Energy and Electron Configuration Quiz
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what does c stand for?
speed of light; 3 × 10^8 m/s
what does v stand for?
frequency (in Hz)
what does λ stand for?
wavelength (in m or nm)
what does h stand for?
Planck's constant; 6.626 × 10^-34
what does c =
λ x v
what does E =
h x v or (h x c) / λ
orbitals
geometric shapes around nucleus where electrons are found
what does each row on the periodic table represent?
energy level
how many energy levels are there?
7
what are the 4 types of atomic orbitals?
s, p, d, f
how many electrons can the s orbital hold
2
how many electrons can the p orbital hold
6
how many electrons can the d orbital hold
10
how many electrons can the f orbital hold
14
how many valence electrons can there be?
8 when full
what does each block on the periodic table represent
types of atomic orbitals
what shape does the s orbital have
circle
what shape does the p orbital have
figure 8 / infinity
what are the 3 rules of electron configuration
aufbau principle, pauli exclusion principle, hund’s rule
aufbau principle
electrons enter the lowest energy orbitals first
pauli exclusion principle
atomic suborbital may have up to 2 electrons and they must be paired in opposite directions
hund's rule
when you have degenerate (same energy) orbitals, fill each suborbital up halfway, then pair electrons together
electron configuration (notation)
n + orbital + # electrons in orbital; for example 1s1 is hydrogen
what does n represent?
energy level
how are energy levels arranged?
lower the energy level, closer it is to the nucleus
orbital notation
make boxes for each suborbital, follow 3 rules of electron configuration and use arrows to indicate direction of electrons
noble gas notation
shortened way of expressing electron configuration; use noble gas (last row on the periodic table) right before the element and put it in brackets, then continue electron configuration
electron configuration exception
silver and chromium’s row have the s and d orbitals swapped
electron configuration of sodium (Na)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
electron configuration of Barium (Ba)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2
orbital notation of phosphorous (P)
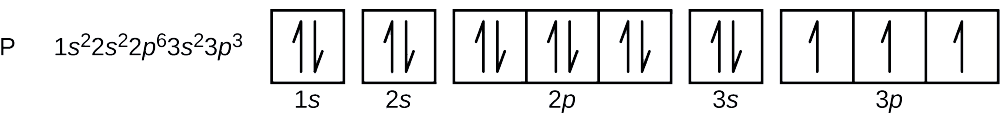
what is the noble gas notation of magnesium (Mg)?
[Ne] 3s2
what is the correct electron configuration of silver (Ag)
[Kr] 4d10 5s1