Micro MCQ Exam III
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
The process that ensures no circulating B cells recognize "self" antigens is called:
A. Class switching
B. Clonal selection
C. Somatic recombination
D. Clonal deletion
E. Conjugation
Clonal deletion
How does interferon fight a viral infection in an infected host?
A. It is a viricidal protein.
B. It induces antiviral proteins (AVP) in virus-infected cells.
C. It boosts the production of B cells in a virus-infected host.
D. It activates inactivate AVPs in virus-infected cells.
E. It is produced in virus-infected cells and induces AVP in neighboring cells
It is produced in virus-infected cells and induces AVP in neighboring cells
Most of the dangerous pathogenic fungi can do which of the following?
A. Grow as yeast in an environmental reservoir outside the host
B. Produce endotoxin
C. Escape the immune system by living inside red blood cells
D. Produce spores within the host's body
E. Get inhaled as mold spores and transition to yeast in the host's body
Get inhaled as mold spores and transition to yeast in the host's body
What is a major difference between an infection and an intoxication?
A. The consequences of an intoxication are not as serious as those of an infection.
B. An infection is more acute than an intoxication.
C. An intoxication usually results in disorientation and neural paralysis.
D. An intoxication is best treated by passive immunization.
E. An infection is best treated by inducing active immunity in an ill patient.
An intoxication is best treated by passive immunization
A person has a Staphylococcal skin infection. Another person acquires the same infection by sleeping on the same sheet as the first person. The sheet in this scenario serves as a/an__________.
A. host
B. portal of entry
C. fomite
D. reservoir
E. vector
fomite
The common cold is most frequently caused by _______________.
A. Human rhinovirus
B. Corynebacterium
C. Group A Streptococcus
D. Varicella-Zoster virus
E. Adenovirus
Human rhinovirus
According to the "hygiene hypothesis", ____________________________________.
A. washing hands appropriately is the single best way to reduce disease transmission
B. childhood illness leads to a more robust immune response as an adult
C. lack of exposure to gut flora leads to fewer Treg cells and more autoimmune diseases
D. being "too clean" leads to death of your native flora
E. you need some good bacteria to fight off the bad ones
lack of exposure to gut flora leads to fewer Treg cells and more autoimmune diseases
What is the main function of TC (cytotoxic) cells in the immune system?
A. to release perforin and granzymes
B. to initiate the complement system
C. to activate B cells
D. to activate TH cells
E. to activate PMNs
to release perforin and granzymes
A patient is suspected of having been infected with Norovirus, which is an acute viral illness. The patient's blood serum is tested by direct ELISA, and tests positive at a titer of 1:16. This compares with a pre-immune serum testing positive at a dilution of 1:8. Interpret the result.
A. The test is not valid. An indirect ELISA should have been used for this.
B. The patient currently has no circulating antigens from Norovirus in his blood.
C. The patient has not been infected with Norovirus.
D. The patient is currently infected with Norovirus.
E. The patient has been infected with Norovirus
The test is not valid. An indirect ELISA should have been used for this
Which of the following is associated with antigen presentation by phagocytes, but not by epithelial cells?
A. MHC-II picks up an antigen from the phagolysosome.
B. MHC-II picks up an external antigen circulating in the blood serum.
C. MHC-I picks up an antigen from the phagolysosome.
D. MHC-II picks up an antigen from the phagocyte's cytoplasm.
E. MHC-I picks up an external antigen circulating in the blood serum
MHC-II picks up an antigen from the phagolysosome
What would be the most apparent way to distinguish rubeola from rubella?
A. Patients with rubella have a much higher fever.
B. Jaundice is present in cases of rubeola.
C. Rubella has a much more prominent rash.
D. White spots are present in the lining of the mouth in cases of rubeola.
E. Rubella is a respiratory disease
White spots are present in the lining of the mouth in cases of rubeola
Which of the following is NOT associated with tuberculosis?
A. long-term treatment with multiple antibiotics
B. lung necrosis
C. vertical transmission
D. survival of the organism in macrophages
E. bone and liver granulomas
vertical transmission
What is the function of a Toll-like receptor (TLR)?
A. It allows the immune system to recognize when a viral infection has occurred.
B. It allows bacteria to bind the FC part of antibodies.
C. It allows pathogens to bind specifically to epithelial cells.
D. It allows TH cells to bind specifically to B cells.
E. It allows macrophages and dendritic cells to bind specifically to pathogens.
It allows macrophages and dendritic cells to bind specifically to pathogens
What are "pathogenicity islands"?
A. Endemic disease foci with high prevalence of a particular disease.
B. Plasmids on which multiple antibiotic resistance genes are located.
C. Patches of membrane receptors to which pathogenic bacteria bind.
D. Groups of pathogenic bacteria bound to M cells.
E. Clusters of virulence factor genes that can be transmitted by horizontal gene transfer
Clusters of virulence factor genes that can be transmitted by horizontal gene transfer
The most common immune disorder in the US is selective IgA deficiency. People who suffer from this will be more likely to get ______________ than other people.
A. respiratory and digestive illnesses
B. viral infections
C. blood borne illnesses
D. systemic lupus erythematosis
E. allergies
respiratory and digestive illnesses
What do tetanus and gangrene have in common?
A. There is an effective vaccine for both diseases.
B. Both are generally treated by amputation of the affected body part.
C. They have very similar symptoms, including tissue necrosis.
D. They both require anaerobic conditions for the bacteria to grow.
E. They are both caused by A-B neurotoxins.
They both require anaerobic conditions for the bacteria to grow
The upper part of the healthy respiratory tract has a native flora, but the lower part is axenic. What is mainly responsible for this?
A. rapid exhalation that expels organisms from the lungs
B. IgA produced in the upper respiratory tract
C. the membranous folds of the vocal cords
D. ciliated epithelial cells that line the upper respiratory tract
E. the acidic pH at the back of the throat
ciliated epithelial cells that line the upper respiratory tract
In general, antibodies can defend against pathogens in any of six ways. However, IgM and IgA can only use a few of these methods. Which of the following could be used by both IgM and IgA to inactivate pathogens?
A. TH cell activation
B. NK cell activation
C. Complement activation
D. Opsonization
E. Neutrilization
Neutrilization
How does a phospholipase toxin kill cells?
A. By digesting fatty acids, causing the lipids to not pack together as well
B. By preventing uptake via membrane fusion
C. By adding ADP + ribose to stop protein synthesis
D. By removing the head groups, thus destroying the amphipathic nature of the phospholipid
E. By preventing phospholipid synthesis
By removing the head groups, thus destroying the amphipathic nature of the phospholipid
A 30-year-old patient presents to a clinic with heart arrhythmia and joint pain. A few weeks previously, while camping in the Maine woods, he had noticed an unusual rash "like a bull's-eye" that had gone away. How had he likely become infected?
A. by inhaling fungal spores in an aerosol of dry leaves
B. through skin puncture or abrasion
C. by drinking water contaminated with rodent urine
D. by the bite of a small tick
E. by eating contaminated food
by the bite of a small tick
What cellular process allows billions of different antibody Fab fragments to be produced from only a few hundred genes?
A. Somatic Recombination
B. Clonal Selection
C. Clonal Expansion
D. Class Switching
E. Promoter Multiplicity
Somatic Recombination
Immune tolerance in T cells involves positive selection. What does that mean?
A. T cells are not allowed to proliferate if their T-cell receptor recognizes MHC-II of thymus cells.
B. T cells are not allowed to proliferate if their antibodies recognize antigen in the thymus.
C. T cells are only allowed to proliferate if their MHC-II recognizes macrophages in the thymus.
D. T cells are only allowed to proliferate if their T-cell receptor recognizes MHC-I of thymus cells.
E. T cells are only allowed to proliferate if their MHC-I recognizes antibodies in the thymus.
T cells are only allowed to proliferate if their T-cell receptor recognizes MHC-I of thymus cells
Anthrax spores can survive for many years in soil. Soil is a ______ for anthrax.
A. portal of entry
B. fomite
C. reservoir
D. vector
E. host
reservoir
An acute inflammatory respiratory disease associated with inhalation of aerosols from rodent urine, and especially prevalent in the southwest United States is _________________________.
A. Adenovirus
B. Hantavirus
C. Cryptosporidiosis
D. Histoplasmosis
E. Coccidioidomycosis
Hantavirus
How are TH (helper T) cells involved in the humoral immune response?
A. Cytokines from TH cells cause B cells to turn into antibody-producing plasma cells.
B. TH cells kill infected cells by releasing perforin and inducing apoptosis.
C. Antibodies are modified by TH cells so that they are active.
D. Macrophages produce antibodies in response to TH cells.
E. TH cells produce antibodies
Cytokines from TH cells cause B cells to turn into antibody-producing plasma cells
What do precipitin and agglutination tests have in common?
A. Both involve electrophoretic separation of the antigens.
B. Both involve labeled secondary antibodies.
C. Both require diffusion of antigen and antibody through a gel.
D. A positive test is indicated by a white line between the antigen and antibody spots.
E. Both require that the antibodies have at least two antigen binding sites.
Both require that the antibodies have at least two antigen binding sites
It is important to treat Strep throat (streptococcal pharyngitis) aggressively as soon as it is noticed.Why?
A. The virus that causes it can also cause meningitis.
B. The longer it persists, the more likely you are to get it again.
C. Antibodies produced against it could damage heart valves and kidneys.
D. It could invade the throat tissues and cause necrosis.
E. It could develop into pneumonia if allowed to persist too long
Antibodies produced against it could damage heart valves and kidneys
What is the role of the B7 protein in the immune response?
A. It is secreted by TH cells to stimulate B cell clonal expansion and differentiation.
B. It is a protein on TC cells that allows them to bind to TH cells.
C. It is a type of antibody produced by effector B cells.
D. It is produced by infected macrophages to help stimulate T cells.
E. It is a receptor on macrophages that recognizes pathogens
It is produced by infected macrophages to help stimulate T cells
Bob has had tuberculosis. If a TB skin test is performed on Bob, what will happen?
A. Nothing, unless his TB is active at the time of the test.
B. He will form immune complexes to the injected antigen.
C. After a few days, he will show a red rash at the site where the TB antigen was injected.
D. He will show a red rash over his whole body within a few hours.
E. He will show a red rash within a few minutes at the site where the test was performed
After a few days, he will show a red rash at the site where the TB antigen was injected
Most of the time you do not take antibiotics for a sinus infection; however, if you are a child and have more than three cases of sinusitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) within a few months, a doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics. What is the concern that prompts antibiotic use in this case?
A. If the Hib infection is during flu season, the doctor is concerned that you will spread the flu.
B. Antibiotics may be needed to disrupt the Hib biofilm that has formed in your lungs.
C. Chronic Hib infections can cause ear damage or lead to conditions such as epiglottitis or meningitis.
D. Such prolonged sinusitis might develop into pneumonia.
E. Antibodies produced against Hib can also damage your kidneys.
Chronic Hib infections can cause ear damage or lead to conditions such as epiglottitis or meningitis
The most effective way to reduce the incidence of nosocomial spread infections is to_______________________.
A. Have health care workers wash their hands between each patient they touch.
B. Separate patients into wards, grouped by the disease they have.
C. Fit HEPA filters in all patient rooms.
D. Use more antibiotics in hospitals.
E. Disinfect operating rooms better between surgeries
Have health care workers wash their hands between each patient they touch
One reason why a vaccine against malaria has proven difficult to design is that the malaria parasite _______________________________.
A. can swim through a tissue, avoiding humoral immunity
B. lives in red blood cells, where it can avoid both cellular and humoral immunity
C. covers itself with host antigens
D. has a virus-like protective coating that prevents antibody binding
E. has no surface proteins
lives in red blood cells, where it can avoid both cellular and humoral immunity
Upon receipt of cytokine signals from effector TH cells, macrophages ______________________.
A. begin recruiting the membrane attack complex to kill invading bacteria
B. produce a more potent oxidative burst that includes nitric oxide
C. differentiate into long lived memory macrophages
D. become antigen presenting cells
E. undergo class switching and begin to secrete antibodies
produce a more potent oxidative burst that includes nitric oxide
Elderly patients on long-term oral penicillin therapy often acquire the infectious disease pseudomembranous colitis, caused by Clostridium difficile. How does penicillin use affect the course of this disease?
A. Penicillin has no effect on the course of this disease.
B. Penicillin reduces the severity of the C. difficile infection.
C. Penicillin triggers a hypersensitivity response in the patient.
D. Penicillin creates a "super" strain of C. difficile that is more infectious.
E. Penicillin kills native flora, allowing C. difficile to colonize.
Penicillin kills native flora, allowing C. difficile to colonize
Infection with Pseudomonas is best treated preventatively. It is very difficult to treat once an infection has already occurred. Why?
A. They type of patients it infects are not able to tolerate most antibiotics.
B. It lives inside macrophages, where antibiotics cannot penetrate.
C. It forms biofilms, which are very difficult to treat with antibiotics.
D. It is highly invasive, spreading throughout the body very rapidly.
E. It is Gram positive, but most antibiotics only treat Gram negative infections
It forms biofilms, which are very difficult to treat with antibiotics
Which of the following is true for a direct ELISA, but not for an indirect ELISA?
A. The test can be made more sensitive by conjugating latex beads to the known antigen.
B. The test can be used to detect a latent infection.
C. Anti-FC secondary antibodies are used to detect the primary antibodies.
D. The test uses an enzyme reaction to visualize antibodies.
E. To begin the test, known antibodies are bound to the bottom of a microtiter well.
To begin the test, known antibodies are bound to the bottom of a microtiter well.
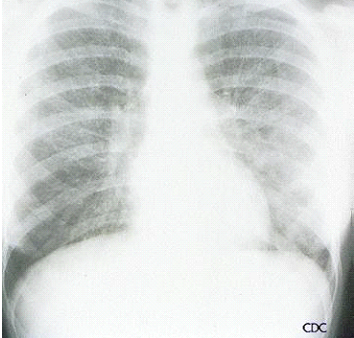
A college student presented to a campus clinic with a low-grade fever and a cough that had developed over the course of a few weeks.She said she felt tired. No lymph node swelling was apparent. A chest X-ray is shown at right.A sputum sample was stained, but no organisms were visible. The diagnosis would most likely be ___________________.
A. Tuberculosis
B. Histoplasmosis
C. Pertussis
D. Streptoccal pneumonia
E. Mycoplasmal pneumonia
Mycoplasmal pneumonia
A new virus is discovered. It is airborne, has a reservoir in geese, has a high ID50 for humans, has a segmented genome, and has not yet evolved balanced pathogenicity. Which part of this information is good news, and why?
A. Its reservoir in geese. That makes it potentially easy to eradicate.
B. Its segmented genome. That allows you to break it up more with a vaccine.
C. Its not being a balanced pathogen. At least it has not yet evolved to become as deadly as it could be.
D. The high ID50. At least it takes a lot of it to kill you.
E. Its being airborne. You can avoid it by staying a meter away from other people.
The high ID50. At least it takes a lot of it to kill you