microbio exam 1 study guide
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
what is refraction
the bending of light as it passes from one substance to another
especially substances of different densities
this is what allows eyes and microscopes to focus light into a visual image
Why does refraction happen?
happens because light changes speed and direction when passing at an angle between materials of different densities
what is the normal line?
an imaginary line of 90 degrees that is perpendicular to the surface, separating two different media at the specific point where light strikes it
serves as a reference for measuring the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction
how does light bending depends on whether it is going from an area of low density to high density?
light beams will bend towards the normal line
how does light bending depends on whether it is going from an area of high density to low density?
light beams will bend away from the line
what is refractive index?
the ratio of speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in a specific medium
how do you calculate refractive index?
n= speed of light in a vacuum ( c ) divided by the speed of light in a medium ( v )
what is the lowest possible refractive index?
1 in a pure vacuum
what does increasing the refractive index means for how that material can bend /refract light
the higher the number, the stronger the material bends light
material slows down more, causing it to bend or refract more towards the normal line when entering
what is resolution?
the smallest distance at which 2 different objects can be seen as separate from each other in an image
for this, smaller numbers are better
the smaller the resolution the sharper the image
how do you calculate resolution?
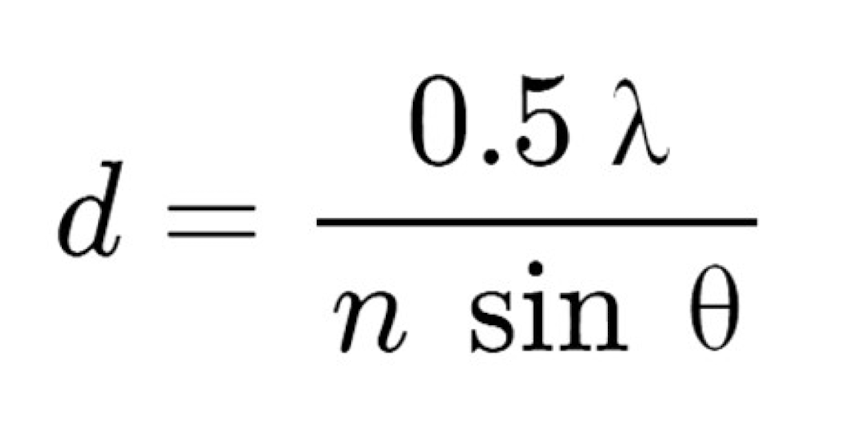
what are the factors that can affect resolution?
the wavelength of light used
the refractive index of the lens
the lens half angle
what is the resolution of the human eye?
0.1 millimeters or 100 micrometers
why do the systems that we use must provide both magnification and a greater resolution than the human eye
human eye has limitations so we must use those systems to provide greater magnification because it enlarges the image to make it easier to see and resolution to help distinguish between adjacent small features
what are the functions of the condenser?
focus and align light into a single beam
what is the objective lens?
creates a magnified image from focusing the refracted light onto the retina
what is the ocular lens?
further magnifies the image made by the objective lens
how does the microscope creates an image?
condenser lens focus and align light into a single beam
the light will pass thru the microbial sample or specimen
light will refract as it passes through the specimen
refracted light from the sample is focused to create a magnified image by objective lens
the image made by objective lens is further magnified by ocular lens
what is contrast?
the darkness of the image background relative to the specimen
what are the ways that we can provide contrast to a microscopic image?
thru manipulation of light or chemical treatment
what is staining?
using chemical dye to give an image color and contrast
has two groups which are simple and differential stains
what are simple stains?
using a single dye that chemically binds to cellular structures
what are differential stains?
multiple dyes that bind differently to cellular structures
allows us to classify microbes based upon their staining properties
what are the drawbacks of staining?
the staining process kills microbes and can’t visualize live cells
how does a dark-field microscope work?
works by using an Abbe condenser with a dark-field stop to block direct light
the only light that enters the objective is the light that passes through the specimen itself
what kind of images does dark-field microscope produce
images that will always have a bright image of the specimen on a dark background
what does dark-field stop do?
creates a hollow cone of light
what does the Abbe condenser do?
focuses the cone of light at an angle rather than directly onto the specimen
How does interference microscopy provide contrast?
by using a modified optical system to create contrast using constructive and destructive interference
what are the two types of interference microscopy?
constructive and destructive interference
what is constructive interference?
areas that are especially bright
what is destructive interference?
areas that are especially dark
how could you tell a phase contrast from a DIC image?
DIC images do not show phase halo
what does phase contrast provide?
produces a strong 2D contrast with very bright edges
what is phase halo?
bright, fuzzy edge to the images
what is differential interference contrast?
produces a slightly weaker contrast that appears 3D
How does fluorescence microscopy work?
by using dyes that give off light when struck by visible light of a specific color
filters in the microscope allow only the emitted light from the specimen to reach the eye
what are the advantages of staining live cells?
fluorescent dyes typically do not kill live cells
dyes can be attached to antibodies to identify and stain specific proteins
why do light microscopes have a maximum limit of resolution?
because light microscopes can only reliably interact with object bigger that its wavelength
½ of wavelength of light being used
what is the max resolution?
0.2 micrometers
how do electron microscopes allow us to overcome the resolution and magnification limits?
they replace visible light with electrons
they use electromagnets rather than glass lenses to focus
How are electrons focused in an electron microscope
electromagnets focus electrons to provide both magnification and resolution
How do transmition electron microscopes work?
produce 2D images that are a slice through a microbe
allow us to visualize the internal structures of microbial cells and viruses
magnifies structures more than 100000x
How do scanning electron microscopes work?
uses an electron bean to scan the surface of a microbe
produces a 3D image of the outer surfaces of a microbe
what are the pros and cons of TEM and SEM?
TEM can produce images with higher magnification and better resolution
limitations are that it can only visualize small sections of a microbe
SEM can visualize lower magnification and worse overall resolution
How does Cryo-EM work?
freezing samples in liquid nitrogen
How does Cryo-EM produce images?
an electron beam takes images of the specimen at multiple angles
what is the smallest resolution achieved so far with cryo-em?
2.8 angstrom
what is are bacteria?
single celled organisms that lack a nucleus and most other internal organelles
what are archaea?
superficially similar to bacteria but are an evolutionary distinct domain of life
typically live in an extreme or unusual environments
genetically closely related to eukaryotes than bacteria
what are eukarya?
all eukaryotic cells
in microbio those are fungi and protists
what is plasma membrane?
flexible outer covering of a cell
what is the cytoplasm?
highly organized, water-based inside part of a cell
what are ribosomes?
machines used by the cells to make proteins
what are chromosomes?
genetic information that is stored on one or more chromosomes
what are the basic two shapes of bacterial cells?
coccus (spherical) and bacillus ( rod-shaped)
what are the arrangements of the bacterial cells?
duplo: pairs
strepto: chains
staphylo: clusters, like grapes
polisades: side-by-side arrangements of bacilli
what are the major functions of cell walls in bacteria?
providing cell shape and resistance to osmotic stress
cell wall prevents distortion of the cell membrane
provides resistance against physical damage
allows bacteria to stick to other cells
protects bacteria from being identified by the immune system
what are the two types of cell wall?
gram positive and gram negative
what is special about gram positive cell walls?
made almost entirely of a thick layer of peptidoglycan
has teichoic acid
what is so special about gram negative cell walls?
consists of thick layer of peptidoglycan and a second plasma membrane, the outer membrane
do not have teichoic acid but have lipopolysaccharides or LPS, that can also stick to cells
what is peptidoglycan?
is a mesh made of polymers of sugars
peptido -is partially made of protein
glycan - partially made of sugars
what is teichoic acid?
able to attach pr stick to molecules on the surface of another cell
what is the backbone?
the rigid, helical, sugar chain that forms the main scaffold of the bacterial cell wall
made of alternating sugars NAM and NAG that are liked together into a long, straight chain
what are the functions of the backbone?
main structural framework
gives the cell wall physical shape and integrity
resists osmotic pressure
provides the base structure that everything else attaches to
what are stem peptides?
attach to each NAM sugar or a short peptide chain ( a little tail)
connection points between sugar chains
allows the wall to be cross-linked
what is a cross linkage?
a bond between stem peptides on different peptidoglycan chains
they are relatively loose connections so this allows the cell wall to have some flexibility and elasticity
what is a lipopolysaccharide?
lipo : fat
polysaccharide: part sugar
different molecule but same function as teichoic acid, sticking to cells
Why can LPS/endotoxin make Gram negative infections very serious?
consists of lipid A, core polysaccharide, and o antigen
when gram negative bacteria die, or break, or multiply, lipid A gets released
What are the potential effects of endotoxin in the body?
can cause a severe inflammatory response
extremely high fever with chills and shivering
organ stress can cause sepsis
What are the first step of the Gram stain?
add crystal violet
it stains all bacteria purple
gram + is purple
gram - is purple
EVERYONE IS PURPLE
What is the second step of Gram stain?
add iodine
mordant makes dye less soluble so it adheres to cell walls, clumps crystal violet
gram +: still purple
gram -: still purple
EVERYONE IS PURPLE BUT THE DYE IS LOCKED IN
What is the third step of Gram stain?
add alcohol
alcohol dissolves crystal violet
gram +: remains purple
gram -: loses its dye, becomes colorless
GRAM + AND GRAM - SEPARATE
what is the fourth step of Gram stain?
add safranin ( pink or red dye that stains any colorless cells)
gram +: stays purple ( purple masks pink)
gram - : takes up safranin and becomes pink/red
What is the structure of acid-fast cell wall
contains thick layer of peptidoglycan
has a special layer of fat-based molecules, mycolic acid
also has a plasma membrane
how is acid-fast cell wall similar to gram + and gram - cell walls?
gram +: thick layer of peptidoglycan
gram -: outer membrane behaves like thick wax
how to identify acid fast and non-acid fast bacteria on an acid fast stain?
instead of gram staining, you perform acid-fast staining
acid fast appears red or pink
non-acid fast appears dark blue or purple
How does the acid-fast cell wall affects the ability of bacteria to be resistant to disinfection, the immune system, and to antibiotics?
unique chemistry of acid-fast cell wall makes mycobacteria resistant to disinfection
can resist dehydration by heat, most water-based cleaners, most typical antibiotics
acid fast cell walls resist destruction by the immune system
what is mycobacteria?
the most common acid-fast bacteria belong to a group of rod-shaped bacilli bacteria
the most dangerous is mycobacterium tuberculosis
How does the immune system handle tuberculosis bacteria that it can’t destroy?
immune system walls off TB by forming granuloma
it prevents spread thru the body and keeps TB in a sleeping state to limit the tissue damage elsewhere
can’t kill it → cages it → granuloma
What can happen if TB left untreated?
lung failure
How do you treat TB?
special antibiotics can penetrate the waxy mycotic acid layer
What are the clinical problems related to the difficulty of treating TB?
treatment is expensive and poor patient compliance
what is the cell envelope?
a protective, multilayered structure surrounding the cytoplasm
primarily consisting of the inner cell membrane, a peptidoglycan cell wall, and, in Gram-negative bacteria, an outer membrane with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
what structures can be a part of the cell envelope?
slime capsule, slime layer, peptidoglycan, lipoteichoid acid, cytoplasmic membrane
what is the slime layer?
adhesion structure made of loosely packed and unorganized sugars
how does the slime layer look like on a typical microscope?
lack of organization makes it appear fuzzy on microscope images
what does the slime layer provide?
adhesion because the concentrated sugars have a chemical stickiness
what is a capsule?
an adhesion structure made of densely packed and organized sugars
what does capsule do?
just like slime layers, it has chemical stickiness
how do capsules look like on a microscope?
appears sharp because of how organized it is
white border around cells because its density prevents it from being stained
what is an s-layer?
a protein-based outer surface covering
what is the basic structure of s-layer?
is built from many copies of a single s-layer protein that bind together in a layer 1 protein thick
are able to self assemble into a crystal like surface
what are the types of proteins s-layer is build from?
built form glycoproteins that are sometimes modified in certain species to add carbohydrate chains
how is the s-layer anchored to the cell?
in gram + is anchored to teichoid acid
in gram - is anchored to lps
what are adhesion structures used for?
sticking to cells and surfaces
why does bacteria need adhesion? ( especially ones that cause disease)
they can be easily removed by physical forces or fluid flow
some bacteria can work together as a community to adhere by forming a biofilm
what are the three major adhesion structures?
fimbriae
pilus
biofilm
what are fimbirae and what are the made from?
adhesion structure made from proteins
is think, hair like, usually dozens or 100s per cell
what are pilli and what are the made from?
adhesion structure that is also made of protein
usually larger and fewer in number that fimbriae