the asexual cell cycle
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
G1
cell increases in sizze
ribosomes, RNA produced and preparation for DNA synthesis
S
DNA synthesised
G2
cell checks the fidelity of DNA and prepares for nuclear divisions (+more cell growth)
G0
occurs sometimes, where the cells are inactive ‘quiescent’
what happens to the DNA during interphase?
the chromosome in S-phase forms 2 sister chromatids
during mitosis, the chromosomes segregate and the overall amount of DNA ends up the same
prophase
chromosomes condense so they are now visible
sister chromatids are held togethwe by a protein called cohesin
later in prophase, the nuclear membrane breaks down (also called prometaphase)
the mitotic spindle
cytoskeletal structure, largely made of microtubules (polymers of small tubulin protein subunits)
the spindles separate sister chromatids into different daughter cells
this happens because the microtubules contract to pull chromosomes towards the pole
kinetochores
large protein complex that connects that centromeres to microtubules
metaphase
centromeres align at the spindle equator- midway between the 2 poles
microtubules attach to each pole- tension between these keeps chromosomes in the centre
anaphase
sister chromatid cohesin breaks down
chromatids become separate chromosomes
centromeres start moving to opposite poles
depending on the centromere- each chromosome can form a V shape as it is dragged behind the centromere
telophase
chromsomes arrive at the cell poles
chromsomes decondense- no longer visible thread-like structures
daughter nuclei reform
cytokinesis
division of the rest of the cellow
cleavage furrow (animals) or cell plate (plants) forms in-between the 2 poles
constriction to give 2 daughter cells
can be symmetrical or give 2 uneevenly shaped daughter cells (budding yeast)
bidge chromosome
a chromosome that erroneously has 2 centromeres is pulled towards both poles at once. Ends up being broken
acentric chromosome
lacking a centromere, unable to segregate properly
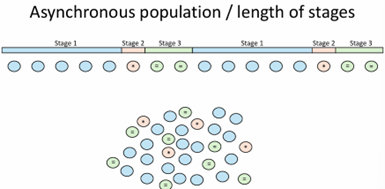
asynchronous population/ lenght of stages