Lesson 4.2 Calculating dissociation constants and concentrations
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:22 PM on 1/24/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
1
New cards
What is the ICE table method for equilibrium calculations?
I = Initial concentration, C = Change in concentration, E = Equilibrium concentration. Set up columns for each species and use stoichiometry to relate changes.
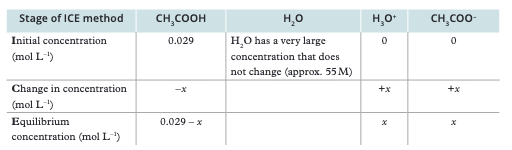
2
New cards
When can you assume [HA]initial ≈ [HA]equilibrium for weak acids?
When Ka is very small (Ka < 10⁻⁴), dissociation is minimal so the change in acid concentration is negligible. You MUST state this assumption when using it
3
New cards
How do you calculate Ka given initial concentration and pH?
Step 1: Find [H⁺] = 10⁻ᵖᴴ. Step 2: [A⁻] = [H⁺] (equal amounts formed). Step 3: [HA]eq ≈ [HA]initial (if Ka small). Step 4: Ka = [H⁺][A⁻]/[HA]
4
New cards
Worked example: Calculate Ka for 0.029 M CH₃COOH with pH 3.15
[H⁺] = 10⁻³·¹⁵ = 7.08 × 10⁻⁴ M. [CH₃COO⁻] = 7.08 × 10⁻⁴ M. [CH₃COOH]eq ≈ 0.029 M (assumption). Ka = (7.08 × 10⁻⁴)² / 0.029 = 1.8 × 10⁻⁵
5
New cards
How do you calculate pH from Ka and initial concentration?
Step 1: Set up ICE table with x = [H⁺] formed. Step 2: Ka = x² / [HA]initial (using assumption). Step 3: Solve for x. Step 4: pH = −log(x)
6
New cards
How do you calculate pOH and pH for a weak base using Kb?
Step 1: Use ICE table to find [OH⁻] = x. Step 2: Kb = x² / [B]initial. Step 3: Solve for x = [OH⁻]. Step 4: pOH = −log[OH⁻]. Step 5: pH = 14 − pOH
7
New cards
What assumption must you STATE in exam answers for weak acid/base calculations?
"Because Ka (or Kb) is very small, the dissociation is minimal, so [HA]equilibrium ≈ [HA]initial" — Always state this when you use the approximation
8
New cards
How are "hydronium ions" and "hydrogen ions" related?
They are used interchangeably. H₃O⁺ (hydronium) = H⁺ (hydrogen ion). Both represent the same species in aqueous solutio