grade 10 History midterm study
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/147
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:37 AM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
1
New cards
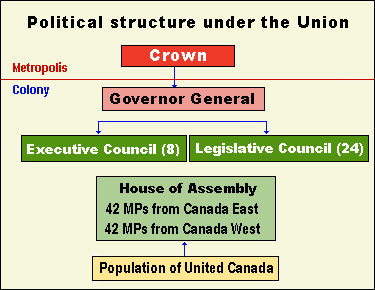
how did the political structure under the union go?
crown, govenor general=excutive council=legislative council, house of assembly, population of united canada
2
New cards
how many members were in the excutive coucil?
8
3
New cards
how many members were in the legislative council?
24
4
New cards
for the house of assembly how many mps were their from canada east and canada west?
canada east=42 canada west=42
5
New cards
when was the union act adopted?
1840
6
New cards
what was the union act?
it united upper and lower canada into one province of canada. it enabled a single legislative council to govern wit crown assent. the act ruled that the assembly should consit of an equal number of representatives from both provinces
7
New cards
when was the first responsible government formed?
1848
8
New cards
who were the 2 guys that forme the first responsible government?
Baldwin and Lafontaine
9
New cards
what did the responsible government look like? (order)
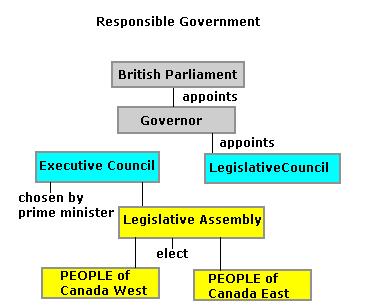
10
New cards
until what year did Baldwin and Lafontaines alliance hold to?
1851
11
New cards
what were the problems with the responsible government? what laws were made that people were unhappy about?
a law granting amnesty to the patriots and a law compensating victims of the rebellions.
12
New cards
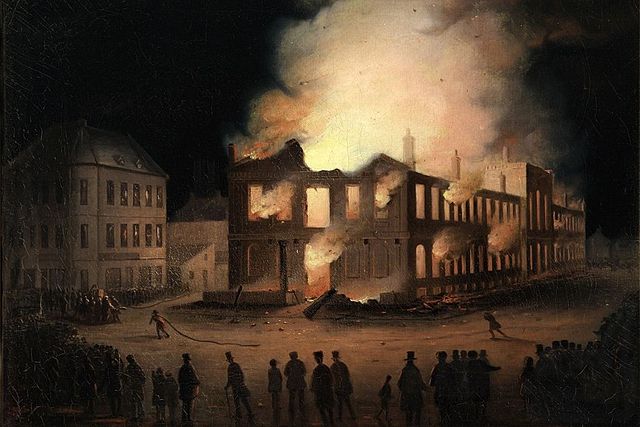
what was the result in these laws being made?
montreal 1849, the rioters burnt down the parliament in hope that lafontaine would be in there

13
New cards
Who was the leader for upper canada?
Robert Baldwin
14
New cards
Who was the leader for lower canada?
Louis Lafontaine
15
New cards
what was the name of the alliance between baldwin and lafontaine?
Alliance of reformers
16
New cards
what was baldwin and lafontaines objective?
to bring french into the government
17
New cards
how was the leader of the excutive council chosen (they would hold the position of the prime minister)?
they had to get elected in
18
New cards
the reform government passed a bill that reignited tensions between francophone, what was the name of the bill?
rebellion losses bill
19
New cards
were french canadians a minority in the legislative assembly?
yes
20
New cards
what is a metis?
a person whos mother and father arent from the same origin, half aboriginal half french canadian
21
New cards
what is anticlerical?
it’s a person that doesn’t beleive that the church should be at the top
22
New cards
whats another word to say anticlerical
secular
23
New cards
what is annexation
an action by which part or all of a states territory comes under the control of another state
24
New cards
What is ultramonatism
this group of people believed the church was at the top, if they didn’t like a decision the government made the could change it
25
New cards
What does excommunicate mean
you get cut out of the church and got shammed, you can’t be burried in a catholic cemetary and can’t go to church and they say you’re going to hell
26
New cards
anticlericalism?
they wanted the church and politics separate
27
New cards
who was the first prime minister of the responsible government
lafontaine
28
New cards
what is a double mahority
upper canada and lower canada parties come together
29
New cards

who is this and what party did he run
George brown, the grits
30
New cards

who is this and what party did he run
George Etienne Cartier, parti bleu
31
New cards
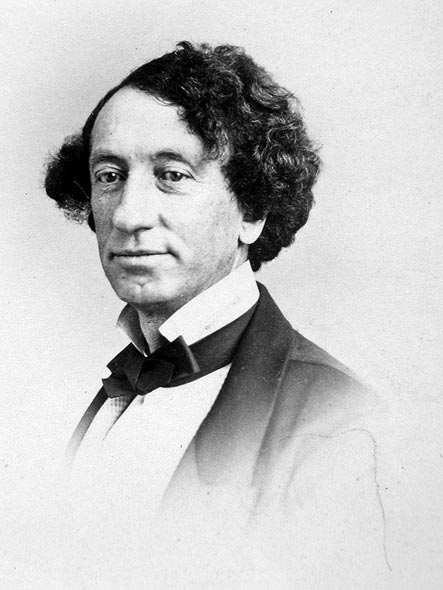

who is this and what party did he run
john A mcDonald, conservatives
32
New cards
who were the rioters that burnt down parliment
the english
33
New cards
what were durham’s 4 reccomendation’s
more immigrants, assimilation, responsible government, join upper and lower Canada (only 1 legislative assembly)
34
New cards
what was a two party system
reformers split into ‘moderates’ and ‘radicals’, because of the split political parties were formed, liberals and conservatives
35
New cards
when was the great coalition formed?
1864
36
New cards
what did George brown want to end
the period of instability
37
New cards
who did George Brown want to form an alliance with
the conservative leaders of upper and lower canada
38
New cards
what idea did the great coalition introduce to all the british north american colonies
confederation, this union would create a larder economic unit and protect them against an aggressive neighnor
39
New cards
what did the great coalition have to do in order for the idea of confenderation to work
they had to convince the other colonies that the idea could work
40
New cards
who were the members appart of the great coalition
George Brown, John A Macdonald and George Etienne Cartier
41
New cards
What year was the charlottetown conference
1864
42
New cards
which colonies were already meeting and what did they want to discuss?
The maritime colonies and they were meeting to discuss the idea of a union
43
New cards
was the great coalition invited to this meeting?
yes but they were not made very welcome but they didn’t give up
44
New cards
in the end what did they agree on?
they all agreed that a larger union has some merit and they decided to meet up again in october to iron out the details
45
New cards
what year was the Quebec conference?
1864,same year
46
New cards
what happened in this conference?
they agreed on federalism as the political framework for the union, they adopted 72 resolutions
47
New cards
what did the 72 resolutions summarize?
the division of power(federal and provincial), proportional representaion and the construction of a railway linking all of the provinces in the federal union
48
New cards
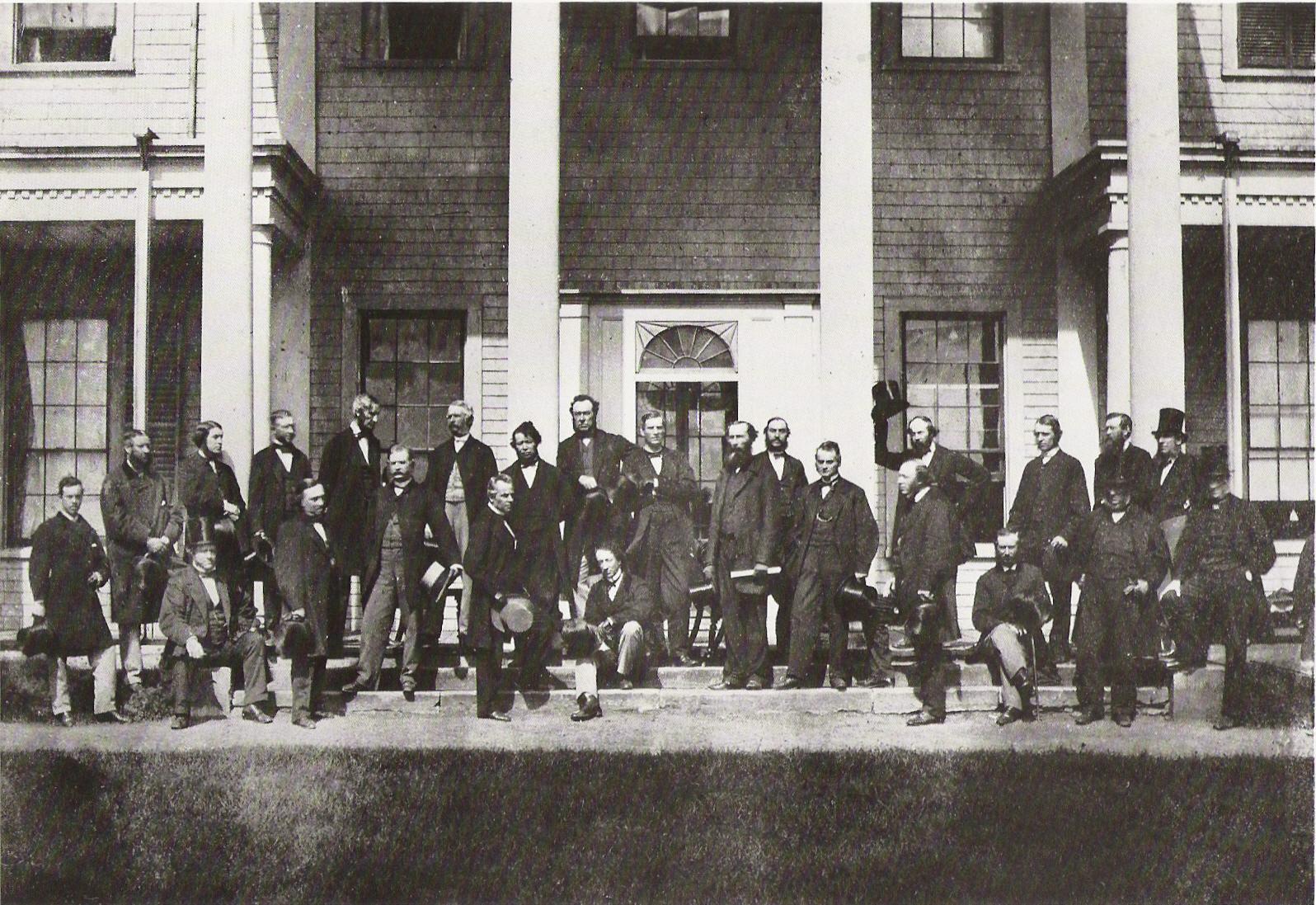

what conference was this?
charlottown confeerence
49
New cards
what were the reactions?
maritime provinces of newfoundland and pei worried about having to pay the debt for the canals and railwaywhich their provinces would not benefit from. they also had small populations so proportional representation did not favour them. nova scotia was also worried but they signed because of the railway link to the province of Canada
50
New cards
Did upper and lower canada support the idea of confederation?
Upper Canada did lower Canada did not
51
New cards
Who was Darcy McGee?
he was a immigrant from Ireland and was a politician
52
New cards
What year was the London conference
1866
53
New cards
what was the London Conference
the bill went to London to be passed by the british parliment.
54
New cards
Who made changes and what were they?
John A Macdonald, the BNA now included residual powers and power of disallowance, he insisted that the federal government have more than the provincial governments, Canada is federation because of these changes
55
New cards
What year was the BNA act
July 1st 1867
56
New cards
What was the BNA act?
It formally united the colonies entering Confederation and established federalism - meaning the distribution of powers between the federal Parliament and the provincial legislatures.
57
New cards
why did they join together for the great coalition?
they joined together for federation
58
New cards
when was the reciprocity treaty
1854-1864
59
New cards
what was the reciprocity treaty
it was a free trade agreement between the us and canada
60
New cards
what was the red river and northwest rebellions
metis got kicked out of the territory for them
61
New cards
who ran the group for the red river rebellion
louis reil
62
New cards
clear grit party
george brown rep by pop
63
New cards
what is rep by pop
representation by population
64
New cards
what were the liberals
radicals, they were anticlerical, known as the parti rouge in lower canada and clear grits in upper canada, parti rouge was led by: Antoine-Aime Dorion and clear grits was led by george brown
65
New cards
what were the conservatives
they were the moderates, in lower canada they were pRTIE Bleu led by george etienne cartier and upper canada called conservative party led by john a macdonald
66
New cards
what kind of members was parti blue made up of
buisinessmen and they enjoyed the support of the catholic clergy
67
New cards
what were the members for the conservative party like
most of the mebers were protestant, anglophone and loyal to the british crown
68
New cards
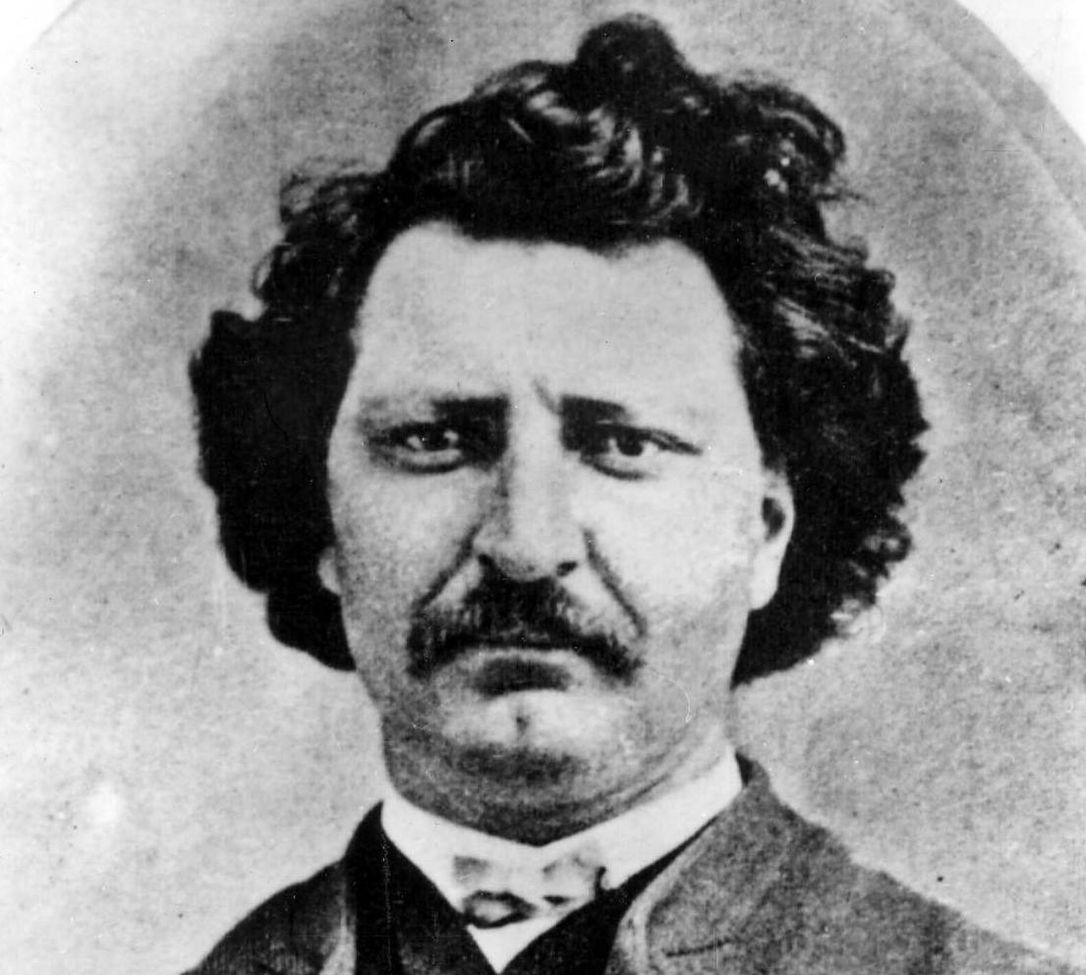

who is this
louis reil
69
New cards
what did he have to do with the creation of manitoba
Riel, a passionate defender of the Métis, advocated guarantees for their land, language and political rights. His leadership inspired the creation of Manitoba as Canada's fifth province on July 15, 1870
70
New cards
what happened when reil hid in america for a bit
the government sold his land
71
New cards
why was reil on the run
he was wanted for the murder of thomas scott
72
New cards
when and why was reil executed
1884 in regina for high treason for his role in the resistance to canadian enroachment
73
New cards
what was reil known as back then and now
he was known as a traitor and now a hero
74
New cards
what was famine
it threatened indigenous people of the west, arrival of thousands of colonists and building of the railroad reduced hunting and fishing territories
75
New cards
in exchange for their lands what did the government propose
first nation groups settle on reserves, they also garanteed them hunting fishing and trapping rights it also promised financial and food assistance as well as education
76
New cards
what was the purpose of residential schools
it was to assimilate=control
77
New cards
what year was the indian act
1876
78
New cards
explain the act
if you did not go to the reserve you were considered a minor you couldn’t have your own land no loans ect
79
New cards
with the indian act what couldnt they do
they couldn’t have dances, rituels, ceremonies ect
80
New cards
what year was the economic crisis
1873-1878
81
New cards
what was the financial crisis
new canadian buisinesses were competing with American businesses , the price of raw materials such as wheat and lumber were decreasing
82
New cards
population growth
Macdonalds final goal was to settle the west. using newly built rail network it made it easier to move newly arrived immigrants to the west and settle there, increase in population would help the domestic marcket
83
New cards
due to the population growth in Quebec where did many people move to
mechanized farming equipment and lack of land available , many people moved to the city (looking for jobs) or the other areas
84
New cards
Between 1840-1900 its estimated that almost 10% of the population left the province why did most of them move to America
in search of land, jobs and “better” future
85
New cards
what was the plan the catholic clergy came up with in attempt to stop this flow of french migration
with the help of the provincial government the catholic clergy encouraged families to settle in new areas of the province
86
New cards
what were the new agricultural areas
temiscamingue, bas saint laurent and lac st. jean
87
New cards
what was the pataroe famine
famine=starvation, patatoe famine in ireland lasted 2 years but had a huge impact, many people in ireland died from hunger and disease. many people went to an island for quarantine 80,000 people, many arrived sick from horrible transatlantic journey
88
New cards
what was the quarantine area
Grosse ile
89
New cards
what was the group institut Canadien do montreal
it was a group founded by young professionals and intellectuals in montreal, they had debates and started up a library and a newsaper to dicuss events, philosophical ideas ect…they did not like the idea of catholics and protestant members discussing issues that shouldnt be discussed
90
New cards
what was the guibord affaire
In July 1869 the bishop, supported by Rome, placed the Institut under an interdict. In Nov 1869 Joseph Guibord, who explicitly refused to renounce his membership in the Institut, died, and Bourget denied him burial in consecrated ground. That action opened more than 5 years of violent argument.
91
New cards
what was the role of the women (1840-1880)
they were considered to be minors and could not do anything without the consent their fayher or husband, women started demanding the right to vote and attend universities.
92
New cards
what year did McGill open it’s doors to women for studies in literature, philosophy and history.
1884
93
New cards
was it the same for francophone women
they were only allowed to access to english insitutions
94
New cards
what years was the first phase of industrialization
1850-1896
95
New cards
what this industrialization stimulated by
population growth, reciprocity treaty and development of domestic market factory-textiles(fabricks), shoes tabaco production
96
New cards
were the living conditions good
no
97
New cards
everyone worked everyday except for 1 day which day was that
sunday-known as gods day
98
New cards
what were the labour group
unions
99
New cards
what were the years for the second phase of industrialization
1896-1929
100
New cards
who worked in the factoris
men women and children but men were paid more