NUR3125 - Cell and Tissues PlayPosit
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
structure of eukaryotic cell
plasma membrane
nucleus - DNA & RNA
cytoplasm & organelles:
- ribosomes
- ER
- golgi apparatus
- mitochondria
difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
eukaryotic has organelles (ribosomes, ER, GA, mitochondria)
plasma membrane function
regulates what comes in and out of the cell via phospholipid bilayer and its proteins
nucleus function
contains DNA and controls the cell
nuclear membrane function
separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
ER function
protein synthesis and transport
lipid synthesis
smooth vs. rough ER
RER has ribosomes attached
mitochondrion function
undergoes cellular respiration to produce ATP/energy
golgi apparatus function
processing and packaging of proteins
microtubule function
maintenance of cell shape, cell motility, chromosome movements in cell division, organelle movements
apart of cytoskeleton of cell
ribosome function
protein synthesis
lysosomes function
digesting cellular substances
cytoskeleton function
"bones and muscle" of cells
name and describe the 8 cellular functions
1. movement - muscle cells generate forces
2. conductivity - nerve cells → electrical potential
3. secretion - mucous gland cells
4. excretion - cells rid waste products
5. metabolic absorption - cells take in and use nutrients
6. respiration - cells absorb oxygen and transform nutrients into ATP; cell respiration or oxidation
7. reproduction - grow tissue and replace cells
8. communication - vital to survive
what is energy metabolism? types?
chemical tasks of maintaining cellular function
anabolism and catabolism
anabolism vs catabolism
uses energy to build molecules
breaks down molecules (carbs, fats, and proteins) into energy needed for cell function
ATP
major source of cellular energy
aerobic vs anaerobic metabolism
presence of oxygen to produce energy
lack of oxygen in producing energy
types of membrane transport mechanisms
passive transport - diffusion (facilitated and passive) and osmosis
active transport
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
diffusion + its types
a type of passive transport where there is a movement of solutes from an area of greater concentration to lesser without energy
facilitated: membrane protein facilitates the diffusion, such as glucose going from the outside → inside cell
passive: substances diffuses across the plasma membrane without proteins until it reaches equilibrium; includes oxygen, alcohol, and CO2
osmosis
passive diffusion that includes the movement of water down concentration gradient (high to low) across a semipermeable membrane
active transport + example
transport of a molecule across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient (low → high) using energy and a membrane protein
ie. ATPase pump - NA+ molecule moves from inside → outside as there is a high concentration in the outside
K+ molecules move from outside → inside as its concentration is higher on the inside
tissues
groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
4 types of tissues
epithelial - covers most of internal and external body surfaces (simple squamous, transitional, stratified squamous epithelium, etc.)
connective - binds tissues and organs together (adipose cartilage, bone, blood)
muscle - composed of myocytes (striated, cardiac, and smooth muscle)
nervous - specialized cells, neurons, and glia
what is cellular adaptation?
change in cell structure and function due to its environment
cell atrophy vs hypertrophy
decrease in cell size (thymus gland, gonads, and disuse atrophy)
increase in cell size due to mechanical stimuli (hypertension → heart pumps blood harder → left ventricle hypertrophy → difficult to send blood to systemic circulation)
hyperplasia + examples
increase in # of cells
ie. part of liver removal → cells divide faster
metaplasia vs. dysplasia
replacement of one mature cell (smoking → columnar ciliated epithelial cells are replaced by stratified squamous epithelial cells → loss of protective mechanism)
abnormal changes in size, shape, and organization of mature cell but not a true adaptive change; does not indicate cancer and may not progress to cancer (epithelial tissue of the cervix)
benign vs. malignant tumors
remain at the original site
named according to the tissues from which they arise and include "-oma"
spread far beyond tissue of origins (known as metastasis) with a rapid growth rate and microscopic alterations
named according to the tissues from which they arise (carcinoma - epithelial, adenocarcinoma - ductal or glandular, sarcoma - mesenchymal, lymphoma - lymphatic, leukemia - blood forming cells)
carcinoma in situ
early-stage cancer, specifically pre-invasive epithelial malignant tumors of glandular/epithelial origin that have not broken through the basement membrane or invaded the surrounding stroma
causes of cell injury/death
physical agents - contusions, lacerations, fractures, incised wound, stab wound, puncture wound
radiation injury
chemical injury - over the counter and prescribed drugs
nutritional imbalances
hypoxic injury - shortage of oxygen; most common cause of CI; common cause of HI is ischemia
free radical injury - oxidative stress due to excessive reactive oxygen species
types of cell death
necrosis and apoptosis
apoptosis
programmed cell death/suicide either as a normal physiological or pathological process
examples of apoptosis as normal physiological processes
cells in embryonic process, endometrial cells during menses, breast tissue regression after breastfeeding
examples of apoptosis as pathologic processes
cases where there is too much or too little apoptosis such as Alzheimer's/ALS/Parkinson's, carcinogenesis, autoimmune disorders
which type of cell death is ONLY pathological? which can be both?
necrosis
apoptosis
necrosis + examples
cell death in an organ/tissue that is still alive (some cells may die but rest of tissue in organ remains to function)
cellular changes after local cell death include rapid loss of plasma membrane, swelling of organelles, enzymatic digestion of cell components, and inflammation
always pathological
coagulation, liquefaction, caseous, and fatty necrosis
gangrene
mass of tissue undergoing necrosis (dry or wet)
clostridium: gas gangrene infection of tissue by anaerobic bacteria
process of apoptosis vs. necrosis
condensation of chromatin → membrane blebs → cellular fragmentation →apoptotic body → phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and fragments
swelling of ER and mitochondria + membrane blebs → breakdown of plasma membrane, organelles and nucleus, leakage of contents, amorphous densities in mitochondria → inflammation → explosion in cell
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of condensed DNA molecules (chromatin) that contain the genes (23 pairs in humans)
how many chromosomes do gametes have and why
23
they are haploids → allows for the correct number of chromosomes to be restored when two gametes fuse during fertilization
diploids
2 sets of chromosomes/23 pairs
chromatin
DNA with proteins
genes
basic units of inheritance in the chromosomes; made up of DNA
building blocks of chromosomes
DNA → chromatin → chromosomes
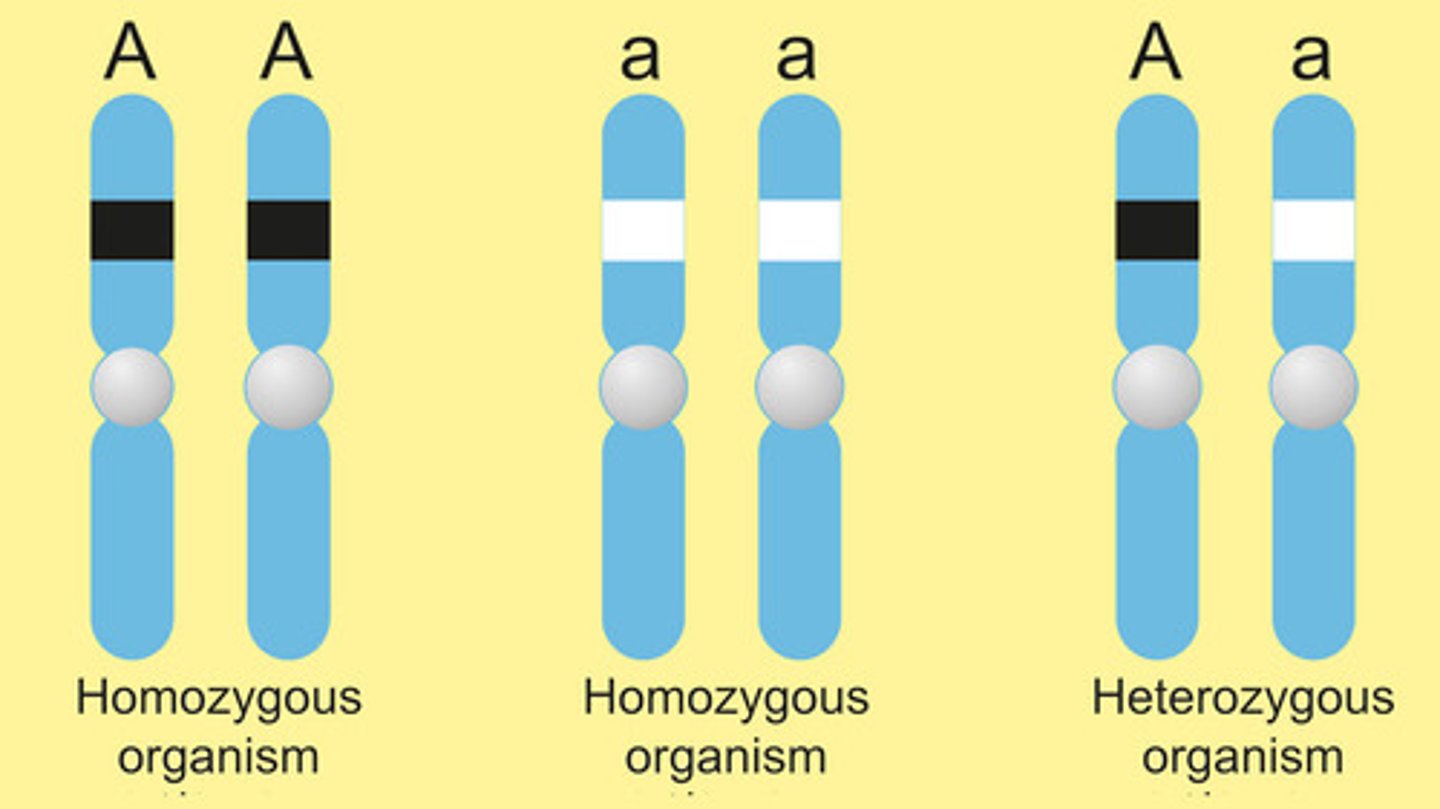
homozygous vs heterozygous
loci (a specific location on a chromosome where a gene or genetic marker is found) on a pair of chromosomes that have identical alleles
loci on pair of chromosomes with different alleles
allele
different forms of a gene
DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid)
double helix model made of nucleotides that codes for proteins
how info is processed
nucleotides → DNA → RNA → amino acids → proteins
mutation
alteration of genetic material
genotype
the genetic constitution of an individual organism.
phenotype
observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment
dominant vs recessive allele
allele that is observable
allele whose effects are hidden
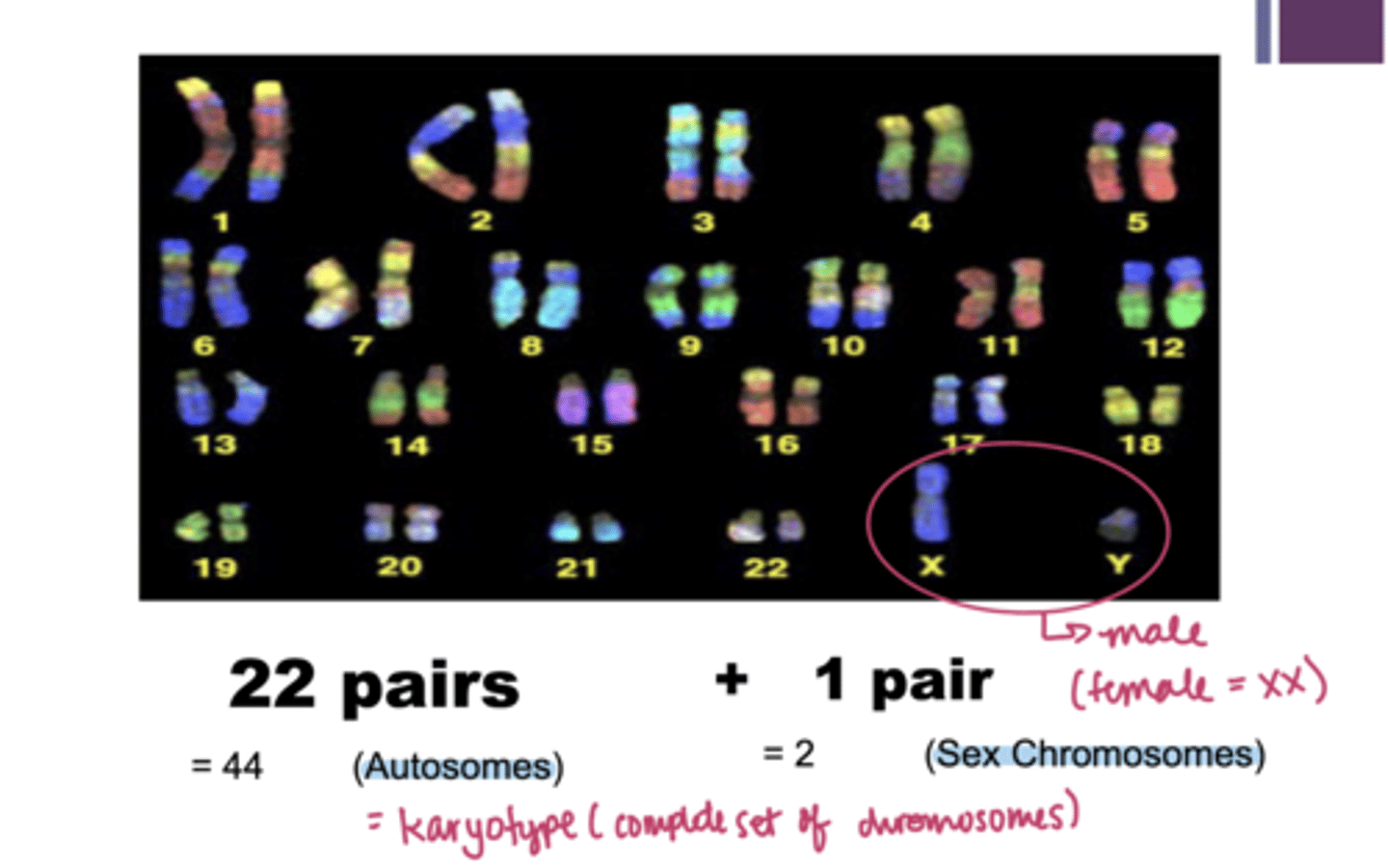
autosomes
the first 22 of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in males and females
sex chromosomes
one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the human that will determine the sex
females - XX
males - XY
karyotype
the number and visual appearance of the chromosomes in the cell nuclei of an organism or species.
transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
translation
genetic information coded in mRNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm
chromosomes in zygote vs gamete
46
23
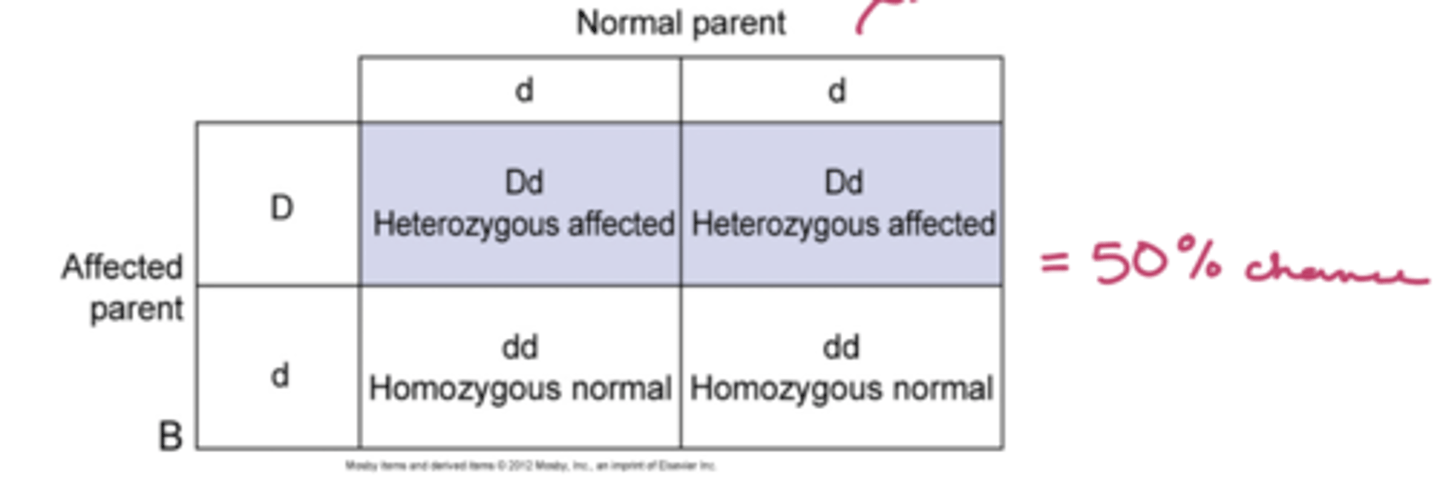
autosomal dominant inheritance
pattern of genetic inheritance where a copy of a mutated gene from one parent can cause a genetic condition in child; a way of inheriting a gene where 1 parent has the affected/dominant gene
in autosomal dominant inheritance, which sex offspring is affected?
male/female offspring affected equally
in autosomal dominant inheritance, if one of the parents is heterozygous affected, the children have a __% of being affected
(draw punnett square)
50%
in autosomal dominant inheritance, if both of the parents is heterozygous affected, the children have a __% of being affected
(draw punnett square)
75%

marfan syndrome
an autosomal dominant disorder whose primary causes are ocular (retinal detachment), skeletal (join hypermobility, spinal deformities, pigeon chest, long body), and cardiovascular anomalies (mitral valve prolapse and aortic valve disease)
autosomal recessive inheritance
two recessive alleles must be present for trait to be displayed
in autosomal recessive inheritance, what sex offspring is affected?
male/female affected equally
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if both parents are unaffected but are carriers for the trait, each offspring has a __% chance of being affected
(draw punnett square)
25%
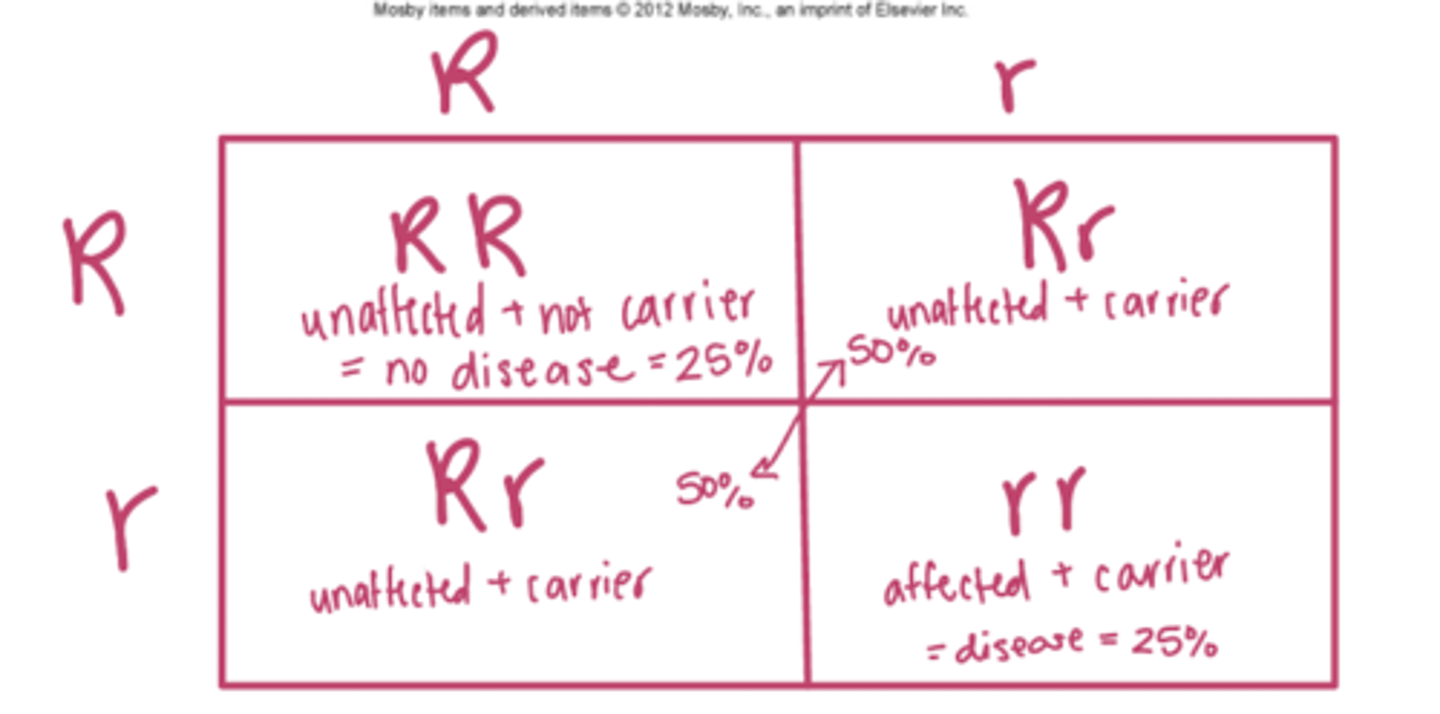
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if both parents are affected, __% of their children will be affected
(draw punnett square)
100%
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if one parent is affected and the other is not a carrier, __ of their offspring will be ______ but will be ______
(draw punnett square)
all, unaffected, carriers
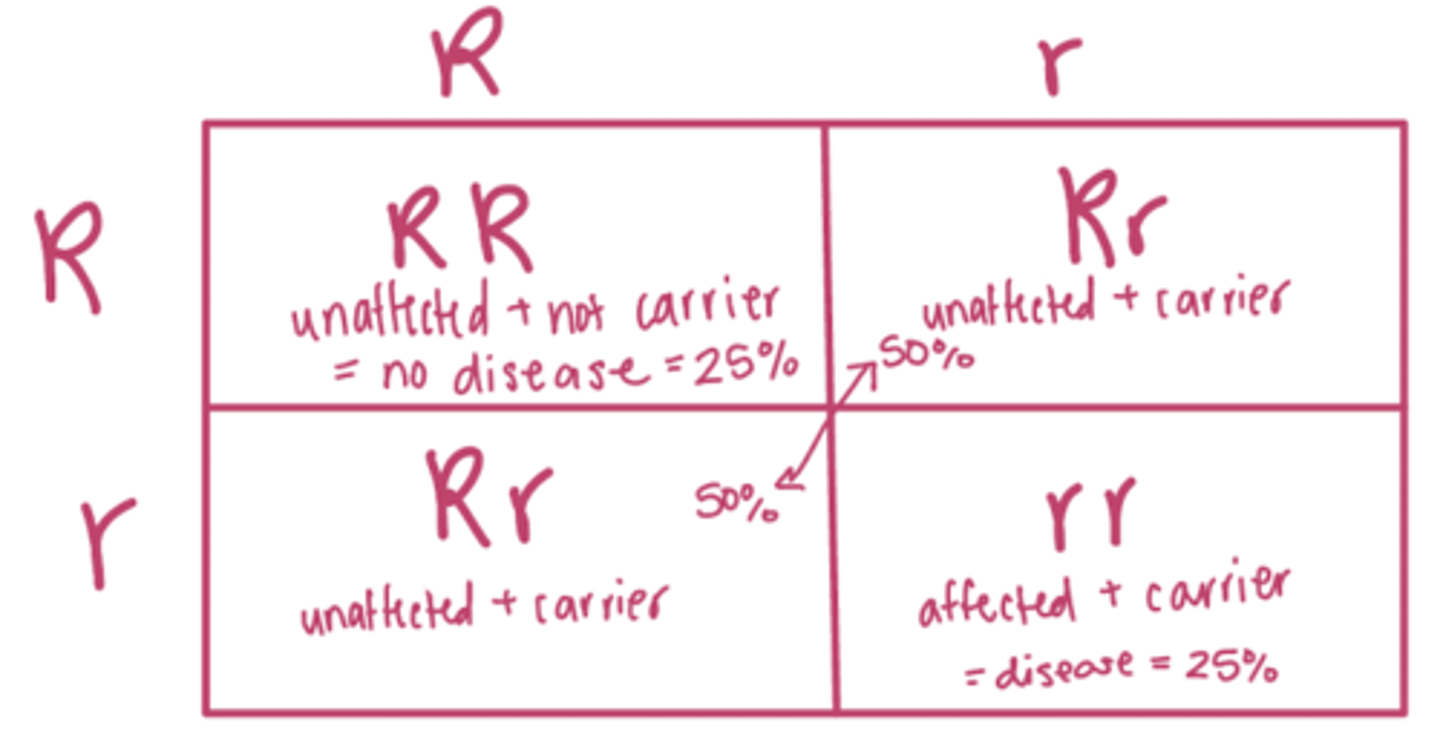
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if one parent is affected and the other is a carrier, each of the offspring will have a __% chance of being affected
(draw punnett square)
50%
cystic fibrosis
an autosomal recessive disorder due to the mutation in gene CFTR on chromosome 7
chloride transport decreased, affected organs in the GI, respiratory, and reproductive system
sweat test shows elevated chloride
phenylketonuria
an autosomal recessive disorder where there is an inability to convert phenylalaine to tyrosine, a precursor to melanin → mental retardation, elevated phenylalanine, fair skin, decreased melanin, ezcema
tay-sachs disease
an autosomal recessive disorder where there is a failure of lysosome function and thus an accumulaton of glycolipids → destruction of neurons in brain, SC, ANS → mental retardation and motor problems → blindness, seizures, and death
sex-linked inheritance
Inheritance of a genetic trait located on the sex chromosomes
most x-linked disorders are what and mostly affect who and why
recessive
male - females have another X to counteract/override the abnormal gene
in x-linked recessive disease, affected males cannot transmit the affected gene to ___ but they can to all _____.
(draw punnett sqaure)
sons, daughters
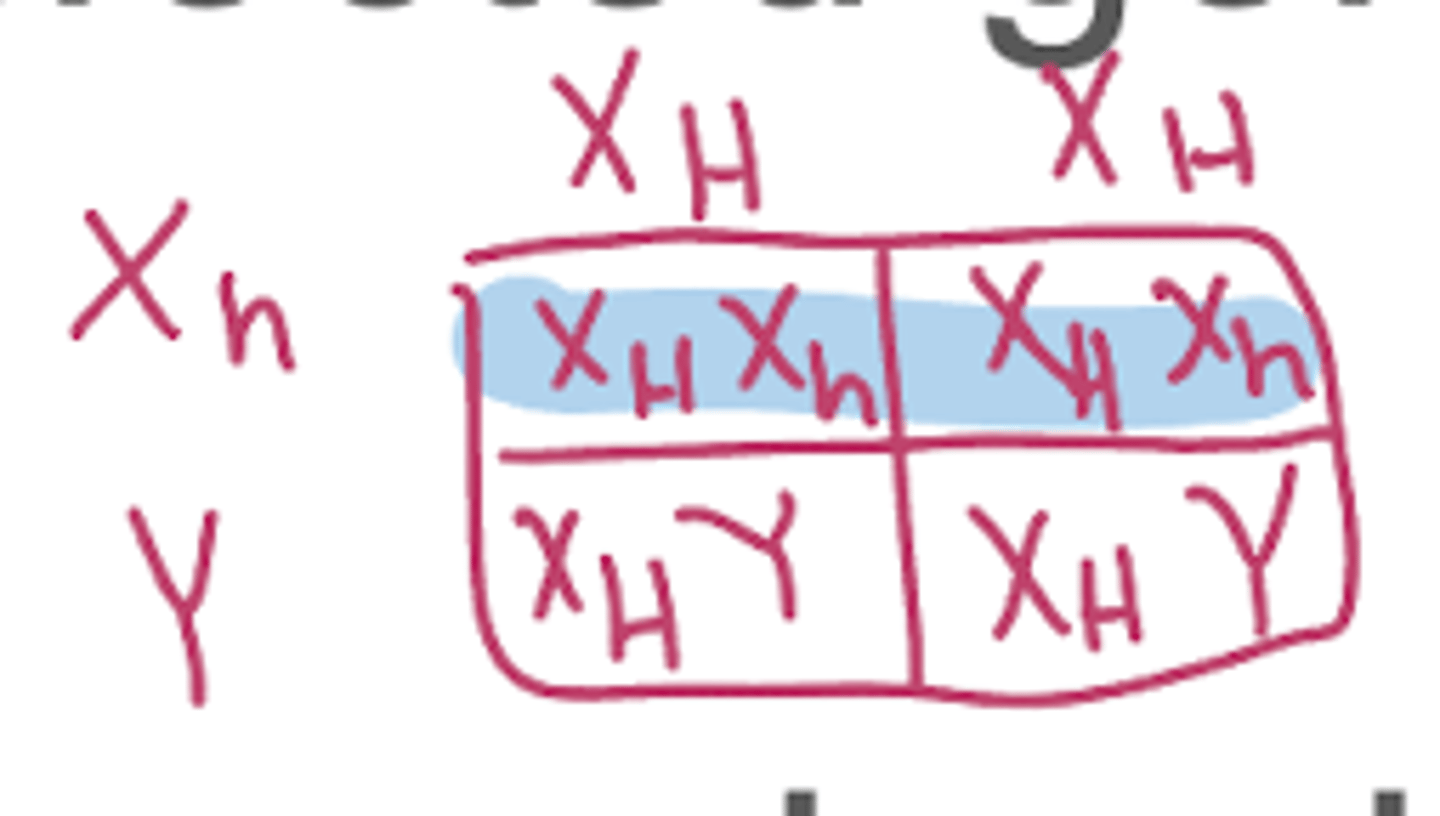
in x-linked recessive disease, sons of female carriers have __% risk of being affected
50%
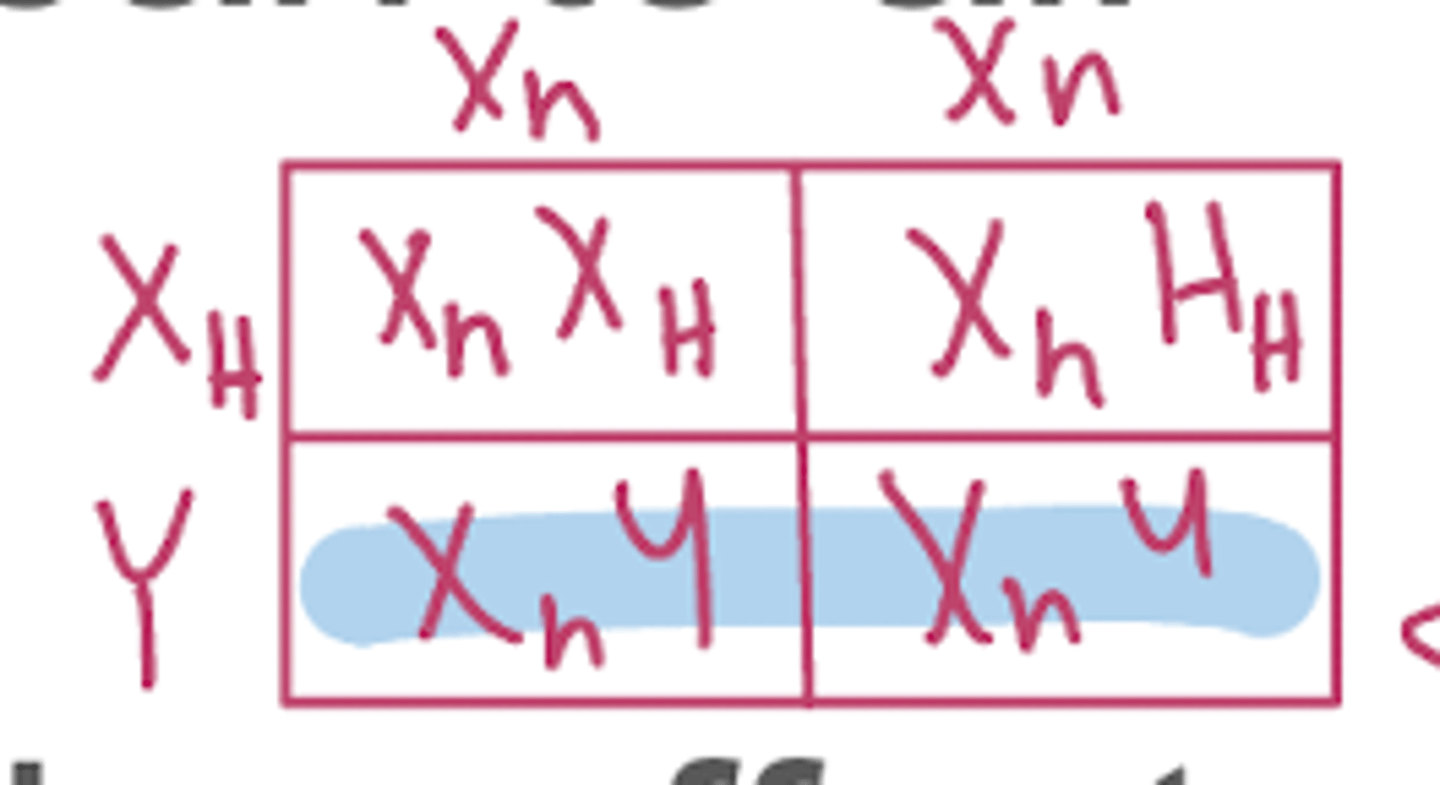
causes of chromosomal disorders
alterations in the structure of one or more chromosomes with rearrangement/deletion of chromosome part
abnormal number of chromosomes
down's syndrome
chromosomes 21 has 3 copies instead of 2 (+1 chromosome)
risk increases with maternal age
protruding tongue, flat nasal bridge, small ears, metal retardation, heart problems
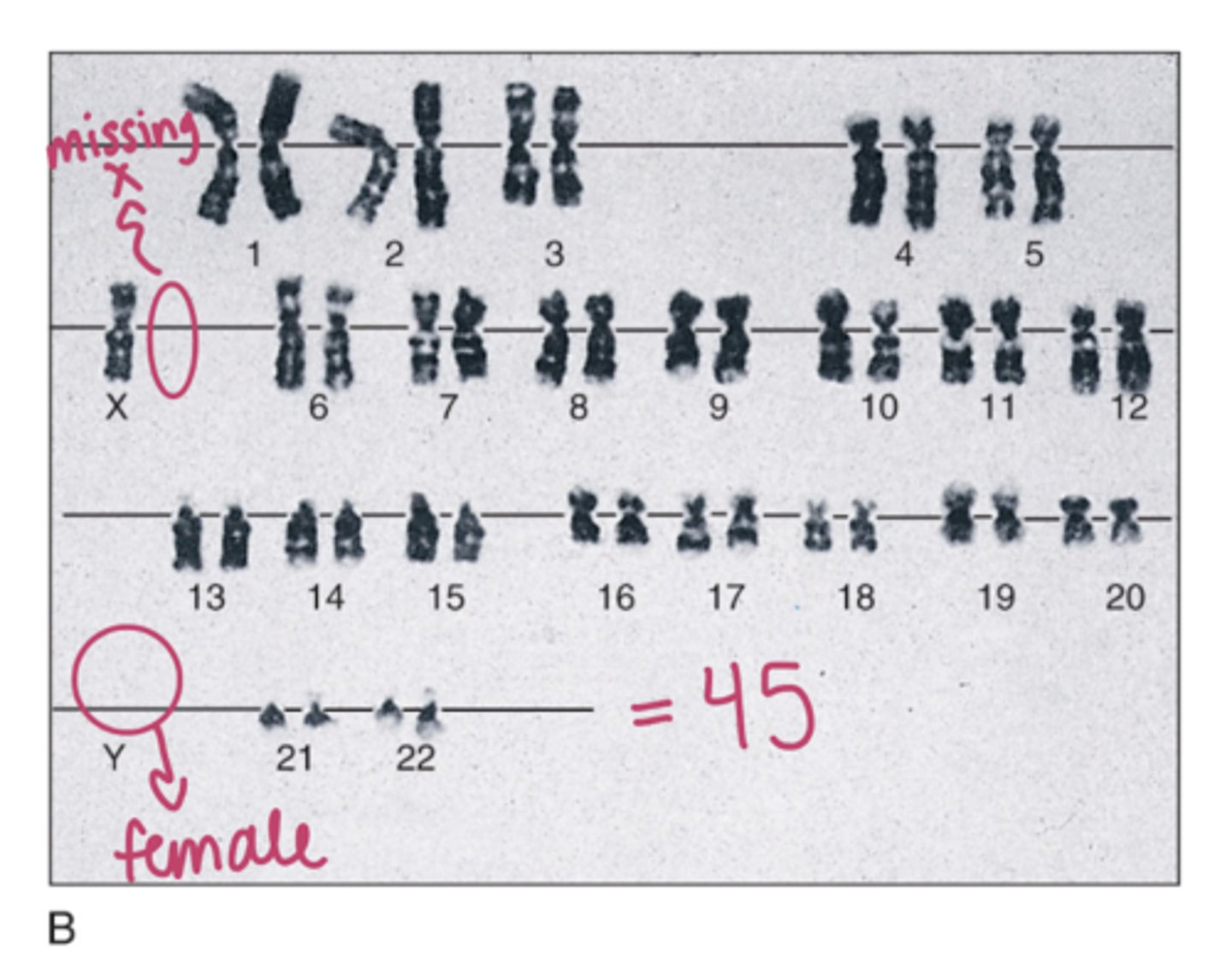
turner syndrome
a chromosomal disorder in females in which either an X chromosome is missing, leading to 45 chrosomes (-1)
short statue, webbing neck, lack of secondary sex characteristics, absent ovaries, coartctation of aorta and bicuspid aortic valve, some difficulty driving and nonverbal problem solving