you created it, you own it by default
* if you design something while working for a company, they own it
* myth: changing 20% of a design= you can use it (WRONG)
* if you created it, you own it by default
* if you design something while working for a company, they own it
* myth: changing 20% of a design= you can use it (WRONG)
7
New cards
what can you copyright?
* anything created that is tangible (drawings, photographs, music, etc…)
* ideas, words, and names cannot be copyrighted
* ideas, words, and names cannot be copyrighted
8
New cards
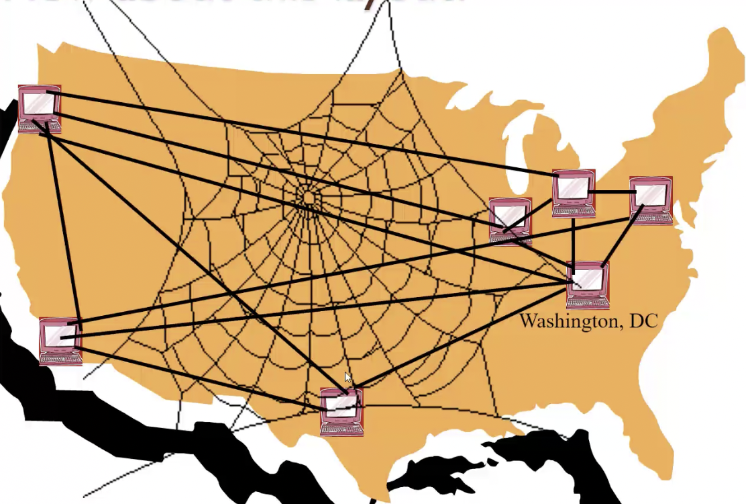
computer network
group of computers that can talk to each other (wired, satellites, etc…)
9
New cards
the internet (1969)
* a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standardized protocol suite (TCP/IP)
* a network of networks
* hardware (not software)
* a network of networks
* hardware (not software)
10
New cards
how the internet works
* uses TCP/IP (no direct line at the outset of a message)
* the idea behind the standard protocol were funding by ARPA of the US department of defense in 1969 (originally called ARPANET)
* opposite of your home telephone where you get a direct line that only you and the other person can use
* 1 connection can break the whole network won’t breakdown
* the idea behind the standard protocol were funding by ARPA of the US department of defense in 1969 (originally called ARPANET)
* opposite of your home telephone where you get a direct line that only you and the other person can use
* 1 connection can break the whole network won’t breakdown
11
New cards
circuit switching
access to one line that nobody else can be on
(ineffective if the line breaks)
(ineffective if the line breaks)
12
New cards
packet
* a small group of bytes consisting of a header (destination/where its coming from) and the body
* often 64 bytes for header and 512 bytes for body
* often 64 bytes for header and 512 bytes for body
13
New cards
protocol
rules for the format and transmission of the data
14
New cards
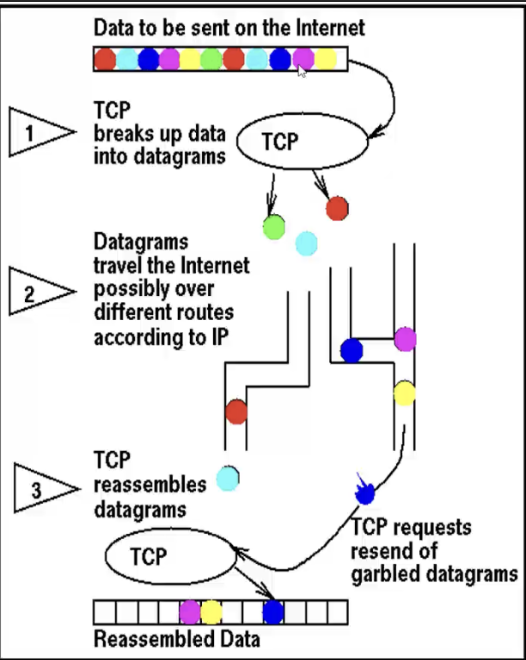
TCP
* packet stops at 1st machine, next machine, and so on until it gets to the final IP address
* packets can take different routes, but all get to the same destination (packet switching)
* packets can take different routes, but all get to the same destination (packet switching)
15
New cards
IP
* like a GPS
* picks a route for a packet which picks the best route
* needs to be able to identify all the machines on the internet
* picks a route for a packet which picks the best route
* needs to be able to identify all the machines on the internet
16
New cards
IP address
* just like your home address (but NOT geographical)
* each machine has its own
* consists of 4 numbers with dots between them
* each number ranged from 0-255 (e.g, 129.100.23.247)
* always 32 bits (newer ones are 128 because we’re running out)
* each machine has its own
* consists of 4 numbers with dots between them
* each number ranged from 0-255 (e.g, 129.100.23.247)
* always 32 bits (newer ones are 128 because we’re running out)
17
New cards
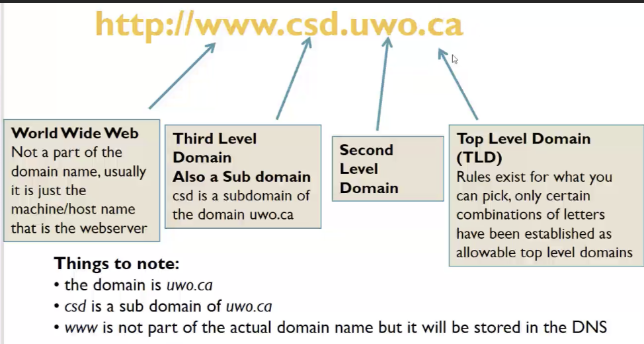
domain names
* numbers are hard to remember (up to 7)
* every machine on the internet gets an IP address
* a DNS (domain name system) maps the domain name to the IP address
* normally a 1-to-1 mapping (not always -- some map more than 1)
* every machine on the internet gets an IP address
* a DNS (domain name system) maps the domain name to the IP address
* normally a 1-to-1 mapping (not always -- some map more than 1)
18
New cards
1973
IP address became standardized
19
New cards
1984
university of Wisconsin decided to name IP address
20
New cards
1985
domain name system is establish
21
New cards
1990
the internet moves beyond the world of the government
22
New cards
when did you start having to pay for a domain name? (year)
1995
23
New cards
when did you pay the NSF $100 for a 2-year domain name
1995-1998
24
New cards
when did domain naming open to private companies?
1998
25
New cards
web server
* contains all the webpages for a company/individual
* web server is stored on the web server machine (host)
* a website is a folder
* web server is stored on the web server machine (host)
* a website is a folder
26
New cards
sub domains
used to organize your web server (like folders and directories)
27
New cards
URL
* established in 1990 by Tim Berners Lee
* points at a web page on the internet
* points at a web page on the internet
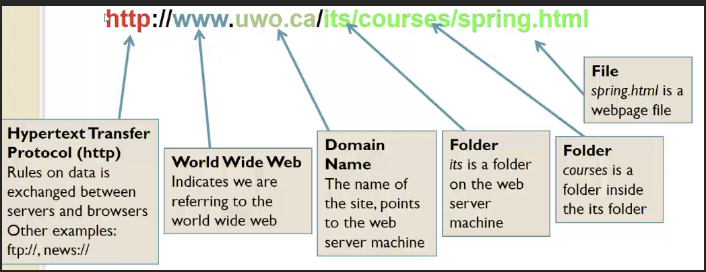
28
New cards
rules for domain names
* each item between a dot is a level
* max 127 levels (125 sub domains)
* each level can be 63 characters long
* the entire domain name can be no more than 255 characters
* must use one of the approved TLDs
* each level must consist of letters, digits, and hyphens
* each level consist of letters, digits, and hyphens
* each level cannot start or end with hyphens and cannot contain a space
* domain names are case insensitive (upper vs lower) -- causes confusion
* max 127 levels (125 sub domains)
* each level can be 63 characters long
* the entire domain name can be no more than 255 characters
* must use one of the approved TLDs
* each level must consist of letters, digits, and hyphens
* each level consist of letters, digits, and hyphens
* each level cannot start or end with hyphens and cannot contain a space
* domain names are case insensitive (upper vs lower) -- causes confusion
29
New cards
top level domain name (TLD)
* an international internet committee that has established the allowable TLDs
* .org, .com, .ca, .net, etc…
* can be registered and restricted (e.g., .Apple)
* Google overtook Microsoft in 2007 as the most visited website
* .org, .com, .ca, .net, etc…
* can be registered and restricted (e.g., .Apple)
* Google overtook Microsoft in 2007 as the most visited website
30
New cards
picking a domain name
* keywords
* be memorable
* avoid hyphens
* .com first (.ca second option)
* keep it short
* kill procrastination (somebody else might take it)
* be creative
* know the rules
* testing (tell your friends and see if they remember)
* learn from monopoly (buy similar domain names)
* which online realtor to use (GoDaddy, etc…)
* be memorable
* avoid hyphens
* .com first (.ca second option)
* keep it short
* kill procrastination (somebody else might take it)
* be creative
* know the rules
* testing (tell your friends and see if they remember)
* learn from monopoly (buy similar domain names)
* which online realtor to use (GoDaddy, etc…)
31
New cards
why not to host your own website
* software is expensive
* continual connection
* technical configurations
* support/server maintenance
* continual connection
* technical configurations
* support/server maintenance
32
New cards
ISP (internet service prodiver)
* access to the internet
* provides user account, email address, web space to host/hold your website
* provides user account, email address, web space to host/hold your website
33
New cards
things to look for in an ISP
* disk space
* bandwidth
* website speed
* database/programming language support
* technical support
* uptime
* web statistics summary (stats)
* scripts availability
* web provider (popularity/reliability)
* bandwidth
* website speed
* database/programming language support
* technical support
* uptime
* web statistics summary (stats)
* scripts availability
* web provider (popularity/reliability)