11. Extracellular Matrix
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
diverse collection or molecules secreted by cells
a. cell adhesion
b. cell to cell specificity
c. barrier = filter-bacterial laminal
d. promote differentiation
e. strength (ex: bones+tendens)
f. turn on receptors - intergin receptors
g. charged surfaces - hydration shell --> bind growth factors
h. tumor microevnironemnt
i. diseases
j. used for medical application
k. stem cell therapy
l. organoids
How important is the ECM to tissue engineering - EpiDerm:
what is the proper ECM?
Dry film Type 1 collagen (cell struck, partly differentiated)
Type 1 collegen --> gel (more differentiation)collagen
Type 1 collegen gel w/ FCS inhibitors (full differentiation)collagen
#3 but first cross x-linked w/ aldehyde (commercial product)
The Big Challenge: Develop methods to grow hESCs without mouse feeder layers
Irradiated mouse fibroblast feeder layers are typically required for growing hESCs
But this introduces animal proteins so frowned upon by the FDA due to the possibility of viruses in animal proteins
New feeder cell-free plates and media have been developed
Nano 3D
a system where cells that rely on a surface to grow (substrate dependent cells) can be induced to form miniature, three-dimensional organs called organoids
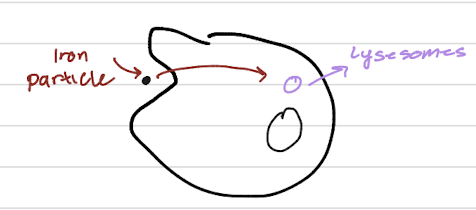
the cellular process of endocytosis (or phagocytosis), where a cell takes in a foreign object, such as an iron particle, and packages it into a vesicle that will be delivered to a lysosome for degradation or processing
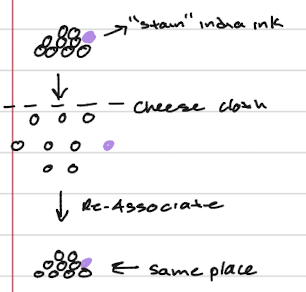
classical experiment - sponges
intact sponge tissue is first separated into individual cells (some stained purple with "india ink"), then passed through a cheese cloth to completely dissociate them
When these individual cells are allowed to settle and interact, they re-associate to form a functional sponge again, showing that cells inherently recognize and stick to each other
classical experiment - embryos
dissociated cells from different tissues, like the purple retina cells and the red liver cells, will self-sort when mixed, demonstrating that cells from the same tissue preferentially adhere to each other

cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
Homophilic adhesion occurs when two identical CAMs on neighboring cells bind to each other, like two cells holding hands with the same type of molecule
Heterophilic adhesion occurs when one type of CAM on one cell binds to a different type of molecule on a neighboring cell
multivalent adhesion involves a third, separate bridging molecule that binds to and connects two CAMs on separate cells

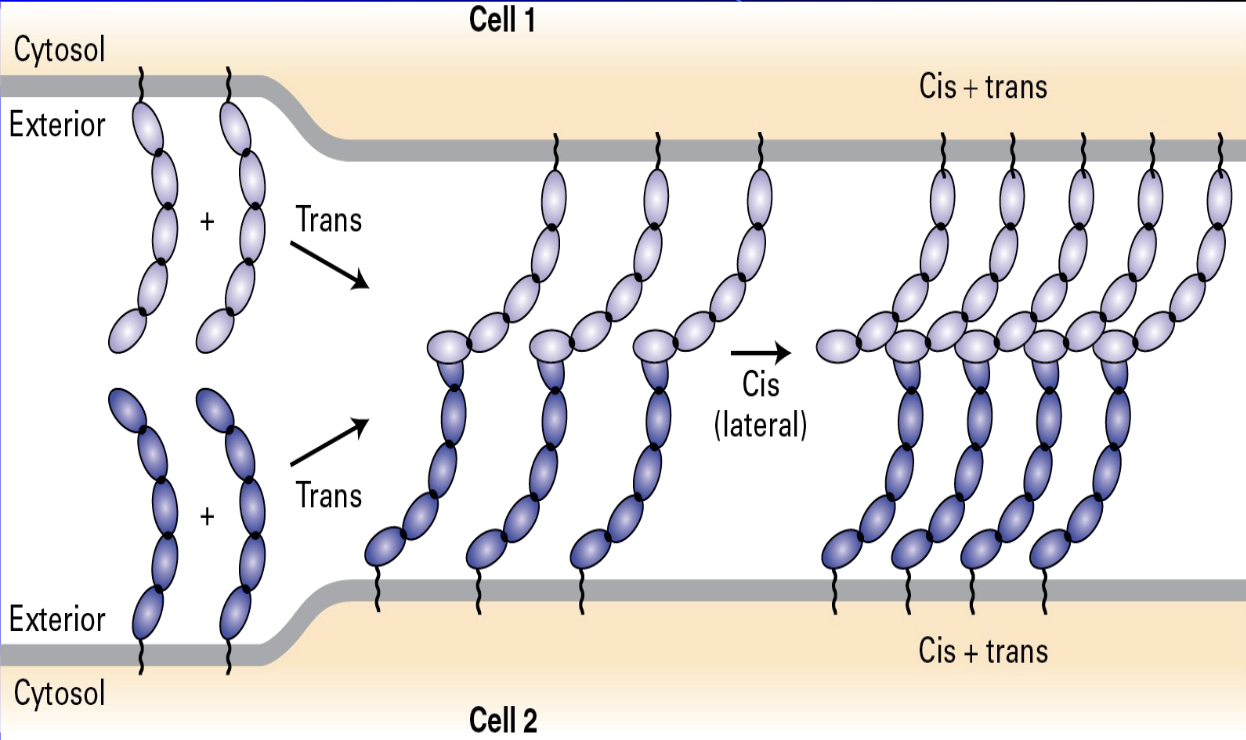
cis vs trans
begins with trans binding, where molecules extending from Cell 1 interact with molecules extending from Cell 2 across the exterior space
followed by the molecules on the same cell membrane associate laterally in a cis binding interaction
The final structure shows a stable, interconnected array involving both cis + trans associations, which provides strong adhesion between the two cells
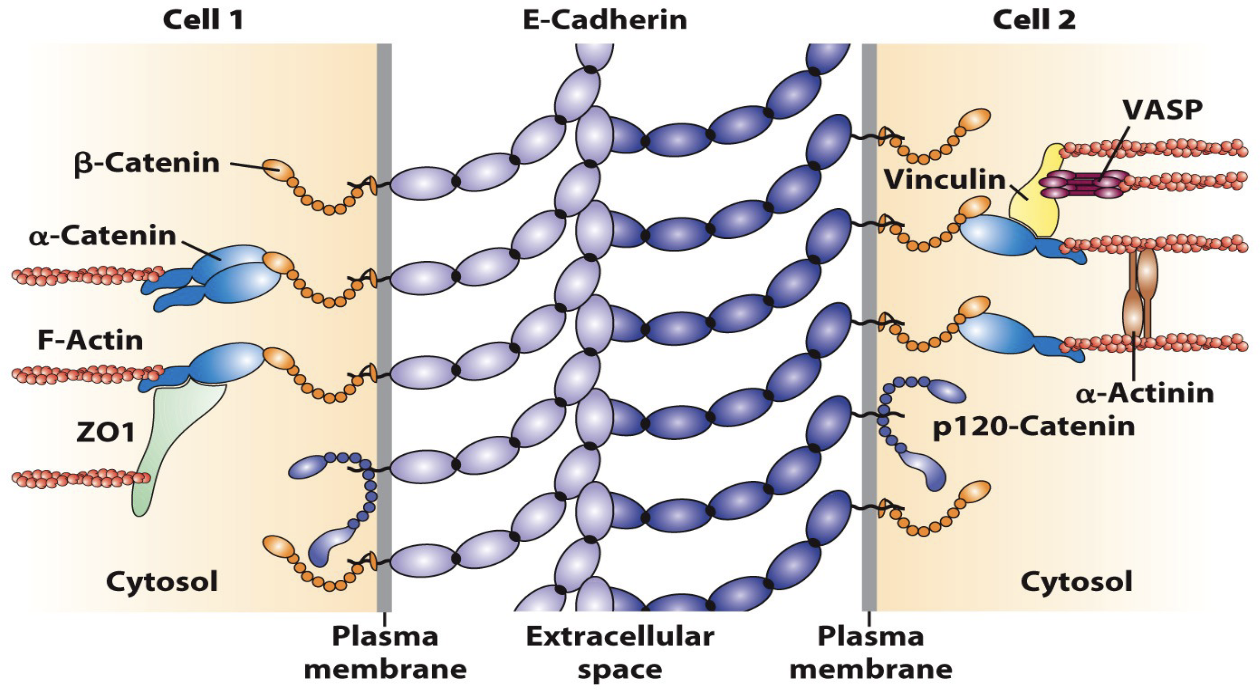
E-Cadherin is linked to the
cytoskeleton
links the plasma membranes of two adjacent cells (Cell 1 and Cell 2) and, crucially, connects to the internal cytoskeleton
span the plasma membrane and interact homophilically in the extracellular space
On the cytosolic side, the E-Cadherin tails are tethered to the F-Actin cytoskeleton via a complex of adapter proteins
β-Catenin, α-Catenin, ZO1, Vinculin, VASP, α-Actinin, and p120-Catenin, form an adherens junction that provides strong mechanical strength and stability to the tissue
cadlherins
a crucial family of Cell Adhesion Molecules essential for holding cells together, particularly in tissues that rely on a surface for structure
strictly calcium dependent; if calcium is removed, they lose their function and cells fall apart
bind to each other through cis/trans binding to link adjacent cells, and their binding specificity is so strong that their mechanisms are subject to competition between types
ex: E (epitellial),N(Neural),P(placenta)
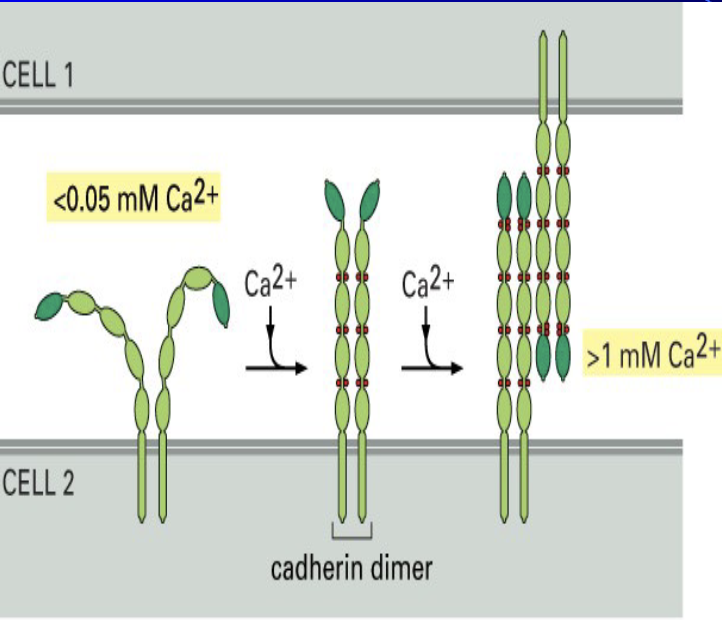
are cadherins homophilic or heterophilic?
Autophagy is the cell's "eating itself" process to recycle damaged components like mitochondria and peroxisomes, starting with the formation of a phagophore that matures into an autophagosome tagged by the protein LC3 before fusing with a lysosome
this lysosomal function can be impaired, leading to non-inherited diseases like silicosis or by certain drugs like chloroquine and bafilomycin A1, which interfere with the degradation process
Ig (Immunoglobulin) supperfamily
a representation of a molecule within this family that participates in hydrophilic binding
N-CAM (Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule), where the "N" stands for neural
These molecules are generally involved in cell-to-cell adhesion and recognition processes, particularly in the nervous system
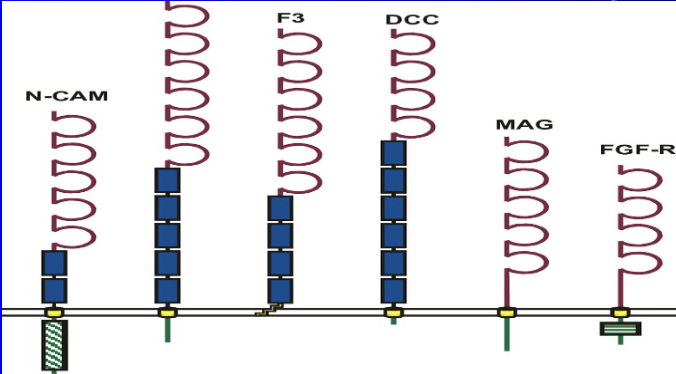
N-CAM Functions
Adhesion: They primarily function by mediating cell adhesion through homophilic interactions, which is essential for organizing cells and tissues
Signaling: NCAM binding can activate intracellular signaling pathways, leading to changes in gene expression and influencing cell functions such as migration, proliferation, and differentiation
Function in the nervous system: NCAMs are critical for neural development, including the formation of the olfactory bulb and hippocampus, neurite extension, axon guidance, and the formation and maintenance
of synapses
Interstitium
Layer of interconnected, fluid-filled compartments supported by collagen bundles and elastin
Compressible and distensible – shock absorber around organs
May explain how cancers metastisize
Source of lymph
Standard fixation procedures drain away the fluid and superficially looks like tears in tissue
First seen with a probe-based confocal laser endomicroscope
examining metastasis in a patient’s bile ductLined by very unusual, flat cells – look like fibroblasts but function unknown and have little cytoplasm with an oblong nucleus
Axonal growth
the axon of a retinal ganglion cell grows toward and targets the optic tectum
The crucial role of N-CAM (Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule) is blocking N-CAM antibodies that blocks axonal targeting, indicating that N-CAM is essential for guiding the growing axon to its correct destination
western blots of N-CAM
The embryo's N-CAM is highly modified by PSA (polysialic acid), a large sugar chain that creates a substantial hydration shell around the molecule
makes the embryonic N-CAM larger and less adhesive
the adult N-CAM, lacks or has significantly reduced PSA modification, resulting in a smaller protein that is more effective at promoting strong cell-to-cell adhesion
ECM - several forms
loosely ordered
basal lamin aka basement membrane/lamellar
loose connector tissue (ex: dermis of skin, conera/stroma)
dense connective tissue (ex: bones, tendons)
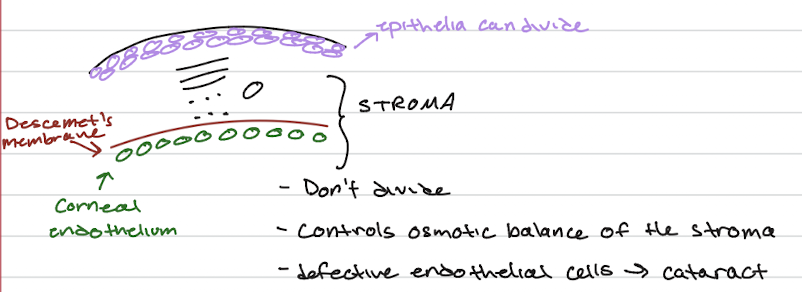
Corneal Transplant Types
First cornea transplant was in 1905 – one of the first successful transplants of all tissue/organs
Penetrating keratoplasty – full thickness cornea in its entirety
Lamellar keratoplasty – limited to diseased areas only
Endothelial keratoplasty – Descemet membrane and endothelial cell layer only
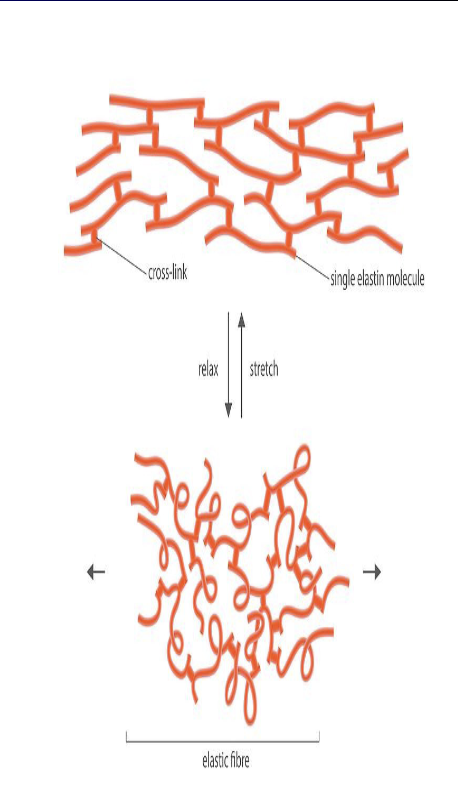
Elastic (Elastin) Fibers
long half-life of 74 years
primary role is to provide elasticity and resilience, allowing tissues like skin and blood vessels to stretch and recoil back to their original shape without damage
stretching ability is essential for the function of the lungs, enabling them to store energy during inhalation and release it during exhalation
a single elastin molecules can cross-link to form an elastic fiber that can readily stretch and then relax to return to its resting state
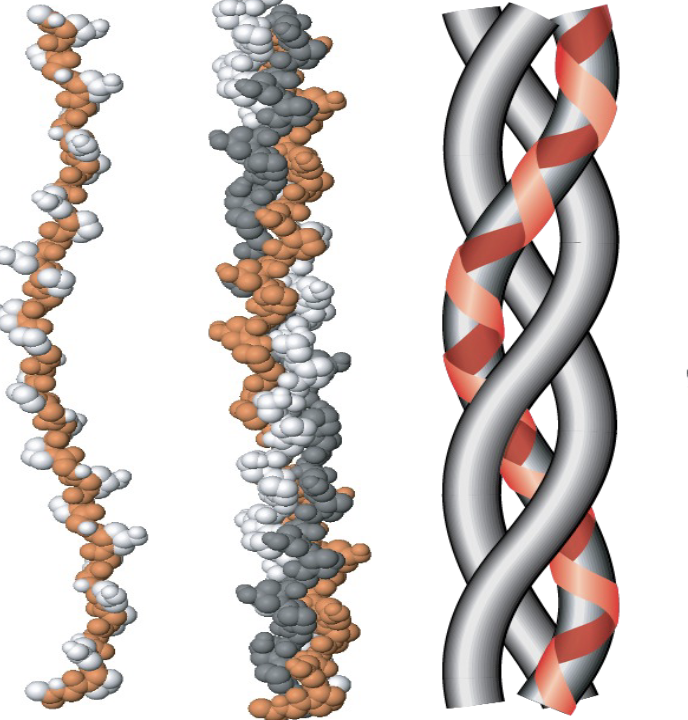
Collagen
most abundent animal protein
fibrous
insoluble in the aqueous solution
triple helix
12+ varieties
every 3rd amino acid is glycine (gly-pro-met-gly)
proline and hydroxyproline
resists stretching
disease states
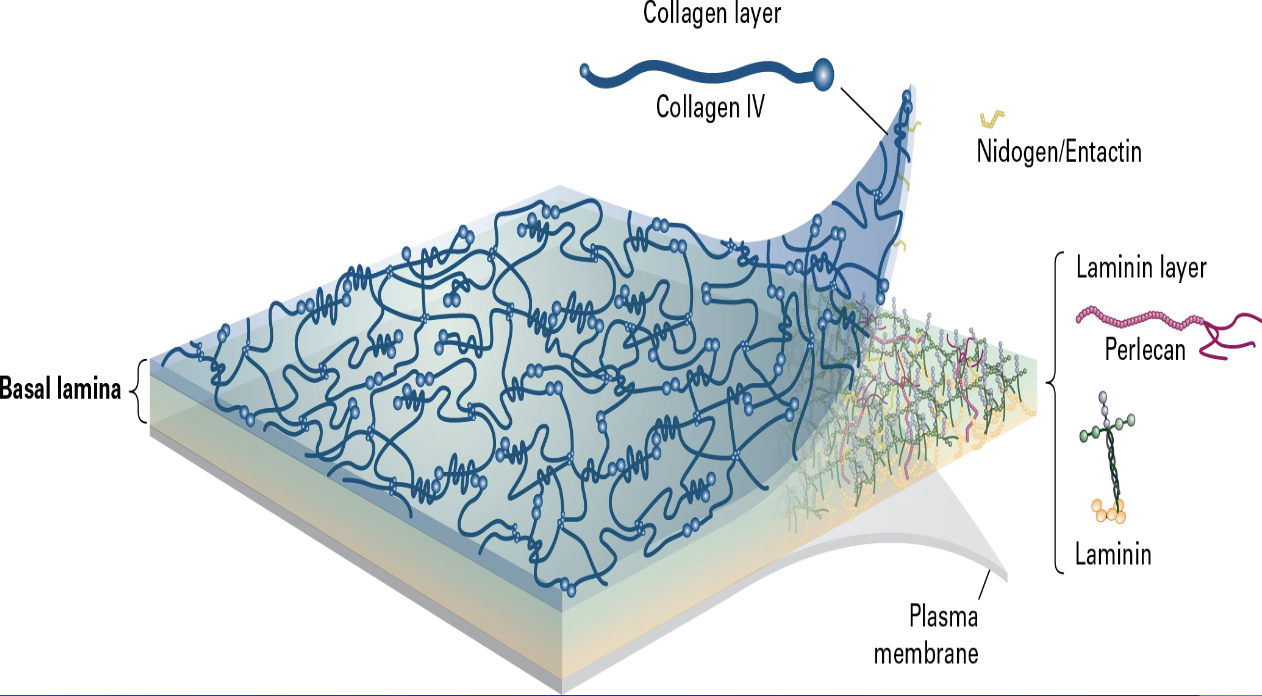
Basal Lamina
specialized sheet of extracellular matrix that underlies epithelial cells
The electron micrograph is situated between the basal surface of the epithelial cell's cytosol and the underlying connective tissue.
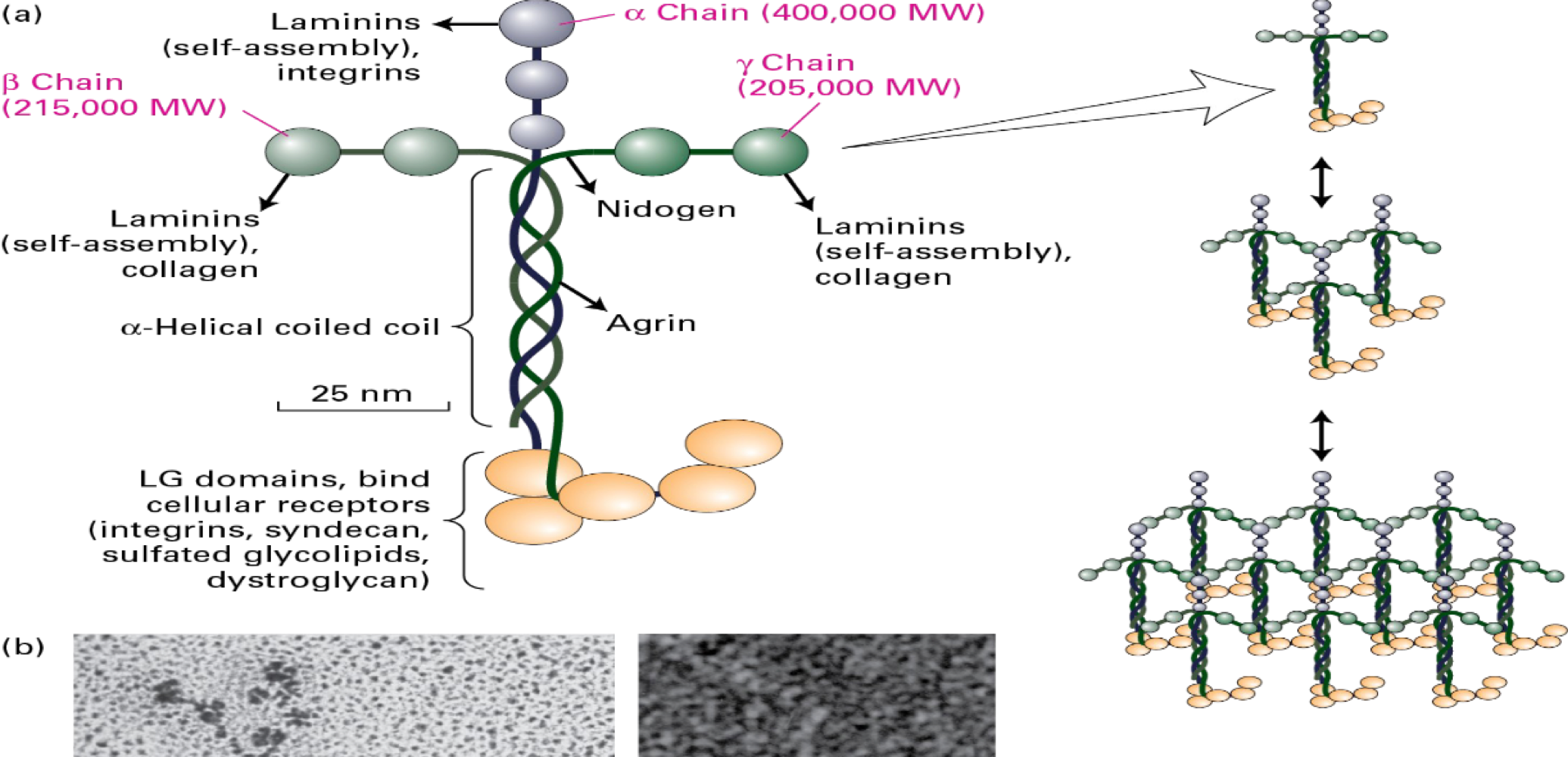
includes an intertwined meshwork of Type IV Collagen, (a connecting layer of Laminin, and the linking glycoproteins Nidogen/Entactin and Perlecan)
secreted by the epithelial cells to provide structural support, filtration, and cell adhesion
Collagen synthesis
RER - signal sequence
N - pro-petide, c-pro-peptide
RER - hydroxylation of proline(vitamin C dependent enzyme)
assembly + HSP 47
pro-collagen is secreted - outside of the cell
lose the pro-peptide
final assembly (Lysyl Oxidase - covalent bond)
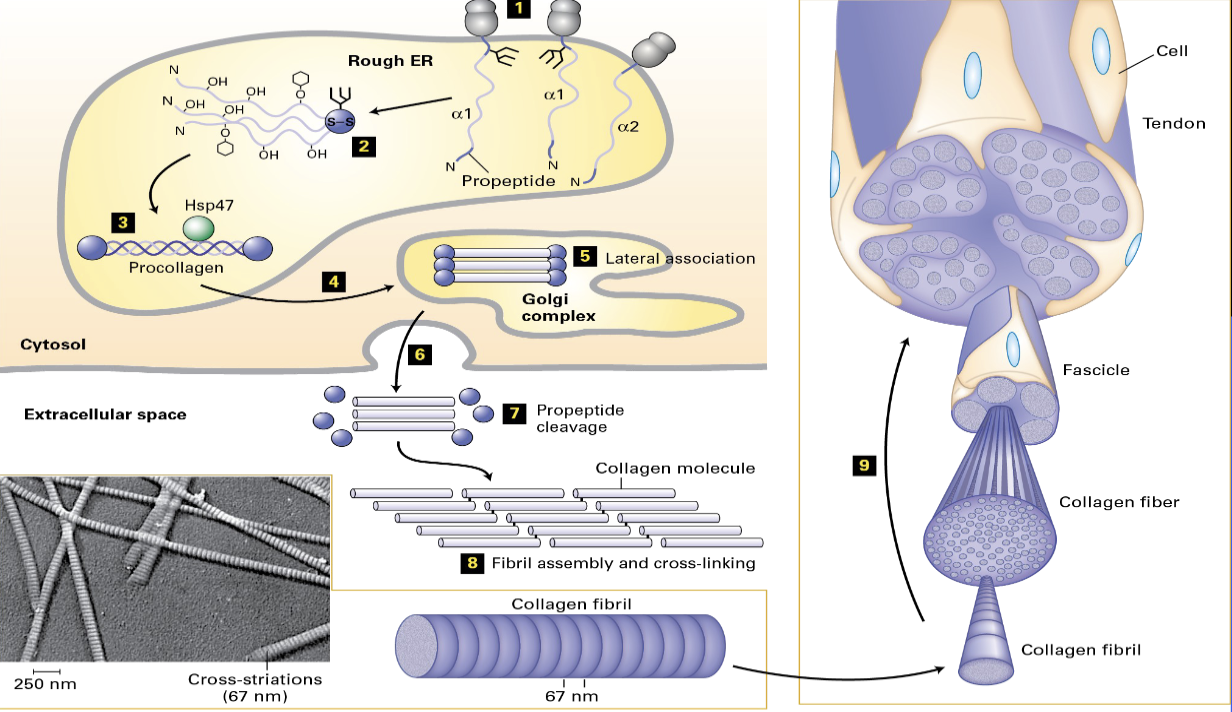
Scurvy
lack of vitamin C
vitamin C is a co-factor for proline hydroxylation
bleeding
1757 - scottish doctor says to suck on limes (limeys)
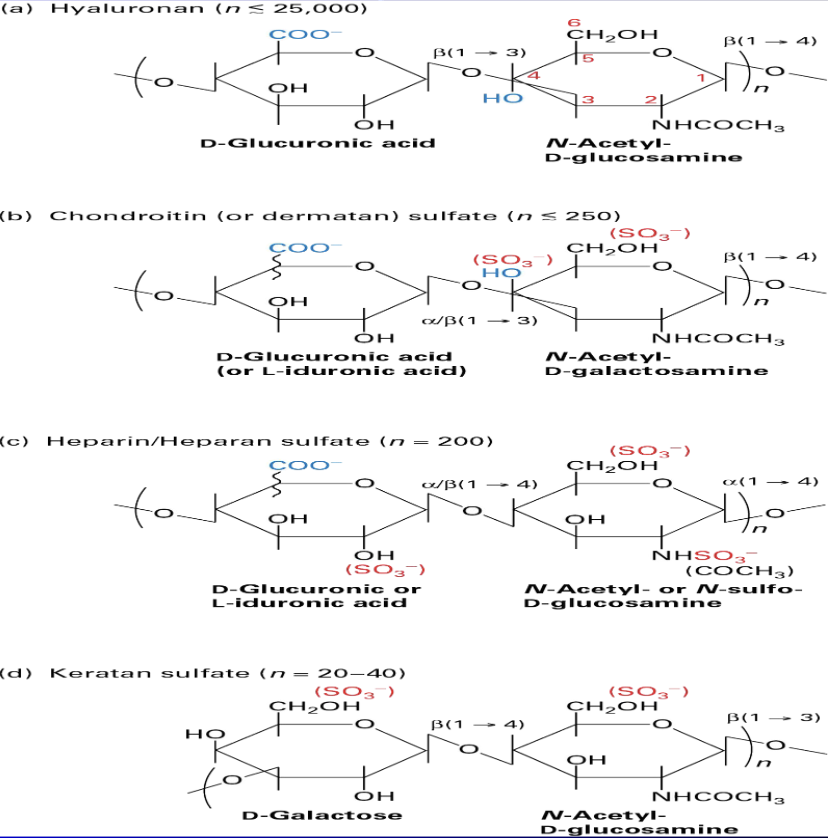
Glycosaminoglycans
not proteins b/c:
repeating disachatides
length --> ums long (longer than a cell)
rigid molecules
bind to cations --> change osmotic pressure, increase hydration shell
resists compression
binds to receptor called CD44 + proteo-glycans
extravasation
SynVisc - asteoarthritis
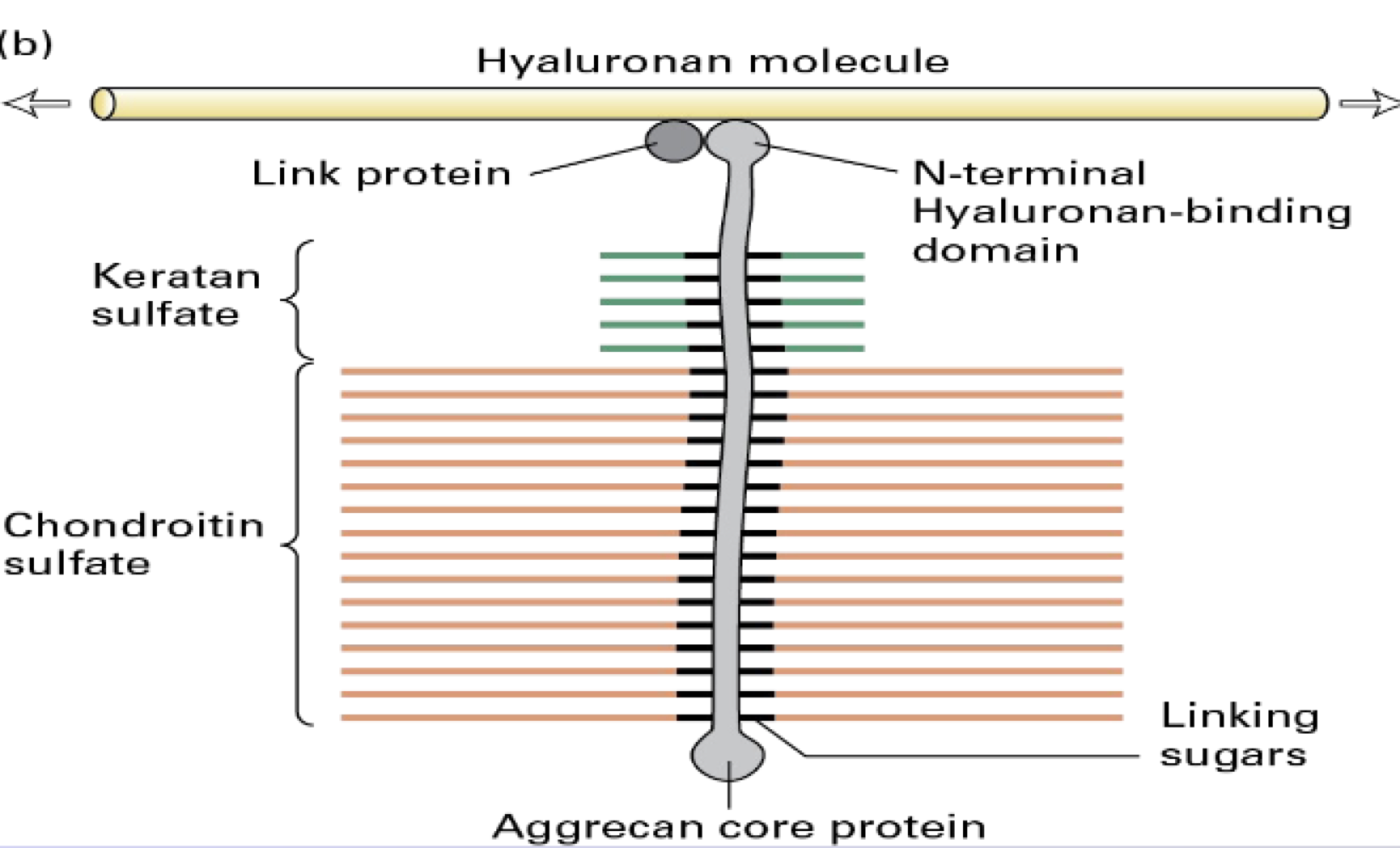
Proteoglycans
protein + glycosaminoglycan
Syndecans - can bind to FGF (growth factos)
overexpression of Syndecan 1 in mice --> obese (in hypothalamus)
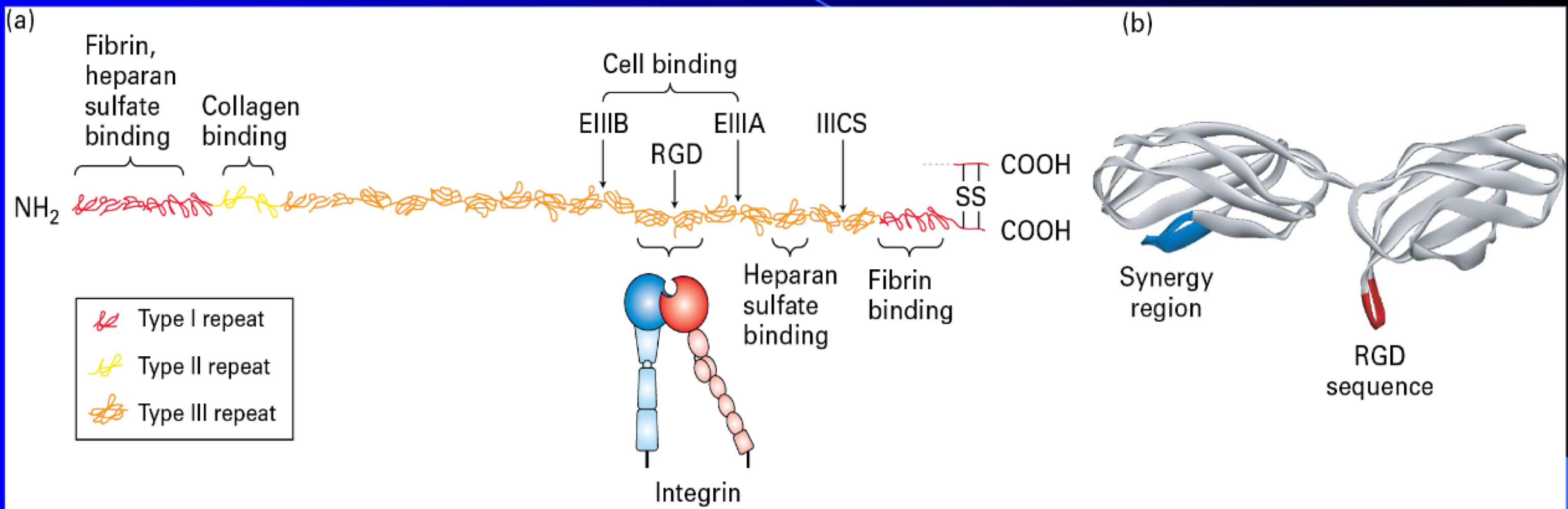
Fibronectin
is multi adhesive (bind to many different ECM molecules)
dimer
important to wound healing
important to morphogenesis
Laminin
multi-adhesive
800 kDa
self-assembly (molecules that requires little to no energy to make a sheet)
neuronal growth in vitro
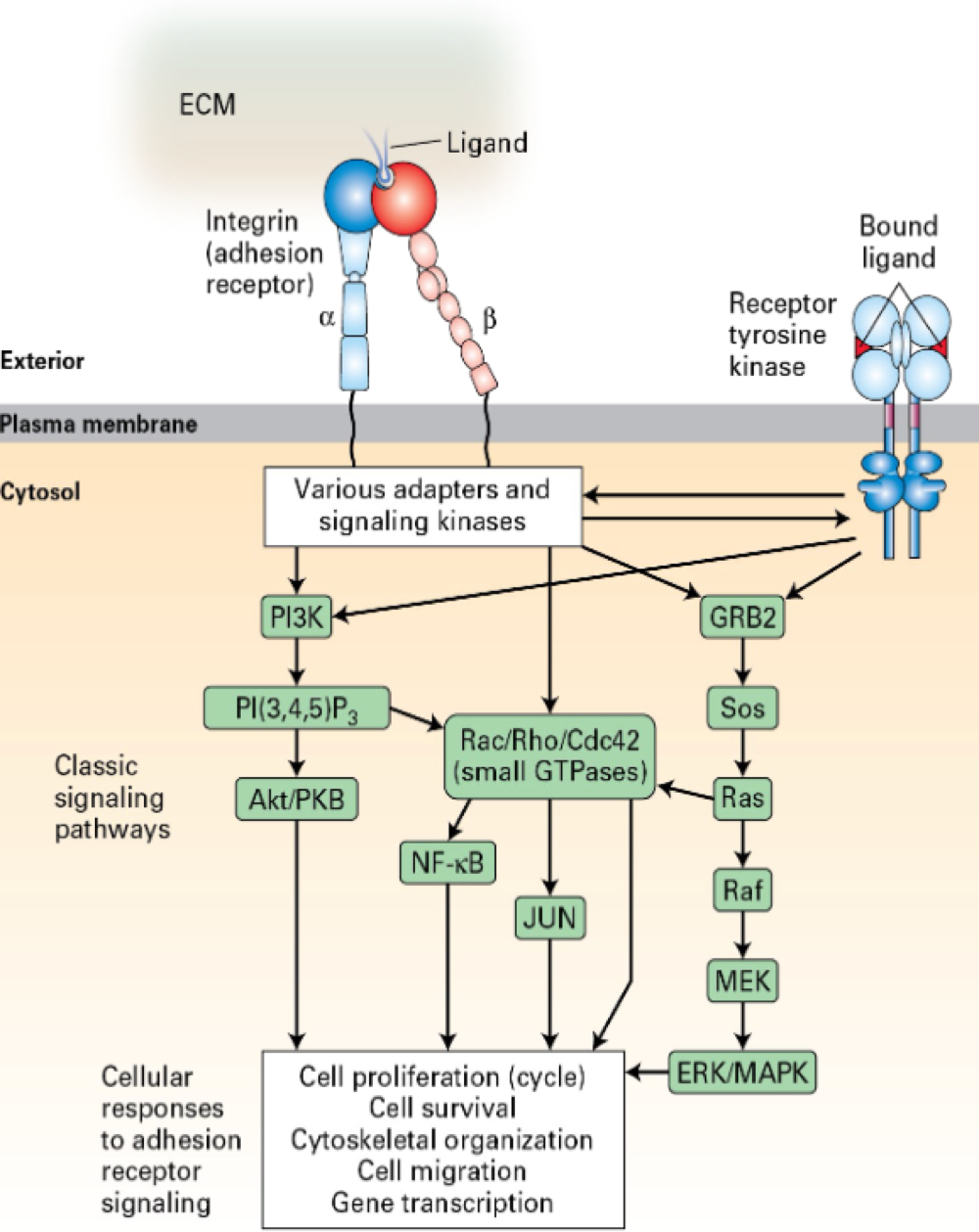
Integrin Receptors (Integrins):
ECM ink to integrins
dimers - α, β subunits
bind to Mg+, Ca+2
lower affinity than GICRs, RTK, etc
lower affinity --> easy detach from sunstrate
higher in number
"cross-talk" w/ RTKs and other like receptors
undergo shift from low to high affinity state
binds to RGD sequence (tri-peptide)
cluster together in "adhesion plaques"
do integrins bind to the RGD sequence?
cells attachment requires a substrate w/ RGD
Leukoctye adhesion deficancy
lacking defetive β2 receptors
par to no extravasation
many infection
hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Duchene Musculr Dystrophy
boys only
"ECM disease"
1-7000 boys
defects-dystrophin,laminin of other compnents
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
varity of ECM related disease
hypermobility - unusal flexibility (1 in 10,000 to 15,000)
classical - elastic skin
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) - Brittle Bone Disase
Type 1:
most common (mildest)
amount of collagen synthesized is low
Type 2:
most sever
collagen helix not formed corrected
death at birth