11 economic performance
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
short run economic growth
an increase in the production of goods and services that occurs without an economy acquiring additional FOP
productivity increase
cost reductions (SRAS)
AD increasing
long run economic growth
an increase ion an economies productive capacity from better quality or quantities of FOP
economic growth an living standards
living standards will increase as long as the population does not increase at a faster rate than the rate of growth
supply side growth
causes by changes in LRAS or SRAS
costs falling, productivity increasing, better FOP
demand side growth
improvements in C + I + G + (X - M)
demand side growth will be inflationary if supply does not increase, unless the economy is operating below full capacity
economic cycle
boom
recession
slump
recovery
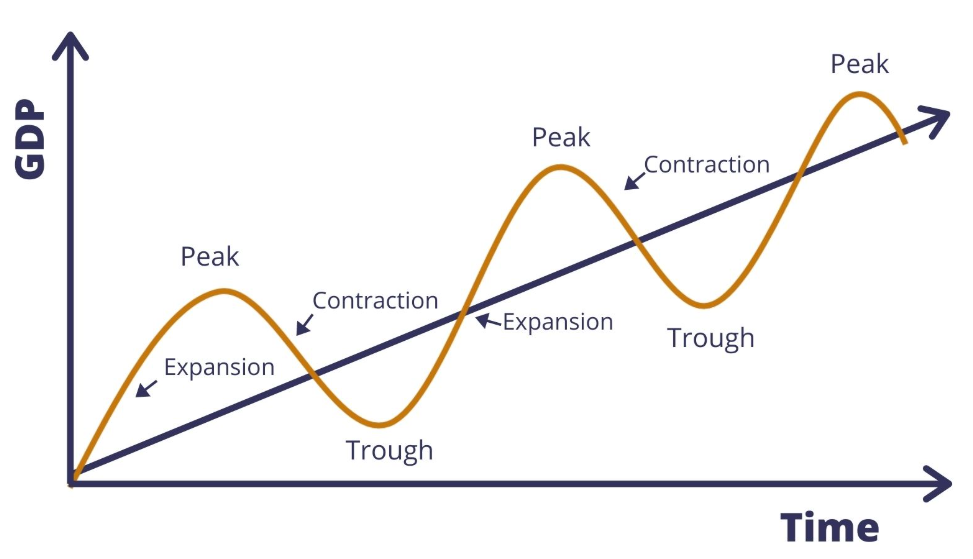
characteristics of a recovery
output and employment begin to increase
consumption increases - multiplier
firms begin to utilise space capacity
business confidence increases - accelerator
rise in consumer spending due to confidence
inflation creeps up
characteristics of arecession
increases FOP costs from boom eat into profits - less investment - AD falls
income and output falls as firms cant employee as many workers
business and consumer confidence falls
spare capacity rises
inflationary pressure falls - negative multiplier
less imports
firms search for new markets aboard
characteristics of a boom
high levels of business and consumer confidence
high levels of demand
increase level of production
high investment
skilled workers become scarce - wages increase - costs increase
goods and services become scarce - inflation - high IR - PP is lower, UK goods not as competitive, wage price spiral
high imports
skills shortages
characteristics of a slump
disposable income is low
main objective of firms is to survive
large gov budget deficit
high unemployment
deflation
reduced demand
low price of capital aids recovery
goods become more competitive internationally
output gap
the difference between actual output and potential output of an economy in GDP
positive output gap - when actual output exceeds potential output
negative output gap when actual output is below potential output
factors moving an economy from one stage to another
replacement investment and technology advancements
economic shock
optimisation - animal spirits - accelerator
government policy
IR change
asset bubbles burst
credit crunch
strong multiplier
stock pilling
herding - factors that can change the economic cycle
where individuals in a market mimic the actions of a larger group, often leading to trends in investment behaviour increasing AD
asset bubble bursting - factors that can change the economic cycle
occurs when the prices of assets rise rapidly and then suddenly decline, often leading to significant economic downturns
stock pilling - factors that can change the economic cycle
the practice of holding large quantities of inventory to meet anticipated demand - stops firms investing and reduces AD
negative equity - factors that can change the economic cycle
a situation where the value of an asset falls below the amount owed on it - house prices fall but mortgage stays the same
political cycle - factors that can change the economic cycle
a change in government may increase or decrease government spending
replacement investment - factors that can change the economic cycle
investment to replace worn-out or obsolete capital goods, thereby maintaining the productive capacity of an economy - bank loan taken out
economic performance of other countries - factors that can change the economic cycle
if other countries the UK exports to are doing well, they are likely to purchase more exports and so AD rises - could happen in reverse
credit crunch - factors that can change the economic cycle
banks stop lending as they have less loanable funds available - could be a result of overlanding to poorer households who cant pa it back
animal spirits - factors that can change the economic cycle
optimisation about how the economy will preform in the future can increase investment via the accelerator and also have a strong multiplier effect - increase in AD
changes in technology - factors that can change the economic cycle
firms will invest to keep up with other firms - increasing AD and AS as costs of production fall and capacity increases
interest rates - factors that can change the economic cycle
higher rates generally dampen spending, while lower rates can stimulate economic activity as there is a lower opportunity cost to saving and borrowing is cheaper, encouraging consumer and business loans
economic shocks - factors that can change the economic cycle
unexpected events that can disrupt economic stability, affecting aggregate demand and supply
advantages of economic growth
increase SOL
increased employment
lower absolute poverty
increased tax revenue
multiplier
accelerator
larger business profits - investment - spending on CSR
high business and consumer confidence
disadvantages of economic growth
inflation - macro conflict
increase imports - worsen BOP
increased prices on exports - worsens BOP and current account - macro conflict
environmental concerns
increased inequality
increased relative poverty
factors that limit economic growth
infrastructure
dependence on exports
vulnerability to shocks
low levels of savings to invest
declining / ageing population
inflation
unemployment
people who are able, available and willing to work but cant find a job despite searching for work
underemployment
when individuals are working in jobs that do not fully utilize their skills or education
unemployment rate
unemployed individuals / total labour force X 100
voluntary unemployment
workers choose to remain unemployed and refuse job offers at the current market wage, they are not attempting to relocate or retrain to make themselves employable
involuntary unbemployment
when individuals are willing and able to work at the current market wage but there are no jobs on offer - recession
structural unemployment
results from the decline/changes in industries in an economy
cyclical unemployment
occurs due to fluctuations in the business cycle, particularly during recessions, when overall demand for goods and services decreases, leading to job losses
frictional
unemployment occurs when individuals are temporarily between jobs, often due to voluntary transitions in employment
casual unemployment
refers to temporary unemployment that occurs when individuals are not consistently employed, often due to seasonal or contract work
demand deficient unemployment
arising from a decrease in AD
technological unemployment
caused by an introduction of labour saving technology
classical unemployment
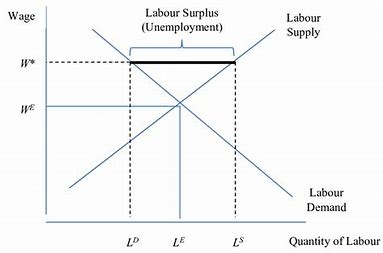
occurs when wages are set above the market equilibrium, leading to a surplus of labour
seasonal unemployment
occurs when people are unemployed at certain times of the year due to seasonal variations in demand for certain jobs
causes of unemployment
demand side factors
lack of AD firms dont need labour (derived demand)
supply side factors
imperfections in the labour market
geographical immobility of labour
refers to the inability or unwillingness of workers to move to different locations for employment, often due to factors like housing costs, family ties, or lack of information
occupational immobility of labour
refers to the inability or unwillingness of workers to change occupations or professions, often due to a lack of transferable skills, experience, or education
natural rate of unemployment
classical def - unemployment when LRAS and AD are in equilibrium
Keynesian def - unemployment at YFE
NRU includes
people who are frictionally unemployed
people who are structurally unemployed
disaffected workers
benefit lifestylists - unemployment trap
determinants of NRU
availability of job information - how quickly the unemployed find a job
level pf benefits - generous may increase unemployment
cost of living in different regions
skills and education
savings/wealth
hysteresis
if workers are unemployed for a long time they may become de-skilled and less employable, leading to a permanent increase in the natural rate of unemployment
where a variable doesn’t return to its original state
consequences of unemployment on inidivduals
fall in living standards
social costs
less financial security
can become deskilled
consequences of unemployment on the economy
reduced consumption
reduced investment
reduced consumer and business confidence
lower tax revenue - worsens budget deficit
hysterisis
advantages of unemployment
falling rate of inflation - no wage price spiral
easier for businesses to recruit - better quality of labour - better productivity - LRAS right
may lead to increased competition for jobs, encouraging businesses to innovate
sunrise and sunset indistries
sunrise industry - developing
sunset industry - declining
the replacement ratio
measures the amount of money a person would get in employment compared to unemployment
disposable income out of work / disposable income in work
unemployment trap
where a person is better off financially from not working due to government benefits or support than by taking a job, leading to disincentives for seeking employment
poverty trap
when someone stays in a lower paid job as they are not better off gaining a promotion
positive impacts of globalisation on employment
Job Creation in Emerging Markets
developing countries have benefited from increased FDI, leading to the growth of manufacturing and service sectors
Example: Countries like India and Vietnam have seen growth in IT and manufacturing jobs due to outsourcing
Access to Global Job Markets
workers can now apply for remote jobs in other countries, increasing employment opportunities
Skill Development and Technological Transfer
Exposure to international companies has increased skill levels, especially in countries integrated into global supply chains
Entrepreneurial Opportunities
Global markets give entrepreneurs access to new customers, suppliers, and partners, encouraging job creation
negative impacts of globalisation on employment
Job Losses in Developed Countries
Offshoring and outsourcing have led to the decline of manufacturing jobs in some developed economies, like the U.S. and parts of Europe.
Wage Pressure and Job Insecurity
Increased competition can suppress wages and lead to more precarious employment, including temporary or gig jobs.
Widening Inequality
Benefits of globalisation are often unevenly distributed, leading to income inequality between high-skilled and low-skilled workers.
Exploitation of Labor
In some developing countries, globalisation has led to poor working conditions, low wages, and child labor, especially in informal or unregulated sectors.
factors that determine real wage unemployment
mismatch between wage levels and market equilibrium
strength and influence of trade unions
existence of minimum wage laws above equilibrium wage
efficiency wage policies by employers
inflexible labor market institutions or regulations
low labor mobility (geographic or occupational)
high unemployment benefits reducing incentive to accept lower wages
weak demand for labor in specific sectors
labor productivity not matching wage expectations
technological change reducing demand for certain job roles
real wage unemployment
unemployment that occurs when real wages are set above the market equilibrium, leading to a surplus of labour supply due to factors like trade union influence, minimum wage laws, and inflexible labour market regulations.
inflation
a sustained increase in the general price level
measuring inflation
retail price index - average price of basket of goods that reflects consumer buying habits
consumer price index
core inflation rate
the rate of inflation excluding volatile items such as food and energy prices, providing a clearer view of the underlying inflation trend
limitations of measuring inflation
different people experience different rates of inflation
CPI doesn’t include housing costs
doesn’t take quality of goods into account'
lad in data collection
problems with inflation
international competitiveness - less demand for exports - worsens current deficit
negative effect on investment
reduced living standards
reduction in value of savings
fiscal drag - people dragged into next tax bracket while real incomes remain the same
hyperinflation
costs of production increase for businesses
labour may be substituted for capital
advantages of inflation
workers moral increase due to pay rise even if its just the money illusion - real income stays the same
decrease in the real value of debt
increase in tax revenue through fiscal drag
increase in business profits depending on costs
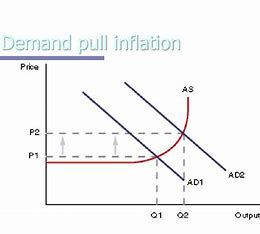
demand pull inflation
inflation occurs as AD shifts right (C + I + G + (X - M)
greater pressure on existing FOP to produce more output as firms try to satisfy demand - closer to YFE - resources become scarcer - FOP increase in price
lower IR
quantitative easing
depreciation of ER
increase in government spending
tax cuts
confidence
exports
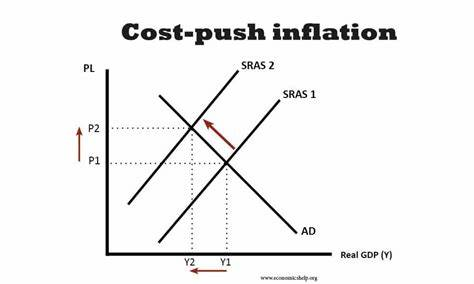
cost push inflation
SRAS shift left due to an increase in costs of production which get passed onto consumers as higher prices
rising wages
high raw material prices
interest rates increase
exchange rate weakens - imports more expensive
wage price spiral
increase in AD - demand pull inflation
price level rises as there is a profit incentive
workers demand higher wages as their incomes are being eroded
firms put prices up to maintain margins after an increase in wage costs - cost push inflation
workers demand higher wages - wage price spiral
quantity theory of money
increases in the money supple will lead to an increase in the PL
M x V = P x T(Q)
expenditure = output
M = money supply
V velocity of circulation - how many times money is used in a year
Increasing money supply leads to higher price levels. p = price level
T(Q) = transactions , real GDP - output of foods available
V and T are fixed so there is a direct relationship between the growth of the money supply and inflation
disinflation
prices are increasing but at a slower rate
deflation
sustained decrease in the general price level, real value of money increases
malevolent (malign) deflation
bad deflation
caused by a decrease in AD
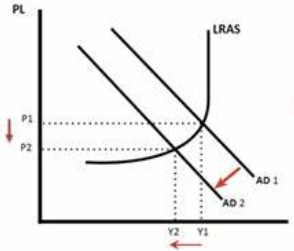
benign deflation
good deflation
caused by a decrease in costs or production or an increase in productivity so SRAS moves right
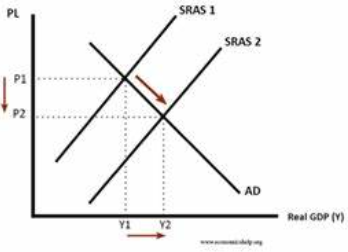
disadvantages of deflation
gives consumers the expectation that prices will fall further so they hold off on spending
further fall in AD
firms may have to reduce prices - less investment
value of debt increases
value of savings rise which encourages people to save more consumption falls
firms dont give pay rises, lowers motivation and productivity
falling asset prices cause a further decrease in AD
if cause by lack of demand, confidence falls
advantages of deflation
cost of living falls while wages remain the same as Keynesian said they are sticky downwards - higher PP
income inequality falls
MPC increases long run growth
exports increase as they are more price competitive
wage settlements
if people, expect prices to rise - employees and trade unions will bargain for higher wages
causes the wage price spiral
adaptive expectations
theory that suggests firms and households use past information as an indicator for the future
rational expectations
theory where individuals use all available information to forecast future economic variables, leading to more accurate predictions than adaptive expectations
positive output gap effect on inflation and unemployment
Inflationary Pressure
High demand pushes up prices.
Firms raise wages to attract scarce labour, leading to demand-pull and cost-push inflation.
Low Unemployment
Firms hire more workers to meet increased demand.
Unemployment falls below the natural rate (may cause labour shortages)
negative output gap effect on inflation and unemployment
Deflationary/Disinflationary Pressure
Weak demand keeps prices low.
Firms may freeze or cut wages
High Unemployment
Reduced production means fewer jobs.
Unemployment rises above the natural rate due to slack in the economy
how can changes incommodity prices effect inflation
higher input costs
wage price spiral
when input costs fall there is less pressure on prices, leading to lower inflation
stagflation
high unemployment, and high inflation occurring simultaneously
short run Phillips curve
as unemployment falls, inflation increases
when unemployment is low, workers are scare meaning they have ore bargaining power to increase wages - cost push inflation
more income generates more consumption, increasing demand - demand pull inflation
macro conflict - if you want low unemployment you have to sacrifice the low inflation objective
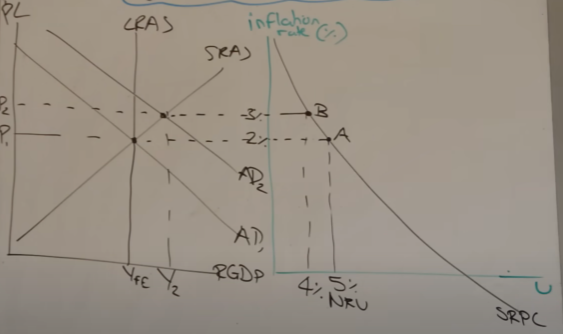
long run Phillips curve
A = unemployment is at NRU with 0% inflation, some workers are voluntarily unemployed
B = an increase in AD reduces unemployment
firms have to increase wages to attract new workers
worker face a money illusion
firms increase prices so inflation increase to 2%
C = workers realise they are no better off
workers leave the labour market
unemployment returns to 8% (NRU)
however inflation is still ta 2%
D = workers will only enter the labour market again if wages raise above 2%
increases firms costs
prices increase
wages now need to be raised in excess of @% to attract new workers
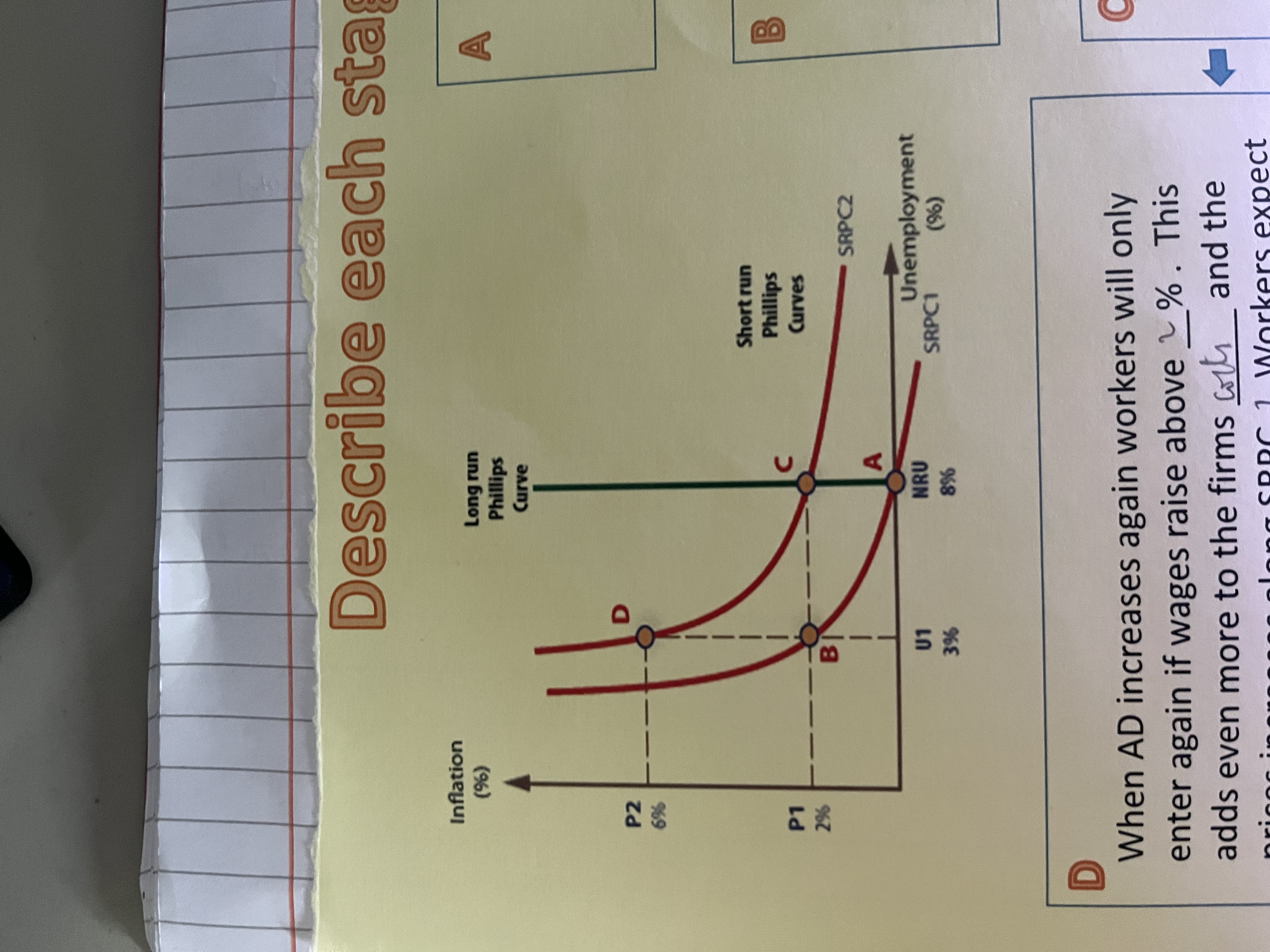
NAIRU
non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment, where inflation remains stable, reflecting the lowest level of unemployment an economy can sustain without causing inflation to rise
what can shift the long run Phillips curve
change in NRU
if it falls the curve moves left
if it rise the curve shifts right
what type of unemployment is at the NRU