GEACM01X MT Coverage
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
COMMUNICATION
comes from the Latin word “communist”, which means common'. To be common means "to come together" or "to commune"- "to share something in common.
COMMUNICATION
is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, feelings, and emotions from one person to another with the use of symbols which may be verbal and/or non-verbal and aims for understanding.
PROCESS OF ORAL COMMUNICATION
The process of exchanging information, thoughts, and ideas through spoken words is commonly referred to as oral communication.
ENCODING
is everything that goes inside the brain of an individual. - involves the sender who, grounded by communicative intentions and goals, decides on assigning codes.
ENCODING
is a systematic arrangement of symbols used by individuals to create meaning.
TRANSMITTING
is the process by which the sender, having assigned codes to come up with thought symbols (message) that are also comprehensible by the participant/s
of the communication, transmits or sends message to its recipient.
Broca's Area of the Brain
the motor speech area, utilized in speech Production
RECEIVING
having been submitted through sound waves and light waves, then comes from the sender then reaches the receiver. It is assumed that the receiver's attention is focused on the communication at hand to facilitate better understanding of
the message transported by the sender.
DECODING
is the process by which the receiver interprets or assigns meanings to the codes transported by the source. The receiver tries to give meanings to these symbols which may be literal or may give associations depending on knowledge and/or experience.
Wernicke's Area of the Brain
area responsible for the comprehension of speech.
SPEECH ACTS
are utterances defined by a speaker's intention and their effect on a listener.
LOCUTIONARY
SPEECH ACT
is the process by which the receiver interprets or assigns meanings to the codes transported by the source. The receiver tries to give meanings to these symbols which may be literal or may give associations depending on knowledge and/or experience.
ILLOCUTIONARY
SPEECH ACT
This is a directive to the audience which could be a promise, an order, an apology, or an expression of thanks. This is an act of saying something that has an intention of stating an opinion, a confirmation, or a denial, giving an advise, making a promise, and among others. This is the act of saying something with an intention.
PERLOCUTIONARY
SPEECH ACT
This act carries out an effector consequence to the listener. One could be inspiring or insulting, persuading, convincing, and scaring. The main goal is to change feelings, thoughts, or actions. This happens when the listener is being affected by what the speaker has said.
METALOCUTION
SPEECH ACT
is used for a speech act that refers to the forms and functions of the discourse itself rather than continuing the substantive development of the discourse.
RESPONDING
response is anticipated by the sender from the receive.
-Cultural Diversity in the Modern World
-Cultural Diversity and Public Speaking
-Complexity of Speech and Language
PUBLIC SPEAKING IN THE MODERN WORLD
ETHNOCENTRISM
is the tendency to view other cultures through the lens of one's own culture, often leading to the belief that one's own culture is superior.
CATEGORIES OF COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS
The Sender's Standpoint
The Receiver's Standpoint
The Sender's Standpoint
Functions are information, instruction,
persuasion, and entertainment.
The Receiver's Standpoint
Functions are personal identity function, social integration function, cognitive function, and escape function.
VERBAL LEVEL
PHYSICAL
AUDITORY
EMOTIONAL
ENERGETIC
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
VERBAL LEVEL
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Surface level
PHYSICAL
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Visible/ Observe cues
AUDITORY
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Audible cues
EMOTIONAL
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Empathetic and sympathetic level
ENERGETIC
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
"X-Factor"
ACADEMIC LEVEL
OPPORTUNITIES OF MAKING A SPEECH
-Enhancement of Communication Skills
-Academic success
-Preparation for professional life
CORPORATE LEVEL
OPPORTUNITIES OF MAKING A SPEECH
-Leadership and career advancement
-Enhanced communication and collaboration
-Conflict resolution and negotiation
Elements of communication
is the process of transmitting information from a sender to a receiver through a communication channel, with various elements involved in encoding and decoding the message. (Claude E. Shannon and Warren Weaver: In their book "The Mathematical Theory of Communication")
COMMUNICATION
comes from the Latin word “communist”, which means common'. To be common means "to come together" or "to commune"- "to share something in common."
COMMUNICATION
is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, feelings, and emotions from one person to another with the use of symbols which may be verbal and/or non-verbal and aims for understanding.
PROCESS OF ORAL COMMUNICATION
The process of exchanging information, thoughts, and ideas through spoken words is commonly referred to as oral communication.
ENCODING
is everything that goes inside the brain of an individual. - involves the sender who, grounded by communicative intentions and goals, decides on assigning codes.
ENCODING
is a systematic arrangement of symbols used by individuals to create meaning.
TRANSMITTING
is the process by which the sender, having assigned codes to come up with thought symbols (message) that are also comprehensible by the participant/s of the communication, transmits or sends message to its recipient.
Broca's Area of the Brain
the motor speech area, utilized in speech Production
RECEIVING
having been submitted through sound waves and light waves, then comes from the sender then reaches the receiver. It is assumed that the receiver's attention is focused on the communication at hand to facilitate better understanding of the message transported by the sender.
DECODING
is the process by which the receiver interprets or assigns meanings to the codes transported by the source. The receiver tries to give meanings to these symbols which may be literal or may give associations depending on knowledge and/or experience.
Wernicke's Area of the Brain
area responsible for the comprehension of speech.
SPEECH ACTS
are utterances defined by a speaker's intention and their effect on a listener.
LOCUTIONARY SPEECH ACT
is the process by which the receiver interprets or assigns meanings to the codes transported by the source. The receiver tries to give meanings to these symbols which may be literal or may give associations depending on knowledge and/or experience.
ILLOCUTIONARY SPEECH ACT
This is a directive to the audience which could be a promise, an order, an apology, or an expression of thanks. This is an act of saying something that has an intention of stating an opinion, a confirmation, or a denial, giving an advise, making a promise, and among others. This is the act of saying something with an intention.
PERLOCUTIONARY SPEECH ACT
This act carries out an effector consequence to the listener. One could be inspiring or insulting, persuading, convincing, and scaring. The main goal is to change feelings, thoughts, or actions. This happens when the listener is being affected by what the speaker has said.
METALOCUTION SPEECH ACT
is used for a speech act that refers to the forms and functions of the discourse itself rather than continuing the substantive development of the discourse.
RESPONDING
response is anticipated by the sender from the receive.
PUBLIC SPEAKING IN THE MODERN WORLD
- Cultural Diversity in the Modern World
- Cultural Diversity and Public Speaking
- Complexity of Speech and Language
ETHNOCENTRISM
is the tendency to view other cultures through the lens of one's own culture, often leading to the belief that one's own culture is superior.
CATEGORIES OF COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS
The Sender's Standpoint
The Receiver's Standpoint
The Sender's Standpoint
Functions are information, instruction, persuasion, and entertainment.
The Receiver's Standpoint
Functions are personal identity function, social integration function, cognitive function, and escape function.
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
VERBAL LEVEL
PHYSICAL
AUDITORY
EMOTIONAL
ENERGETIC
VERBAL LEVEL
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Surface level
PHYSICAL
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Visible/ Observe cues
AUDITORY
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Audible cues
EMOTIONAL
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
Empathetic and sympathetic level
ENERGETIC
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
"X-Factor"
OPPORTUNITIES OF MAKING A SPEECH
ACADEMIC LEVEL
- Enhancement of Communication Skills
- Academic success
- Preparation for professional life
CORPORATE LEVEL
OPPORTUNITIES OF MAKING A SPEECH
- Leadership and career advancement
- Enhanced communication and collaboration
- Conflict resolution and negotiation
Elements of communication
is the process of transmitting information from a sender to a receiver through a communication channel, with various elements involved in encoding and decoding the message. (Claude E. Shannon and Warren Weaver: In their book "The Mathematical Theory of Communication")
What are the models of communication?
Aristotle's Model
David Kenneth Berlo's Model
Wilbur Schramm's Model
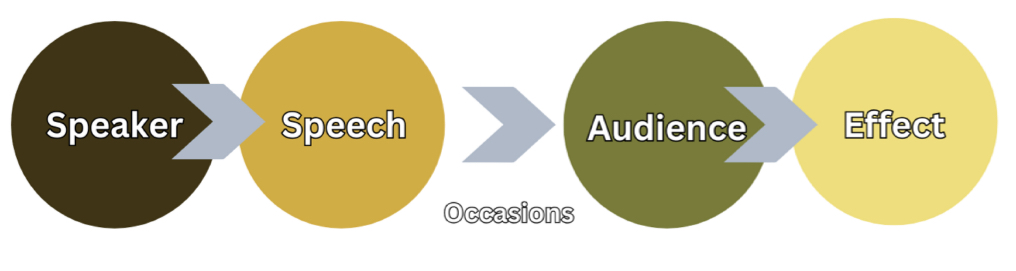
Aristotle’s Model of Communication
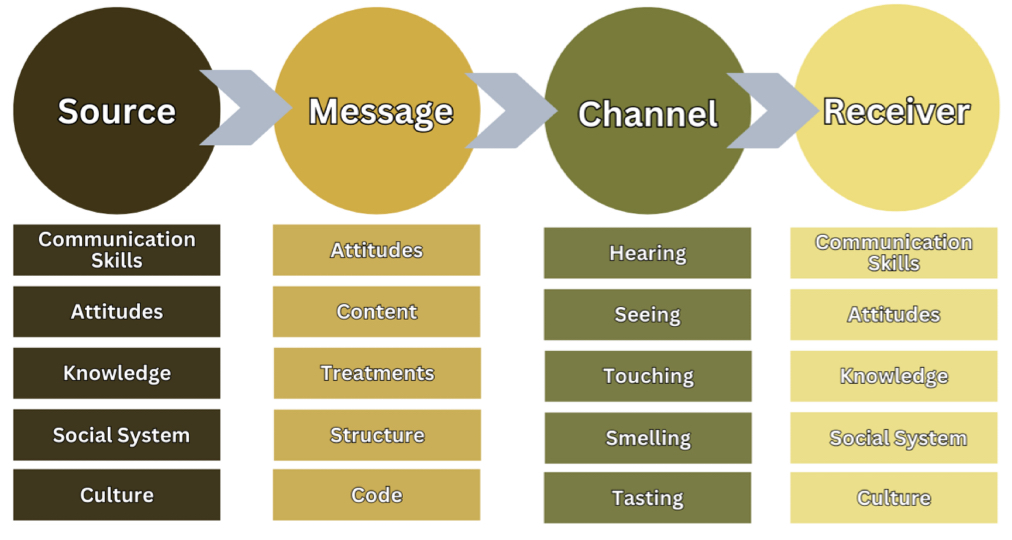
David Kenneth Berlo’s Model of Communication
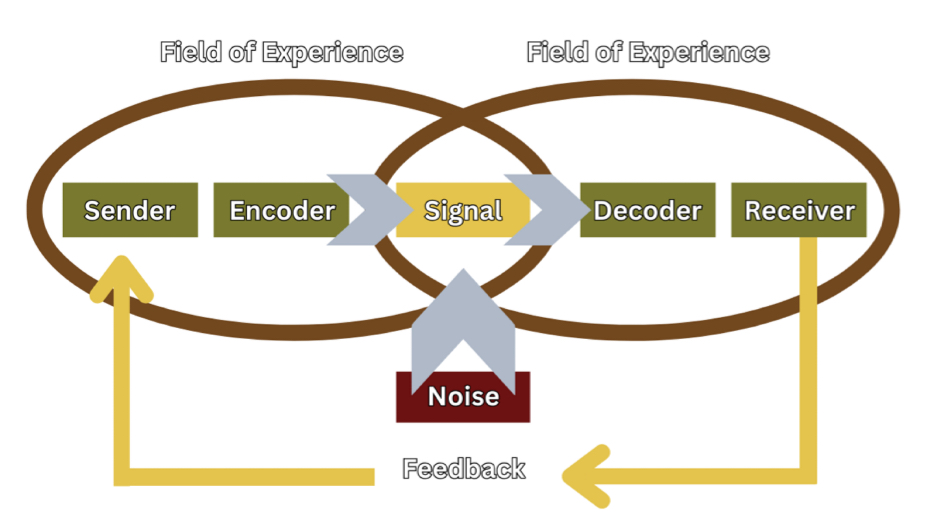
Wilbur Schramm’s Model of Communication
Communication Theories
is a proposed description of communication phenomena, the relationships among them and a storyline describing these relationships.
Examples of Communication Theories
- Altercasting
- Argumentation
- Classical Rhetoric
- Model of Text Comprehension
Altercasting
refers to a communication strategy that involves ascribing or assigning a particular role or identity to someone in order to influence their behavior or perception.
Argumentation
is an interdisciplinary study that examines how conclusions can be supported or undermined by premises through logical reasoning
Classical Rhetoric
is the art of persuasive speaking and writing, originating from ancient Greece and Rome, where philosophers like Aristotle and Cicero established foundational principles such as ethos, pathos, and logos to enhance communication effectiveness.
Model Text Comprehension
describe and explain the processes involved in understanding and remembering verbal information.
Globalization
is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. Globalization has accelerated since the 18^{th} century due to advances in transportation and communication technology.
Communication in Global Context
All over the world, nations are experiencing more and more people from other cultures coming into their countries. Some people give newcomers a warm welcome. Some are less warm, but allow foreigners to thrive. Some reject those who come from a different culture.
The Effects of Globalization on Global Communication
Journalist Thomas Friedman argues that globalization, the integration of economics and technology that is contributing to a worldwide, interconnected business environment, is changing the way we work and relate to people around the world.
Communication in Digital Age
Communication is a vital leadership skill, and the Digital Age has changed the way people communicate. While technology contributes to the noise that often distracts or interrupts people from sending or receiving messages effectively, it can be a great asset for better communication.