Portage Learning Anatomy & Physiology 2: Module 4 Exam
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Which body system supplies cells with oxygen and nutrients and carries away waste?
A. Nervous system
B. Respiratory system
C. Urinary System
D. Circulatory System
D. Circulatory System
The heart is contained in the _______ cavity.
A. Pericardial
B. Pleural
C. Septal
D. Rectoperineal
A. Pericardial
Which layer of heart anchors it to the diaphragm?
A. Endocardium
B. Mediastinal
C. Myocardium
D. Pericardium
D. Pericardium
What is the purpose of the mitral valve?
The mitral valve controls the flow of blood from the left atrium into the left ventricle.
Label the figure below (A-E):
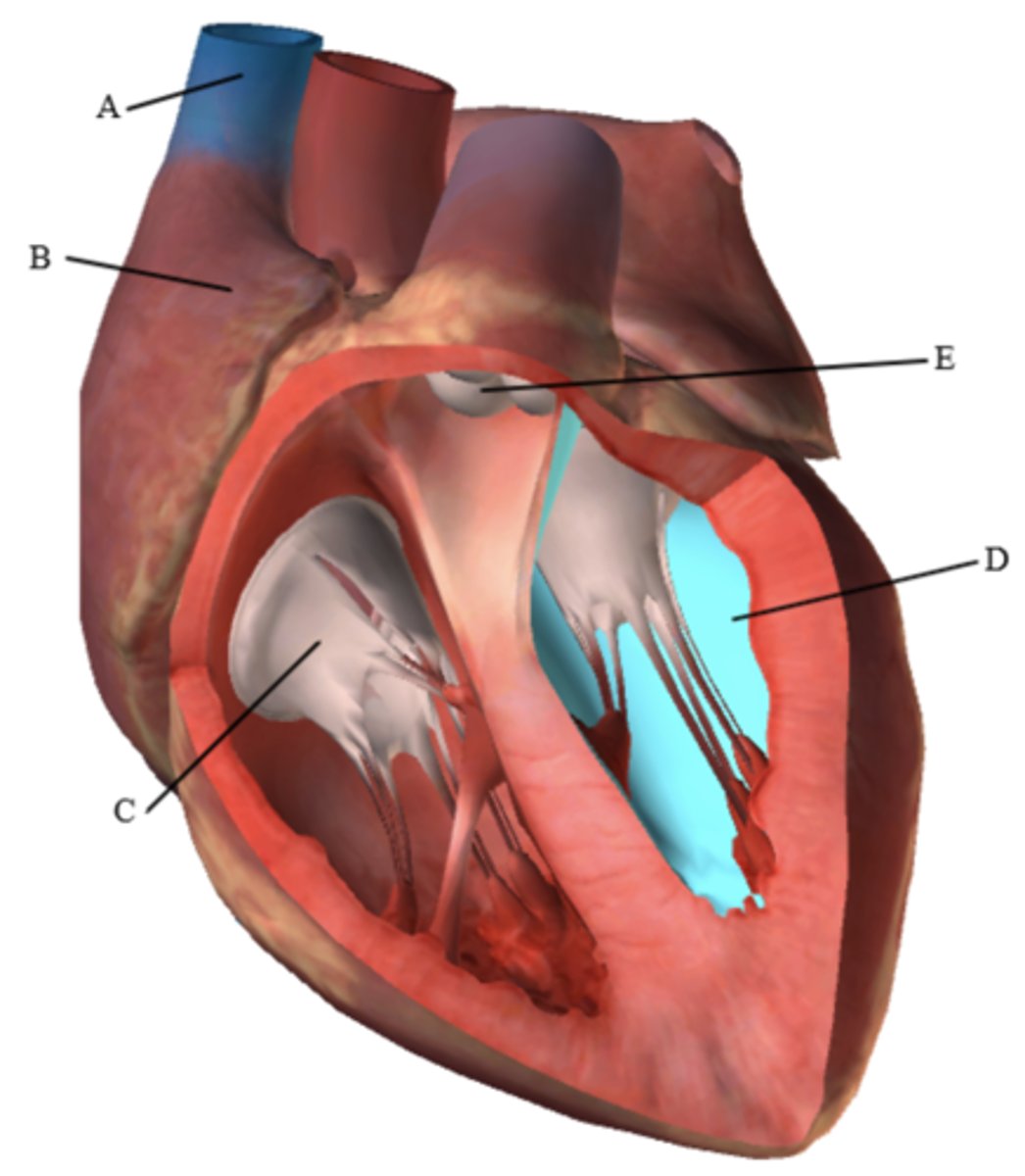
A:
B:
C:
D: (In blue)
E:
A: Superior Vena Cava
B: Right Atrium
C: Tricuspid/Right AV valve
D: Left ventricle
E. Pulmonary Valve
Name the vessel in the figure below: (highlighted in blue, also indicated by the arrow)
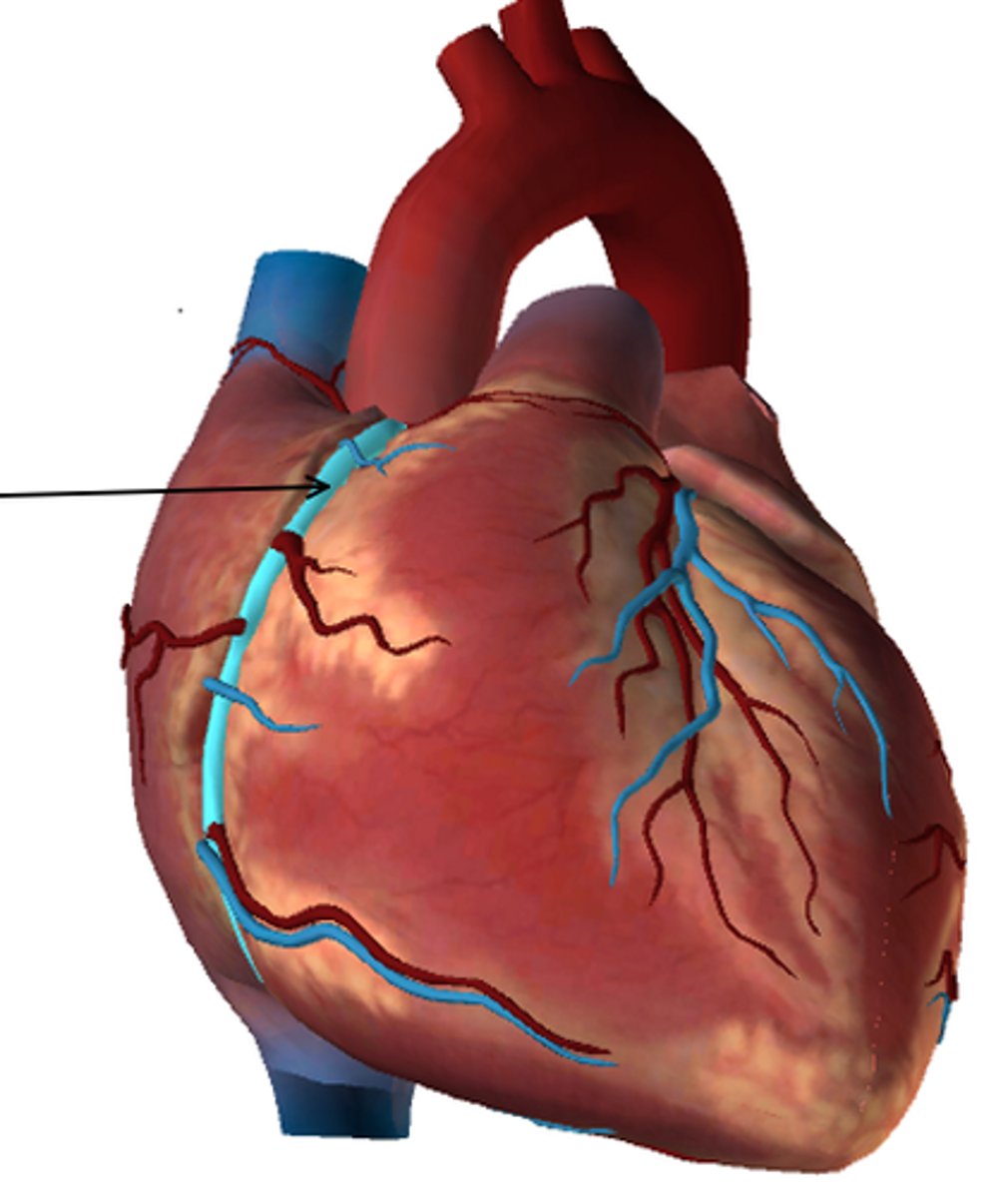
Right Coronary Artery
Name the vessel in the figure below: (highlighted in blue, also indicated by the arrow)
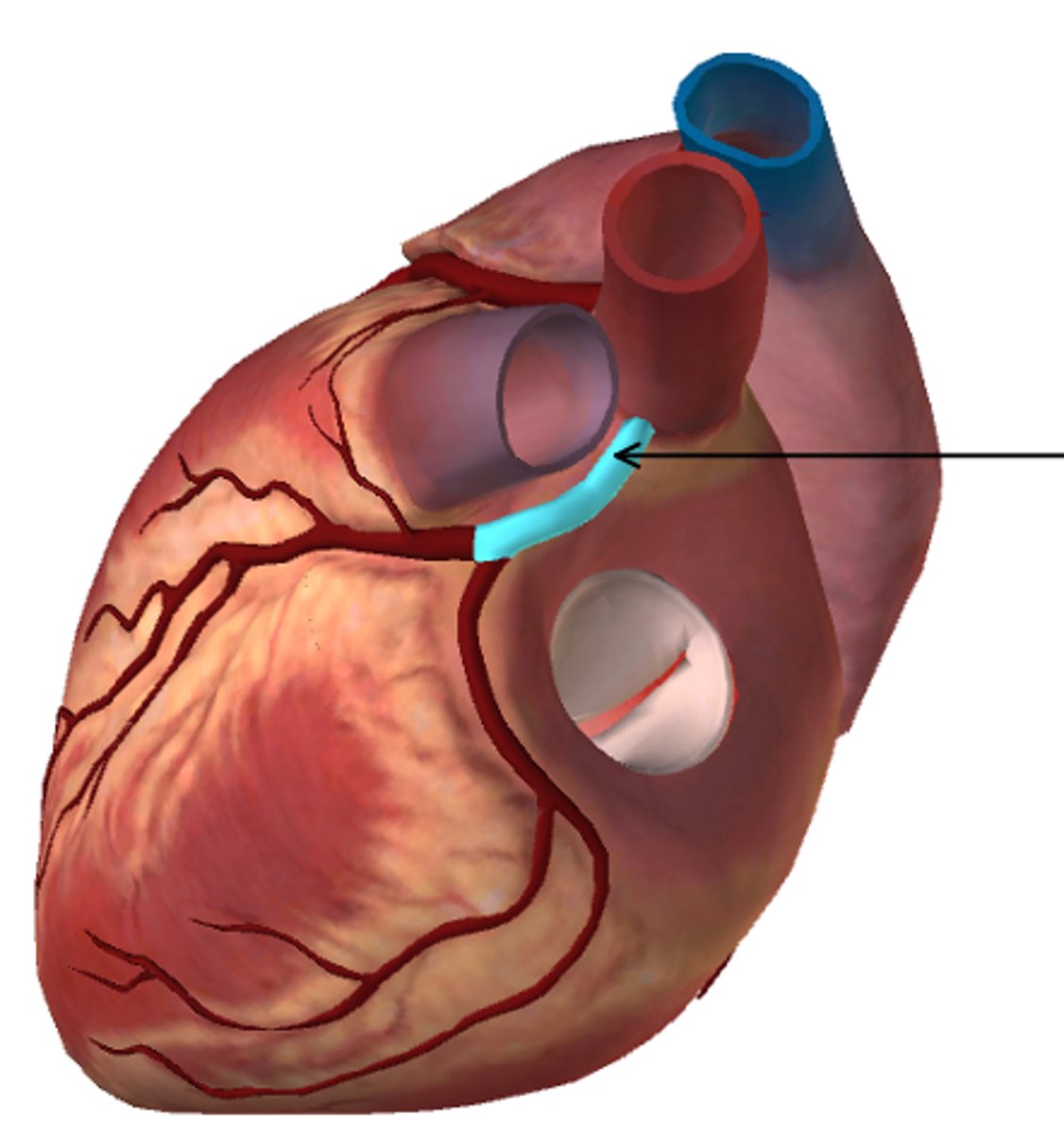
Left Coronary Artery
Name the vessel in the figure below: (highlighted in blue, also indicated by the arrow)
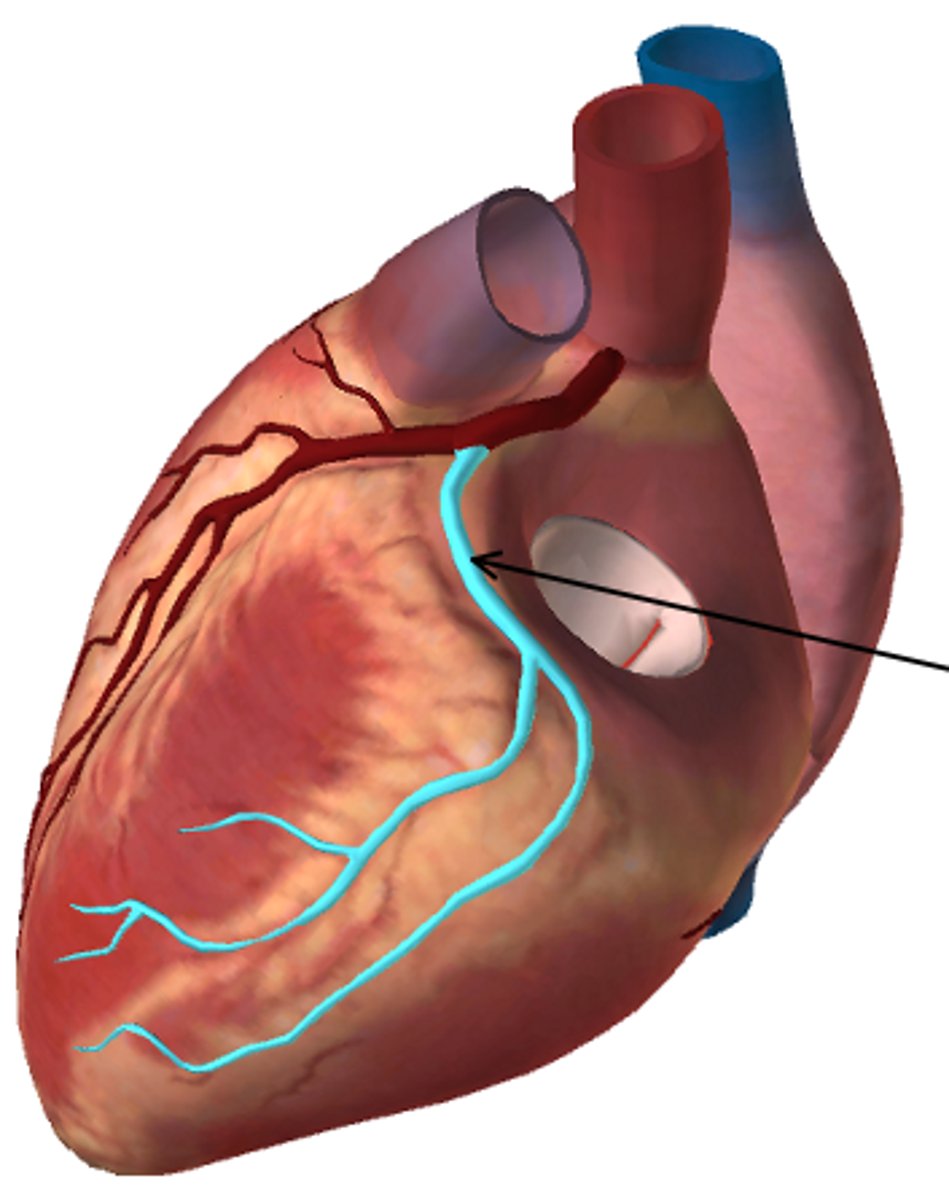
Circumflex branch
True or False: Veins carry blood towards the heart.
True
Which vessel would you expect to be the best place to feel a strong pulse?
A. Subclavian vein
B. Inferior vena cava
C. Common carotid
D. Brachiocephalic vein
C. Common carotid
(Arteries have palpable pulses, not veins)
What is the correct order of blood flow starting from the heart?
A. Artery → arteriole → capillary → venule → vein
B. Arteriole → artery → capillary → vein → venule
C. Artery → capillary → arteriole → venule → vein
D. Vein → venule → capillary → arteriole → artery
A. Artery → arteriole → capillary → venule → vein
Which layer of a vessel contains the muscular layer?
A. Tunica externa
B. Tunica media
C. Tunica intima
D. Vessels do not contain a muscular layer
B. Tunica media
Which layer of a vessel helps anchor it to the surrounding structures?
A. Tunica externa
B. Tunica media
C. Tunica intima
D. Subendothelial tissue
A. Tunica externa
The aortic arch turns to become the _______?
A. Superior vena cava
B. Pulmonary trunk
C. Ascending aorta
D. Descending aorta
D. Descending aorta
A patient had a stroke in their pons portion of the brainstem. What vessel was most likely blocked?
A. Anterior cerebral artery
B. Posterior cerebral artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Vertebral artery
C. Basilar artery
A patient had a stroke in their frontal lobe. What vessel was most likely blocked?
A. Anterior cerebral artery
B. Posterior cerebral artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Vertebral artery
A. Anterior cerebral artery
These two arteries of the circle of Willis arise from the common carotid arteries in the neck.
Internal carotid arteries (left and right)
These two arteries of the circle of Willis rise along both sides of the spinal cord, joining in the brainstem:
Vertebral arteries (left and right)
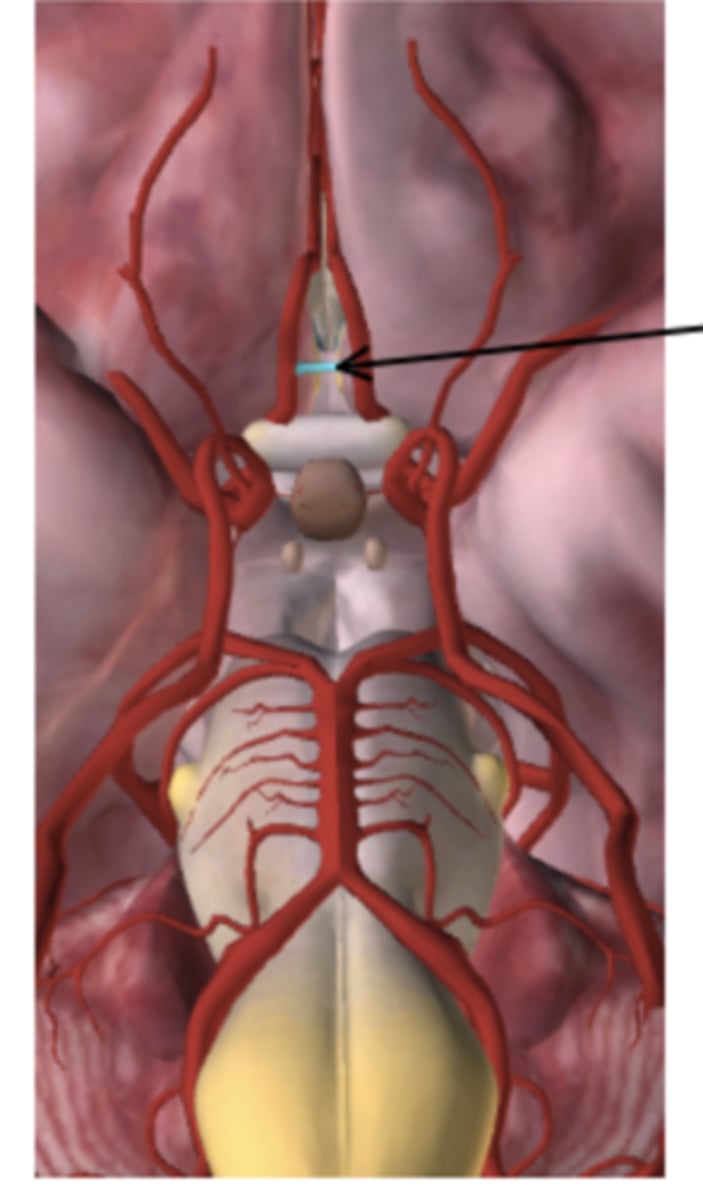
What is the name of the artery in the figure below:
Posterior Cerebral (PCA)
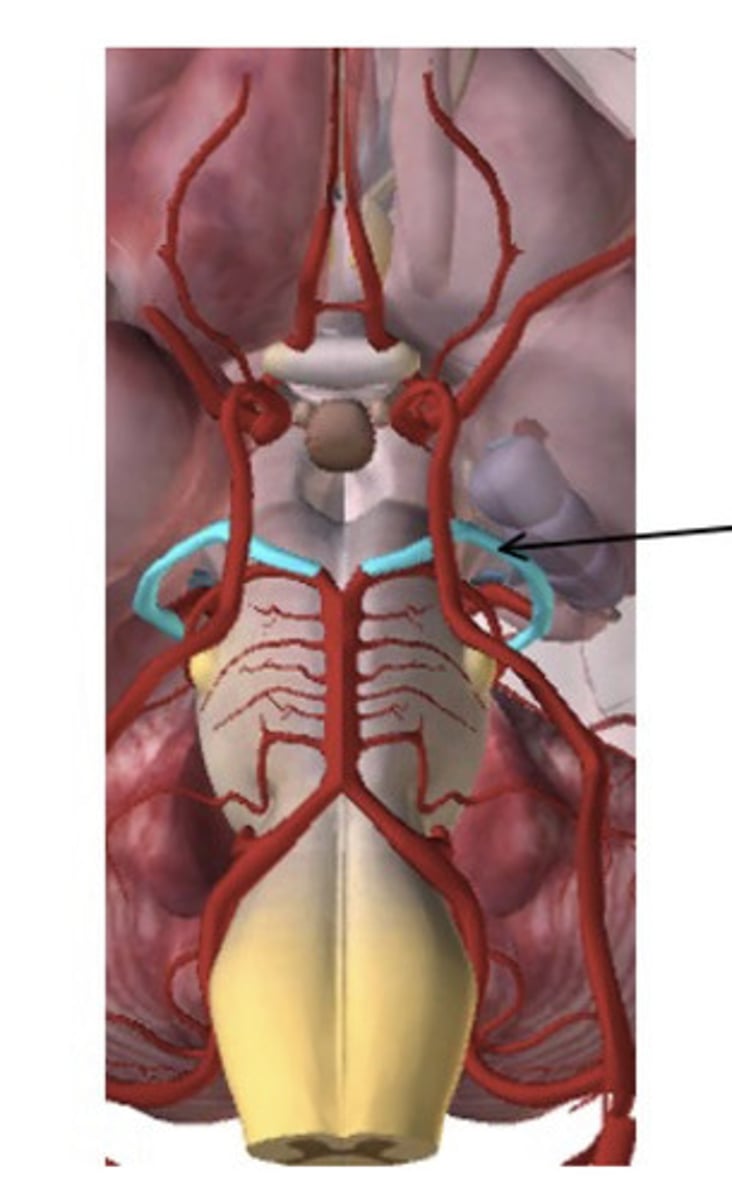
What is the name of the artery in the figure below (in blue also indicated by the arrow)?
anterior communicating artery
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
Which part of the medical equipment (B-F) is squeezed to inflate A?
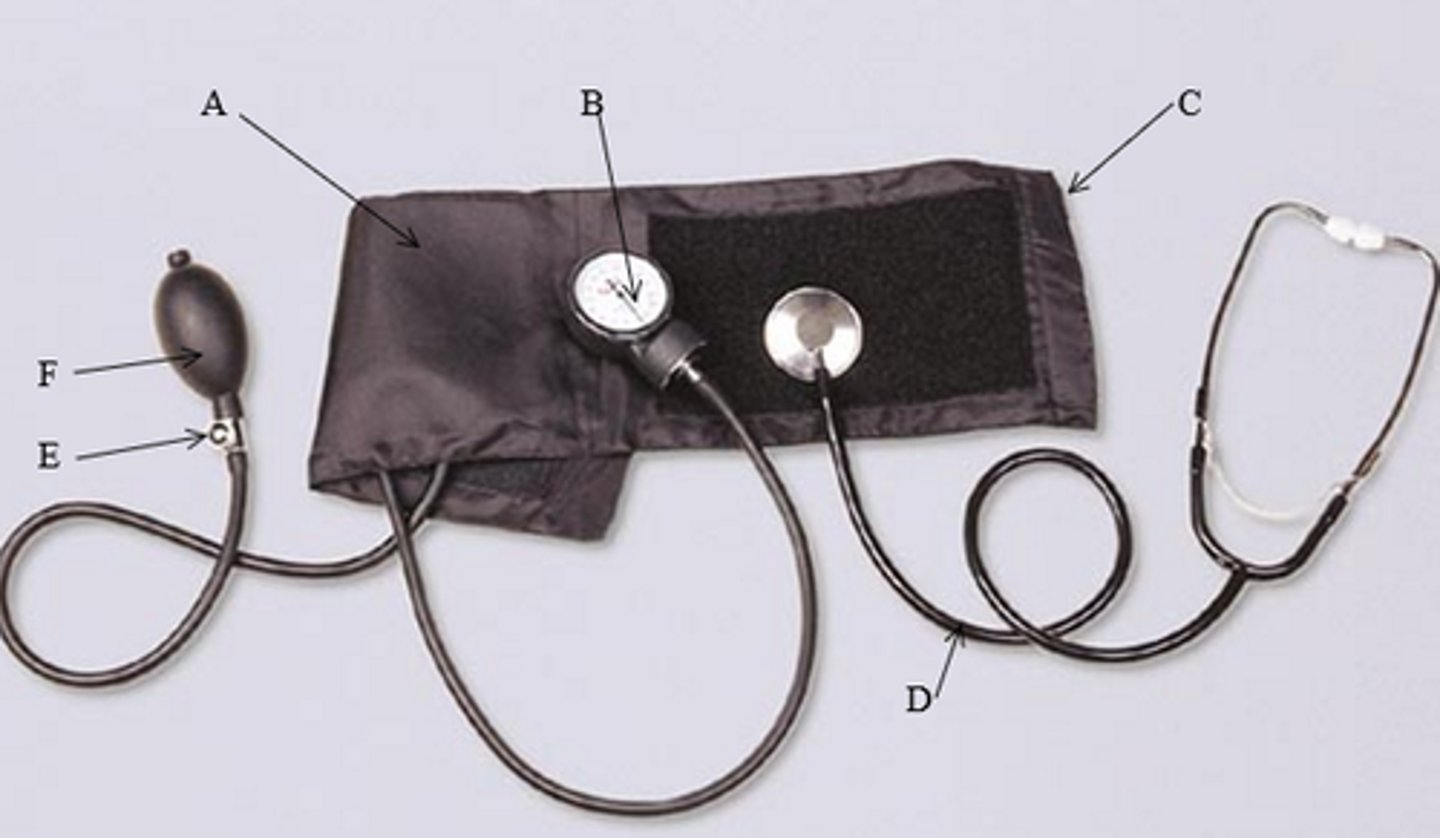
F. The bulb
True or False: The cell portion of blood is called formed elements.
True
True or False: Hydrostatic pressure is the net pressure which pushes fluid into the tissues.
True
The average pH of blood is near:
A. 3.1
B. 5.5
C. 7.4
D. 9.7
C. 7.4
A_______ does not contain a nucleus:
A. White blood cell
B. Red blood cell
D. Megakaryocyte
C. Lymphocyte
B. Red blood cell
Which statement is false concerning the events in the coagulation cascade?
A. Plasmin destroy the fibrin network
B. Fibrin is converted to fibrinogen
C. Platelets becomes trapped in a fibrin network of threads
D. Prothrombin is converted to thrombin
B. Fibrin is converted to fibrinogen
Which statement is true concerning the events in the coagulation cascade?
A. Platelets destroy the fibrin network.
B. Fibrin is converted to fibrinogen.
C. Plasmin becomes trapped in the fibrin threads.
D. Prothrombin is converted to thrombin.
D. Prothrombin is converted to thrombin.
Oxygenated blood is pumped from heart through the _______to the rest of the body.
A. Left, systemic circuit
B. Right, pulmonary circuit
C. Left, pulmonary circuit
D. Right, systemic circuit
A. Left, systemic circuit
The "pacemaker of the heart" is in what location?
A. Right atrium
B. Left atrium
C. Left ventricle
D. Right ventricle
A. Right atrium
You are reviewing your patient's results from an EKG. The findings indicate a problem with ventricular REPOLARIZATION. Where should you look on the EKG to find this abnormal rhythm?
A. T-wave
B. QRS complex
C. P-wave
D. The electrical activity cannot be read on an EKG
A. T-wave
You are reviewing your patient's results from an EKG. The findings indicate a problem with ventricular DEPOLOARIZATION. Where should you look on the EKG to find this abnormal rhythm?
A. T-wave
B. QRS complex
C. P-wave
D. The electrical activity cannot be read on an EKG
B. QRS complex
Your patient's EKG results indicate difficulty with left and right atrial systole. What part of the conduction system is not functioning properly?
A. Atrioventricular node.
B. SA node causes contraction of the left and right atria
C. Bundle of His
D. Purkinje fibers
B. SA node
(causes contraction of the left and right atria)
Which statement is true concerning the cardiac cycle?
A. The atrial contraction time is longer than the ventricle contraction time.
B. The ventricular contraction time is longer than the atrial contraction time.
C. Systole refers to the relaxation of the heart chambers.
D. Diastole refers to the contraction of the heart chambers.
E. C & D are true
B. The ventricular contraction time is longer than the atrial contraction time.
A patient is suspected to have peripheral edema due to heart failure. Which side of the heart would be in failure? Explain your answer.
The right side of the heart would be in failure. When the right side of the heart cannot pump blood into the heart efficiently, the blood and fluid will back up into the veins. This results in swelling of body tissues.
A patient has a diagnosis of right sided heart failure. Which of the following signs/symptoms would they most likely present with?
A. Shortness of breath at rest
B. Swollen ankles
C. All the above
B. Swollen ankles
A patient is admitted to the ER with a myocardial infarction. What signs/symptoms could they display?
A. Shortness of breath
B. Angina pectoris
C. Heartburn
D. Pressure over the chest
E. All the above
E. All the above
Your patient has a diagnosis of atherosclerosis. Is your patient at a higher or lower risk for a thromboembolism? Explain your reasoning.
Higher risk. Thromboembolism is an embolus that becomes lodged in a vessel as it travels. Atherosclerosis is an accumulation of soft masses of fatty materials, often cholesterol, inside arteries. These deposits called plaque accumulate beneath the inner linings of arteries. Plaque can cause a clot to form on the irregular arterial wall. If the clot becomes dislodged it can travel and clog a smaller artery in its path.
Your patient is admitted to the hospital for a coronary artery bypass. Use your own words to explain to your patient about what is going to happen in this surgery.
During this operation, a segment of another blood vessel (often taken from the leg, chest, or arm) is grafted to the heart. One end is stitched to the aorta and the other end to a coronary artery beyond the blockage, creating a new route for blood to flow. Once the heart is exposed, some surgeons may also use laser therapy to help open clogged coronary vessels.
Your patient has a diagnosis of atherosclerosis. Would you expect your patient to also have hypertension? Why or why not?
Yes, it would be expected that the patient would have hypertension. Atherosclerosis is a buildup of fatty material, typically cholesterol, inside the arteries. The plaque deposits will accumulate under the inner linings of the arteries. The plaque will continue to build up causing it to protrude the vessel which interfere with normal blood flow.
Your patient is admitted to the hospital for an angioplasty. Use your own words to explain to your patient about what is going to happen in this procedure.
An angioplasty is a procedure used for a severe clot. The surgeon threads a plastic tube into the artery in the arm or leg towards the heart. The plastic tube will have a balloon attached to the end, it will inflate to force the vessel open.
What layer of the heart is composed of the contractile cardiac muscle?
A. Pericardium
B. Endocardium
C. Myocardium
D. Mediastinal
C. Myocardium
True or False: Arteries have high amounts of stretch with little recoil
False (veins)
Name the vessel in the figure below:
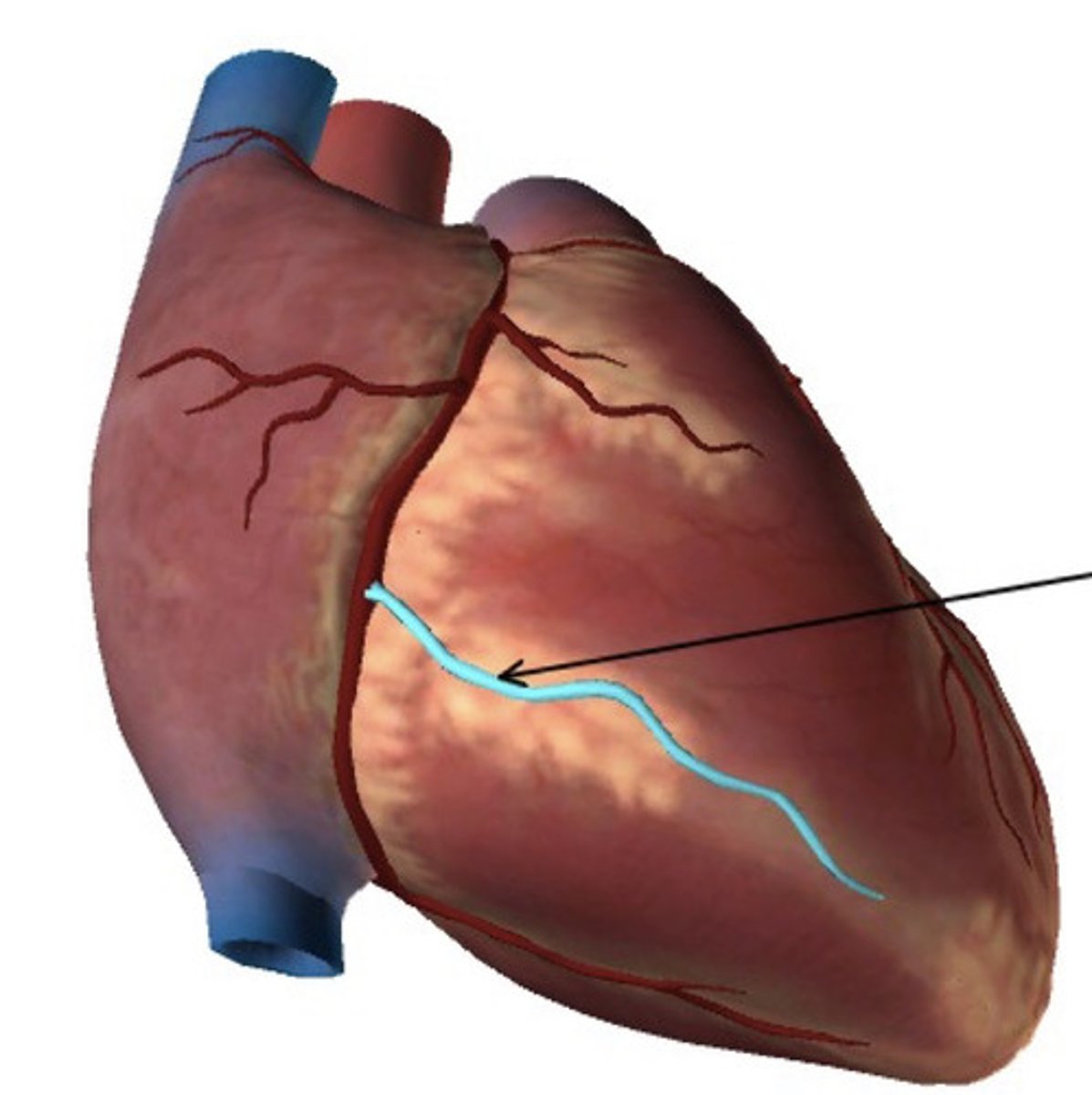
Right marginal artery
Name the vessel in the figure below
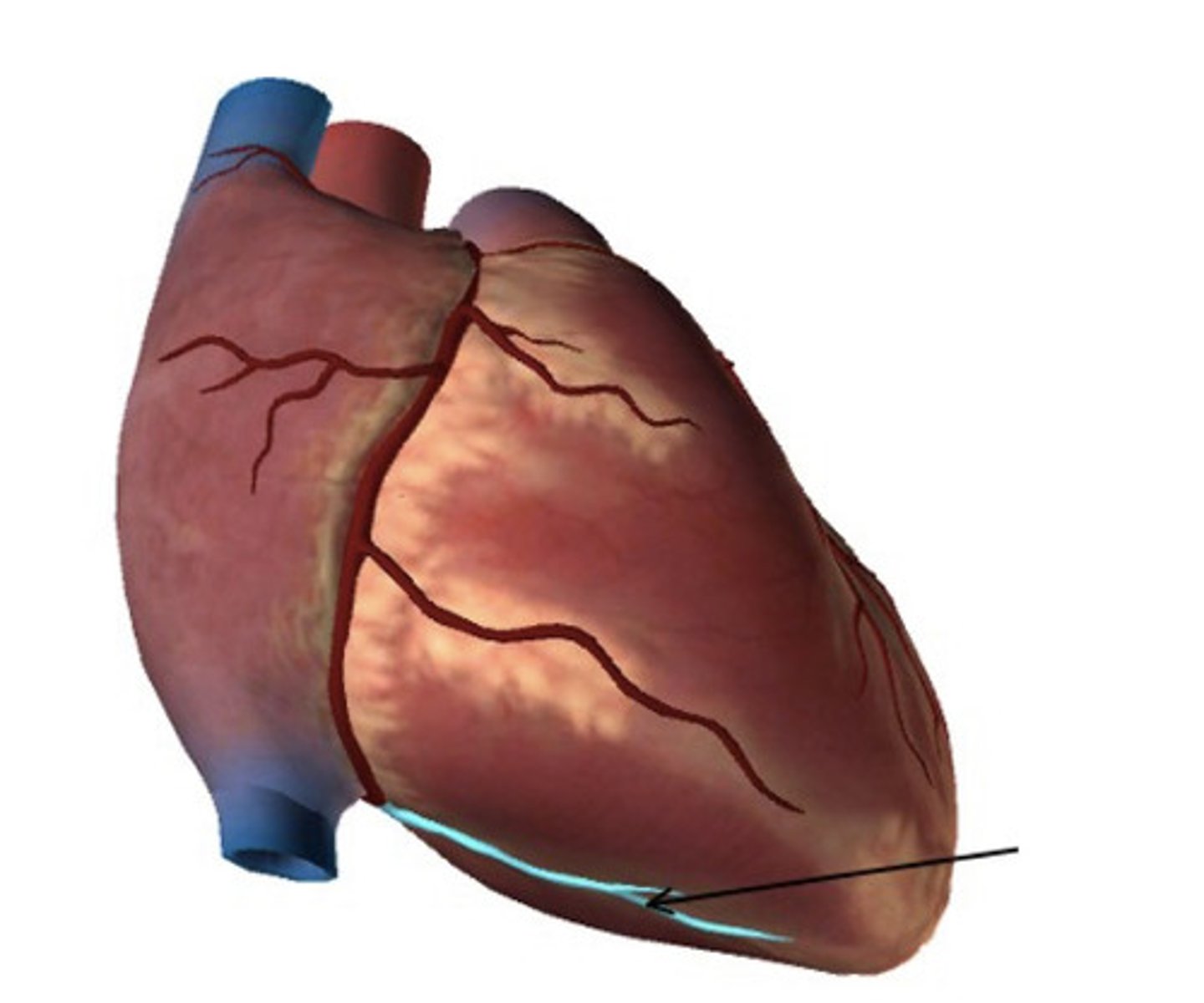
Posterior Intraventricular Artery
What is the purpose of the fossa oval in the fetus?
It's an opening in the interstitial septum that allows the blood to flow from right atrium to left atrium to bypass the undeveloped lungs.