AP MACROECONOMICS: UNIT 1 BASIC ECONOMICS CONCEPTS
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FLVS Course V20 Vocabulary
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
the transfer of a good or the providing of a service, usually involving the exchange of money
every person and society has unlimited wants and needs and limited resources to meet them, which requires choices. economics is the science of those choices.
consumer goods are directly used by the person who acquires them, and capital goods are used to produce consumer goods.
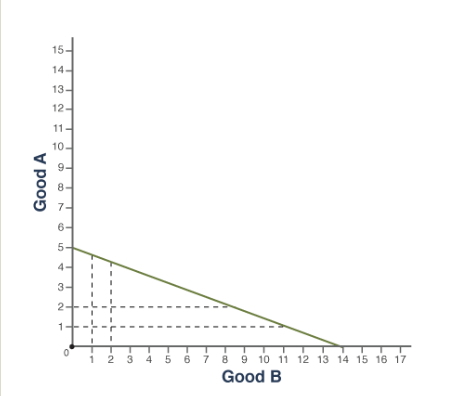
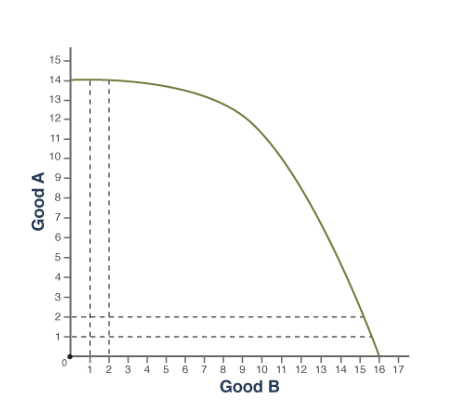
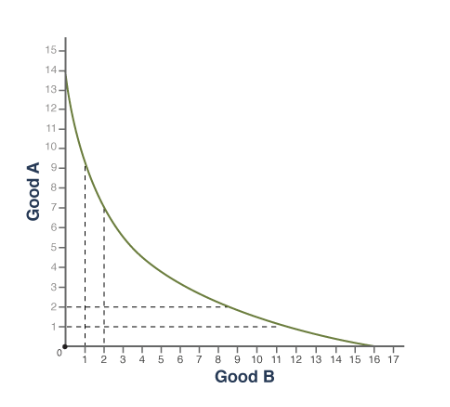
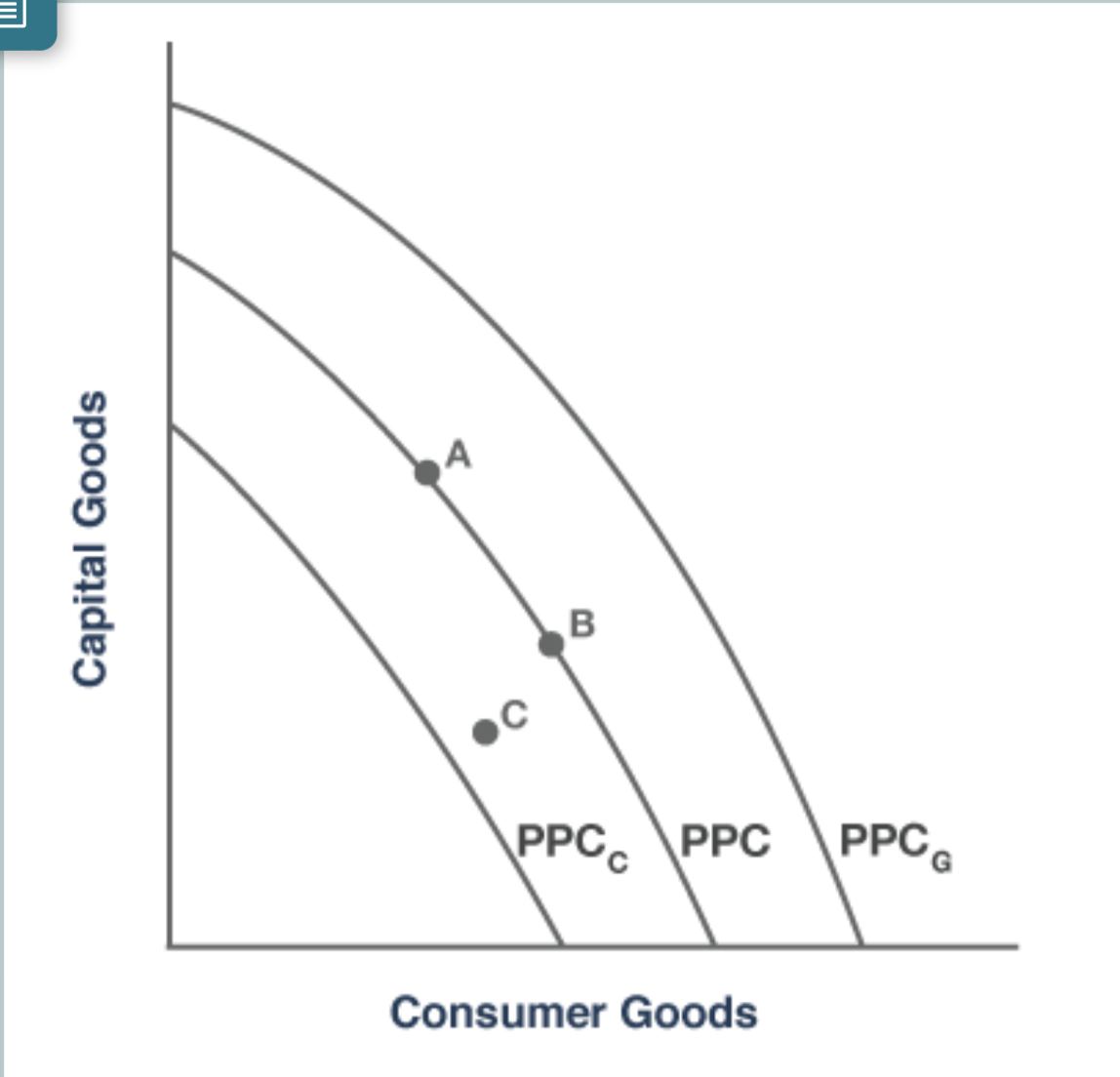
**Technically, it doesn't.** Neither specializing in one's comparative advantage nor trade allows for producingbeyond the production possibilities curve (PPC). However, specialization and trade allows a country's people to benefit by consuming beyond the PPC.
To express a good's opportunity cost as a fraction, the ...
other good's quantity goes under in input problems
demand
the willingness and ability of consumers to buy a range of quantities at every possible price
demand schedule
the quantity that will be purchased of a good or service at every possible price
quantity demanded
the number of units of a good or service that will be purchased at a particular price
Law of Demand
the quantity demanded of a good or service is indirectly related to its price, ceteris paribus
Ceteris Paribus
Latin for "other things equal," meaning all other variables are unchanged
Income Effect
the principle that says as price increases, people are willing to buy less because higher prices take a greater portion of their income
Purchasing Power
the quantity of goods and services that a consumer can buy with an amount of income
Substitution Effect
the change in the demand for a good or service caused by a change in the price of a similar product, one that directly competes with it
The greater the price…
the more likely it is that consumers will find a substitute product to purchase instead, reducing the quantity demanded for the original good.
Law of Diminishing Marginal Unity
as more of a good or service is consumed, the personal satisfaction derived from it decreases with each unit
How does an increase in price affect demand?
It doesn't. An increase in price lowers quantity demanded.
determinants of demand
the factors that move the entire demand curve for a good or service
Law of Supply
the quantity supplied of a good or service is directly, or positively, related to its price, ceteris paribus
Supply Schedule
the quantity that will be supplied of a good or service at every possible price
determinants of supply
factors that change the quantity supplied at every price level
subsidy
a government payment to an individual or business to encourage a certain activity
Left is less…
Right is more
market equilibrium
the price and quantity level where supply and demand are in balance
market shortage
when quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded at the current price
market surplus
when quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded at the current price
market disequilibrium
a condition where there is imbalance between quantity supplied and quantity demanded in a market
price floor
a minimum price set by policy; if binding, will be above market equilibrium
price ceiling
a maximum price set by policy; if binding, will be below market equilibrium