Functional Human Anatomy - Rutgers Exam 1
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
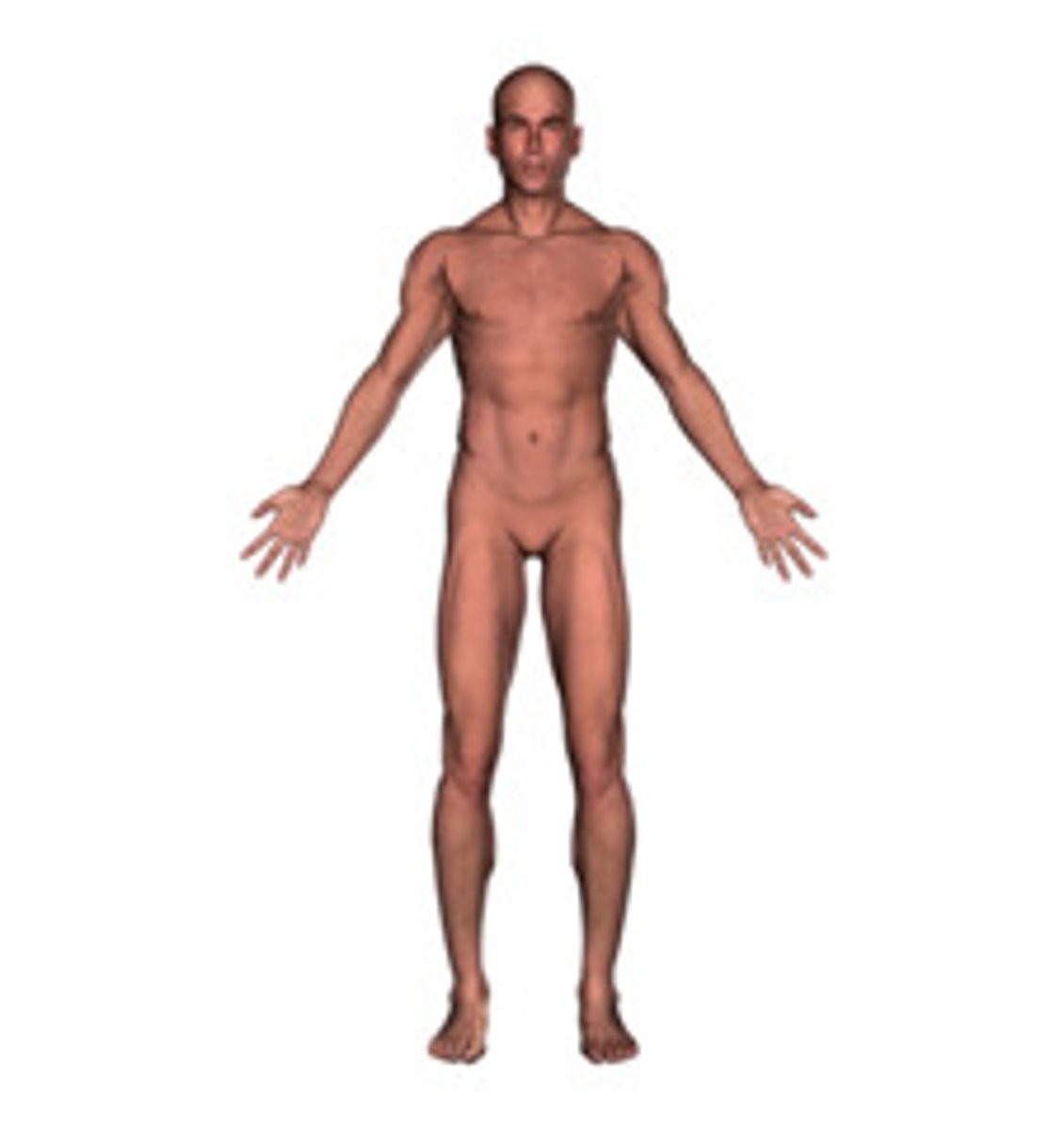
Anatomical Position
Standard reference position. Body upright, palms forward, eye straight ahead, feet together and forward.
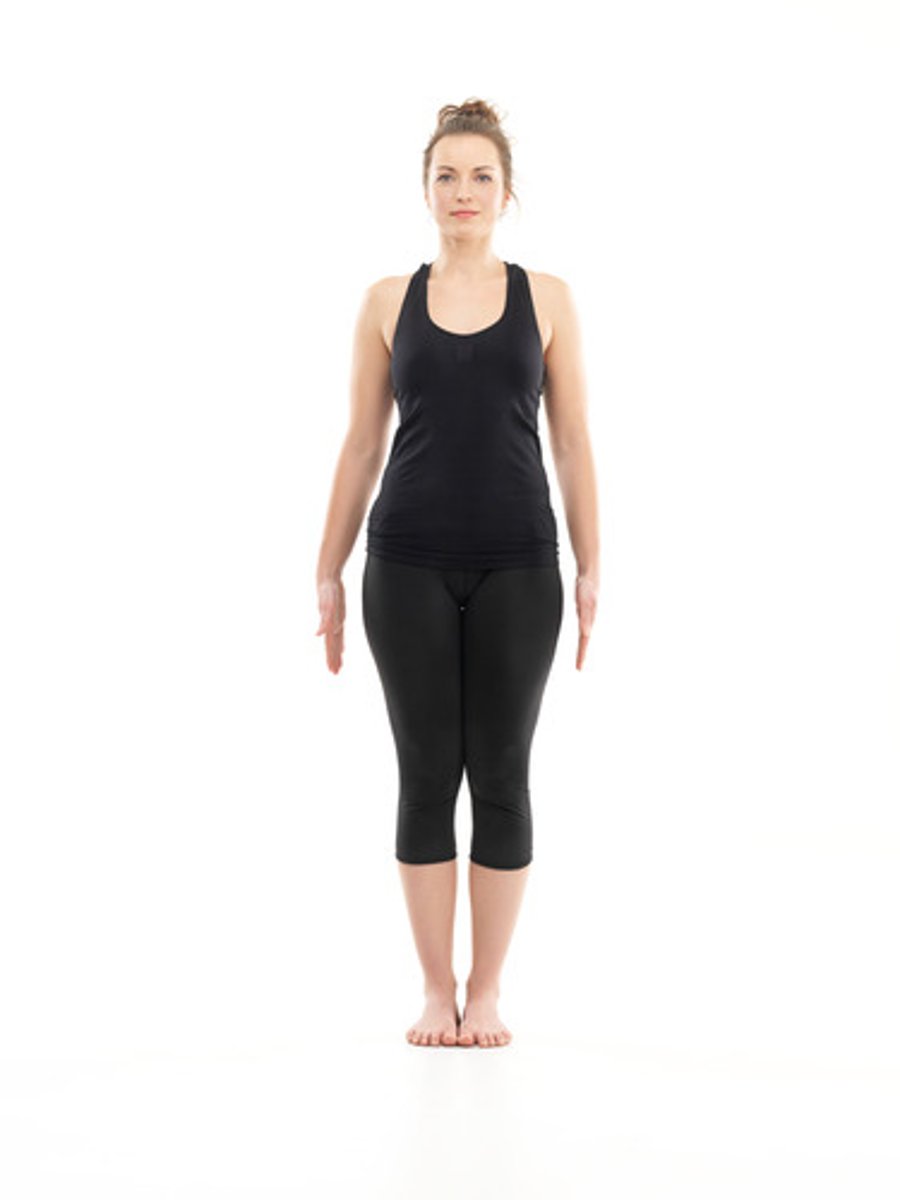
Fundamental Position
More relaxed, palms are facing inwards towards the body.

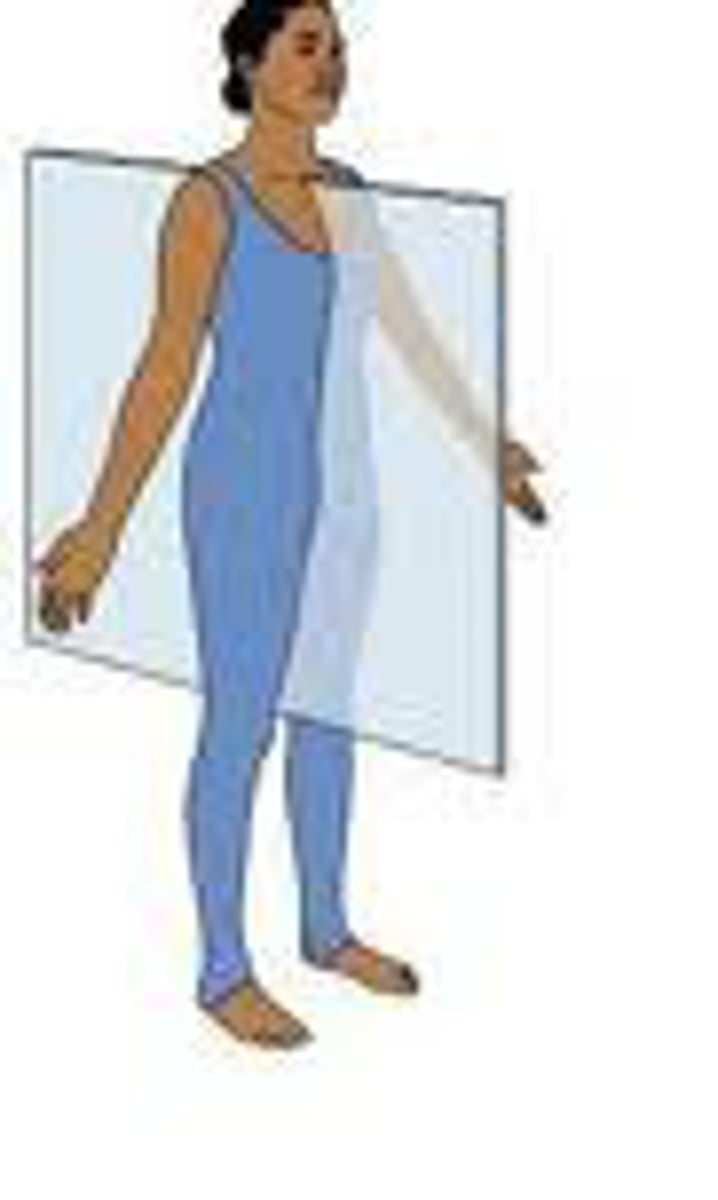
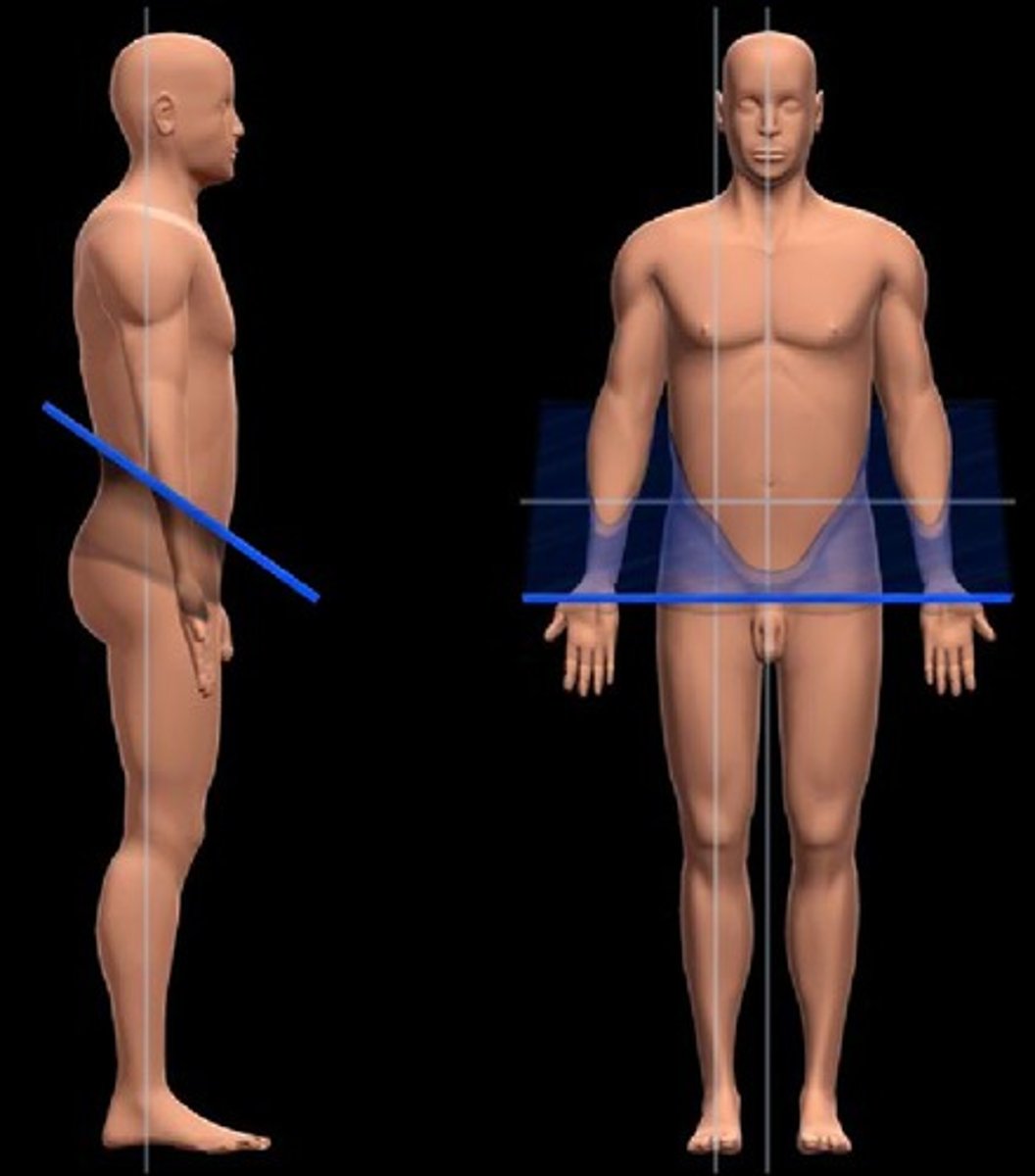
Sagittal Plane
vertical planes passing through the body parallel to the median plane
Midsagittal Plane
bisects the body vertically through the midline marked by the navel, dividing the body exactly in left and right side
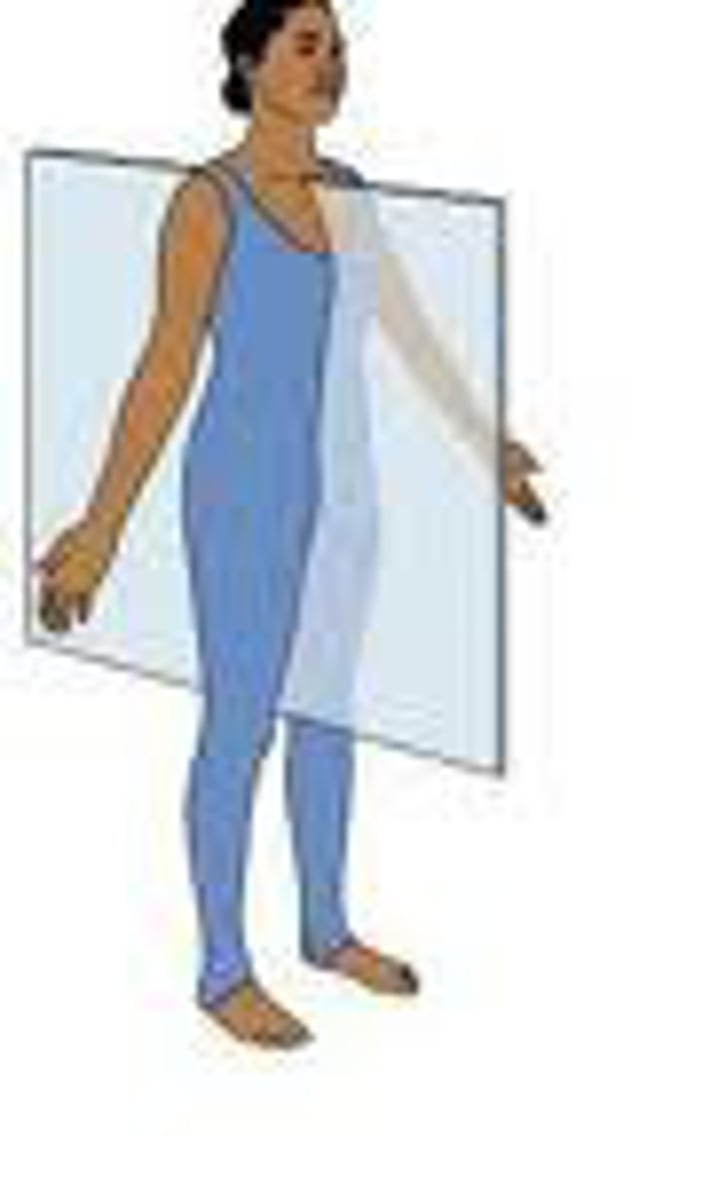
Frontal Plane
divides the body into ventral and dorsal (belly and back) sections
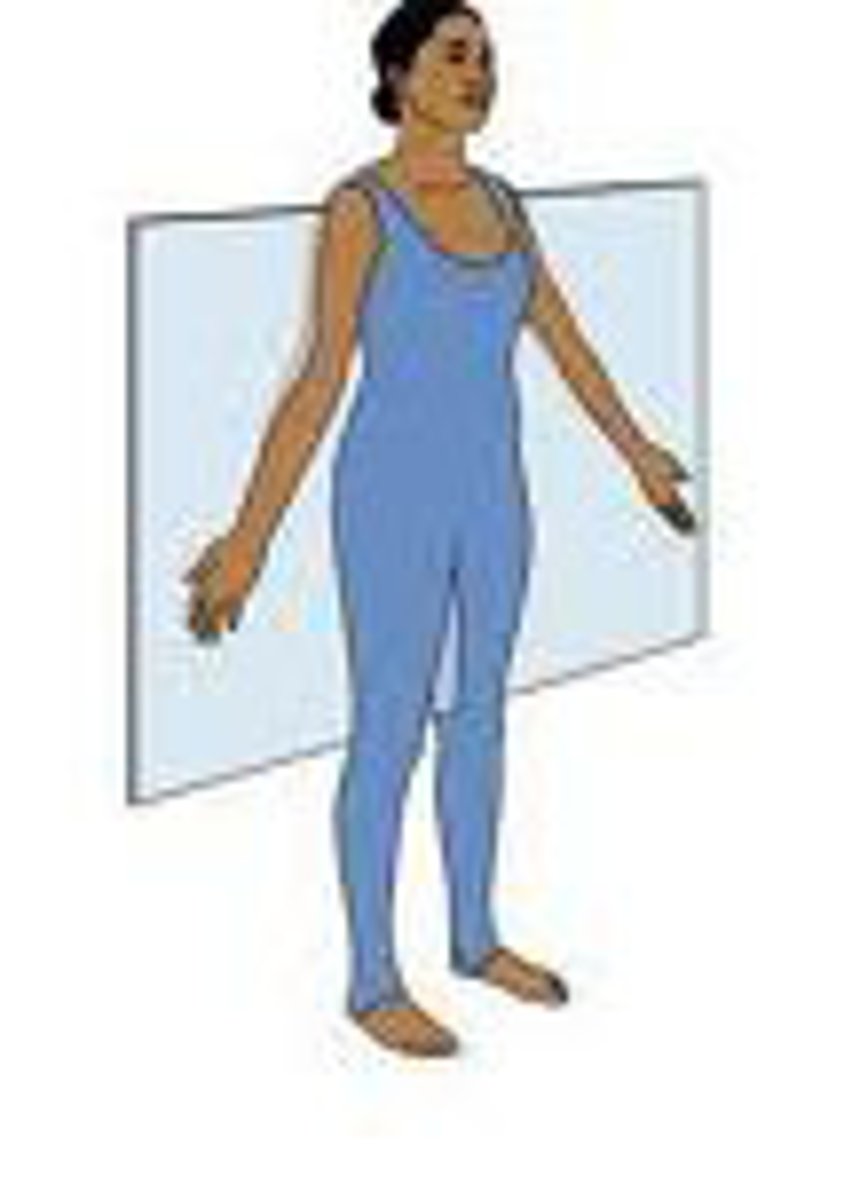

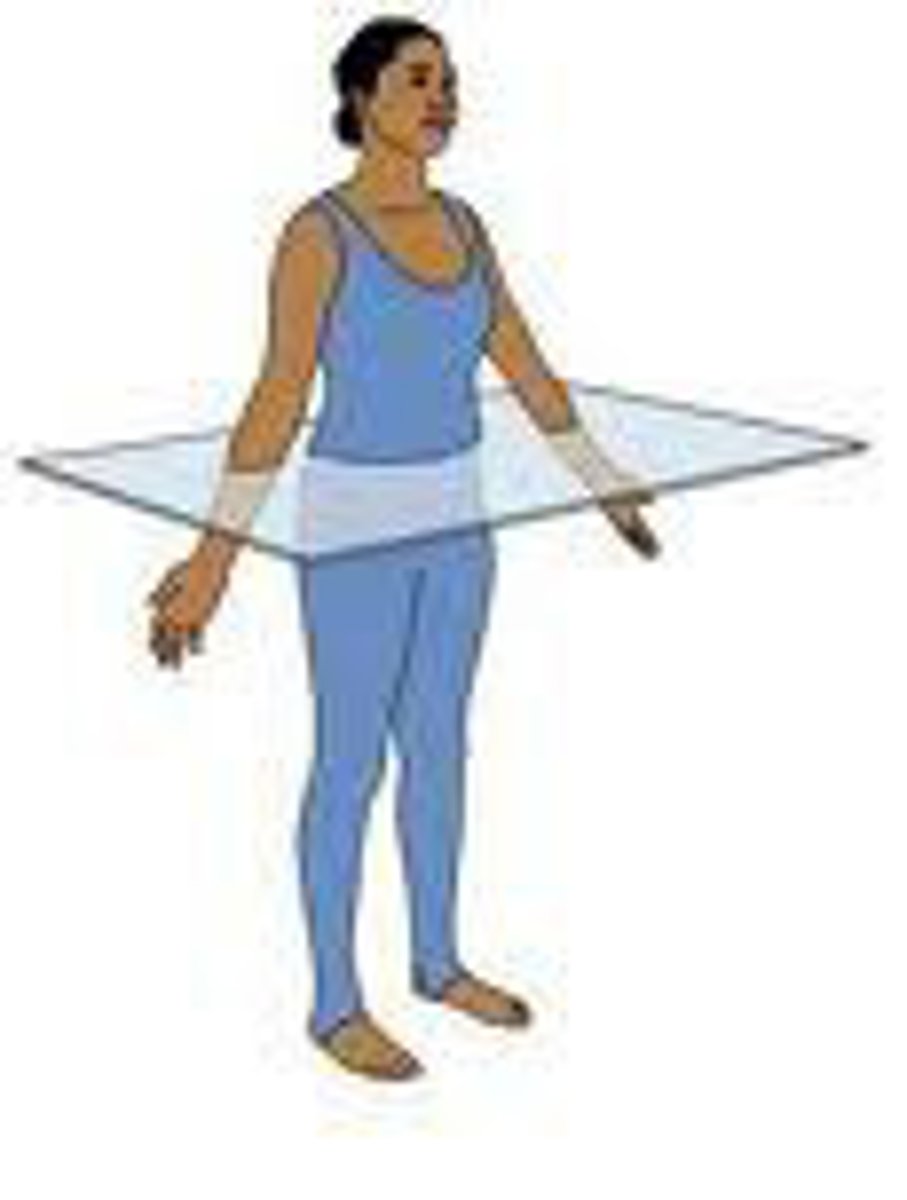
Transverse Plane
dividing the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) portions
Oblique Plane
section of a plane that is not at a right angle
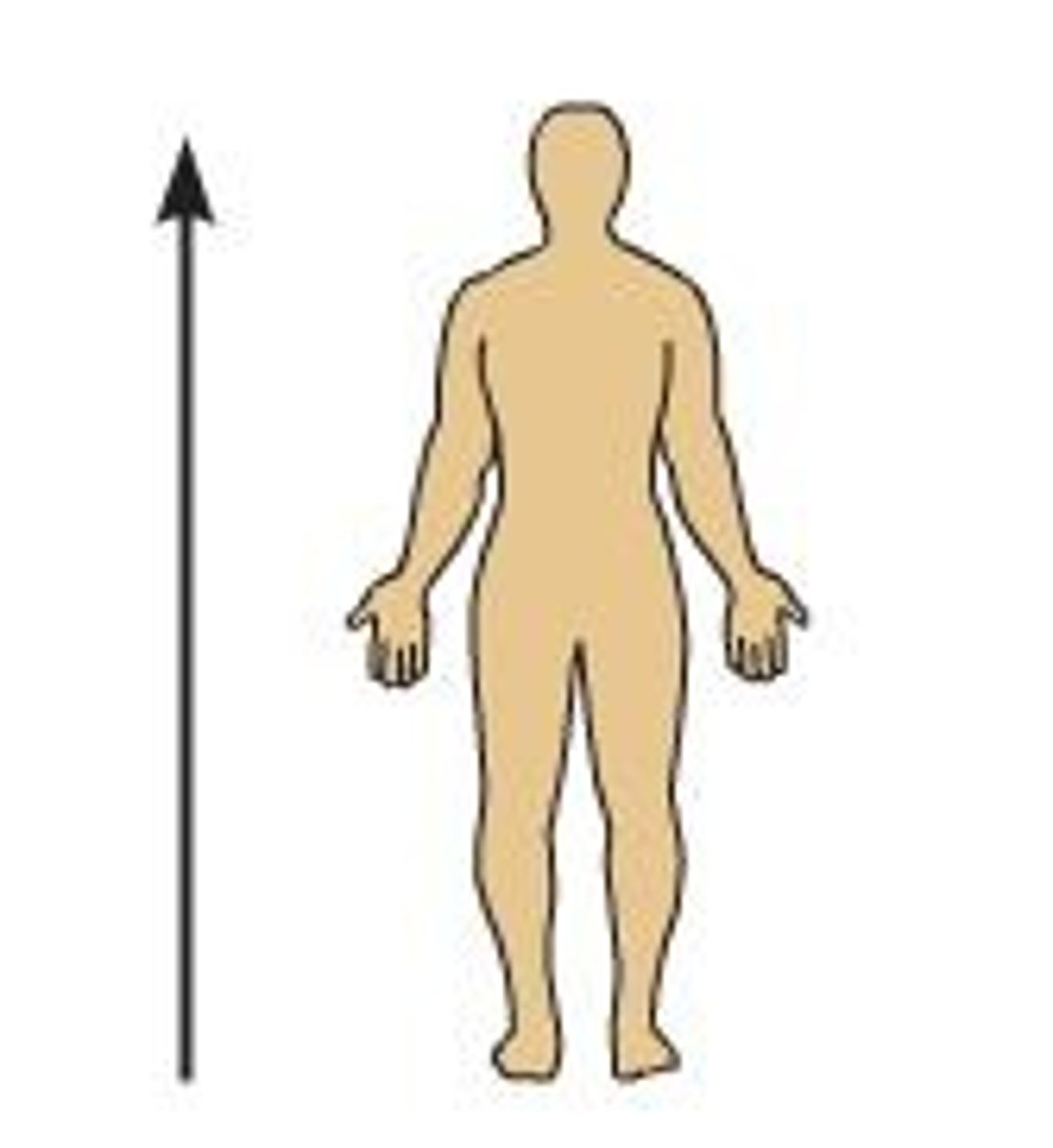
Superior
above - towards the head
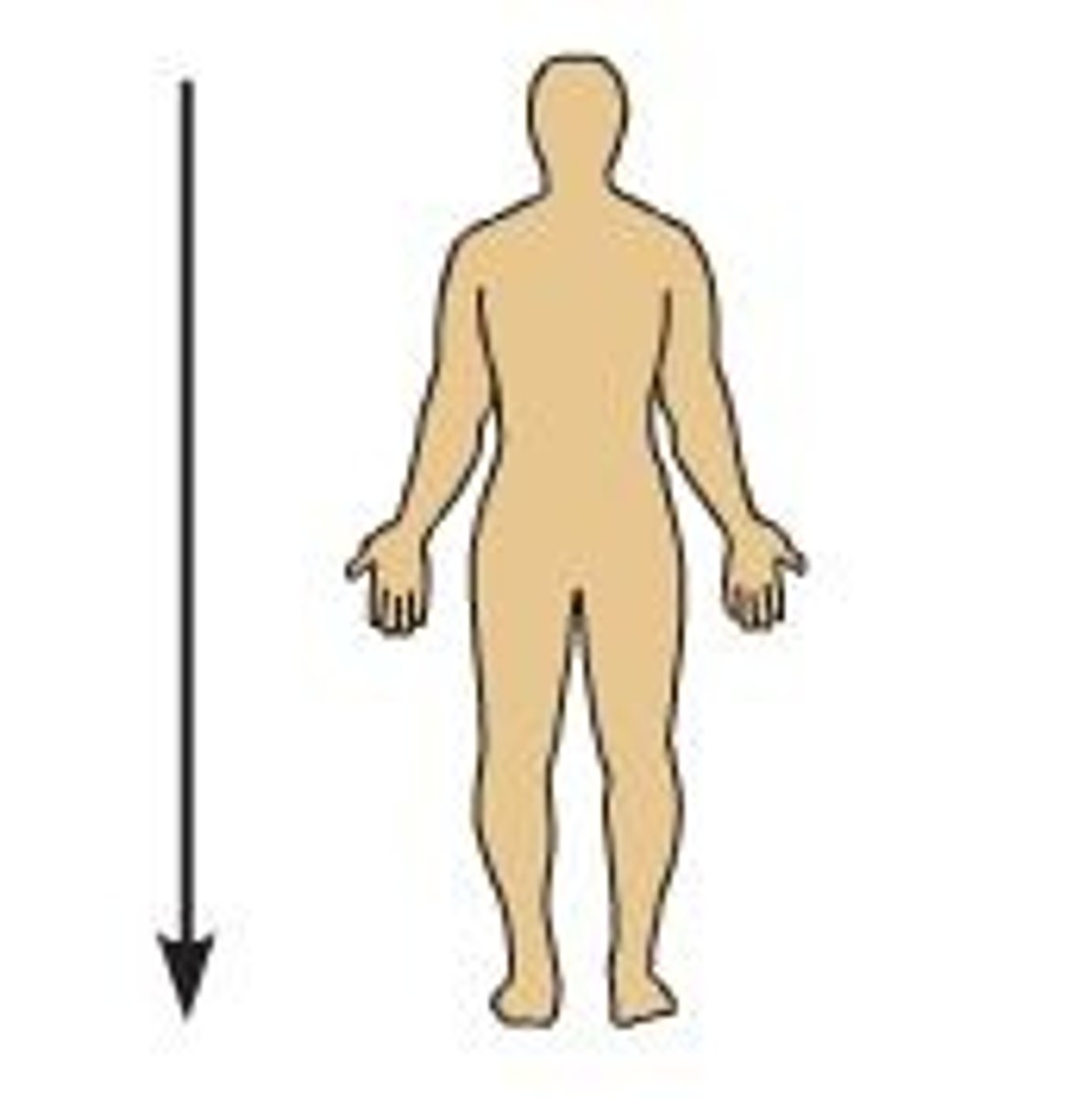
Inferior
below - toward the tail
Anterior
belly side
Posterior
backside
Medial
toward the middle of the body
Lateral
away from the middle of the body
Proximal
close to the trunk
Distal
farther from the trunk
Superficial
on or near the surface
Deep
internal
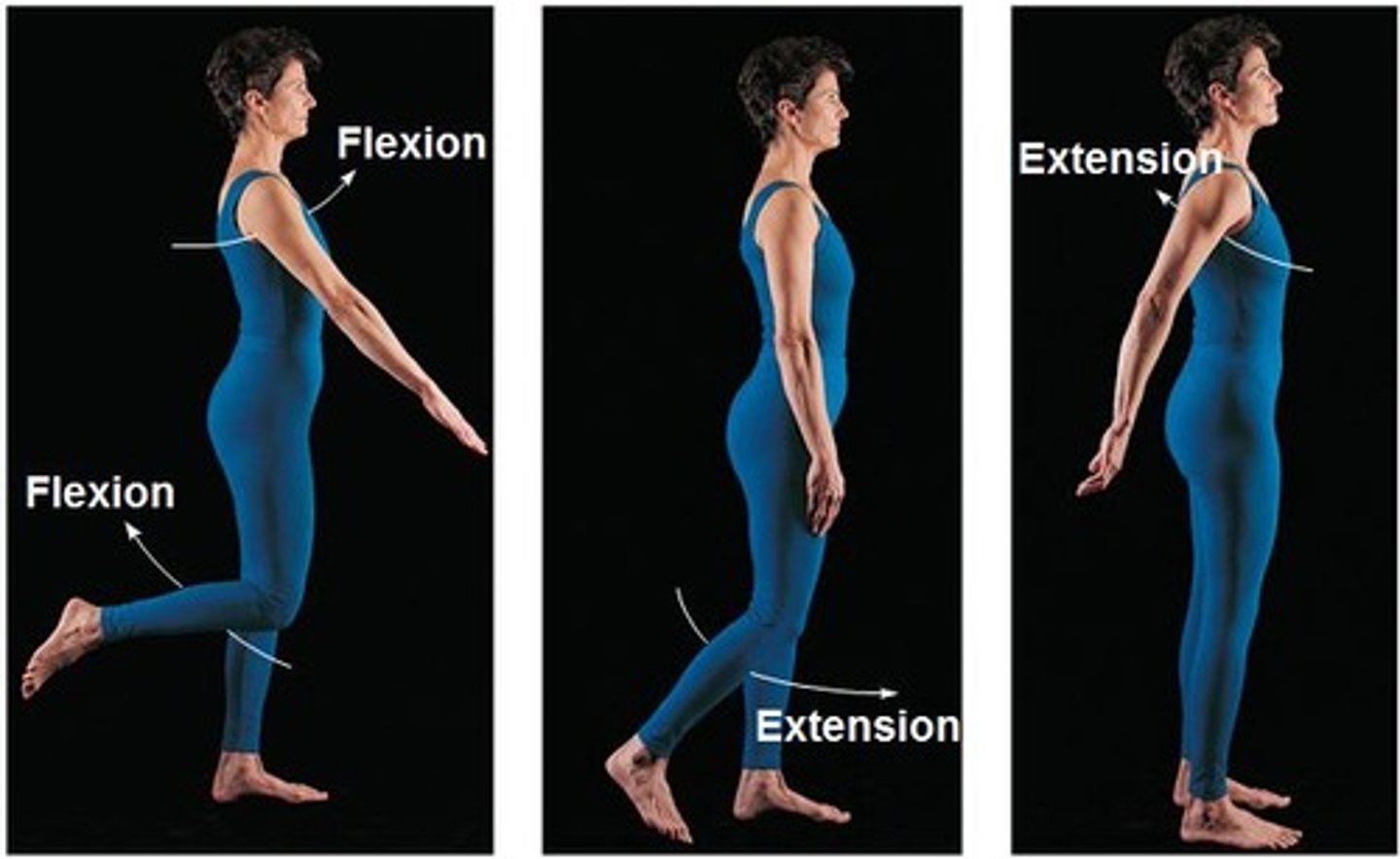
Flexion
decreases the angle
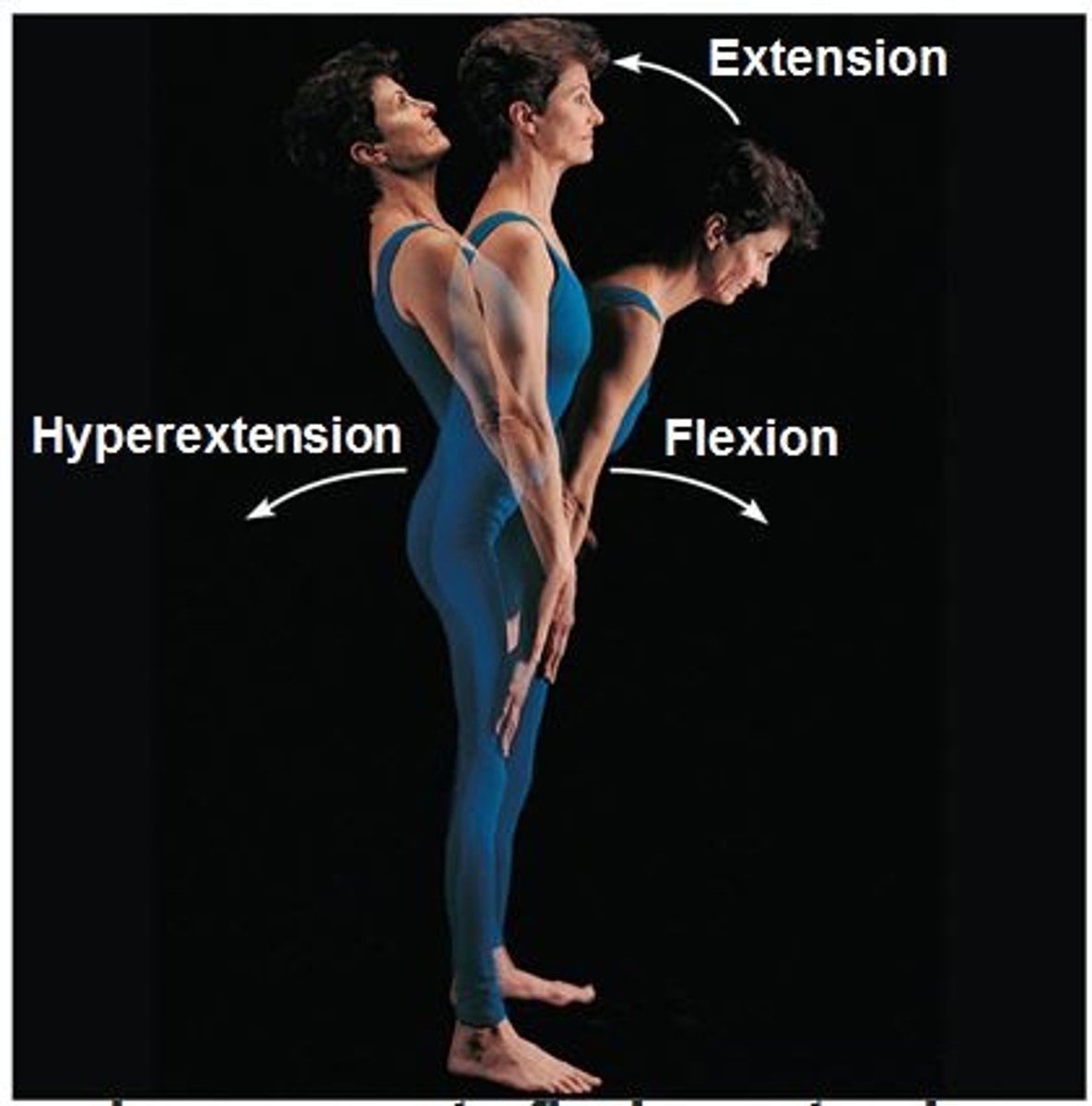
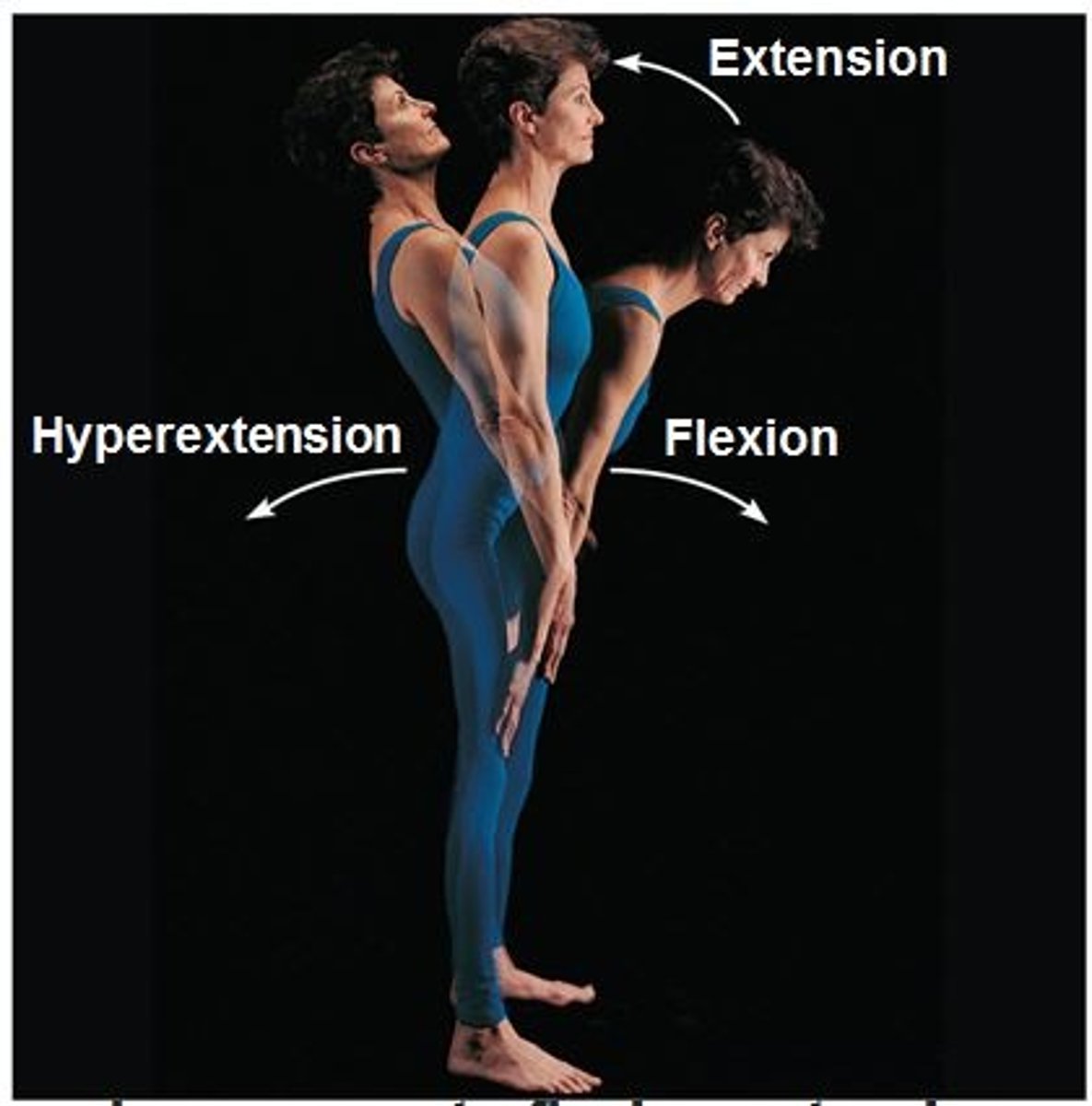
Extension
Increases the angle
Hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position
Lateral Flexion
decreasing an angle on the side of your body (based off spine)
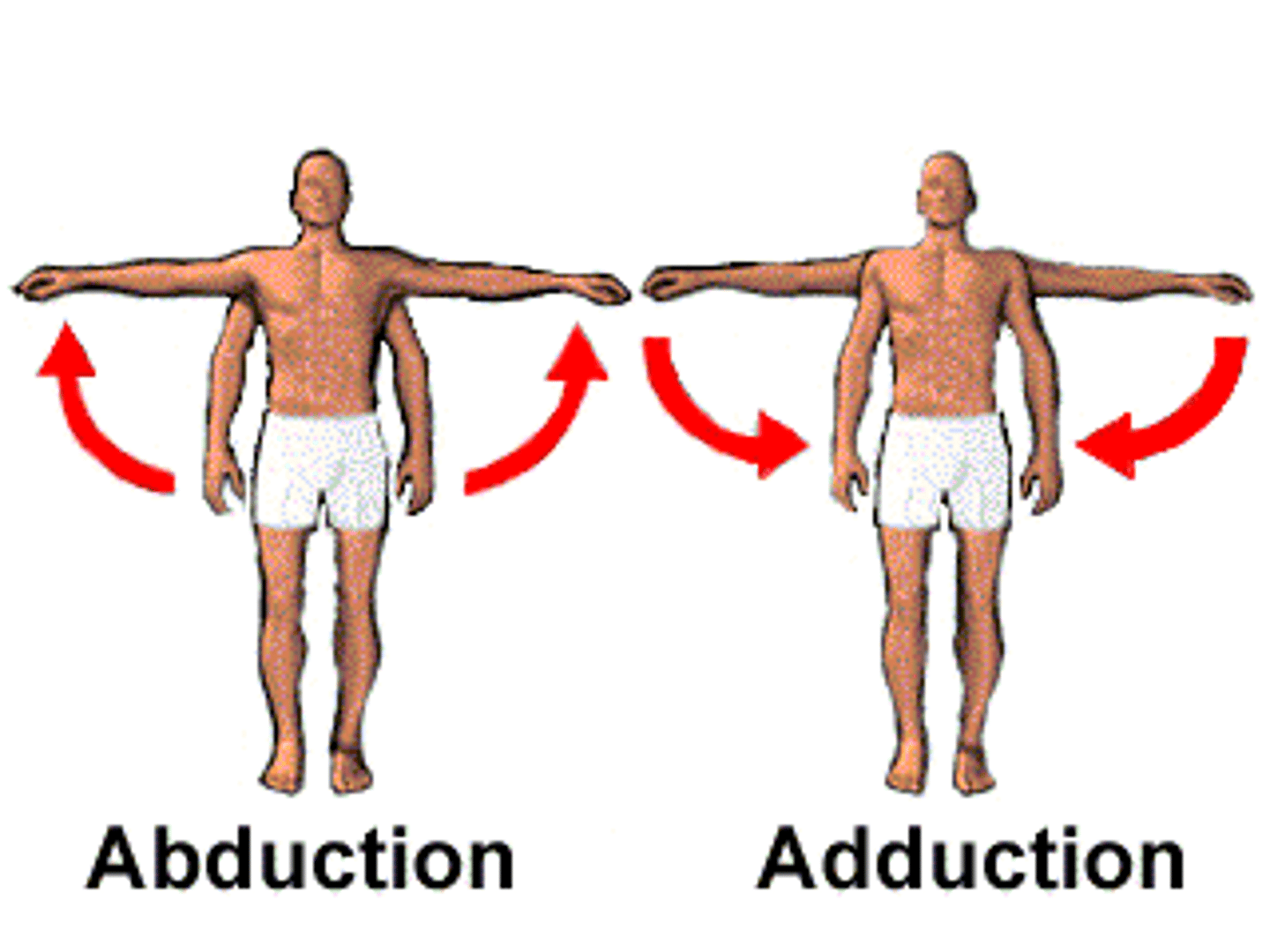
Abduction
up and away from the center of the body
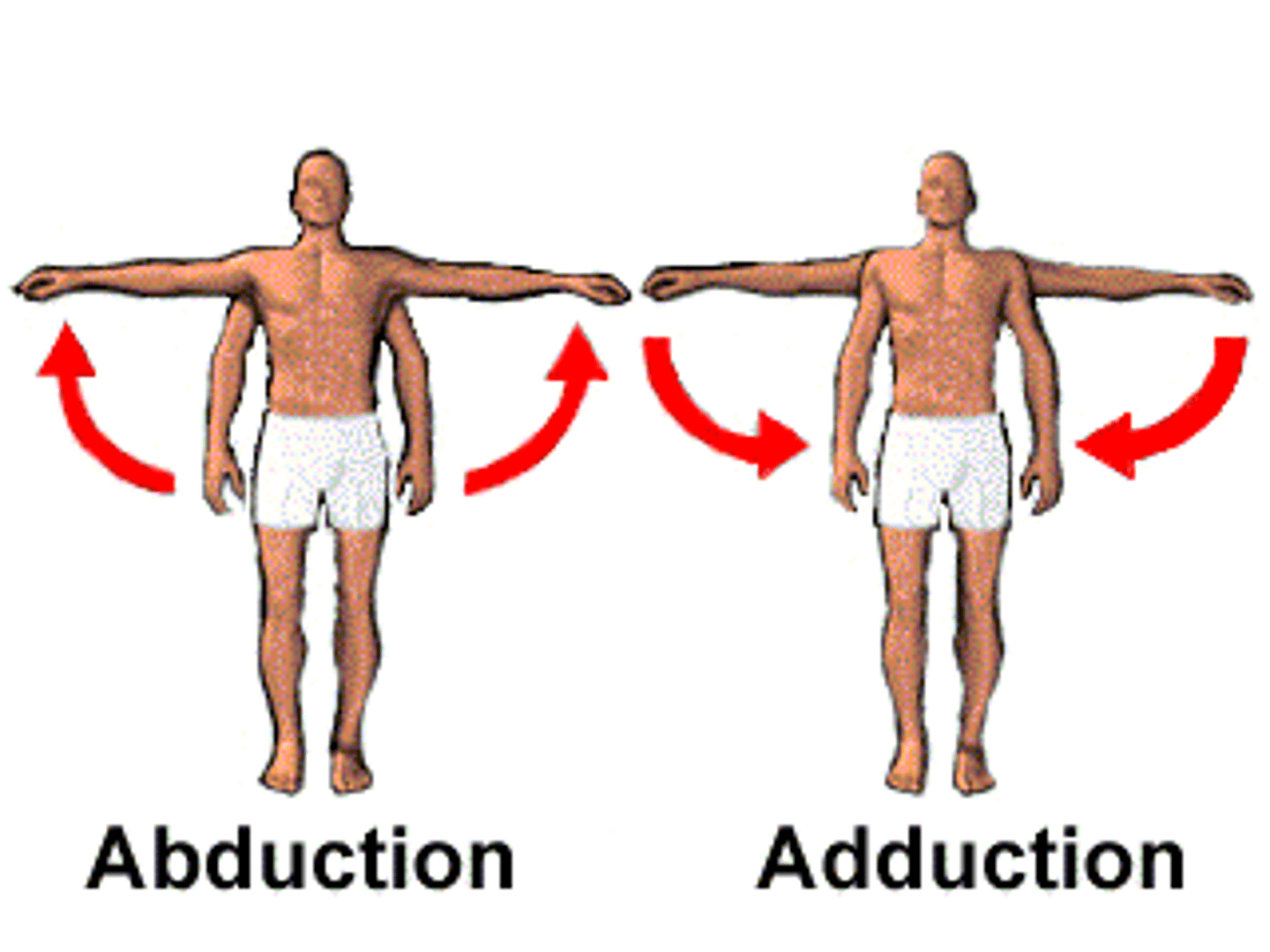
Adduction
moving towards the center of the body
Circumduction
rotation of a limb around axis while reducing or increasing an angle at the joint (ex: arm circles)
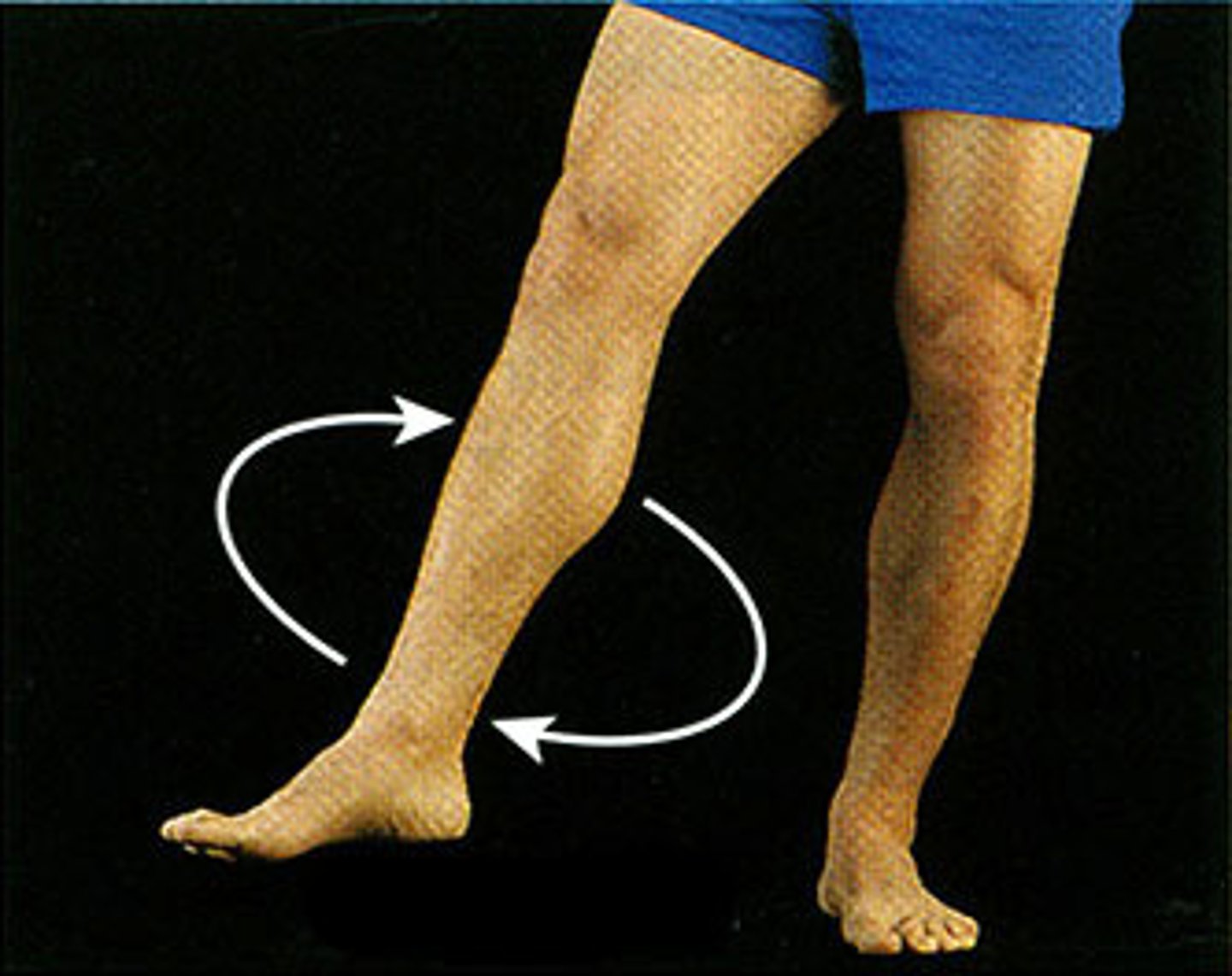
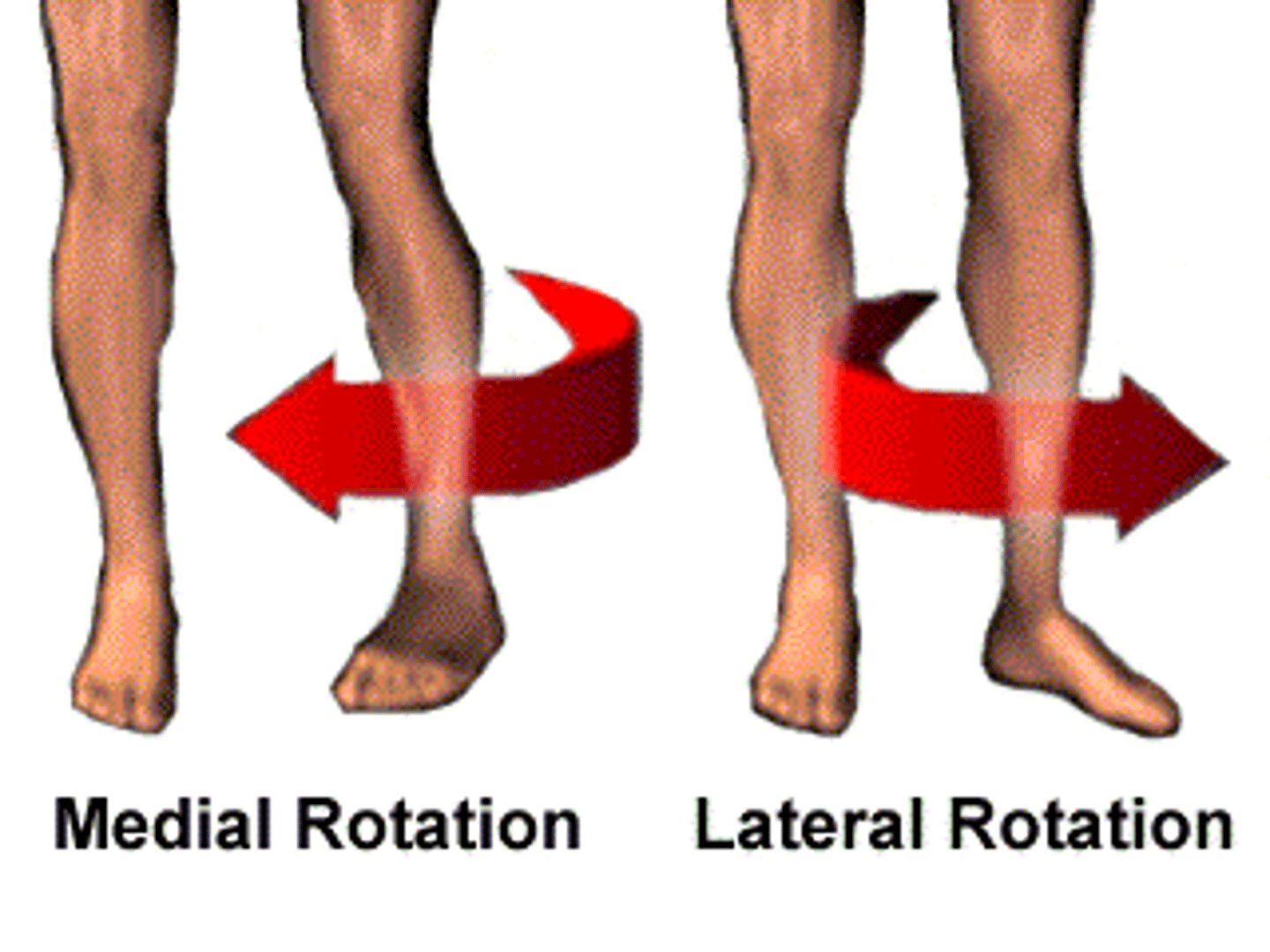
Internal/ Medial Rotation
rotation of a structure towards the midline of the body
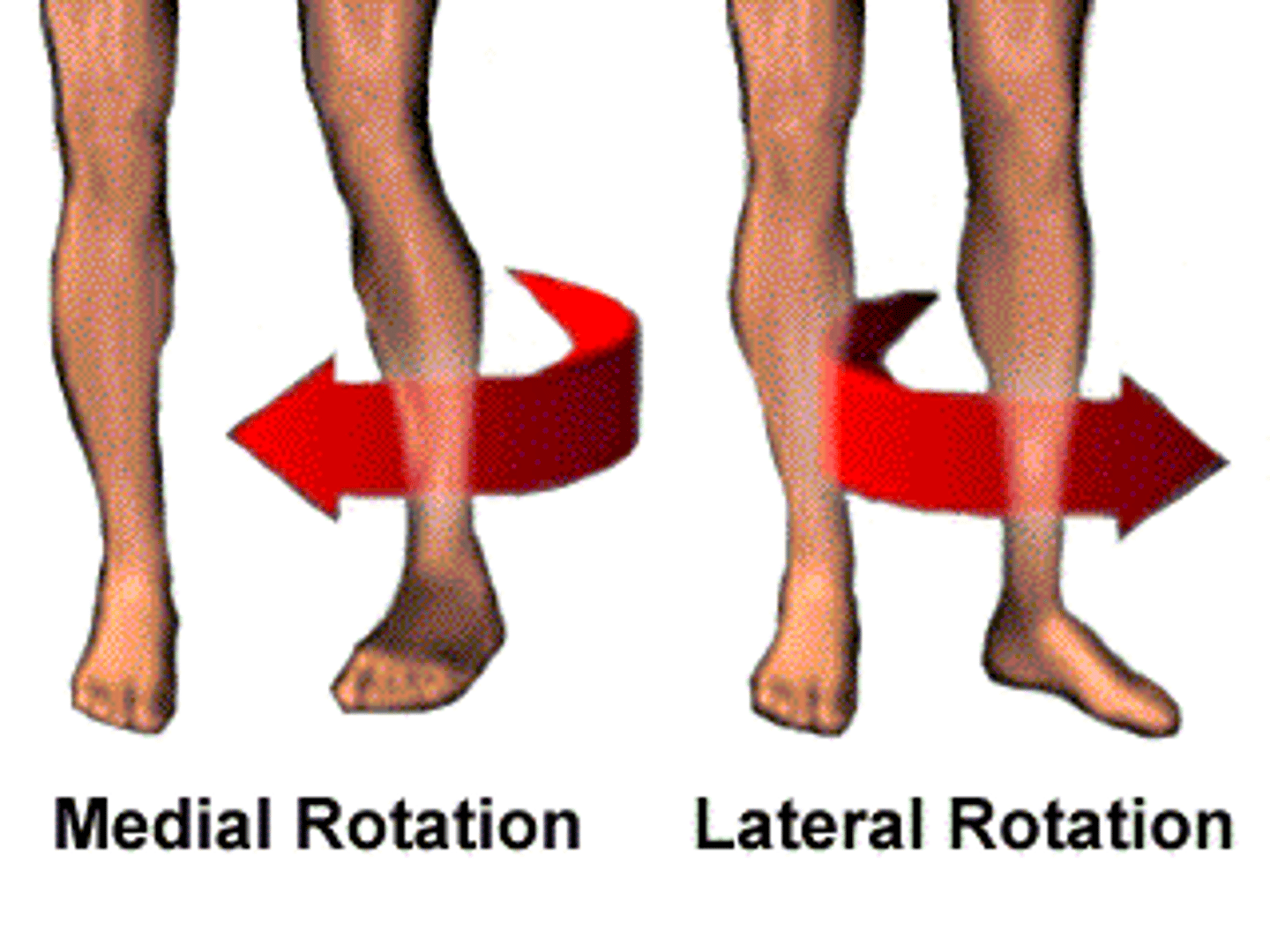
External / Lateral Rotation
rotation of structure away from midline of the body
Supination
unique to forearm, palm faces out
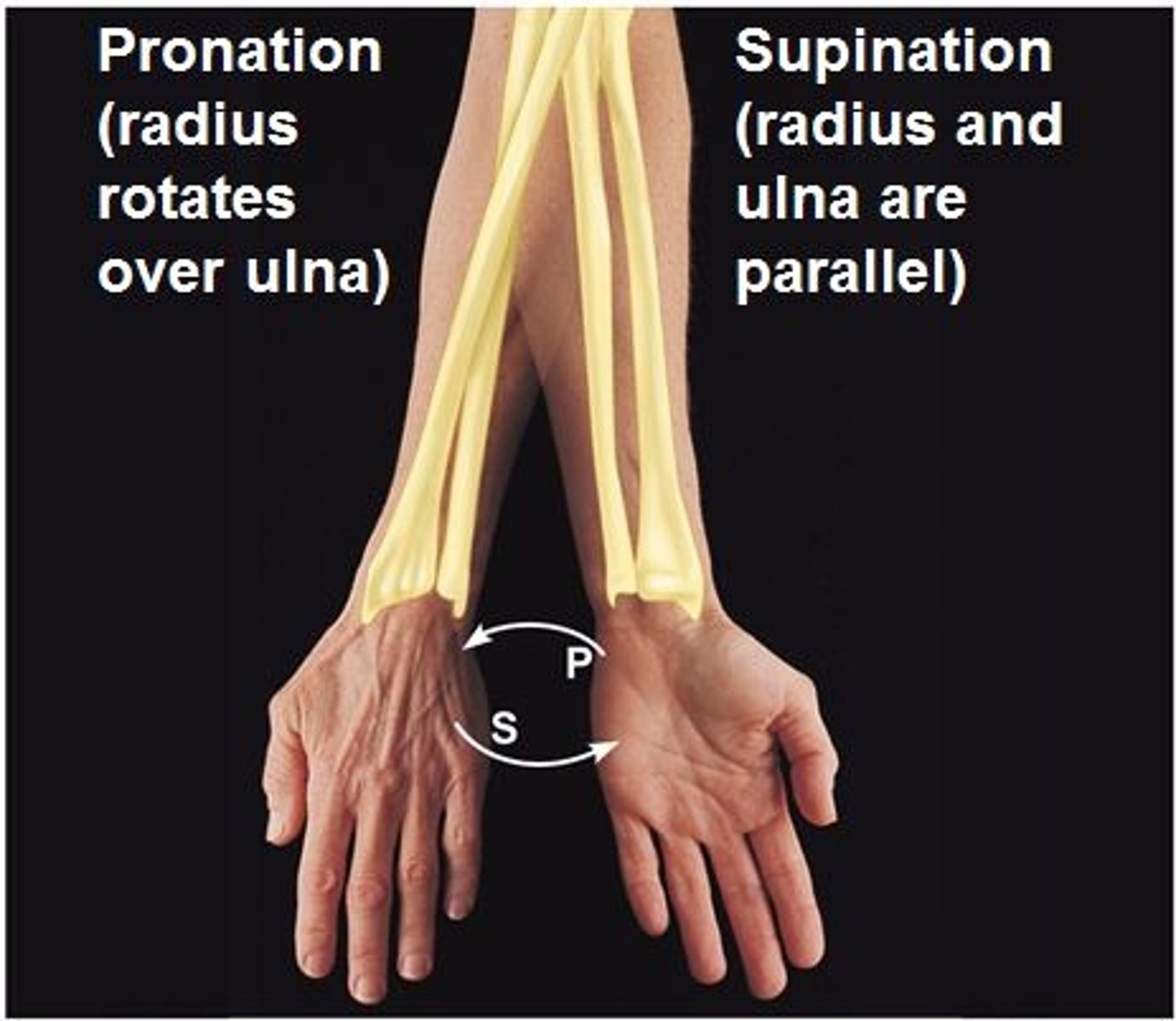
Pronation
unique to forearm, palm faces in
Inversion
unique to ankle, feet pointed towards each other
Eversion
unique to ankle, feet pointed away from each other
Dorsiflexion
unique to ankle, elevation of the top of the foot
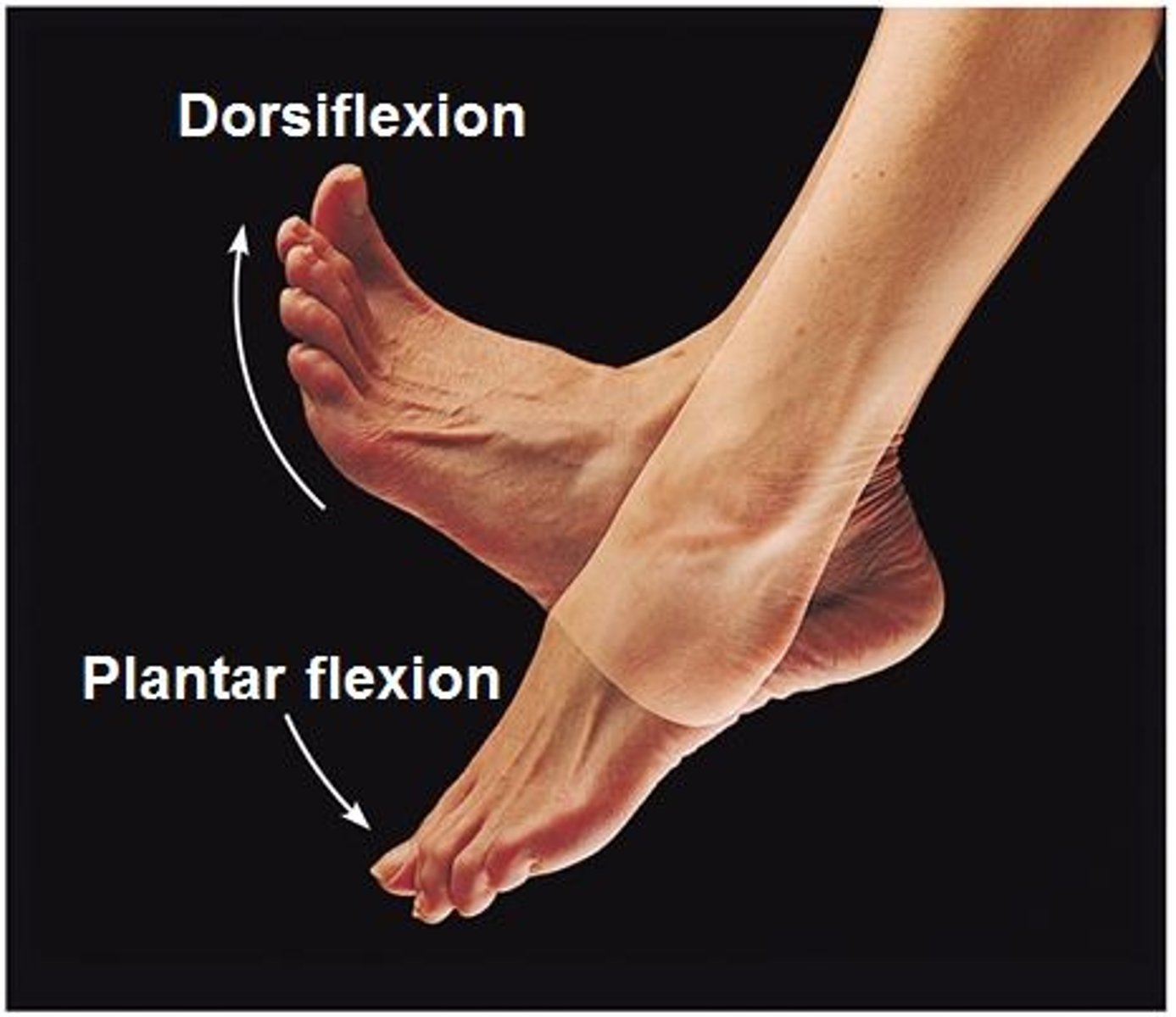
Plantarflexion
unique to ankle, extension of the anke, elevation of the heel (running)
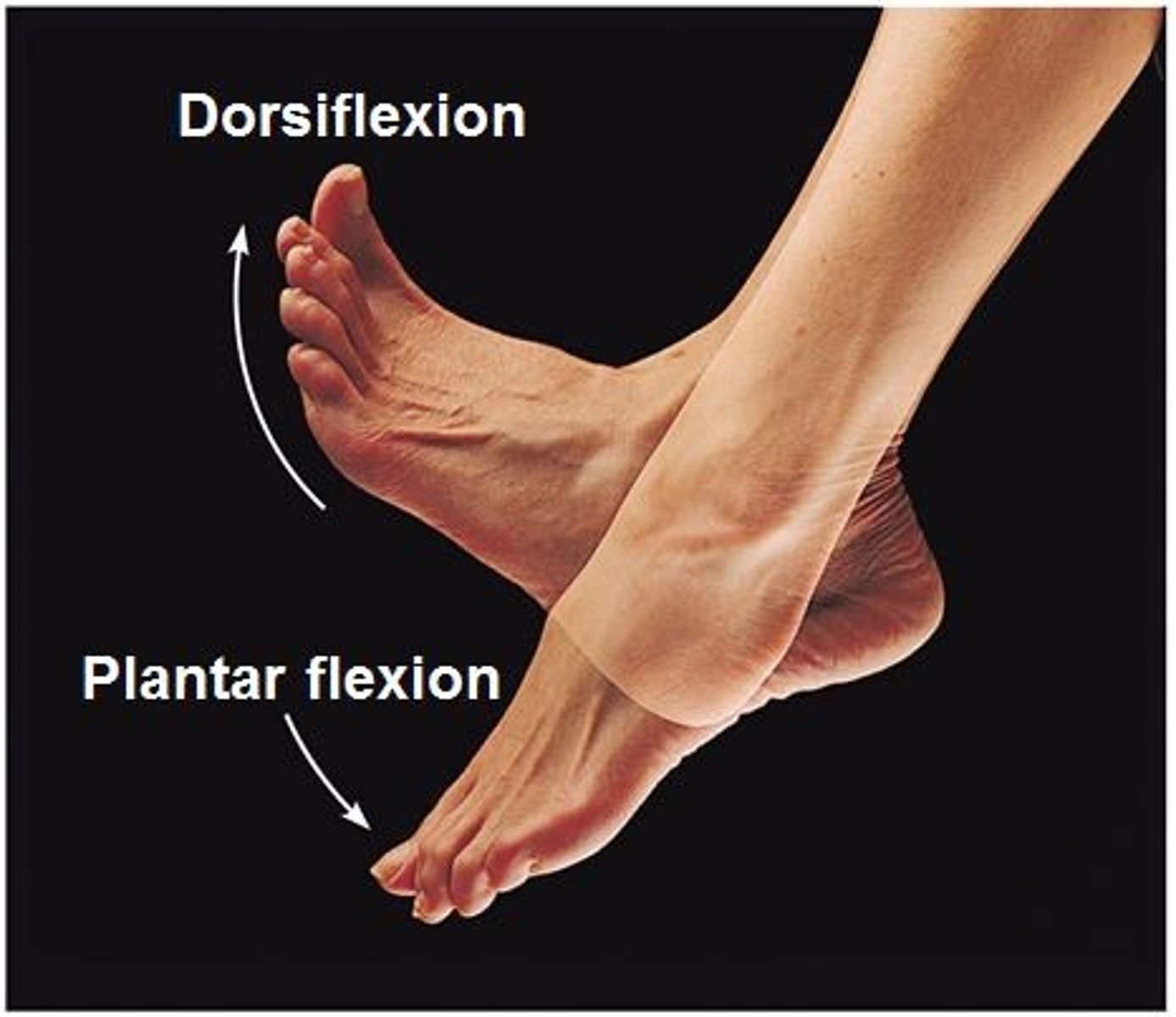
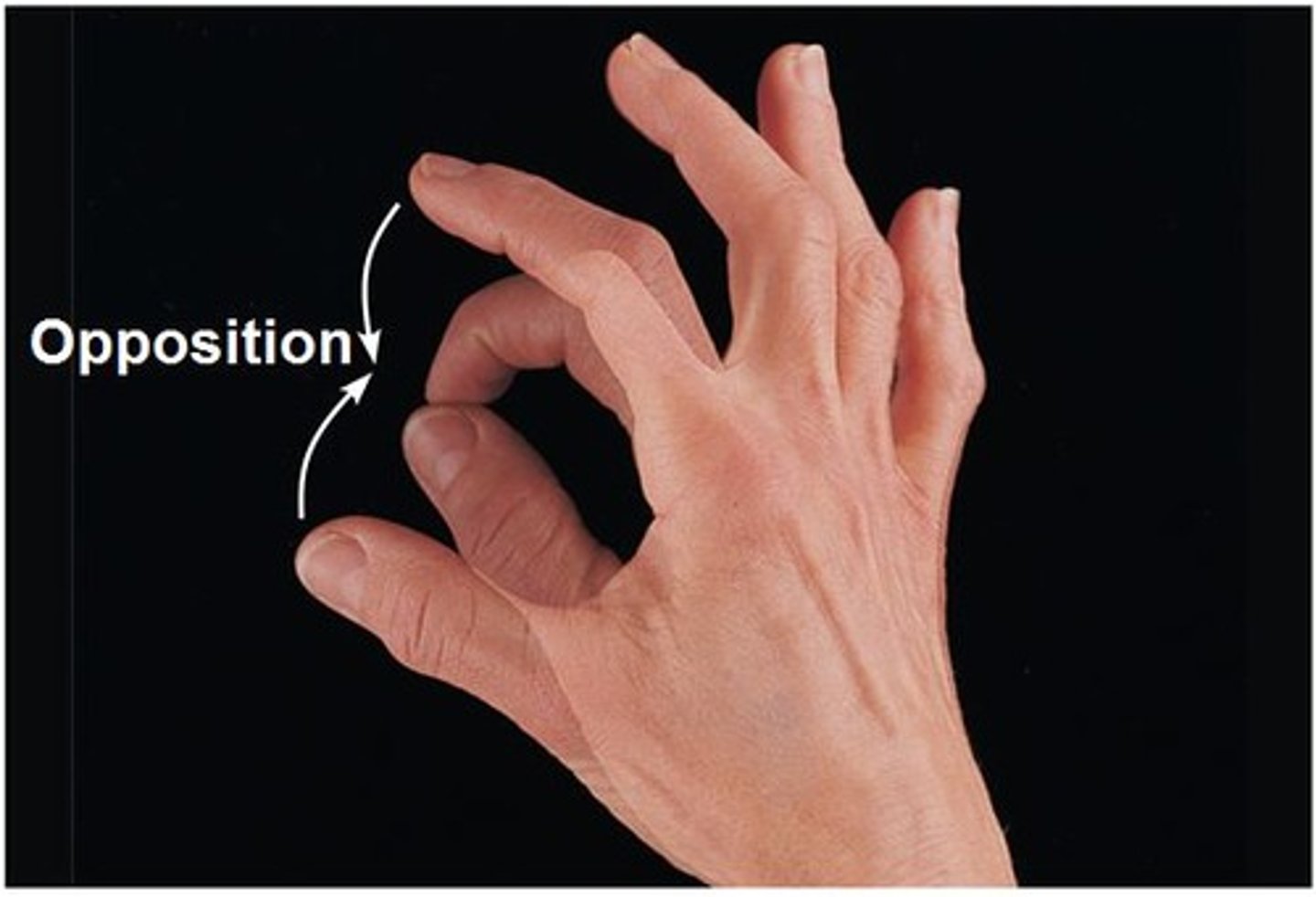
Opposition
thumb movement across the palm of the hand to allow grasp
Protraction
gliding motion that moves a structure anteriorly (slouching)
Retraction
gliding motion that moves structure posteriorly (sitting up straight)
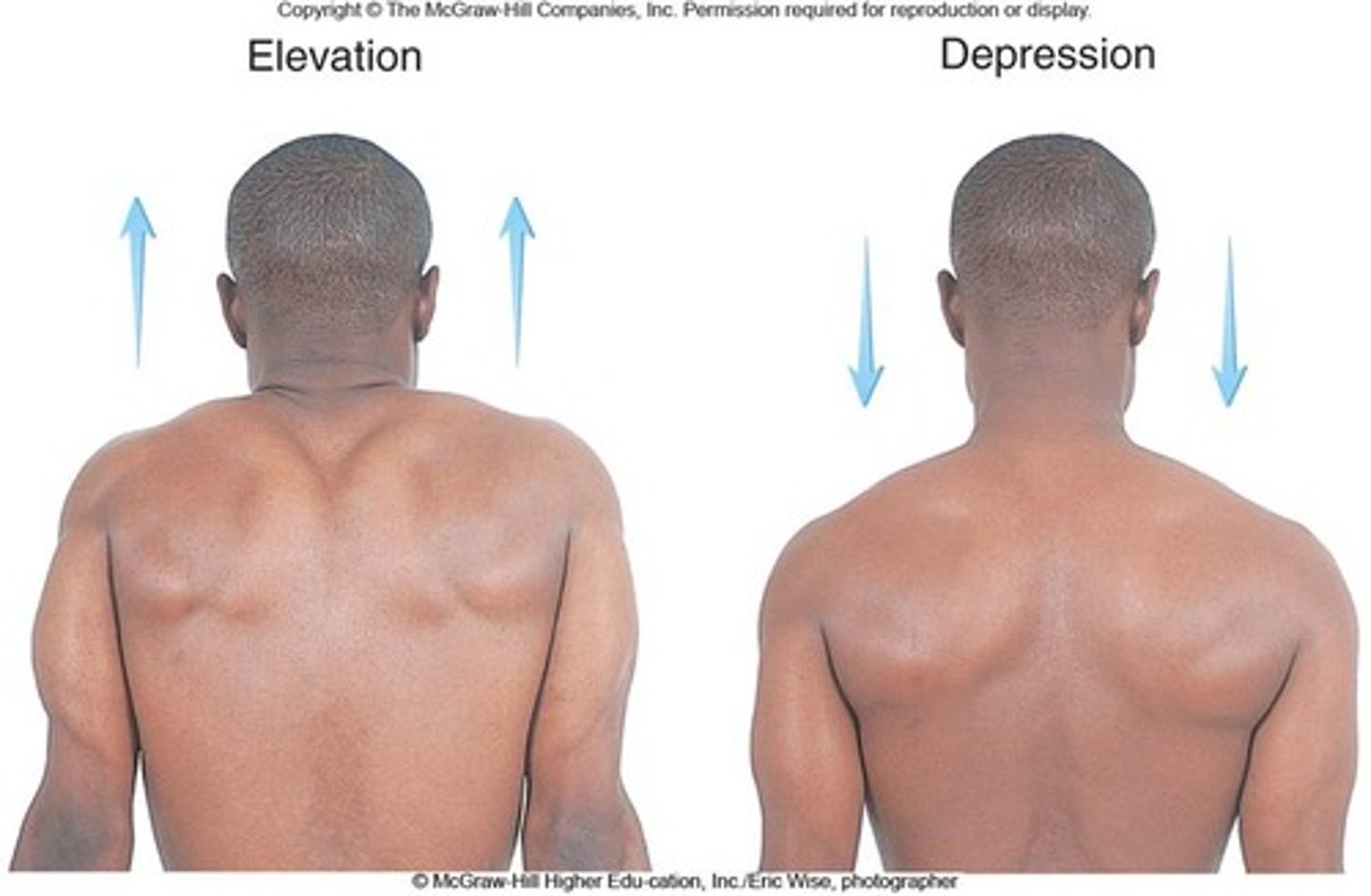
Elevation
moves structure superiorly (shoulders up)
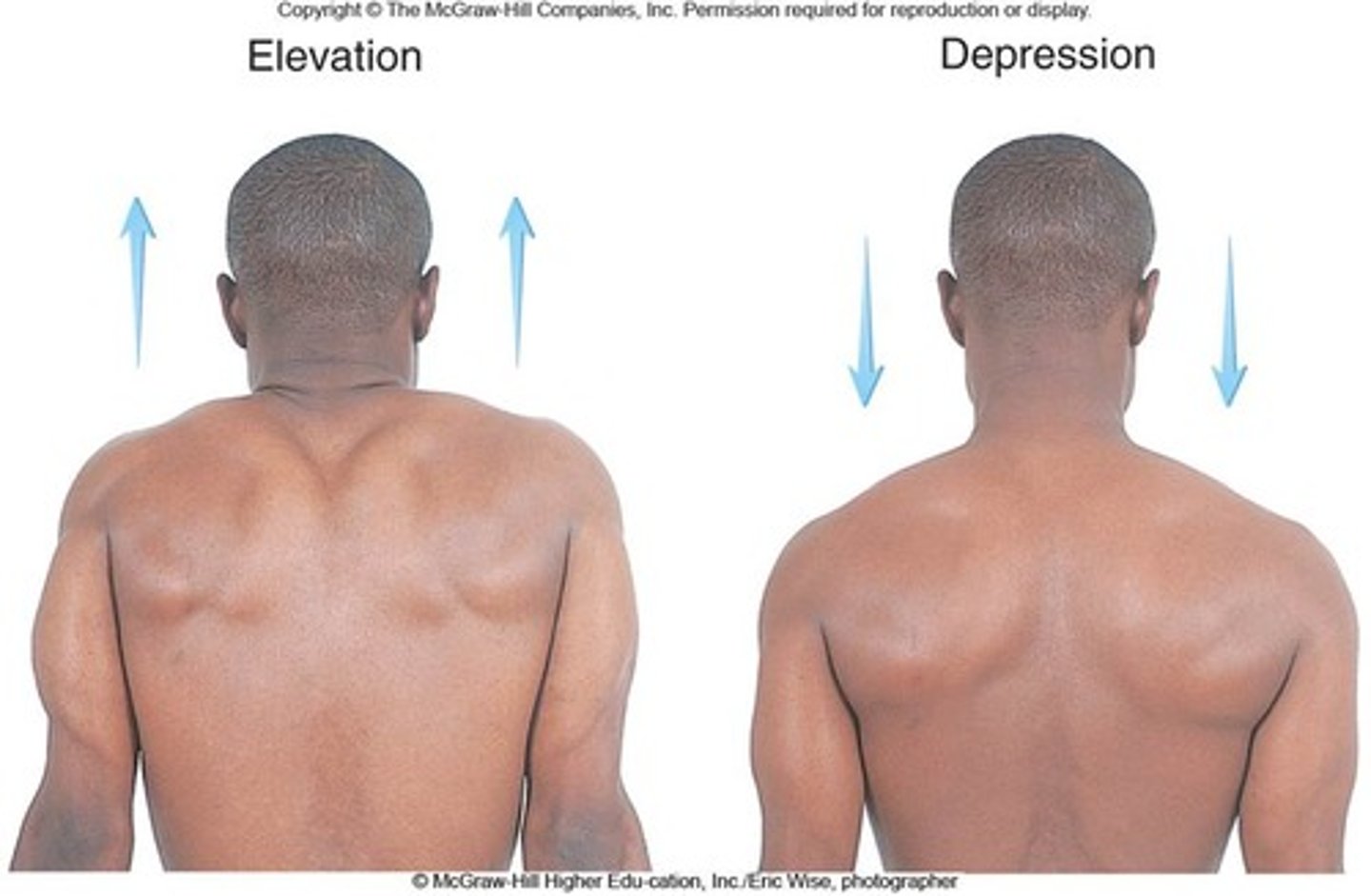
Depression
moves structure inferiorly (shoulders down)
Functions of Skeleton System
Support, Protection, Movement, Storage, Blood cell production
Bone Histology
2/3 Calcium Phosphate (Hydroxyappetite), 1/3 protein-collagen fibers, 2 percent osteocytes and other cells
Bone Tissue - specialized cells
Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
Found in an area with high metabolism (ex. periosteum), Responsible for making new bones, produce collagen, proteoglycans and matrix vesicles
Osteocytes
located in spaces between layers of the hard matrix of the bone
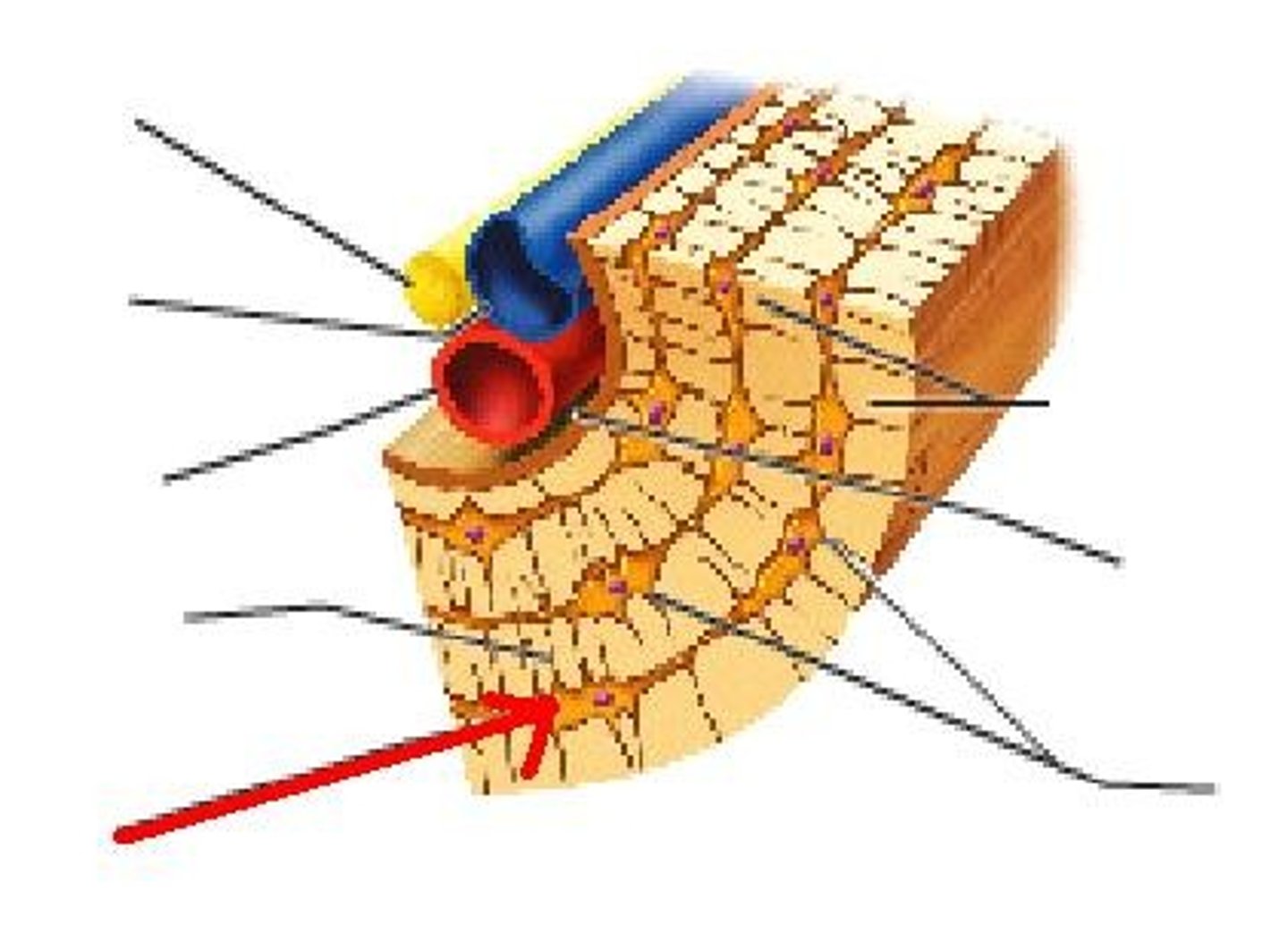
Osteoclasts
secrete acids (dissolves bony tissue by releasing calcium, phosphate, magnesium), requires enzymes, important for bone growth, health, and remodeling
Osseous Tissue Classification
organized collagen fibers within bone matrix (Woven and Lamellar)
Woven Bone
Collagen fibers are randomly organized (osseous tissue) Spongy or compact bone
Lamellar Bone
Collagen fibers are organized into sheets or layers (osseous tissue) Spongy or compact bone
Spongy Bone
Appears as interconnecting rods called trabeculae. Open network surrounded by compact bone. Found at either end of long bones. Much lighter then compact bones meaning it heightens motion and lessens weight.
Compact Bone
Dense bone, few spaces. Solid outer of the bone. Thickness depends on stress of bone.
Bone Shapes
Long Bone, Short Bone, Flat Bone, and Irregular Bone
Appositional growth
Process of adding layers of bone tissue and supporting vessels and innervation to existing bine structures (increasing width)
Wolff's Law
Calcium laid down to stress
Piezoelectric Effect
Pressure on a tissue changes to electrical charge of that tissue
Axial Skeleton
Skull, 3 Auditory Ossicles, Hyoid Bone, Vertebral Column, Rib Cage, Sternum
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral Girdle, Upper Extremities, Pelvic Girdle, Lower Extremities
Synarthrosis
Immovable joint
Ampiarthrosis
Slightly movable joint
Diarthrosis
freely movable joint
Monoaxial
when a joint allows movement only along one axis
biaxial
movement allowed on two axes situated at right angles to one another ex. wrist
multiaxial
when movement is allowed around multiple axes ex. shoulder, hip
Major Joints based on what?
Presence of a joint space, if no joint space, the type of connective tissue on the articulating bones
Fibrous Joints
Common in axial skeleton, most immovable. Includes sutures (thick fiber), Syndemoses (distal upper and lower parts fibers connect between two long bones), gomphxses (tough fibers between boney structures)
Cartilaginous Joints
Common is axial skeleton. Not highly moveable but more moveable then fibrous joints. IncludesSynchondroses (Joint between first rib and manubrium, not supposed to give), Symphysis (gives motion, has to be midline, ex: intervertebral disks)
Synovial Joints
Common in appendicular skeleton. No blood vessels inside joint. Moveable. Ex: knee, shoulder
Includes: articular capsule, joint cavity, synovial fluid, articular cartilage, reinforcing ligaments, nerves, and vessels, articular disks/ menisci, fat pads and bursar
Articular Capsule
Outer: periosteal outer layer from bone, strengthens joint capsule.
Inner: Synovial membrane of loose CT, covers internal, makes synovial fluid
Articulation
two or more bones connect and allow motion
Joint Cavity/ Synovial Cavity
Potential space that holds a small amount of synovial fluid
Synovial Fluid
Found within joint cavity, acts as lubricating fluid in the joint gets squeezed into and out of articular cartilage by joint movement (nourishes and lubricates cartilage, removes waste)
Articular Cartilage
absorbs compression of bone
Articular Discs/ Menisci
Only synovial bones. Found in two spots - TMJ, Knee. Divides joint cavity into two , purpose is to improve the fit
Fat Pads
pads lie between bone surfaces near edge and within the joint, behind patella, fills space, protection
Bursae
small synovial fluid filled pockets within CT surrounding synovial joints, reduce friction and absorb shock, disperses fluid and heat
Influencing Synovial Joint Stability
Closed packed: most stable, max contact and tightness
Open pack: no max contact and tightness
Muscle tendon- most important cant have too much (not stable) or too little (too much flexibility = loss of stability)
Gliding Motion
linear motion where 2 opposing surfaces slide past one another - slight with little rotation
Rotational Motion
movement of bone along its axis (ex: supination and Pronation -ulna and radius)
Synovial Joints that Produce Motion
6- gliding, hinge joint, ellipsoidal, saddle joint, pivot, ball in socket
Gliding Joint
flat or slightly curved, 2 short bones slide one another NO ROTATION
Hinge Joint
Slight rotation (ex: knee, moves in order to keep stability but not too much)
Ellipsoidal Joint
oval face sits in small depression on another socket - Rolling of the joint can be present
Saddle Joint
articular face has shape of saddle, concave on one said, convex on other (ex: thumb, not ball in socket)
Pivot Joint
cylindrical bony process that rotates within a ring of bone and ligamentous support (rotational movement)
Ball in Socket Joint
spherical head of one bone fitting in to spherical socket of another bone (ex: shoulder, hip - multiaxial)
ACL and PCL
tendons by lower median knee/leg
Ankle
mobility - sagital
Knee
Stability
Hip
Mobility -Multiplanar
Lumbar Spine
Stability
Thoracic Spine
Mobility
Scapula
Stability
Functions of Muscular System
movement of body
maintenance of posture
production of body heat
communication
contraction of organs and vessels
contraction of the heart
Property of muscle tissue- Excitability
ability to respond to neural stimulation
Property of muscle tissue- Contractibility
ability to shorten
Property of muscle tissue- Extensibility
ability to contract over a range of resting lengths
Property of muscle tissue- Elasticity
ability of a muscle to return to its original length after contraction
CT of Muscle - Endomysium
surrounds each muscle fiber/cell - innermost layer
CT of Muscle - Perimysium
surrounds bundles of muscle fibers (fascicles) - middle layer
CT of Muscle - Epimysium
covers outside of the entire muscle - outer most layer
Nervous Supply of Muscle
travel in surrounding CT to innervate muscle fibers --> voluntary skeletal muscle fibers are innervated by axons from motor neurons from ventral horn spinal cord (CNS)
T-Tubules of Muscle Cells
______ interconnect to surround myofibrils on path to opposite sides of the cell allowing for:
nerves impulses to be transmitted rapidly to individual myofibrils
transport of nutrients along with extracellular fluid to inner parts of muscle of muscle fiber
Sarcomeres
Composed of bundles of myofilaments which are responsible for muscle contraction
extend from one z-disc to adjacent z-disc