Multi-store Memory Model | Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)
1/18
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Multi-store Memory Model
Conceptualizing how memory is encoded and stored
Studied by
Atkinson & Shiffrin
Studied during
1968
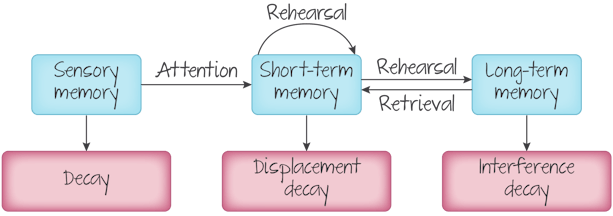
Sensory Memory
Unknown capacity, only registered when given attention. Rapid decay
Short-Term Memory
Activated memory that holds up to 7 pieces of info before it's stored or forgotten
Long-Term Memory
Relatively permanent and limitless storage of memory. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences
Iconic Memory
Visual memory, 0.3 seconds long ☆ animation
Echoic Memory
Auditory memory, 3-4 seconds ☆ knowing what people were talking about a second ago
Haptic Memory
Touch memory, 2 seconds
Displacement Decay
Info that isn't rehearsed decaying to make space
RRehearsalConscious repetition of information to turn into long-term memory
Elaborative Rehearsal
Actively thinking about the meaning of the term, most effective due to existing schemas
Maintenance Rehearsal
Simple repetition, less effective
Engram
Information in long-term memory
Explicit/Declarative Memory
Requires some level of conscious thinking
Explicit Semantic Memory
Facts, rules, concepts, general knowledge. Easiest to recall
Explicit Episodic Memory
Events and Experiences
Implicit/Procedural Memory
No conscious thinking required, skills and conditioning ☆ ice skating
Reductionistic; ignores the non-linear and reconstructive nature of memory
focuses on rehearsal but doesn't account for incidental learning; no explanation for how rehearsal is done; long-term memory is reductionist even though there are 4 types