BIOL 250: Module 3 Quiz
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Causes of Cataracts
-Opacification of the lens caused by aging
-May be congenital
-Result from ocular trauma
-Drug toxicity
-Result of systemic disease (eg. diabetes)
-Long-term, unprotected exposure to sunlight
Importance of early treatment of glaucoma
-the disease can lead to blindness, because any vision lost as a result generally cannot be regained
Visual disturbances of cataracts
-Poor night vision
-Yellowing of fading of colors
-Loss of brightness of color
-Need for bright light for reading
Visual disturbances of glaucoma
-Blurred vision
-Severe pain
-Headaches
-Redness of the eye
-"Halo" around lights
-Cornea becomes hazy
Visual disturbances of macular degeneration
-Mild distortion of central vision
-Seeing wavy lines when looking at lines
-Seeing semiopaque spots in visual field
-Does not affect peripheral field
-Usually painless
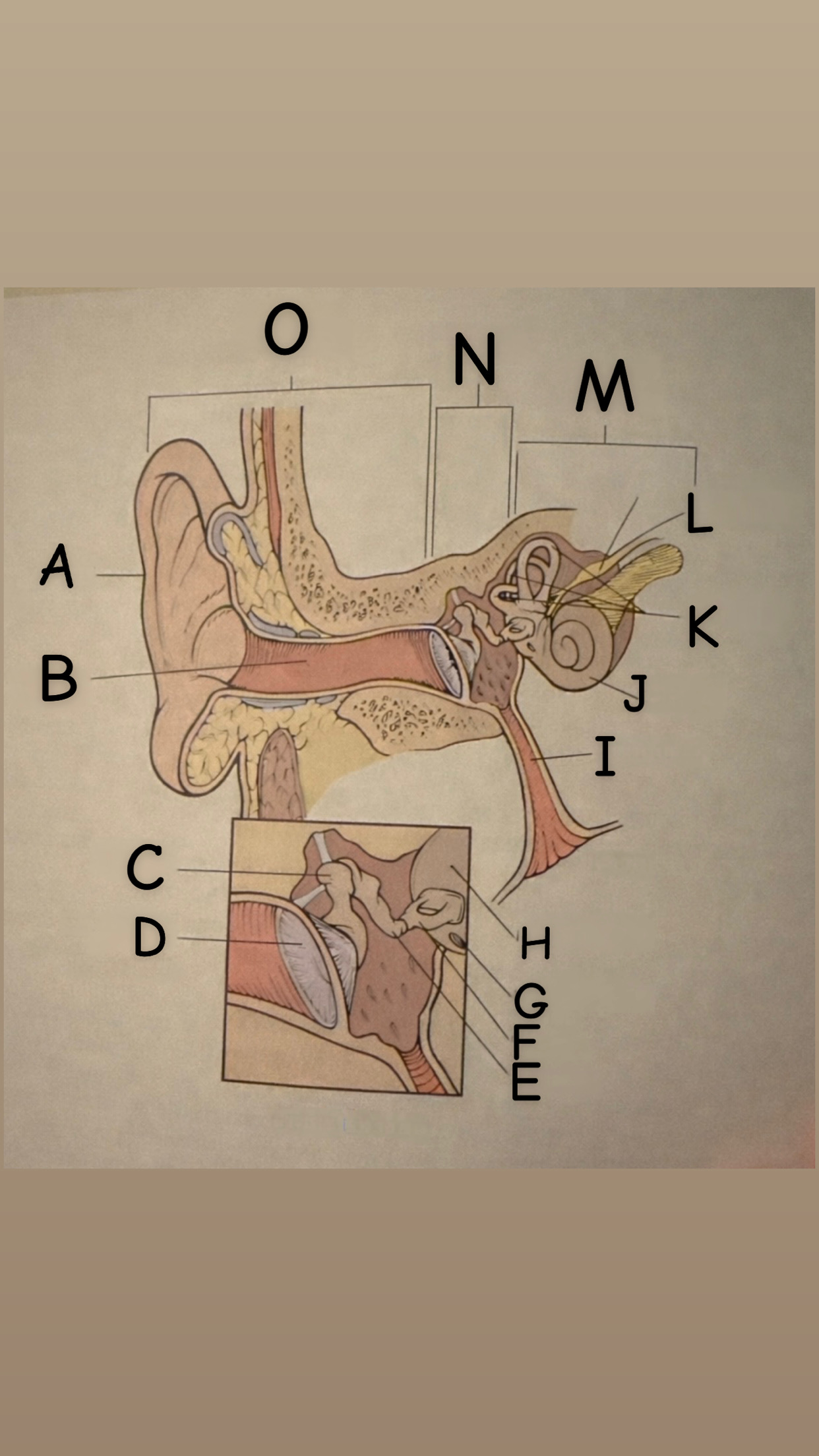
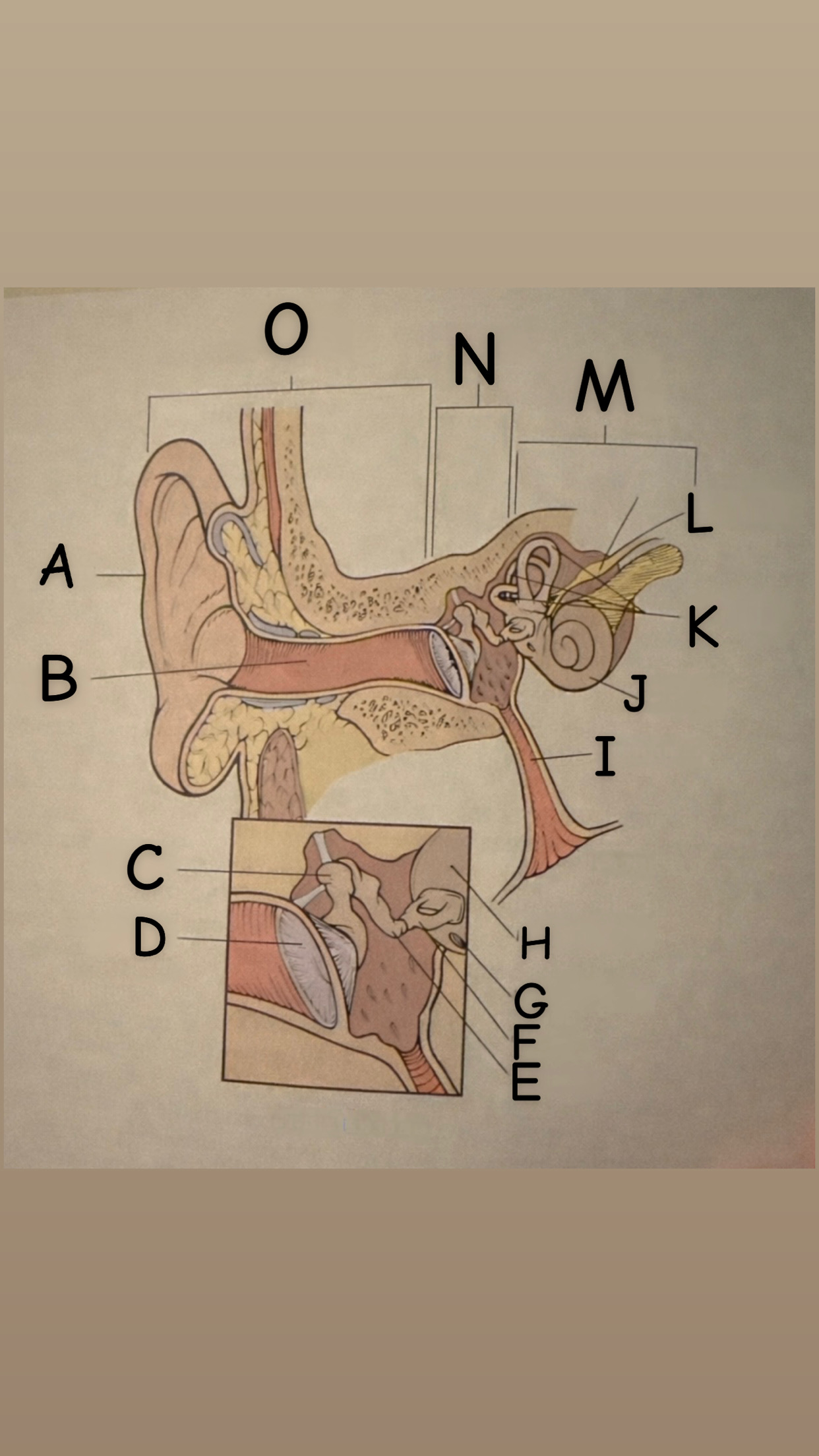
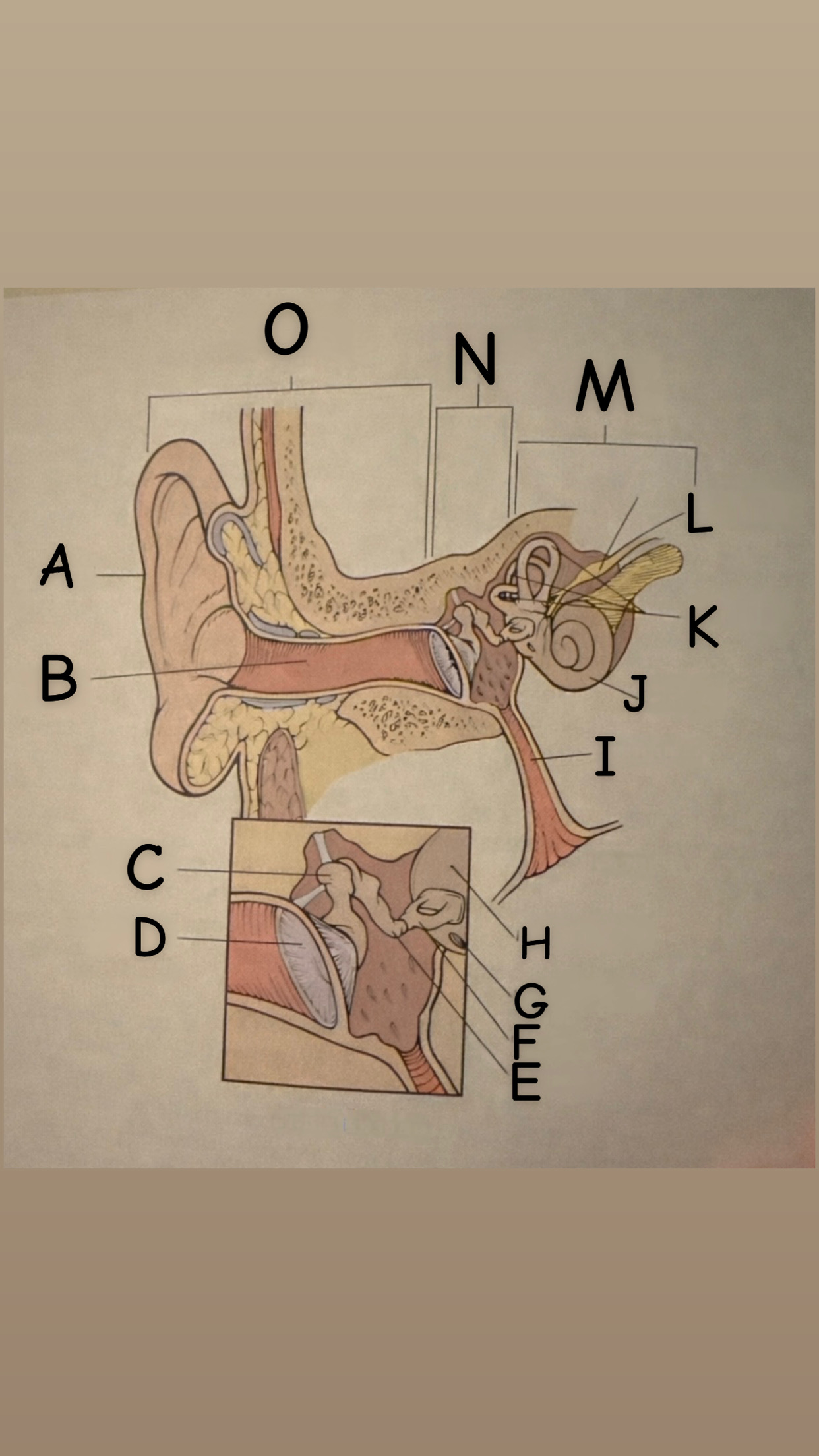
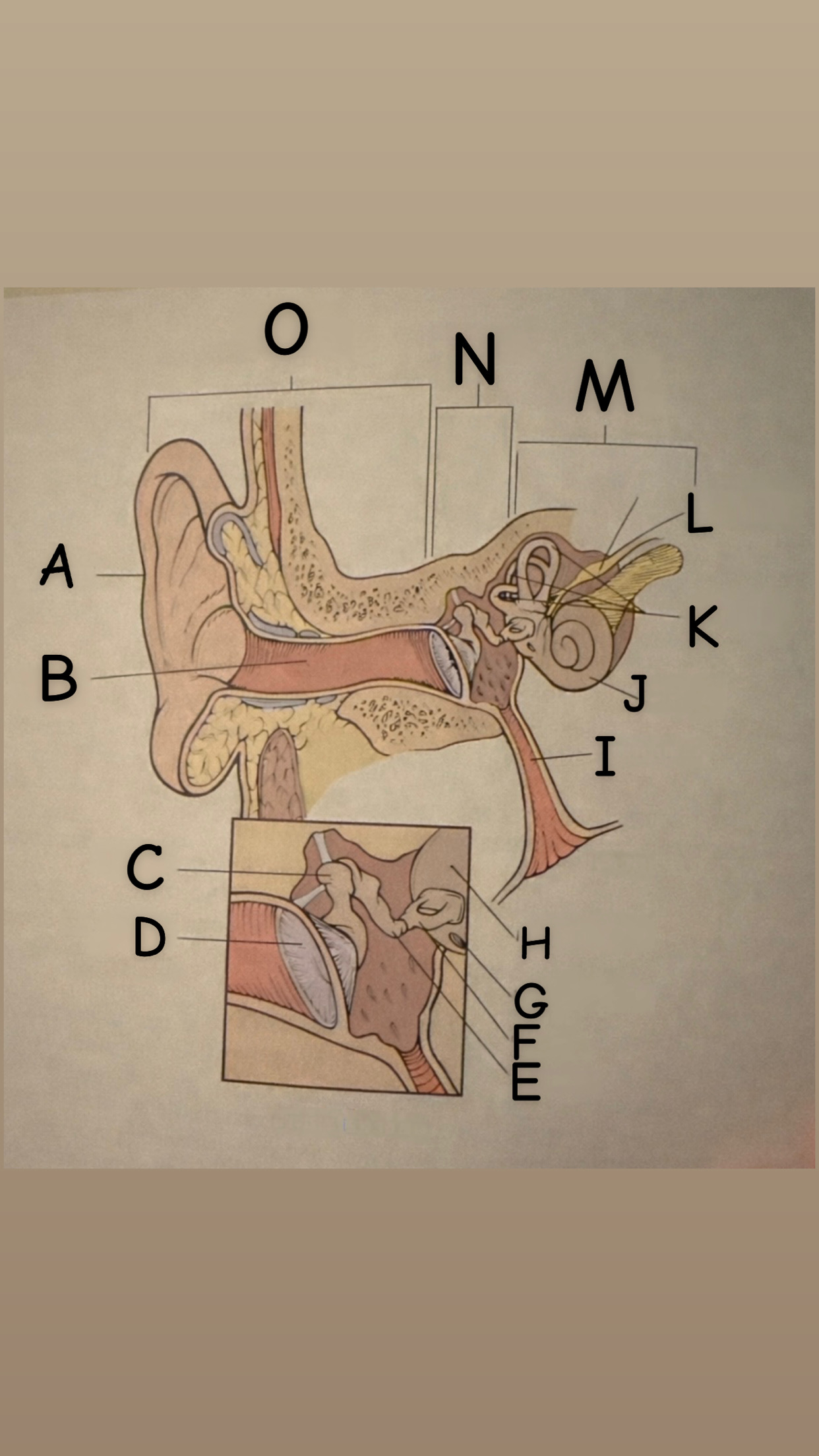
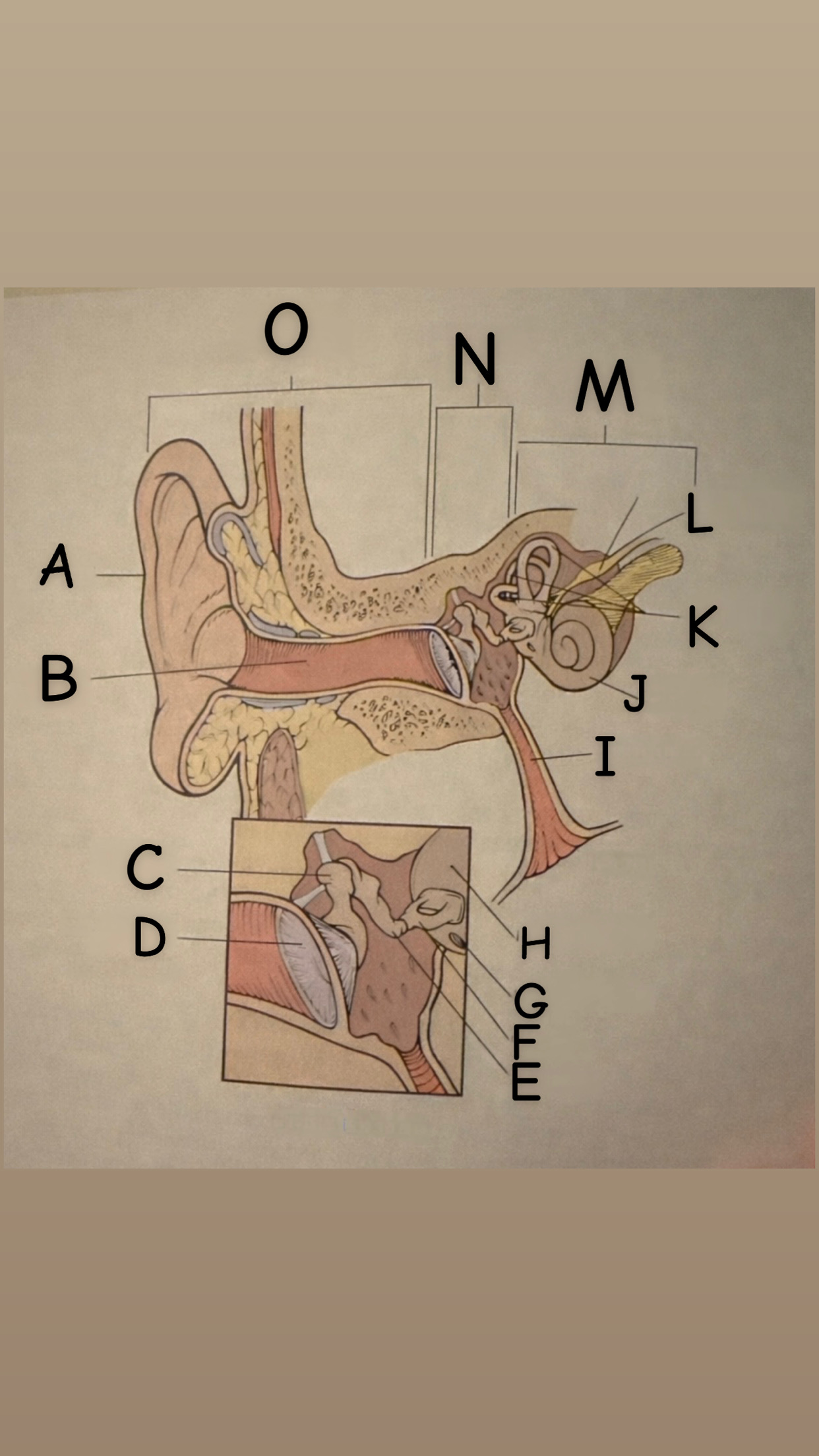
The process of hearing
1. Outer ear (Pinna) collects sound waves, or vibrations, from the environment and channels them to the tympanic membrane (eardrum) which then begins to vibrate
2. The middle ear contains the eardrum an three tiny bones (malleus "hammer", incus "anvil", and the stapes "stirrup") and the eustachian tube which leads to the pharanyx at the innermost is the oval window, the opening of the inner ear. The middle ear receives the sound waves from the vibrating ear drum and relays them along the three bones to the oval window.
3. The inner ear contains two membranes-lined chambers filled with fluid, called the cochlea and the labyrinth. The cochlea contains tiny hair that change the sound waves in the fluid into nerve impulses, which is them transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Conductive hearing loss
-Hearing impairment caused by impairment of the eardrum or bones in the middle ear which conducts sound waves to the cochlea in the inner ear
-Eg. Impacted cerumen, infective otitis externa, swimmers ear, otitis media, otosclerosis
Sensorineural hearing loss
-Hearing loss caused by nerve failure of damage to the cochlea or the auditory nerve
-Sound waves reach the inner ear but are not perceived because the nerve impulses are not transmitted the the brain
-Symptoms: tinnitus and partial to severe hearing loss
Functions of the skin
-Protection
-Sensation
-Synthesis of Vitamin D
-Regulation of body temperature
-Excretion
Common skin lesions
-Macule: Different color than normal skin
-Papule: Small, firm elevated lesion
-Nodule: Palpable elevated lesion
-Pustule: Usually contains purulent exudate
-Vesicle: Thin-walled lesion containing blister
-Plaque: Large, slightly elevated lesion with a
scale
-Crust: Dry surface of dried exudate or blood
Common Skin Lesions
-Lichenification: Thick, dry, rough surface
-Keloid: Increasing mass of collagen resulting
from excessive scar tissue
-Fissure: Small, deep, linear crack or tear
-Ulcer: Cavity with loss of tissue
-Erosion: Shallow, moist cavity in epidermis
-Comedo: Blocks the opening of a hair follicle
Importance of cellulitis treatment
-Affected limb should be immobilized and
elevated
-Cool magnesium sulfate solution compresses
may be used for discomfort
-Warm compresses should be applied to
increase circulation
-Systemic antibiotics are used for infection
Preventive measures for decubitus ulcers
-Frequent inspection
-Alleviation of pressure points over bony areas
-Good sink care
-Early ambulation
-Position changes ever 2 hours
-PROM exercises
-Use of special pads and mattresses
Two most common parasitic insects
-Scabies (Itch mites)
-Pediculosis (lice)
How infestation of scabies (itch mites) and pediculosis (lice) occurs
-Both are spread easily by close physical
contact
-Transmission occurs most often between
children playing together, family members,
and sexual partners
Two common premalignant tumors
-Actinic Keratosis: lesions seen on sun exposed areas of the body, caused by long term exposure to UV portion of sunlight, numbers increase with age
-Nevi: moles, Small dark areas of skin composed of dense
collections of melanocytes?
Three types of skin cancer
-Basal Cell Carcinoma
-Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-Malignant Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Skin lesion appearance
-Shiny bump or nodule that is pearly white, pink,
red, or translucent
-Sore that bleeds, heals, and recurs
-Smooth growth with an indented center and
elevated, rolled edge, or border
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-lesions often present as a crusted or
scaly area with a red, inflamed base
-These forms of skin cancer can develop in
anyone, especially those with a history of sun
exposure
-Chronic exposure to UV radiation has two
main effects that can lead to tumor formation
Malignant Melanoma
-Arises in epidermal melanocytes, cells that
make the brown pigment melanin
-Most occur as solitary lesions
- Change in size, color, or shape, in elevation or the surface; change in surrounding skin
A
Pinna (auricle)
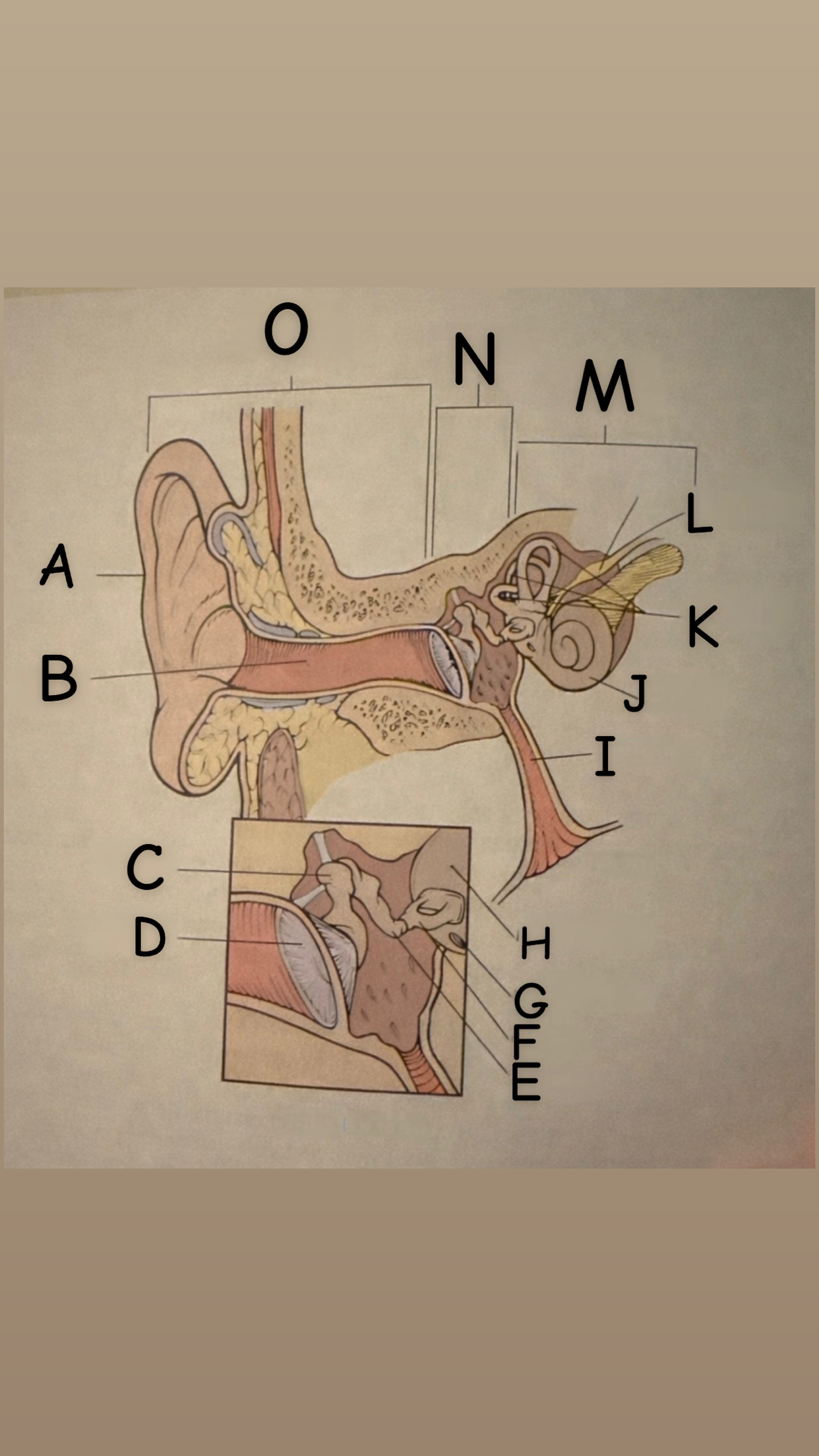
B
External auditory canal
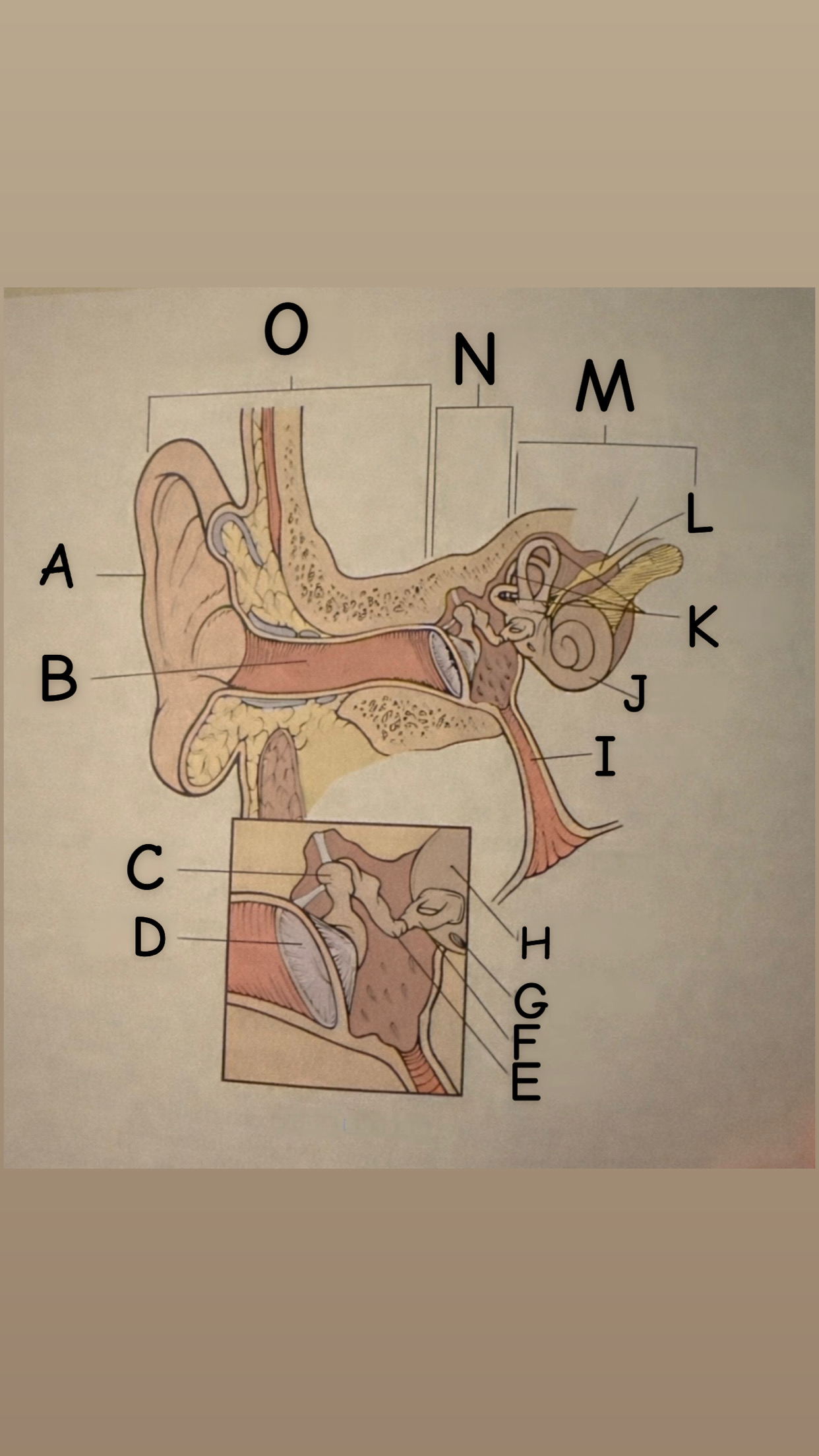
C
Malleus
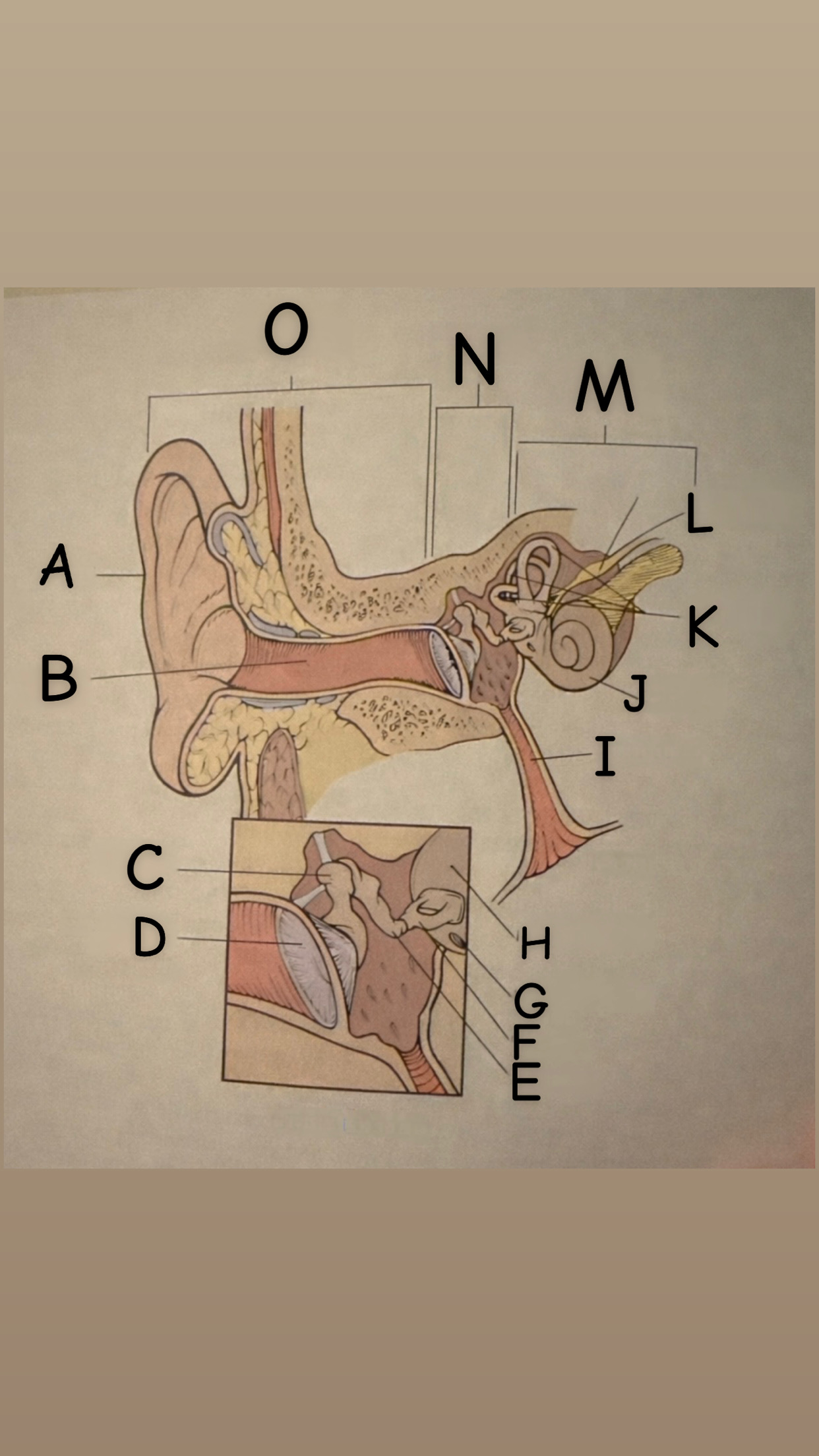
D
Thympanic membrane
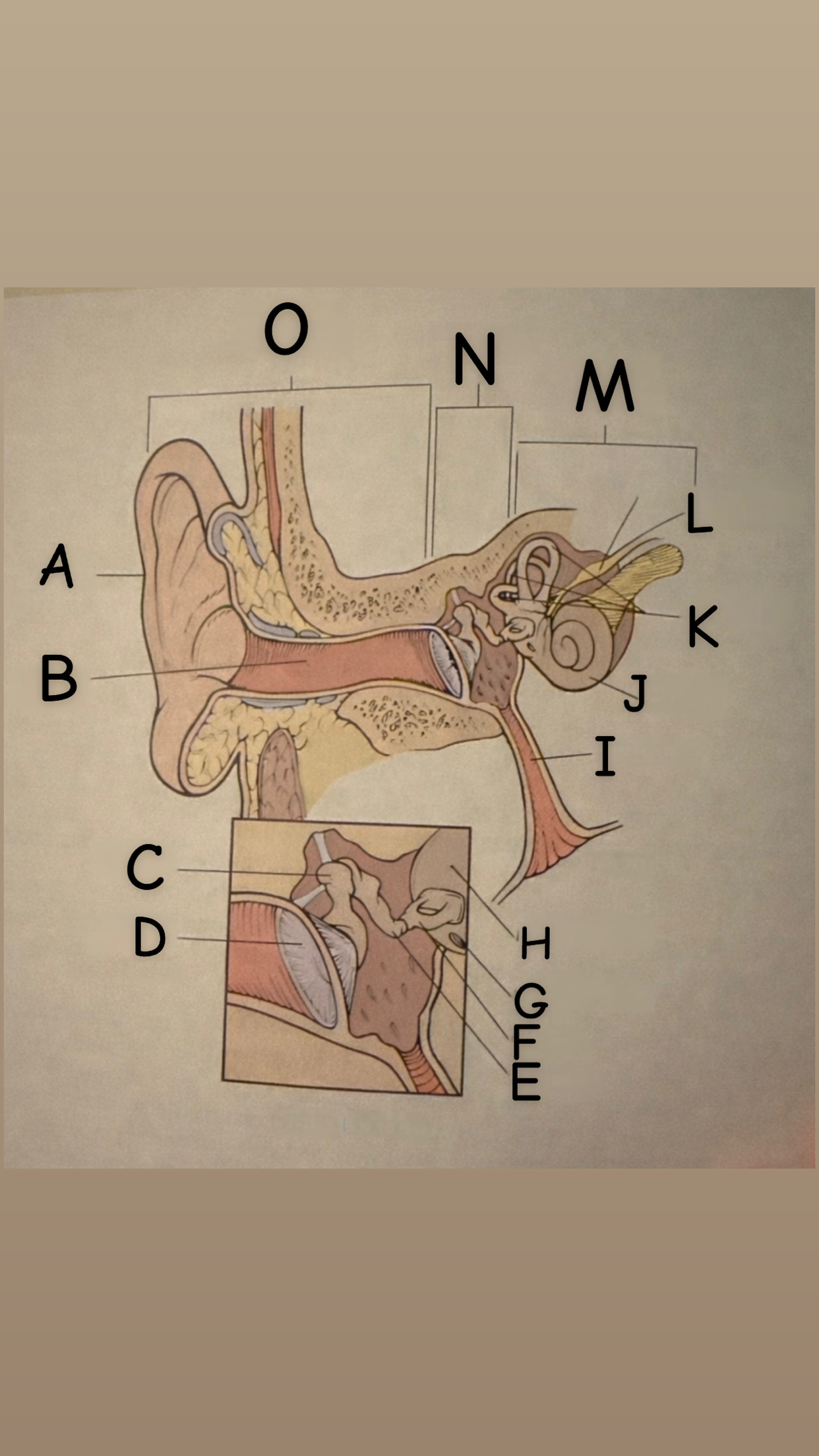
E
Incus
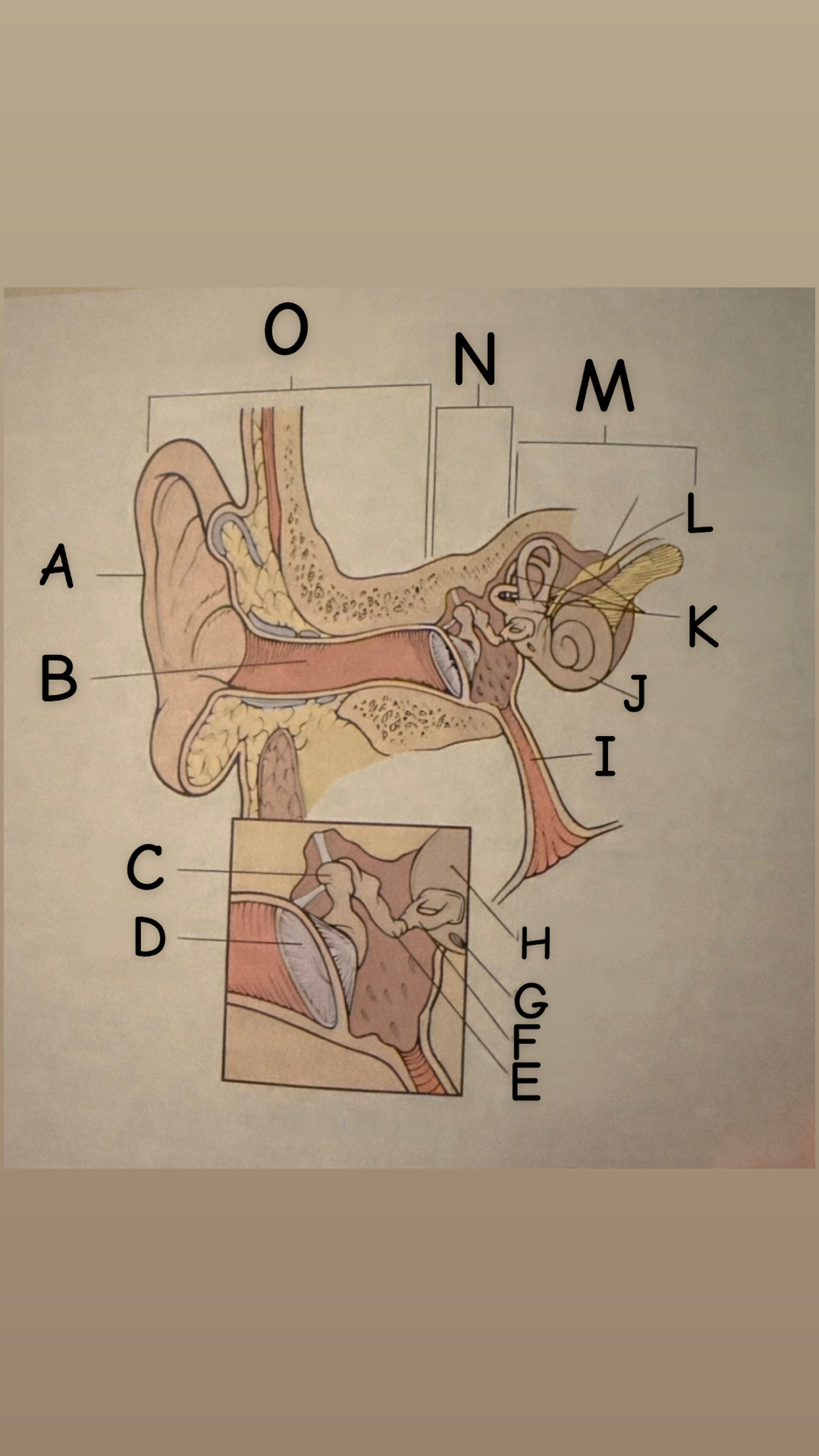
F
Stapes
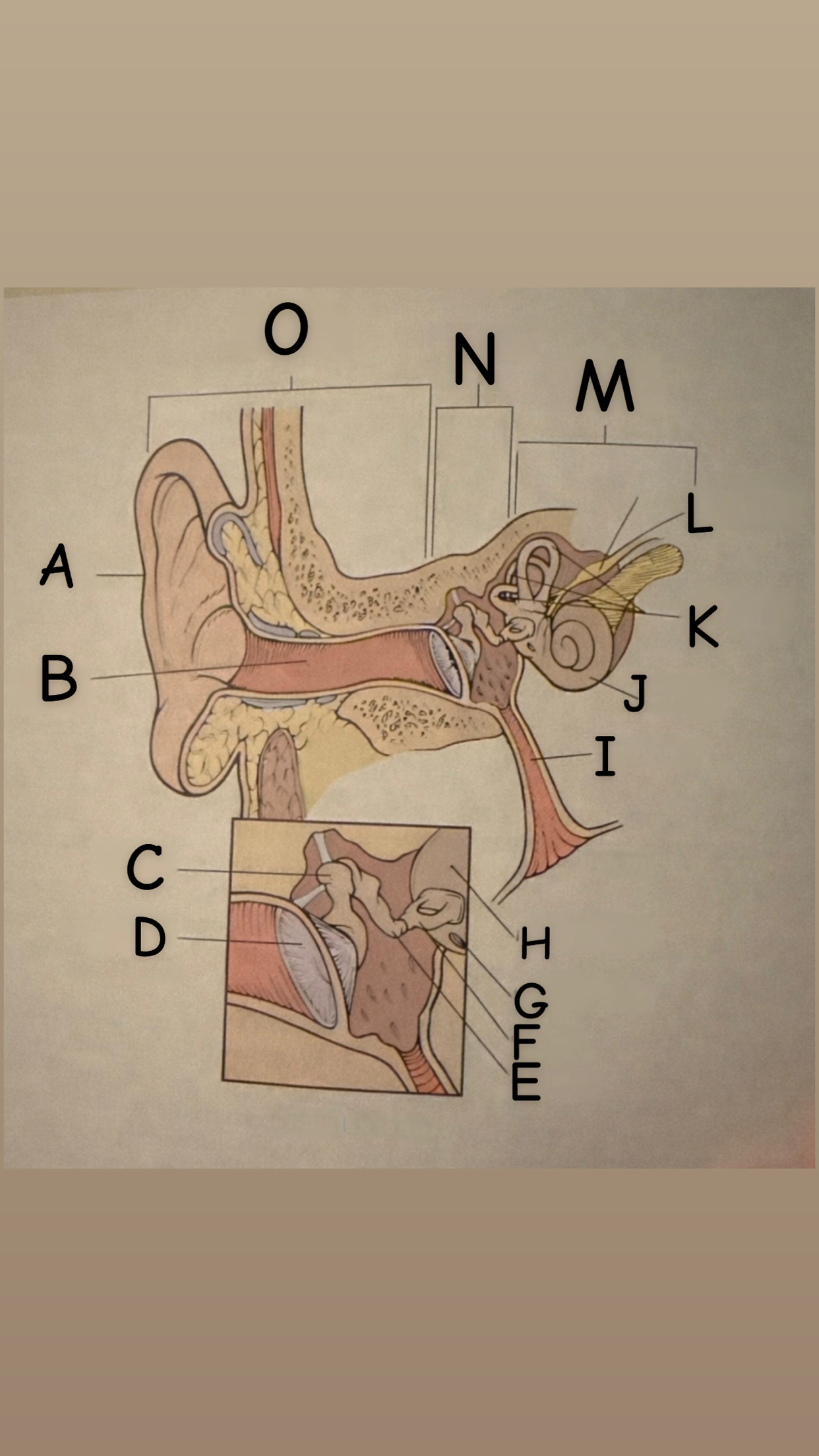
G
Round Window
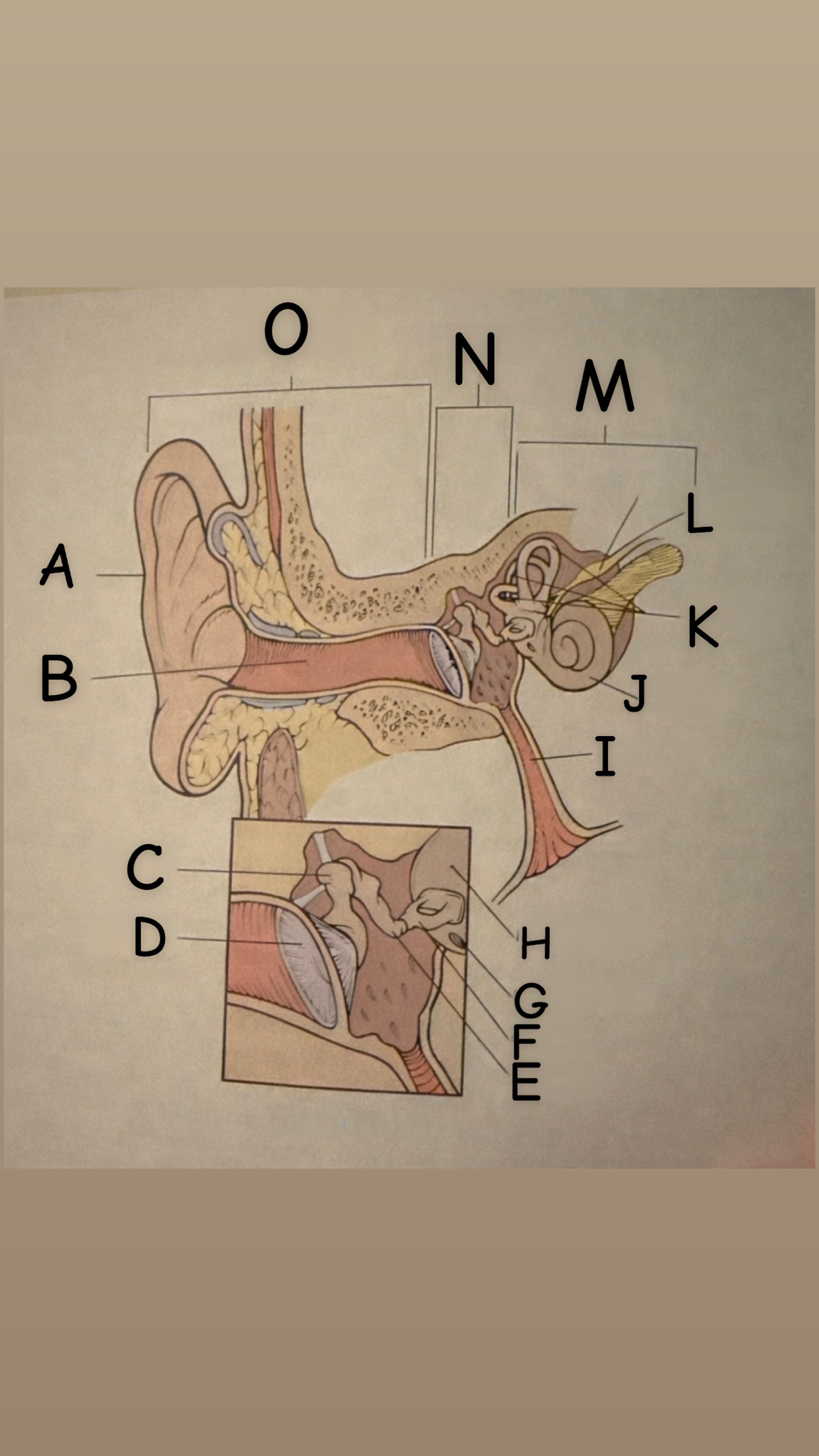
H
Oval Window
I
Eustachian (auditory) tube
J
Cochlea
K
Semicircular canals
L
Vestibulocochlear
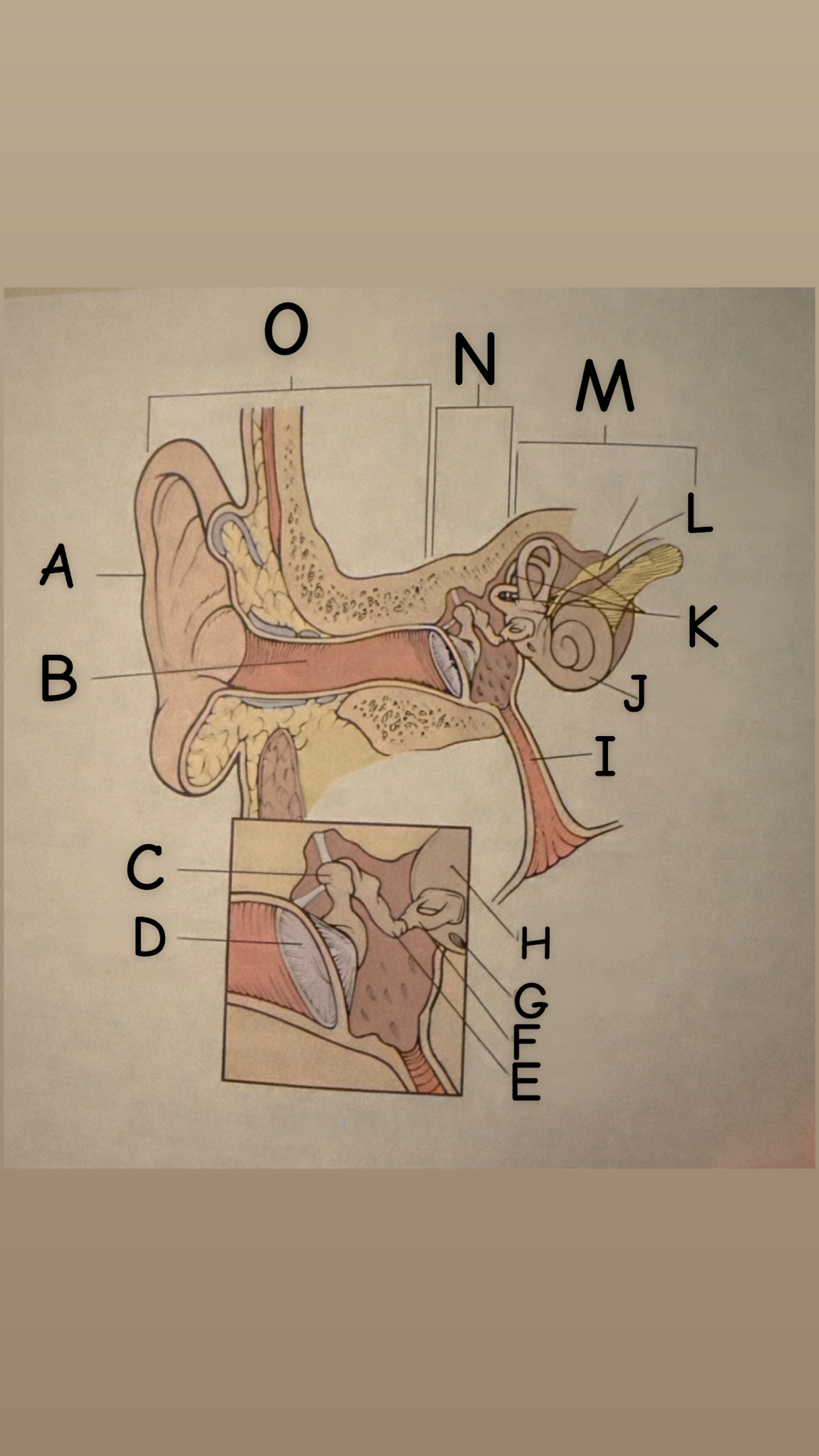
M
Inner Ear
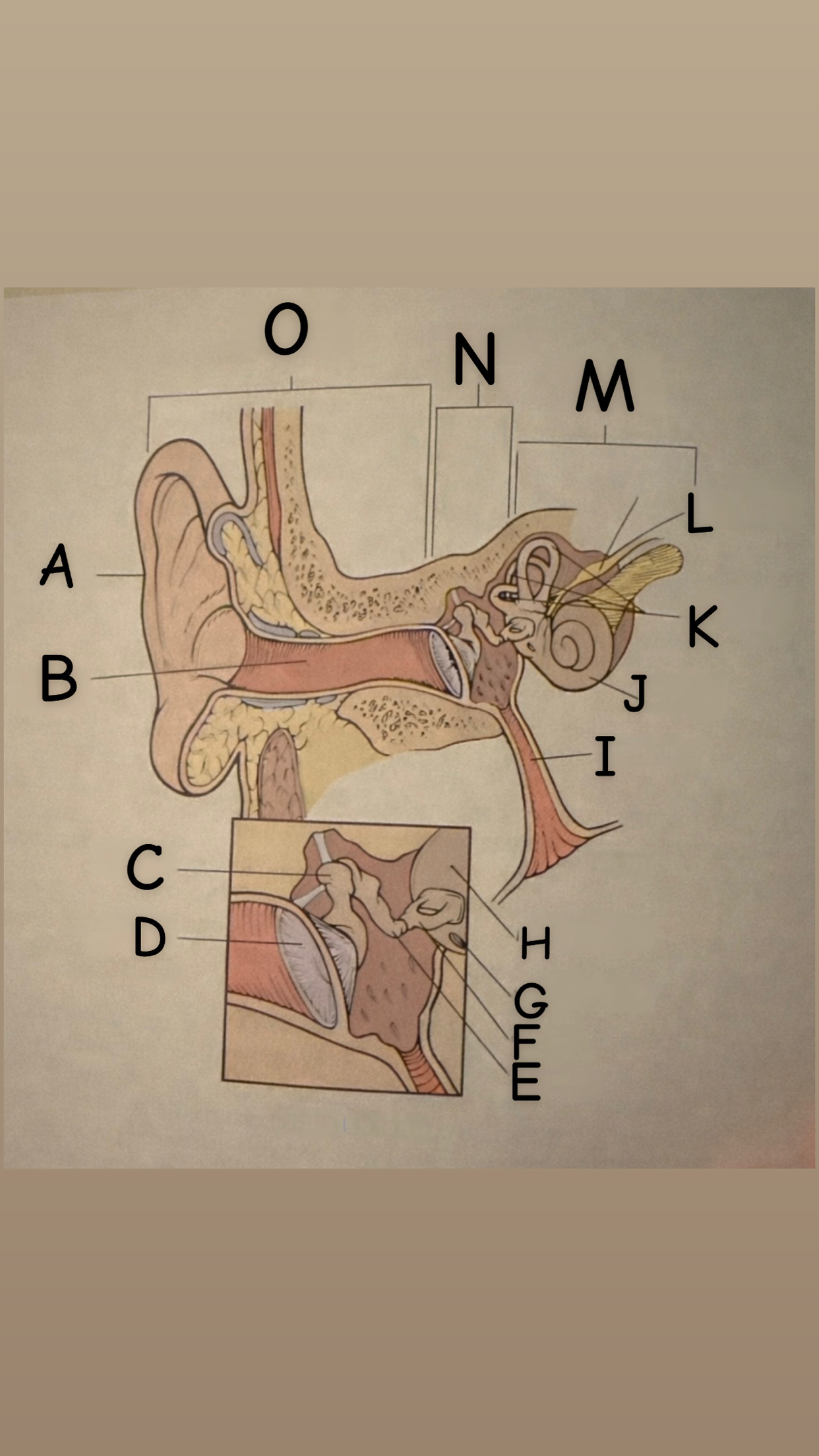
N
Middle ear
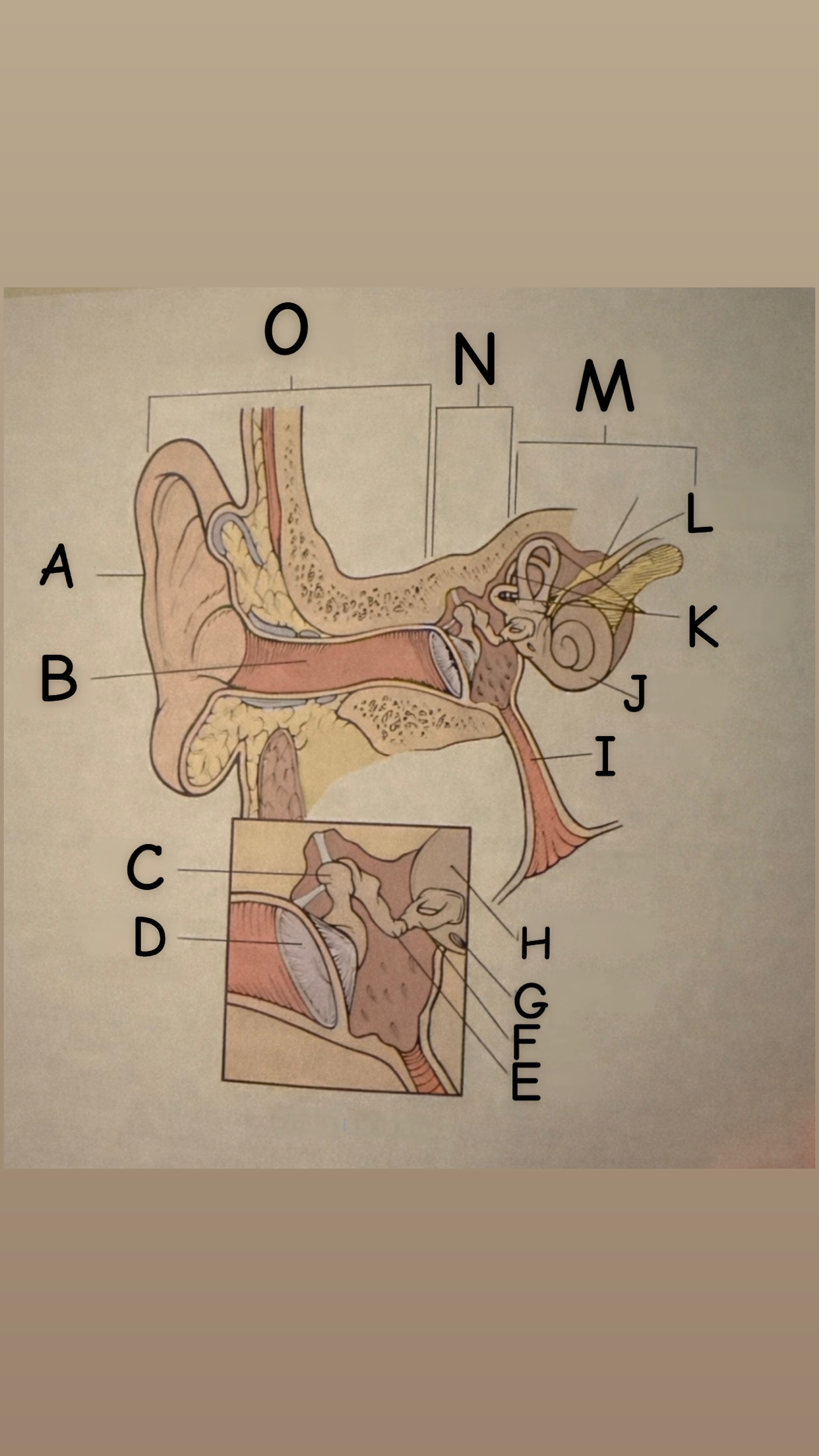
O
External ear