VCE Physical Education Unit 3 SAC 2 (copy)
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
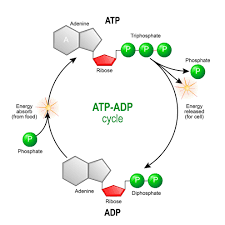
ATP Breakdown
ATP is the energy source for all muscular movements. The ATP is split when a phosphate group is removed from the molecule. When it is split it releases energy.
Creatine Phosphate (Chemical)
Chemical fuel contatining a high-energy phosphate for rapid release of energy.
Limited CP Storage
Carbohydrates
Sugar and starches e.g. bread, pasta, fruit, vegetables.
The bodys preferred source of fuel under exercise conditions.
Fats
Are a concentrated fuel source in dairy products, oils, nuts etc. Preferred fuel source at rest and during prolonged submaximal exercise.
Protein
Protein if found in meat, fish, eggs etc. Used for muscle growth and repair.
Minimal Contribution to energy production during exercise.
At rest exercise Fuel
Fats
Carbohydrates (Aerobic)
Carbohydrates (Anaerobic)
Submaximal Activity Fuel
Carbohydrates (Aerobic)
Fats
Carbohydrates (Anaerobic)
Protein
Maximal Activity Fuel
Carbohydrates
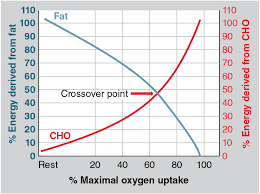
The cross over concept
ATP Cycle
ATP-PC System
Fuel=Creatine Phosphate
Intensity=Maximal <95%
Rate=Explosive
Yield=0.7 ATP PM
Duration=0-10 seconds
Anaerobic Glycolysis System
Fuel=Glycogen
Intensity=High Intensity 95%-85%
Rate=Fast
Yield=2-3 ATP PM
Duration=10-75 seconds
Aerobic Glycolysis System
Fuel=Glycogen/Triglycerides
Intensity=Submaximal 85%-70% or >70%
Rate=Slow
Yield=38 ATP PM or 441 ATP PM (triglycerides)
Duration=75 seconds +
Factors Affecting Contribution
The duration of the exercise
The intensity of the exercise
Whether sufficient oxygen is present
Continuous exercise or intermittent exercise
Available fuel sources
Writing a response
All energy systems contribute to energy production
ATP-PC starts continues to 6-10 seconds
Anaerobic Glycolysis becomes more dominant
Aerobic Glycolysis System increases but never becomes dominant.
Predominant Energy system would be ATP-PC for a 200m event.
Intermittent Activity
Exercise beats that alternate between periods of activity and intensity.
Contributions from the energy systems depends on
Duration
Intensity
Fuel Availability
Weather Conditions
Lactate Inflection Point (LIP)
LIP is the highest exercise intensity where lactate removal and lactate production are balanced.
Beyond LIP
Beyond LIP, lactate production exceeds
Accumulation of Hydrogen Ions causes fatigue
Intensity of LIP
Generally at 85% Max Heart Rate
55-70% VO2 Max
Oxygen Uptake or Vo2
The volume of oxygen able to be taken up by and transported to and used by the body for energy.
Vo2 Max Vs. Vo2
Vo2 Max=The maximum volume of oxygen able to be used by the body.
Vo2=Is the rate of oxygen
Factors Affecting Oxygen Uptake
Body Size
Age
Gender
Training
Genetics
Oxygen Deficit
Is the period of time at the start of the exercise where the oxygen demand exceeds.
Steady State
Is the state in which oxygen equals oxygen demand
Oxygen Debt (EPOC)
At the completion of exercise, oxygen consumption remains elevated, despite a reduction in the demand for energy.
Fast Phase of EPOC
ATP Resynthesise
CP Resynthesise
Restore oxygen to Myoglobin
Slow Phase of EPOC
Return core temperature
Convert Lactic Acid to h2o
Lactic Acid converted to Glycogen/protein
Restore heart rate
Restore other body systems
Acute Respiratory Responses
Increase Respiratory Rate = number of breaths per minute
Increase Ventilation = Volume of air breathed in per minute (RR x TV = V)
Increased Tidal Volume = volume of air breathed in per breath
Increased Pulmonary Diffusion = The transfer of oxygen to the alveoli to the capillaries
Acute Cardiovascular Responses
Increased Heart Rate = Number of beats of the heart per minute
Increased Stroke Volume = Volume of blood pumped per beat of the heart
Increased Cardiac Volume = Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute (HR x SV = Q)
Increased Systolic Blood Pressure = The pressure exerted by the blood against the arterial walls when the heart contracts.
Redistribution of blood flow = Altering the percentage of cardiac output that is distributed to various body sites.
Increased Venous Return = The blood returning to the heart via the venous system
Increased AVO2 Difference = The difference in the concentration of oxygen in the arterial blood and venous blood.
Decreased Blood Volume = total quantity of blood in the body (plasma + cellular)
Acute Muscular Responses
Increased motor unit recruitment = The number and frequency of motor units recruited for the muscular contractions.
Increased muscle temperature = The degree of intensity of heat present in the muscles.
Increased oxygen uptake and consumption = Volume of oxygen that can be taken up and used by the body.
Increased Metabolic By Products = Substance leftover from the metabolic processes.
Decreased Energy Substrate Scores = Fuel sources required for ATP resynthesis.
Relative VO2 Max
Is a better measurement to compare athletes to one another.
Absolute VO2 Max
The amount of oxygen breathed in per minute.
Increased Ventilation Formula
Increased Respiratory Rate x Tidal Volume
Increased Cardiac Output Formula
Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
Before exercise (increased heart rate)
Anticipatory Response
Warming the body up