Architecture of database management systems
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
A database is a shared collection of logically related data and its description.
To meet the information needs of an organization.
To standardise data formats for multiple applications.
Enables seamless data sharing across departments.
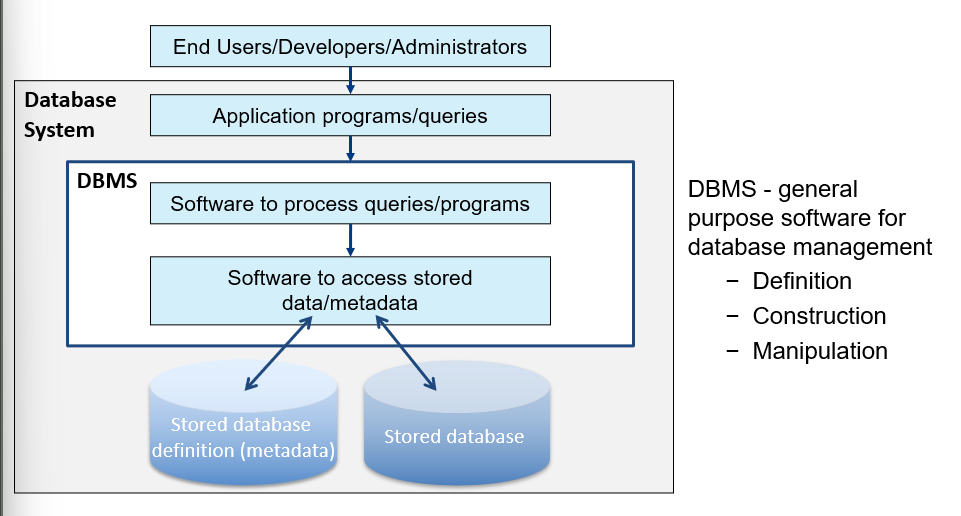
A general-purpose software used to manage electronically stored databases.
It maintains data independently of application programs.
It minimizes data redundancy.
Examples include MS Access and MySQL.
It allows re-use and sharing of the data by many users.
It ensures data consistency and integrity.
It enables concurrent access for many users and provides data access control appropriate to individual users.
database,DBMS ,computer hardware
same data across applications, same data even when replicated
integrity
up-to-date data,correct data
database administrator (dba)
database designer
app programmers
end users
oversee and manage resources: vm, utilized hardware
authorization: for common usage
security policy: app dependant
performance, tuning: can change over time
identify data to be stored and structured to be used
identify constraints
design structural and functional aspects
may be sophisticated/naive, regular/casual.
varying degrees of access
stages in database development
problem analysis
database design
database implementation
database monitoring/tuning