Ch. 15 - Autonomic Nervous System
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
a motor nervous system that controls glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
Also called the visceral motor system
Carries out actions involuntarily
Visceral effectors do not depend on the ANS to function, only to adjust their activity to the body’s needs
ANS is considered the efferent pathway
5 Primary Organs of the ANS:
Viscera of thoracic and abdominal cavities
Some structures of the body wall
Cutaneous blood vessels
Sweat glands
Piloerector muscles
Denervation Hypersensitivity
exaggerated responses of cardiac and smooth muscle if autonomic nerves are severed
Visceral Reflexes
unconscious, automatic, stereotyped responses to stimulation involving visceral receptors and effectors
Reflex Arc
Receptors are nerve endings that detect stretch, tissue damage, blood chemicals, body temperature, and other internal stimuli
Afferent neurons take signal from receptors to the CNS
Interneurons in the CNS make up the integrating center and integrate the info from the afferent neurons
Efferent neurons carry motor signals away from the CNS to effector organs
Effectors carry out the end response
Sympathetic Division
Prepares body for physical activity: exercise, trauma, arousal, competition, anger, or fear
Increases heart rate, BP, airflow, blood glucose levels, etc.
Reduces blood flow to the skin and digestive tract
how we deal with stress
“Fight-or-flight”
Parasympathetic Division
Calms many body functions, reducing energy expenditure and assists in bodily maintenance
Digestion and waste elimination
“Resting and digesting” state
is relatively selective in stimulation of target organ
less neural divergence than the sympathetic division
Cranial nerves it involves are:
Oculomotor nerve (III)
Facial nerve (VII)
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Vagus nerve (X)
vagus nerve is especially recognized
Autonomic Tone
The normal background rate of activity that represents the balance of the parasympathetic and sympathetic systems according to the body’s needs
Parasympathetic tone
Maintains smooth muscle tone in intestines
Holds resting heart rate down to about 70 to 80 beats per minute
Sympathetic tone
Keeps most blood vessels partially constricted and maintains blood pressure
The parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions have….
opposite effects
Somatic Pathway
A motor neuron from the brainstem or spinal cord issues a myelinated axon that reaches all the way to skeletal muscle
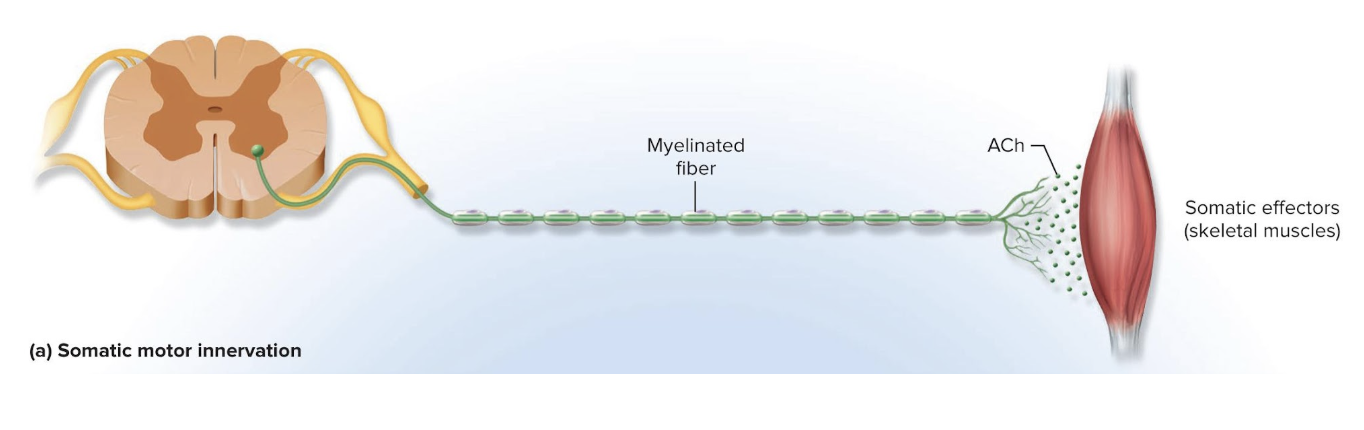
Autonomic Pathway
Signal must travel across 2 neurons to get to the target organ
Must cross a synapse where these two neurons meet in an autonomic ganglion
has synapses with a postganglionic neuron whose axon extends the rest of the way to the target cell
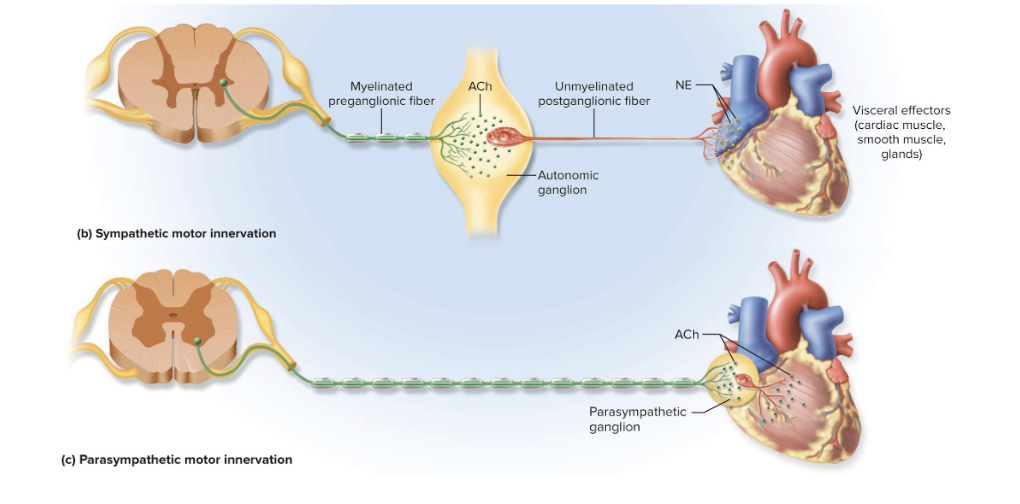
Nerve Fibers of the Sympathetic Division
have relatively short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers
Preganglionic neurosomas are in the lateral horns and nearby regions of the spinal cord’s gray matter
Fibers exit spinal cord through spinal nerves T1 to L2
Lead to nearby sympathetic chain of ganglia (paravertebral ganglia)
Sympathetic Chain of Ganglia (paravertebral ganglia)
a series of ganglia next to both sides of the vertebral column from cervical to coccygeal levels
Sympathetic nerve fibers are distributed to every level of the body
the series of ganglia extends up longitudinally
Each paravertebral ganglion is connected to a spinal nerve by two branches called communicating rami
Preganglionic Fibers in Sympathetic Division
small myelinated fibers that travel from the spinal nerve to the ganglion using the white communicating ramus
myelinated
Postganglionic fibers
leave the ganglion using the gray communicating ramus
unmyelinated
Forms a bridge back to the spinal nerve
extend the rest of the way to the target organ
What are the 3 courses the post ganglionic fibers could follow after entering the sympathetic chain?
Some end in ganglia which enter and synapse immediately with a postganglionic neuron
Some travel up or down the chain and synapse in ganglia at other levels
Some pass through the chain without synapsing and continue as splanchnic nerves
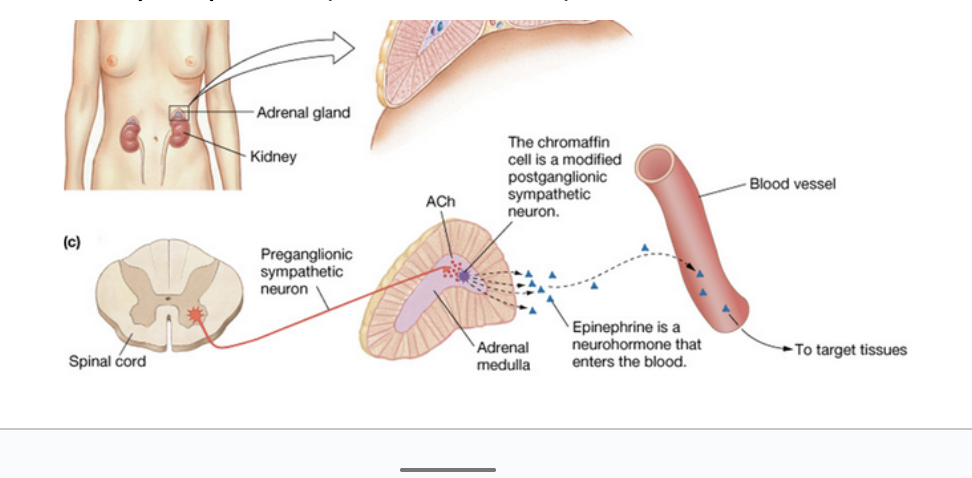
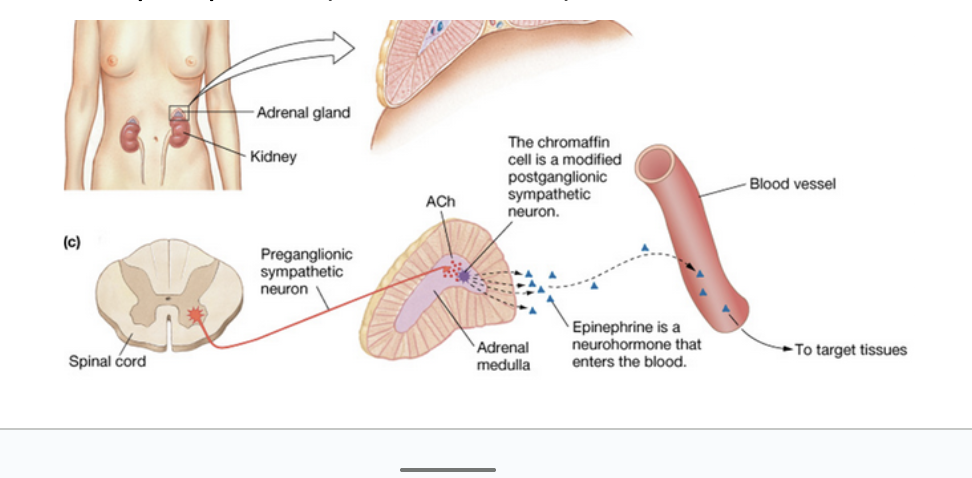
Adrenal Glands
Paired adrenal (suprarenal) glands located on the superior poles of the kidneys
Each is two glands with different functions
Adrenal Cortex
Outer layer of adrenal gland
Secretes steroid hormones
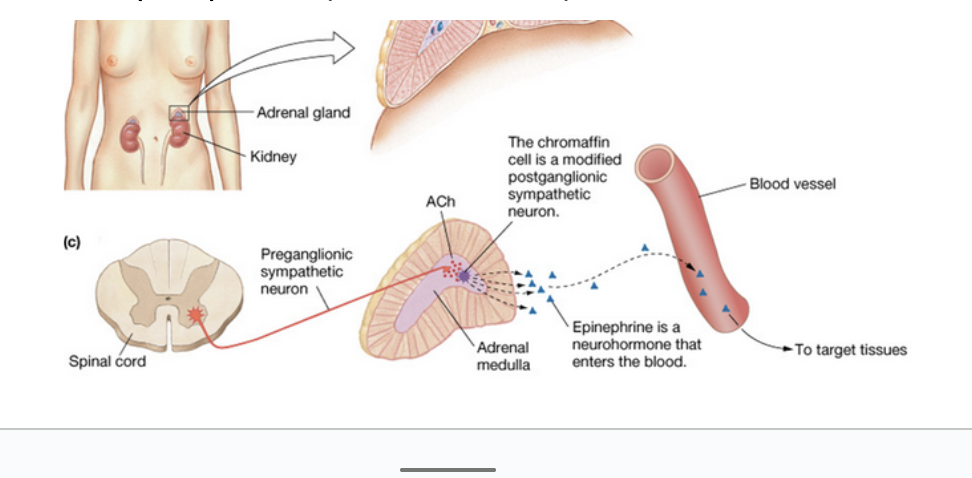
Adrenal Medulla
Inner core of adrenal gland
Essentially a sympathetic ganglion made of modified postganglionic neurons (without fibers)
Secretes a mixture of hormones into bloodstream
Catecholamines—85% epinephrine (adrenaline) and 15% norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
Preganglionic Neurons of the Parasympathetic Division
Origins of long preganglionic neurons:
Midbrain, pons, and medulla
Sacral spinal cord segments S2 to S4
Preganglionic fibers end in terminal ganglia in or near the target organs
Has long preganglionic fibers and short postganglionic fibers
Enteric Nervous System
the nervous system of the digestive tract
Does not arise from the brainstem or spinal cord (no CNS components)
Innervates smooth muscle glands
Composed of millions of neurons found in the walls of the digestive tract
Has its own reflex arcs
Regulates movement of esophagus, stomach, and intestines and secretion of digestive enzymes and acid
Normal digestive function also requires regulation by sympathetic and parasympathetic systems