Bio Photosynthesis Test
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz on 1/19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What are autotrophs?
“Producers”, makes their own energy
What are heterotrophs?
“Consumers”, eats other living things for energy
What is the difference between a photoautotroph and a chemoautotroph?
Photoautotroph: Makes energy using sunlight (plants)
Chemoautotroph: Makes energy using chemicals (bacteria near thermal vents)
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2.O + Light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the definition of photosynthesis?
Using sunlight to synthesize energy from carbon dioxide and water
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The range of all possible electromagnetic radiation (Visible light, micro waves, radio waves, etc.)
What are the colors of the visible light spectrum? (white light)
ROY G BIV (basically the colors of the rainbow)
Which colors have the most energy on the visible light spectrum?
Blue/Purple (shorter wavelengths)
Which colors have the least energy on the visible light spectrum?
Red (longer wavelengths)
Why do you see certain colors? (ex: why are plants green?)
You see the color of the light that doesn't get absorbed by the object (reflected). Plants are green because chlorophyll (pigments responsible for photosynthesis) reflect green, which bounces off of the leaf and goes into our eyes.
What is the main type of pigment in the leaf responsible for photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll
What are the two types of Chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B
What light spectrums/colors does Chlorophyll absorb?
It absorbs red and blue
What light spectrums/colors does Chlorophyll reflect/not absorb?
Green
What are the purpose of Accessory pigments?
Accessory pigments absorb the colors that Chlorophyll doesn’t (green)
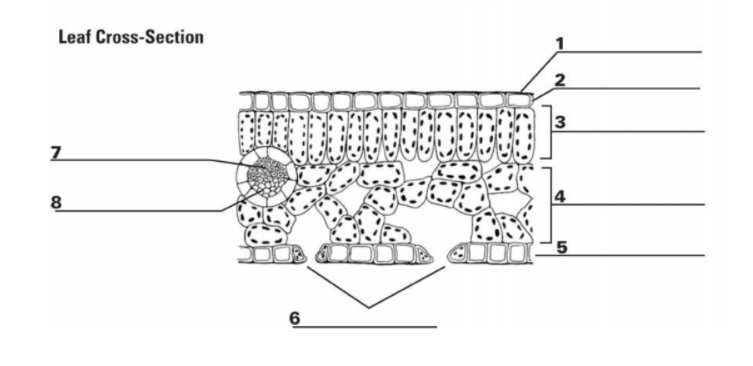
What is “1”?
Cuticle
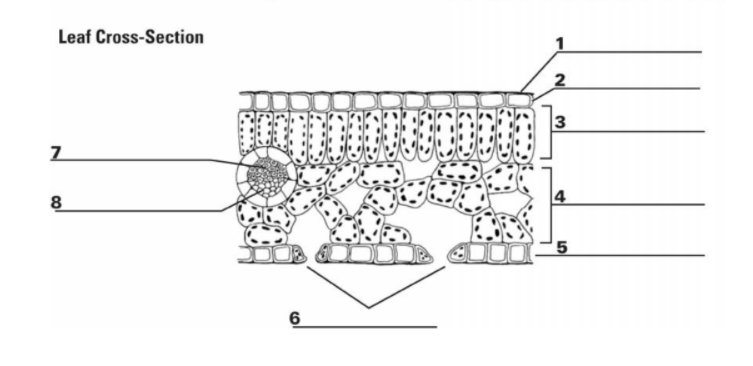
What is the function of “1”?
It is the waxy, water repelling layer that prevents the leaf from drying out
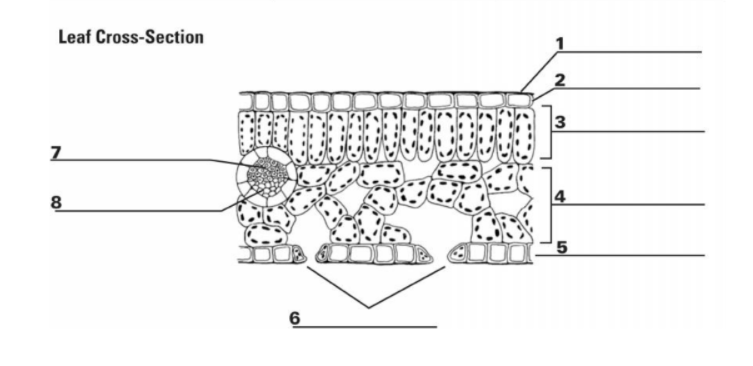
What is “2”?
Epidermis
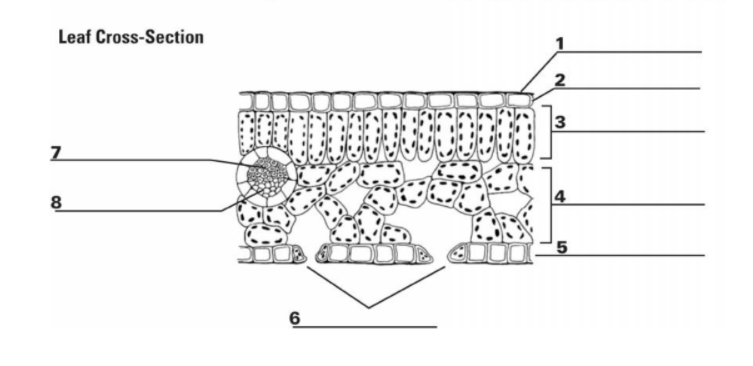
What is the function of “2”?
It is the protective outer layer of cells on the surface of a leaf.
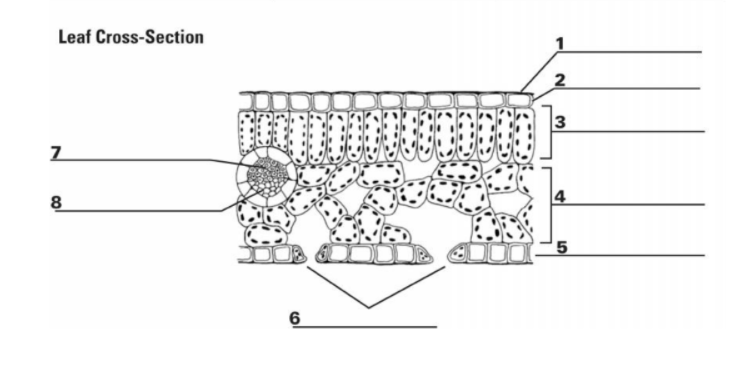
What is “3”?
Palisade Mesophyll
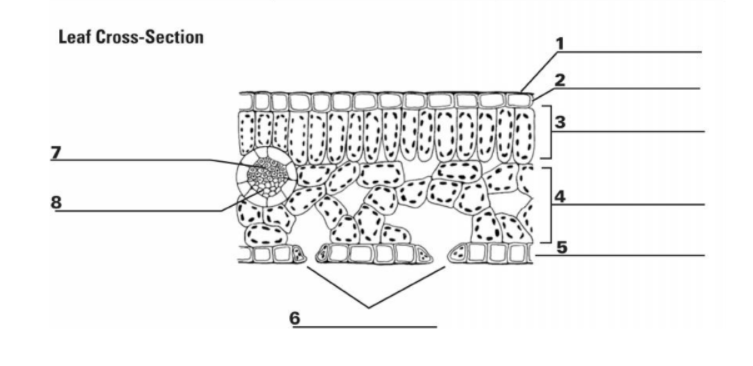
What is the purpose of “3”?
Contains most of the leaf’s chlorophyll used during photosynthesis
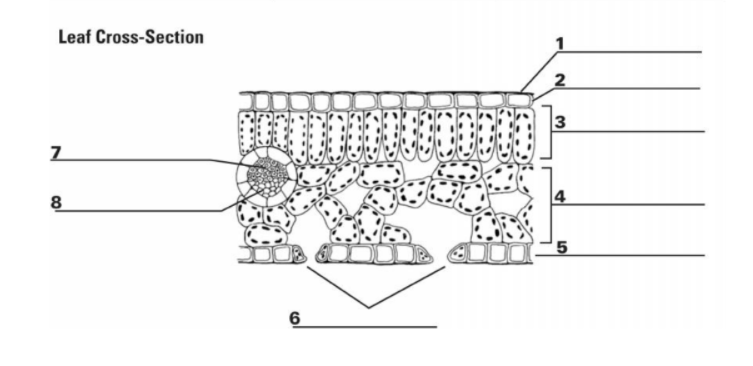
What is “4”?
Spongy Mesophyll
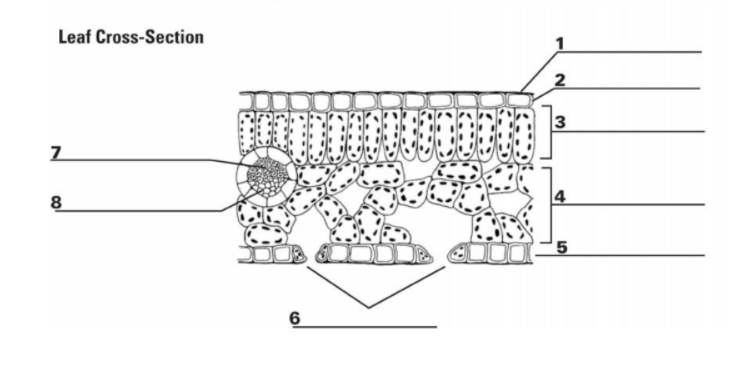
What is the purpose of “4”?
Contains gases in the leaf (involved in gas exchange)
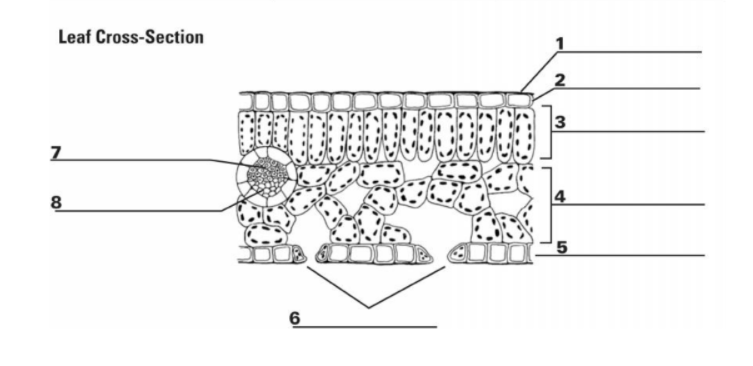
What is “5”? (The things surrounding 6, not the bottom layer)
Guard Cells
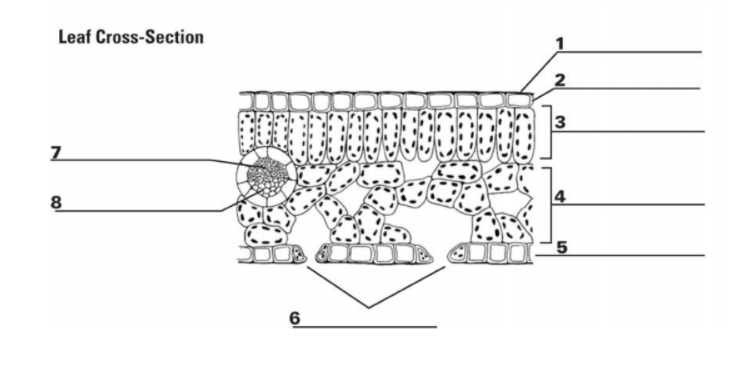
What is the purpose of “5”? (Things surrounding 6, not bottom layer)
They surround a stomata and change shape, which allows the stomata to open and close
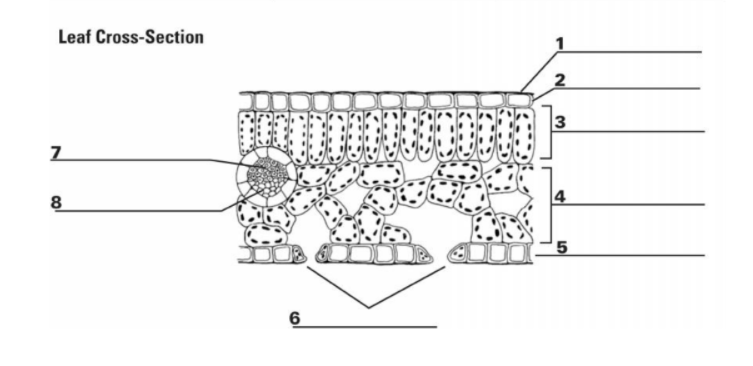
What is “6”? (the holes)
Stomata
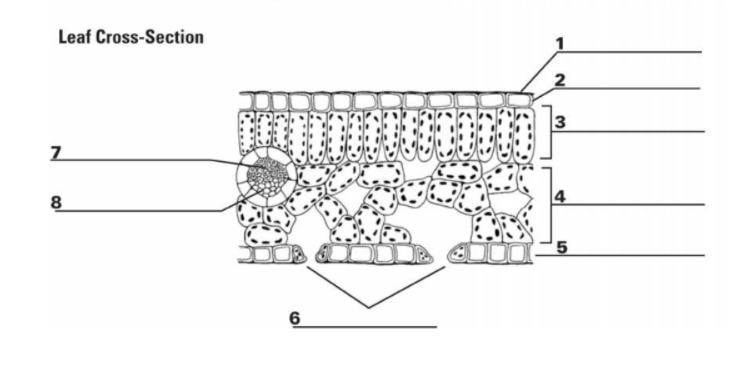
What is the purpose of “6”? (the holes)
A pore or opening in a plant’s leaves where water vapor and other gases leave and enter the plant
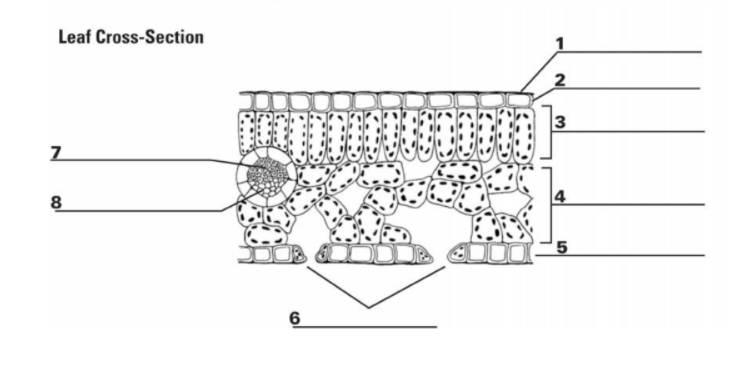
What is “7”?
Xylem
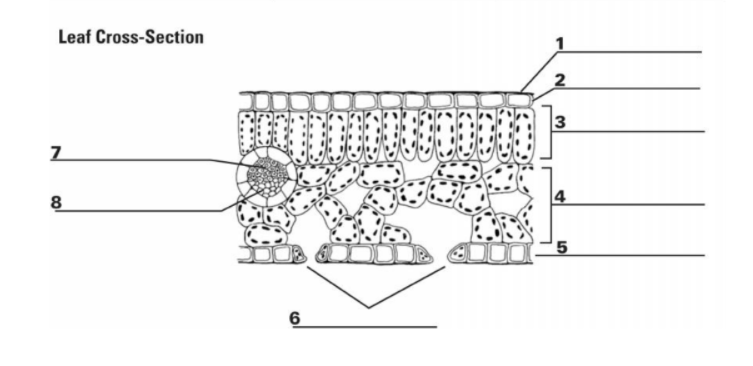
What is the purpose of “7”?
Transports water
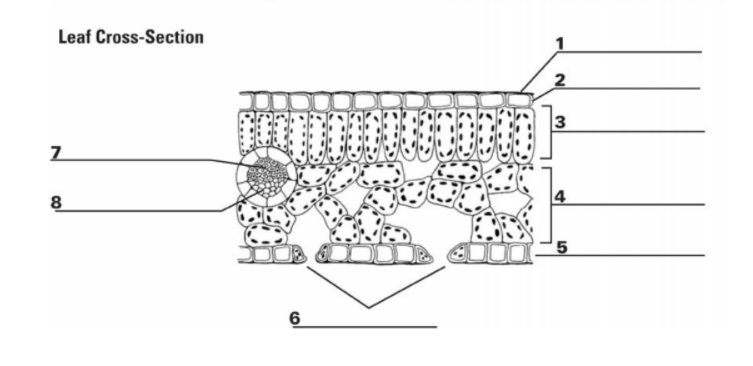
What is “8”?
Phloem
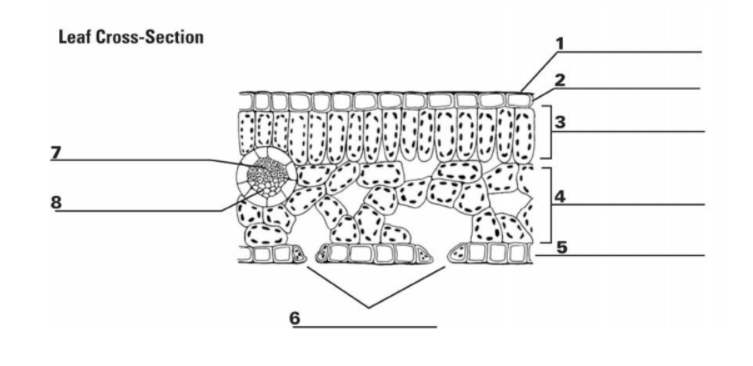
What is the purpose of “8”?
Transports sugar and nutrients
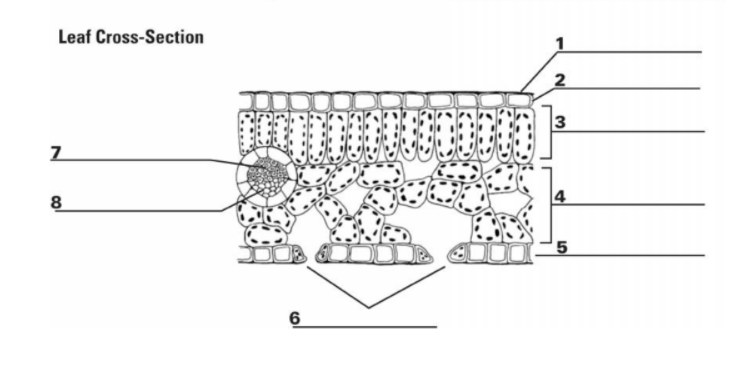
What is the entirety of “7” and “8”?
Vein
What is transpiration?
The loss/evaporation of water through a leaf
Which components of a leaf are used to minimize transpiration?
The cuticle and the guard cells
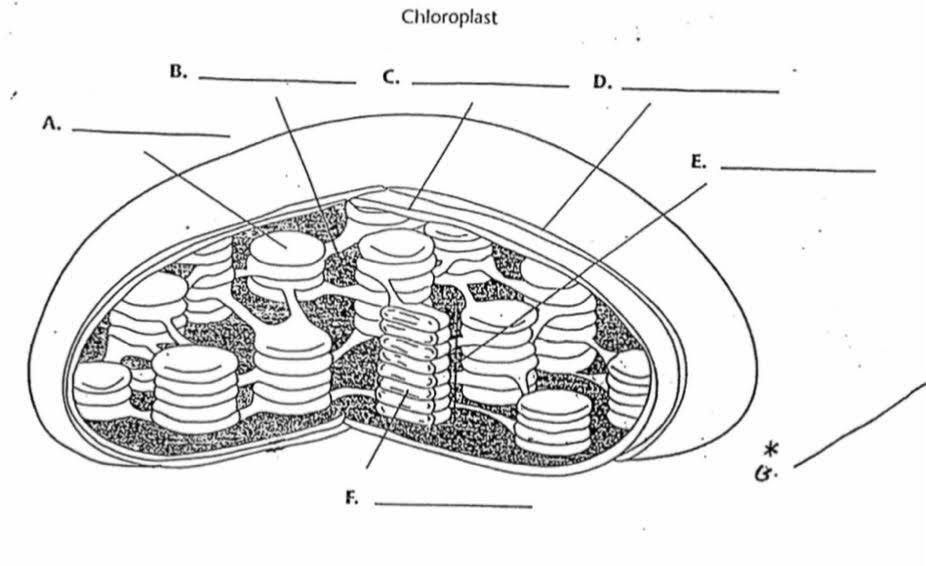
What is “A”?
Thylakoid
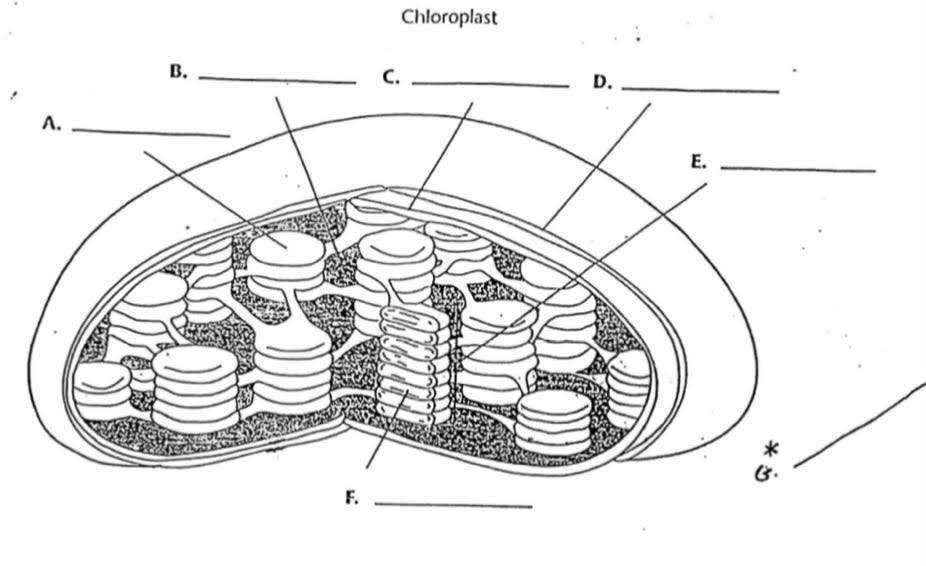
What is the function of “A”?
Membrane bound sacs found inside the chloroplast with pigments inside
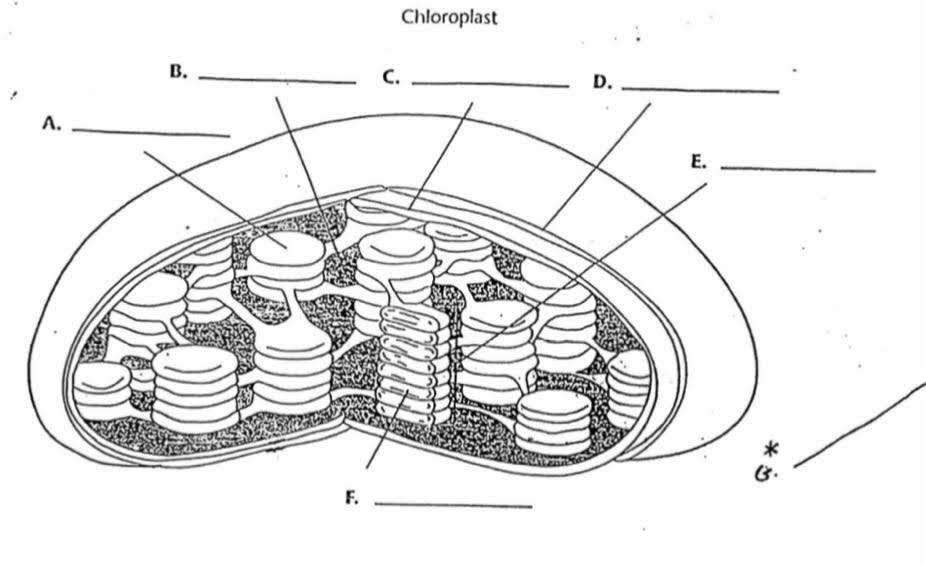
What is “B”?
Stroma
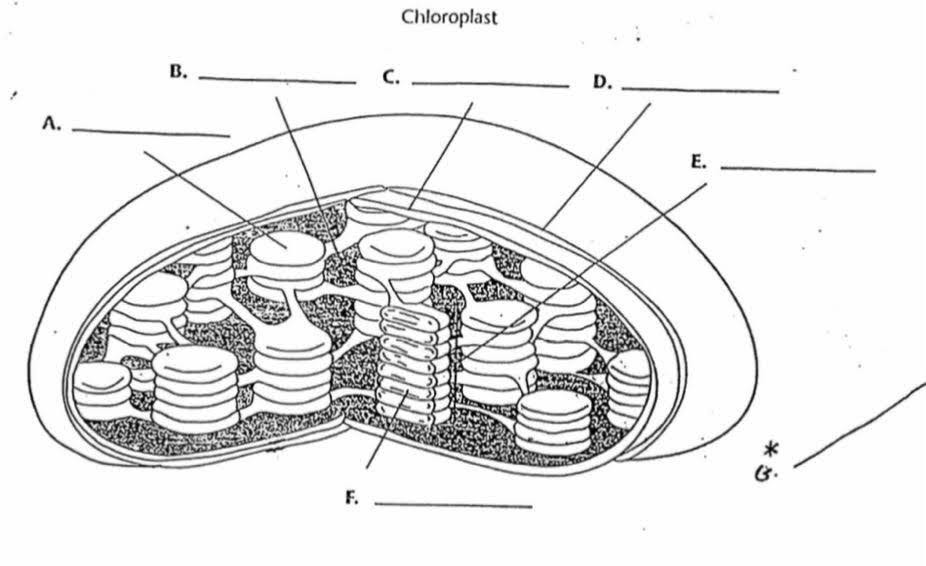
What is the function of “B”?
The area outside of the thylakoids that contain a thick fluid that protects and insulates the chloroplast. It is where sugar/glucose is made
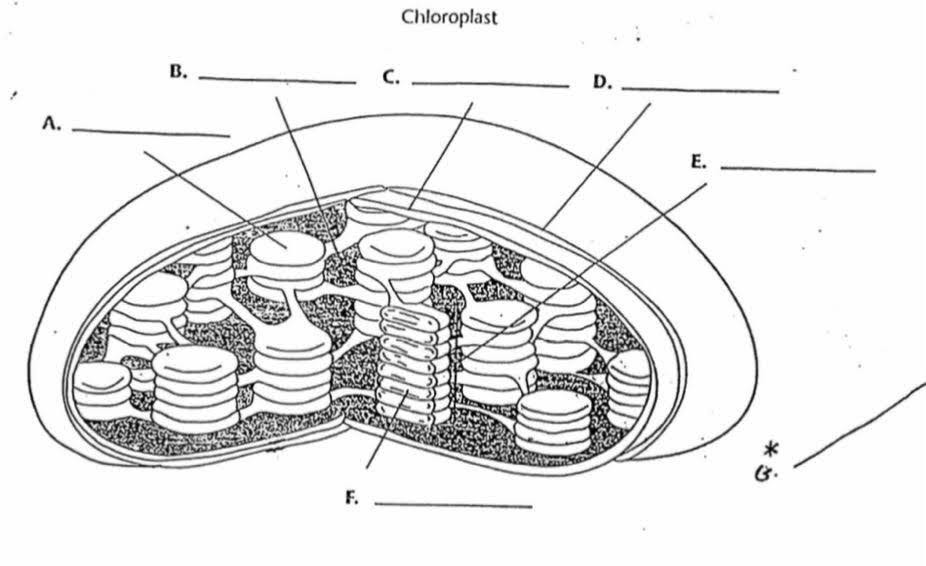
What is “C”?
Inner membrane
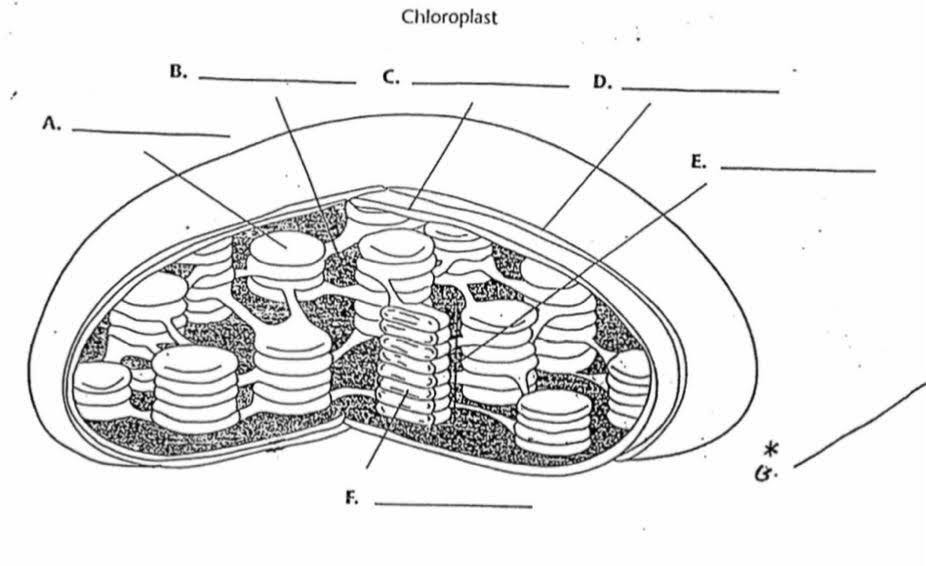
What is “D”?
Outer membrane
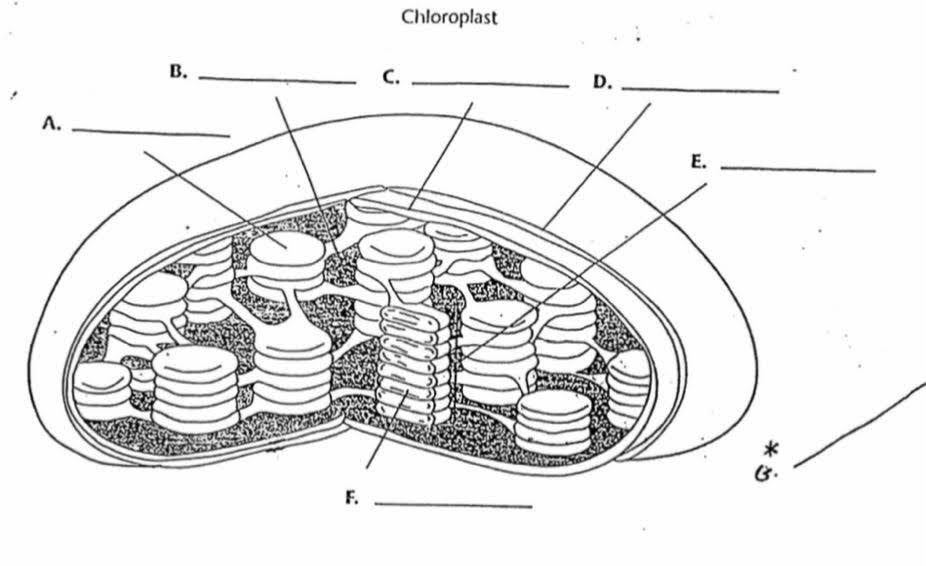
What is “E”?
Granum
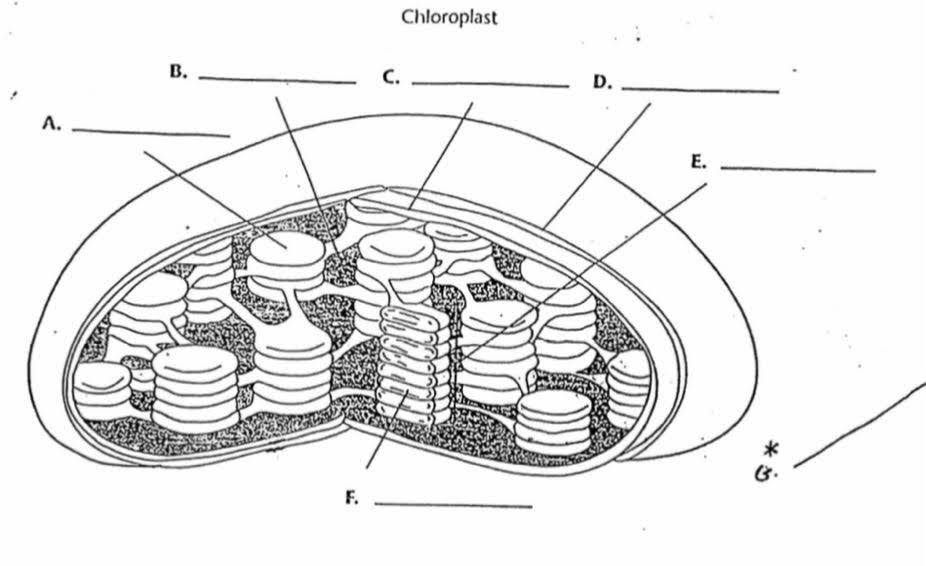
What is the purpose of “E”?
They are stacks of thylokoids that increase surface area for photosynthesis to occur
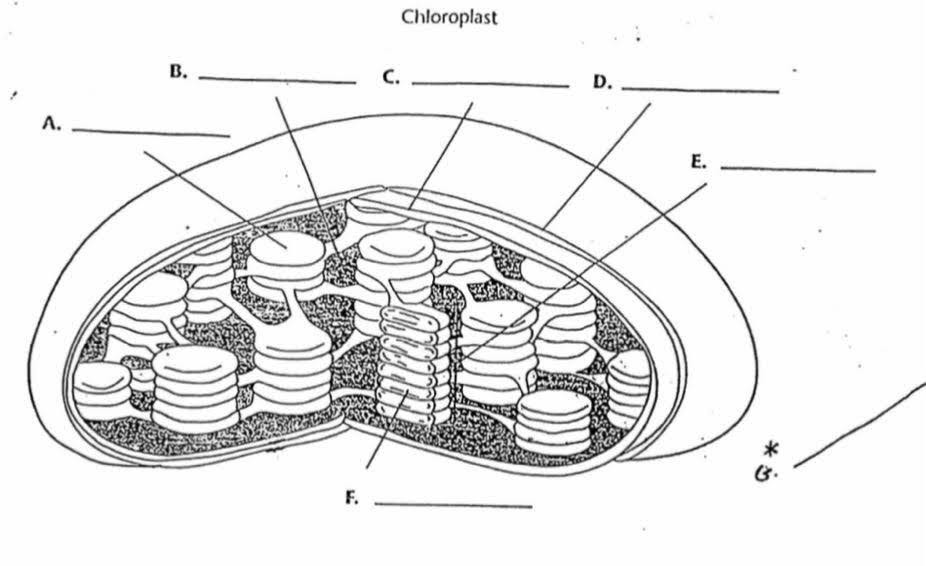
What is “F”?
Lumen
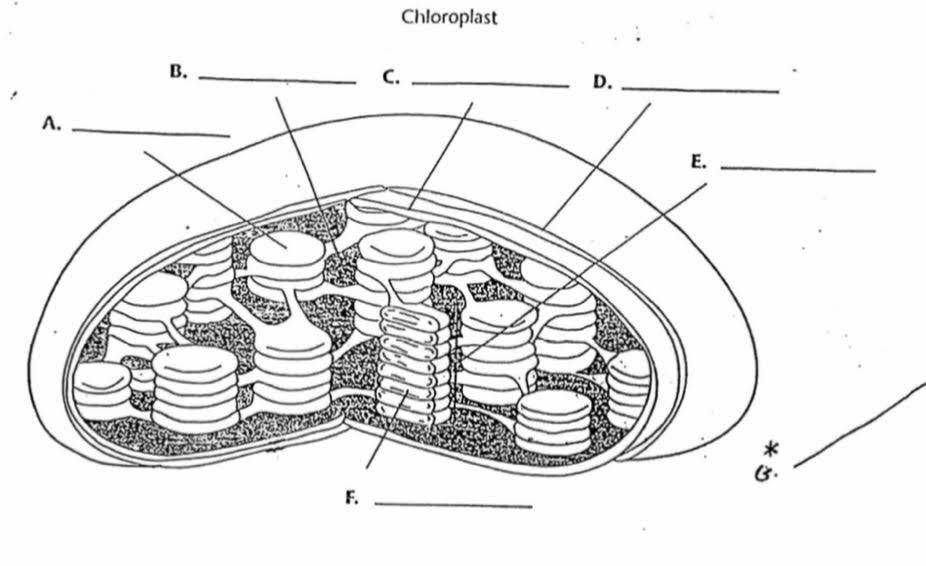
What is the purpose of “F”?
It is the area inside the thylokoid.
What are photosystems?
They are a collection of pigments whithin the thylakoid membrane of a chloroplast.
How do photosystems work?
When one pigment in the photosystem gets “excited” by light hitting it, it transfers energy to a neighboring pigment (loses 2 electrons)
What is a hydrogen ion (H+) concentration used for?
It is used during photophosphorylation when the H+ ions move through the ATP synthase during Facilitated Diffusion to power the ATP synthase so it can make ATP.
What is ATP Synthase?
An embedded protein (also enzyme) helps H+ ions move out of the Lumen. It creates ATP using the energy generated by the moving of H+ ions.
What is the difference between Oxidation and Reduction reactions?
Oxidation = Lost electrons
Reduction = Gained electrons
What is the acronym to remember Oxidation and Reduction?
LEO says GER (Lost Electrons Oxidized, Gained Electrons Reduction)
NADPH is the reduced version of _________.
NADP+
What electron carrier molecule is used during Photosynthesis?
NADPH
What is the full name of ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate
What are ATP’s three components?
Adenine, Ribose, Phosphate group
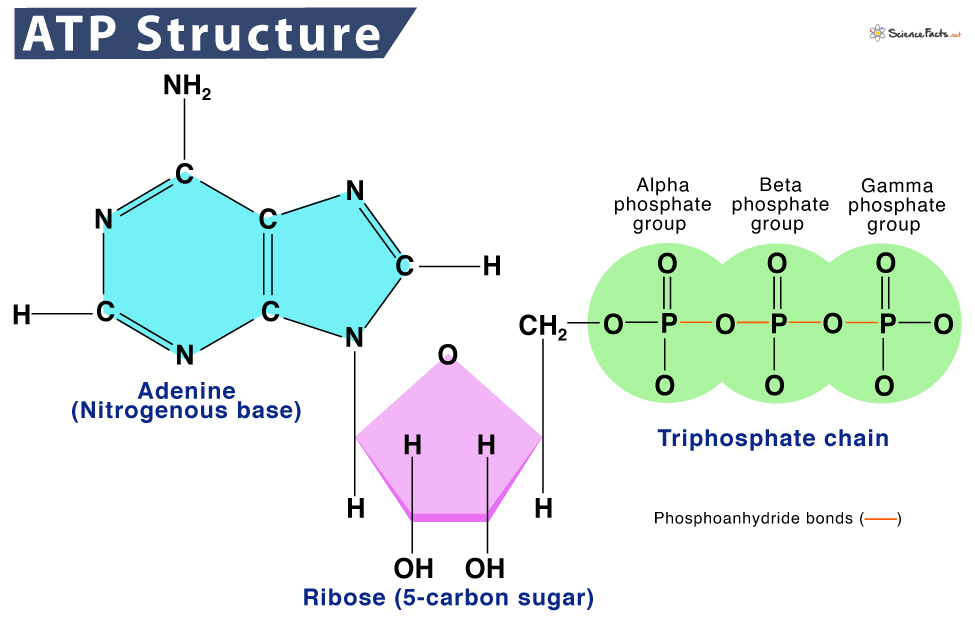
Where is the energy stored in ATP?
Between the Phosphate bonds (energy is released when these bonds are broken)
How does ADP get recharged?
ADP gets bonded to a phosphate group in the ATP synthase after it gets energy from the hydrogen ions moving through it
What is NADPH?
The electron carrier molecule used in photosynthesis
How is NADPH created?
A NADP+ molecule takes a hydrogen ion and 2 electrons and gets recharged
What is the goal of Light-Dependent Reactions?
To recharge ADP and NADP+ into ATP and NADPH
Where do Light-Dependent Reactions occur?
The thylakoid membrane
What are the reactants of Light-Dependent Reactions?
Water and light
What are the products of Light-Dependent Reactions?
Oxygen (waste), ATP, NADPH
What is Photolysis?
The splitting of water (Oxygen and hydrogen ions) during photosynthesis
Why is water split during a Light-Dependent Reaction?
The electrons gained from splitting the water molecule is used to replenish the electrons lost in PS II
What is Photophosphorylation?
H+ ions travel through the ATP synthase during Facilitated Diffusion. ATP synthase gets energy by this and combines ADP to a Phosphate group, making ATP.
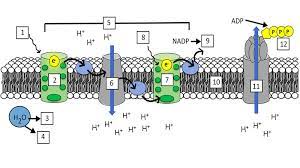
What is “1”?
Light (680 nm)
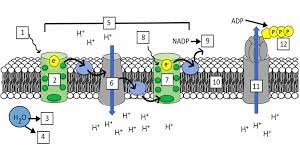
What is “2”?
Photosystem II (PS II)
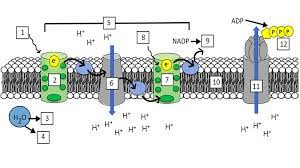
What is “3” and “4”?
H+ ions and Oxygen
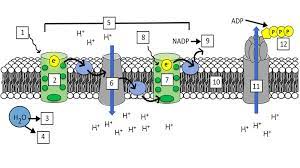
What is “5”?
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
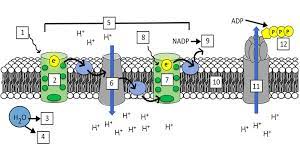
What is “7”?
Photosystem I (PS I)
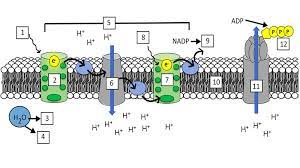
What is “8”?
Light (700 nm)
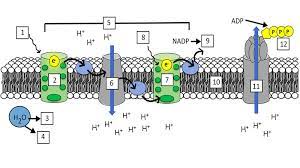
What is “9”?
NADPH
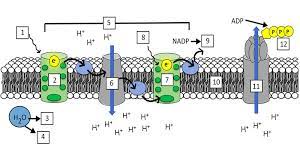
What is “10”?
Thylakoid Membrane
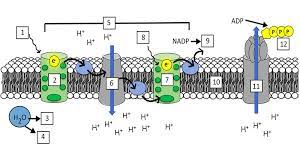
What is “11”?
ATP synthase
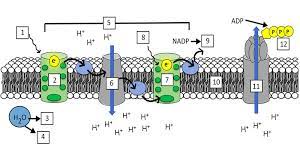
What is “12”?
ATP
What are the steps of the light reaction?
Light excites pigments in PS II
2 electrons exit PS II
Photolysis occurs and replenishes the 2 electrons lost in PS II (also splits H2O into H+ and O)
The electrons from PS II go through the ETC(elctron transport channel) and replenish the electrons lost from PS I
Light excites pigments in PS I, making them lose 2 electrons
Photophosphorylation occurs, making ADP + P into ATP
NADP+ takes the 2 electrons from PS I and a H+ ion and gets reduced to NADPH
What is the goal of the Calvin Cycle?
To change CO2 into sugar molecules (glucose)
Where does the Calvin Cycle take place?
Stroma (inside choloroplast)
Why does the Calivn Cycle take place in the stroma?
It does not need pigments to absorb light for it to take place
What are the reactants of the Calvin Cycle?
3 CO2, 9 ATP, 6 NADPH (per cycle)
What are the products of the Calvin Cycle?
G3P, 9 ADP, 6 NADP+ (per cycle)
How many times does the Calvin Cycle need to take place in order to produce 1 glucose molecule?
2 times
How many ATPs are used to create 1 glucose?
18 ATPs
How many NADPHs are used to create 1 glucose?
12 NADPH
How many CO2 molecules are used to create 1 glucose?
6
What is the 5-carbon molecule that is used in the Calvin Cycle?
RuBP
How many RuBPs are in the beginning of the cycle?
3 RuBPs
How many CO2 molecules are added to the 3 RuBPs? (per cycle)
3 CO2 molecules
What is the enzyme that adds the 3 CO2 molecules to the 3 RuBPs?
Rubisco
What is the process of Rubisco attatching the CO2 to the RuBP, which splits the RuBP into PGAs?
Carbon Fixation
What happens to the 3 RuBPs after carbon fixation?
It gets split into 6 PGA molecules (3-carbon sugars, little energy)
What gets added to the 6 PGA molecules in order to make them into G3P molecules?
6 ATPS and 6 NADPHs
What is the 3-carbon sugar molecule that has a lot of energy (gets turned into glucose later)?
G3P
How many G3P molecules get taken out of one round of the Calvin Cycle?
1
What happens the the other 5 G3P molecules after one is taken out of the cycle?
3 more ATP molecules give it enough energy to remake them into 3 RuBP molecules
What happens to the ADP and the NADP+ made in the Calvin Cycle?
It gets recycled/recharged in the Light Reactions
If 4 glucose molecules are made from the Calvin Cycle, how many ATP molecules were used?
72
If 3 glucose molecules are made from the Calvin Cycle, how many G3P molecules were used?
6
If 5 glucose molecules were made from the Calvin Cycle, how many NADPH molecules were used?
60